-
摘要:目的
煤矿井下普遍存在低照度、弱纹理和结构化的特征退化场景,导致视觉SLAM(visual simultaneous localization and mapping)系统面临有效特征不足或误匹配率高的问题,严重制约了其定位的准确性和鲁棒性。
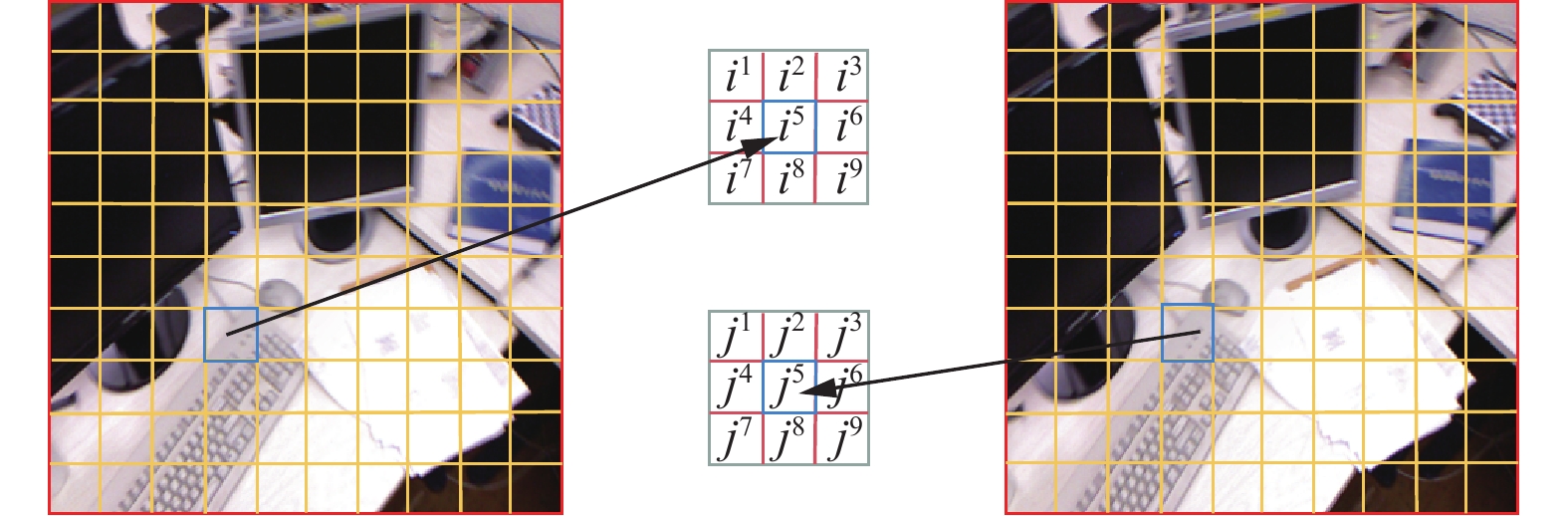
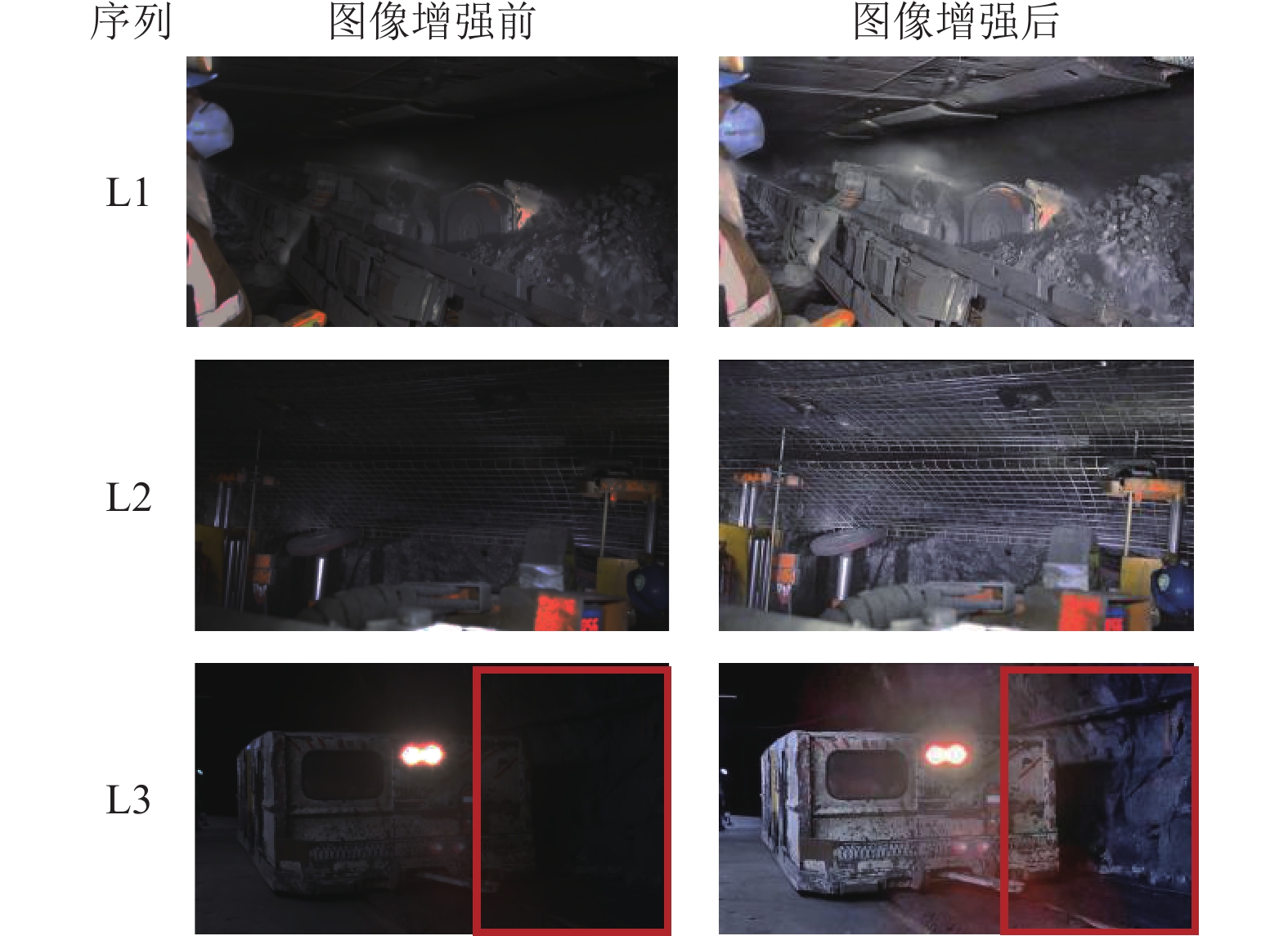
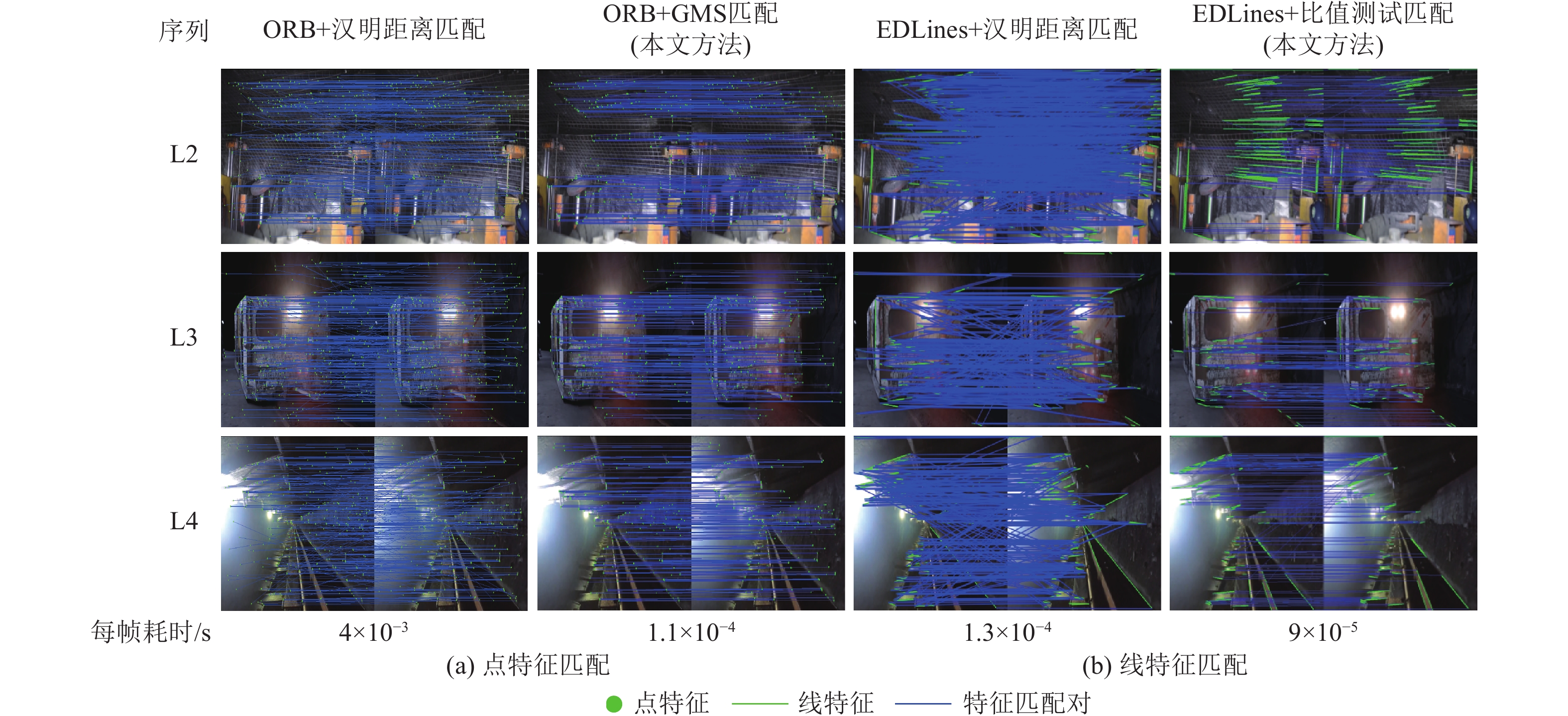
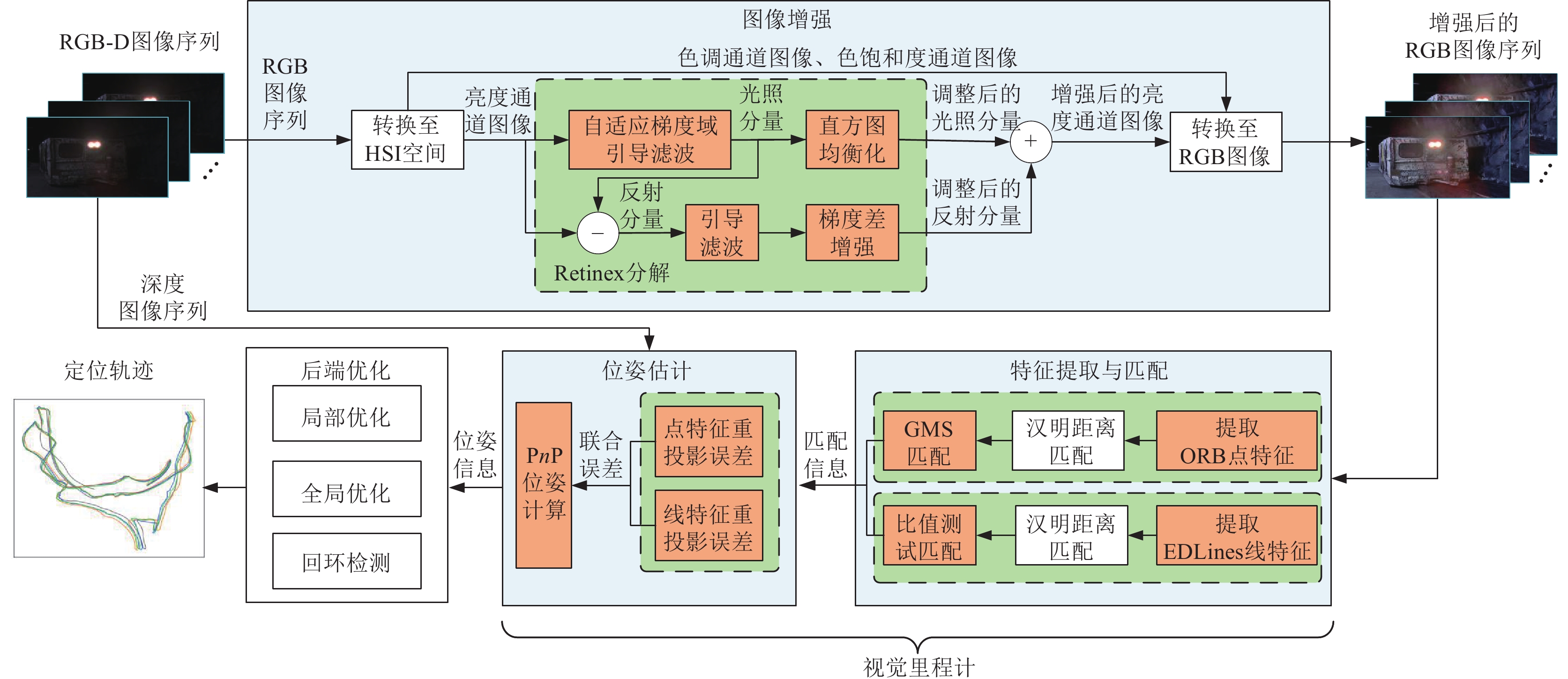
方法提出一种基于边缘感知增强的视觉SLAM方法。首先,构建了边缘感知约束的低光图像增强模块。通过自适应尺度的梯度域引导滤波器优化Retinex算法,以获得纹理清晰光照均匀的图像,从而显著提升了在低光照和不均匀光照条件下特征提取性能。其次,在视觉里程计中构建了边缘感知增强的特征提取和匹配模块,通过点线特征融合策略有效增强了弱纹理和结构化场景中特征的可检测性和匹配准确性。具体使用边缘绘制线特征提取算法(edge drawing lines, EDLines)提取线特征,定向FAST和旋转BRIEF点特征提取算法(oriented fast and rotated brief, ORB)提取点特征,并利用基于网格运动统计(grid-based motion statistics, GMS)和比值测试匹配算法进行精确匹配。最后,将该方法与ORB-SLAM2、ORB-SLAM3在TUM数据集和煤矿井下实景数据集上进行了全面实验验证,涵盖图像增强、特征匹配和定位等多个环节。
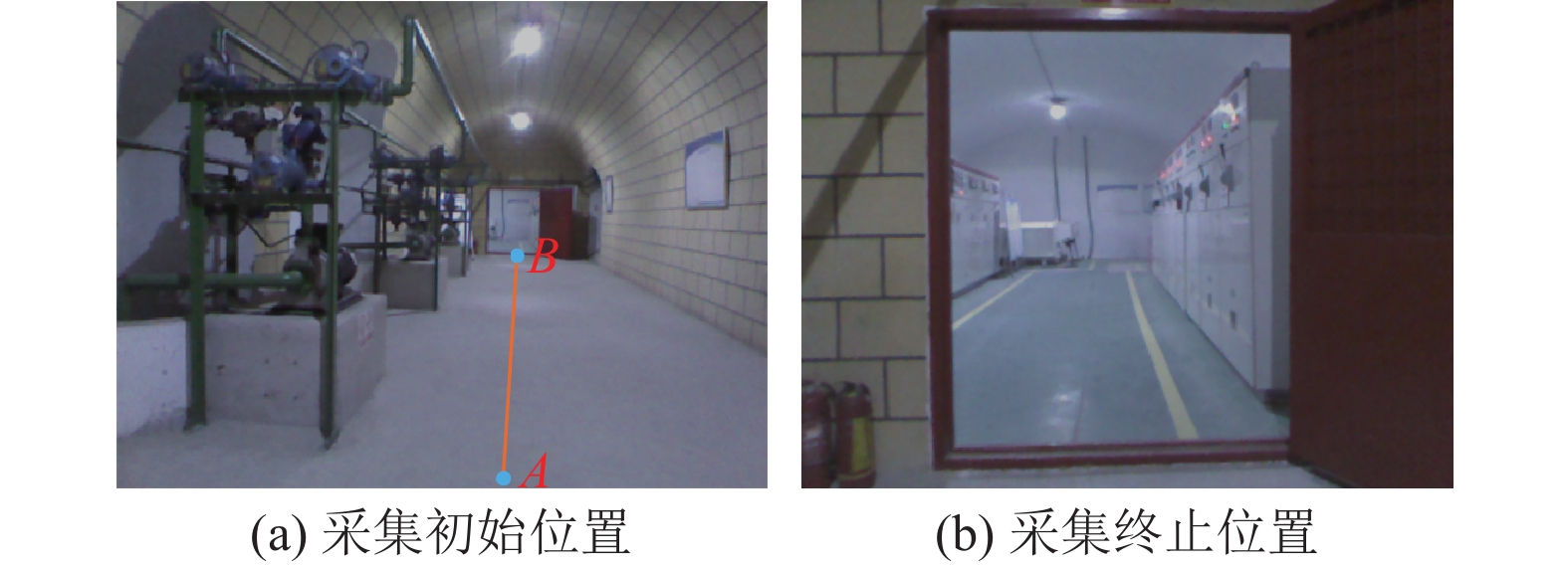
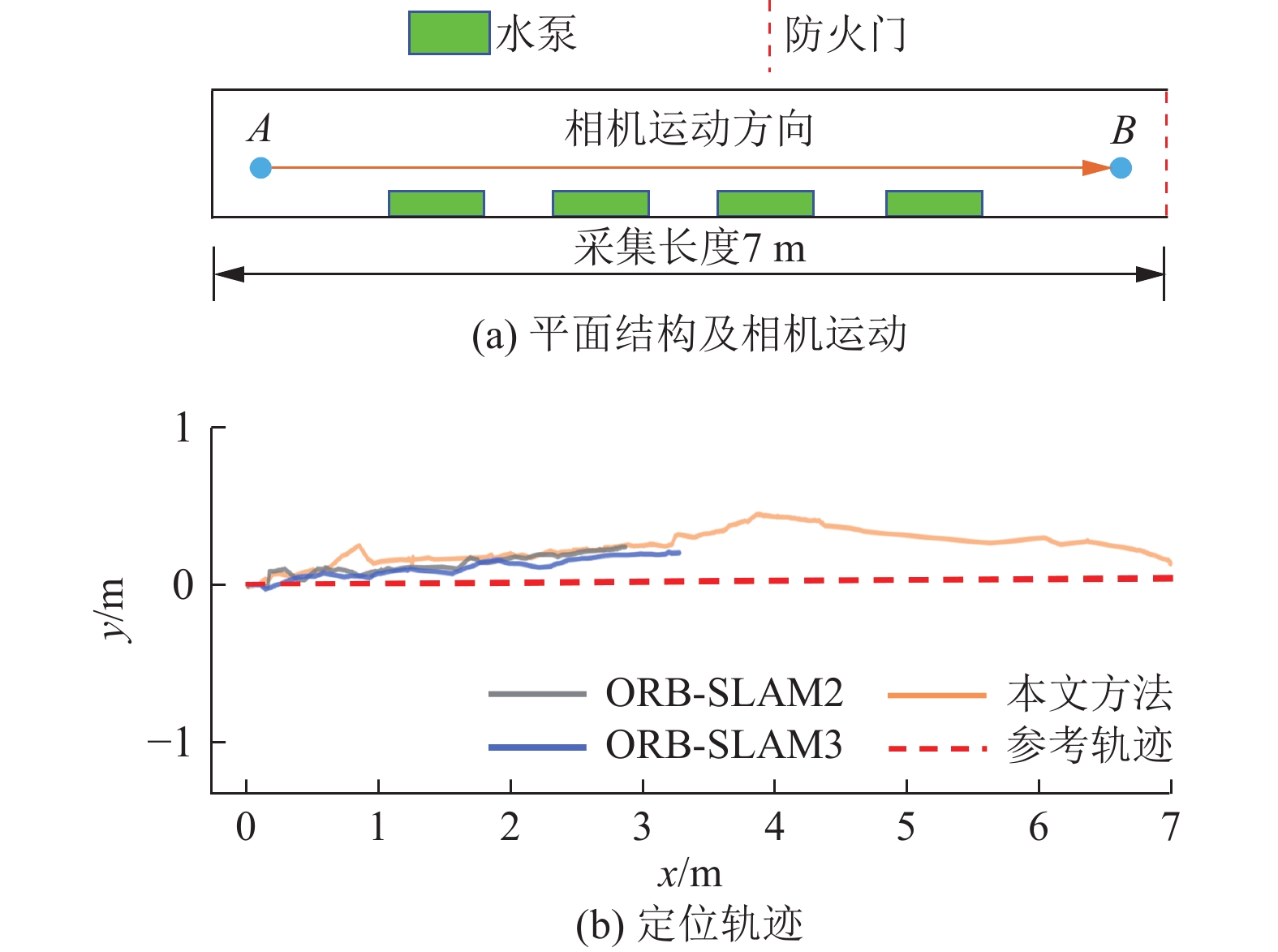
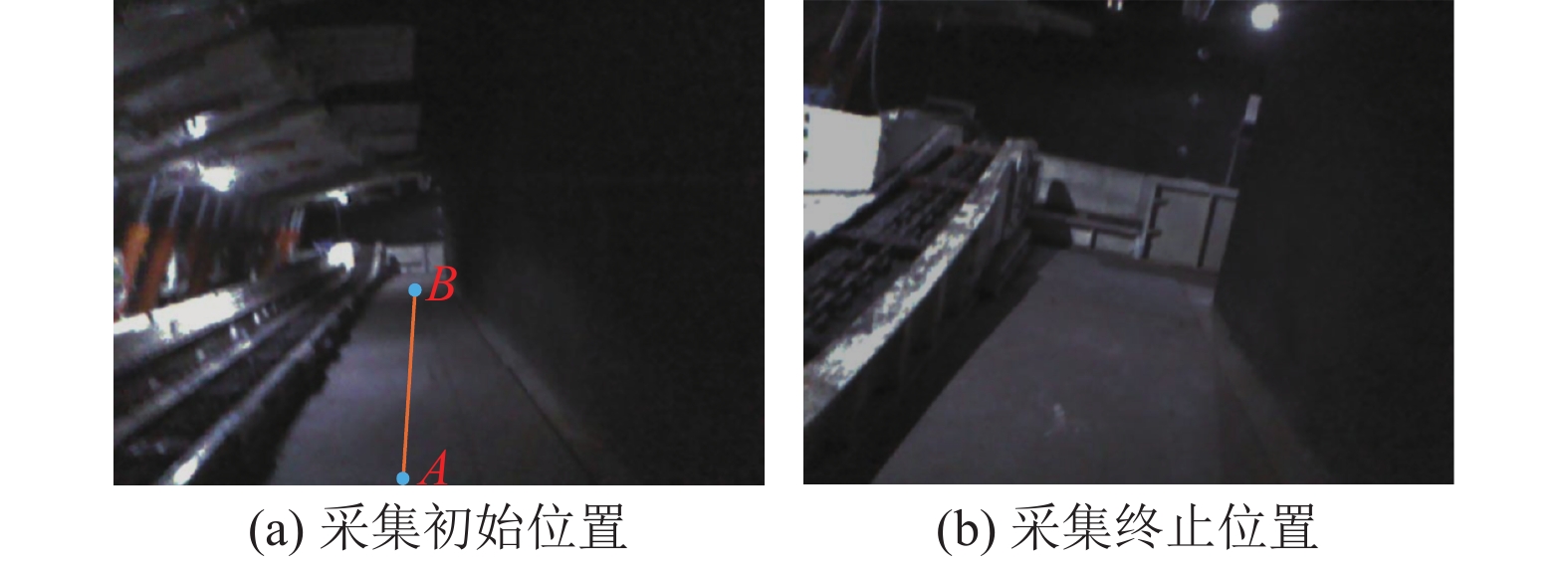
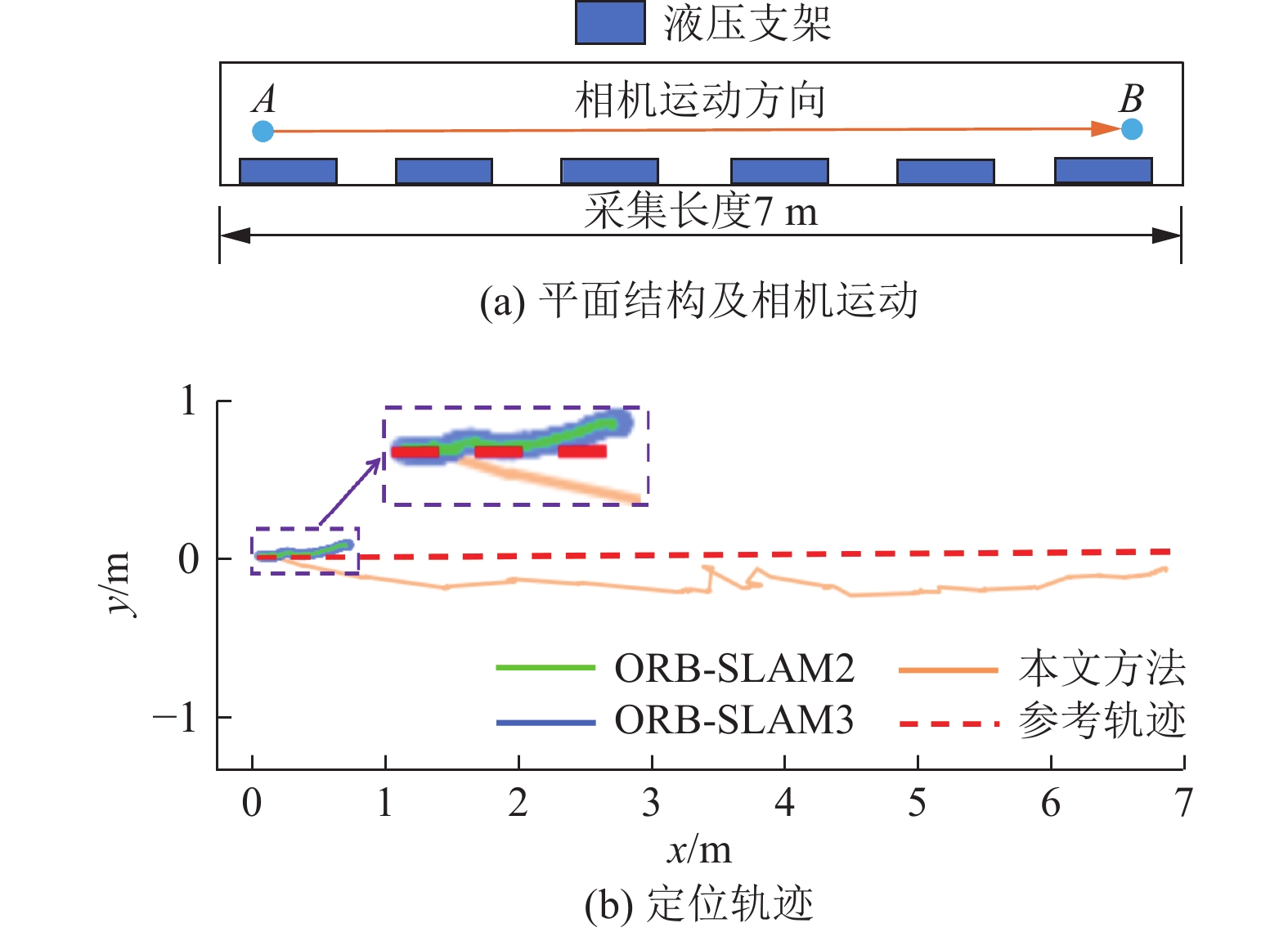
结果和结论结果表明:(1) 在TUM数据集上的测试结果显示,所提方法与ORB-SLAM2相比,绝对轨迹误差、相对轨迹误差的均方根误差分别降低了4%~38.46%、8.62%~50%;与ORB-SLAM3相比,绝对轨迹误差、相对轨迹误差的均方根误差分别降低了0~61.68%、3.63%~47.05%。(2) 在煤矿井下实景实验中,所提方法的定位轨迹更接近于相机运动参考轨迹。(3) 有效提高了视觉SLAM在煤矿井下特征退化场景中的准确性和鲁棒性,为视觉SLAM技术在煤矿井下的应用提供了技术解决方案。研究面向井下特征退化场景的视觉SLAM方法,对于推动煤矿井下移动式装备机器人化具有重要意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveUnderground coal mines commonly exhibit low illuminance, weak textures, and structuralization-induced feature degradation. These scenes lead to challenges of insufficient effective features and high mismatch rates to the visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system, severely compromising its localization accuracy and robustness.
MethodsThis study proposed an edge awareness-enhanced visual SLAM method. First, an edge-awareness constrained low-illuminance image enhancement module was developed. Specifically, images with clear textures and uniform illumination were obtained using the Retinex algorithm optimized using an adaptive gradient-domain guided filter. This significantly improved feature extraction performance under low and uneven lighting conditions. Second, an edge awareness-enhanced feature extraction and matching module was introduced into the visual odometry. A point and line feature fusion strategy was employed to enhance the detectability and matching accuracy of weak textures and features in structured scenes. Specifically, line features were extracted using the EDLines algorithm, while point features were extracted using the Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF (ORB) algorithms. Such feature extraction was followed by precise feature matching achieved using grid-based motion statistics (GMS) and ratio test matching algorithms. Finally, the proposed method, along with the ORB-SLAM2 and ORB-SLAM3 algorithms, was comprehensively verified on the TUM dataset and the dataset of the actual underground coal mine scenes, covering multiple aspects such as image enhancement, feature matching, and localization.
Results and ConclusionsThe results indicate that on the TUM dataset, the proposed method reduced the root mean square errors (RMSEs) of absolute and relative trajectory errors by 4%‒38.46% and 8.62%‒50%, respectively compared to ORB-SLAM2 and reduced by 0‒61.68% and 3.63%‒47.05%, respectively compared to ORB-SLAM3. Experiments on the actual underground coal mine scenes revealed that the location trajectories of the proposed method were aligned with the reference trajectory of camera motion more closely. Furthermore, the proposed method effectively enhanced the accuracy and robustness of the visual SLAM system in the feature degradation scene in underground coal mines, providing a technical solution for its applications in such settings. Research on visual SLAM methods tailored for feature degradation scenes in underground coal mines holds great significance for advancing the roboticization of mobile equipment used in coal mines.
-
-
表 1 图像增强前后客观指标
Table 1 Values of objective indicators before and after image enhancement
序列 图像熵 能量梯度/108 方差/108 L1 原图 6.30 4.05 5.27 增强后 7.25 115.89 10.4 L2 原图 5.89 6.54 3.74 增强后 7.17 299.17 9.46 L3 原图 5.66 4.36 3.56 增强后 7.13 109.96 11.32 表 2 绝对轨迹误差
Table 2 Absolute trajectory errors
序列名 ORB-SLAM2 ORB-SLAM3 本文方法 本文方法均方根误差降低百分比/% 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 相比ORB-SLAM2 相比ORB-SLAM3 f1_desk 0.019 0.016 0.018 0.016 0.016 0.013 15.78 11.11 f1_desk2 0.025 0.022 0.024 0.022 0.024 0.021 4 0 f1_floor --- --- --- --- 0.166 0.142 --- --- f1_room 0.044 0.039 0.107 0.099 0.041 0.038 6.81 61.68 f2_l_loop 0.143 0.110 0.206 0.146 0.093 0.084 34.96 54.85 f3_ns_far 0.080 0.064 0.075 0.061 0.071 0.057 11.25 5.33 f3_s_t_far 0.013 0.011 0.012 0.010 0.008 0.007 38.46 33.33 f3_s_t_near 0.011 0.010 0.010 0.009 0.009 0.008 18.18 10 注:“---”表示该算法在该序列中出现跟踪丢失,无法进行比较。 表 3 相对轨迹误差
Table 3 Relative trajectory errors
序列名 ORB-SLAM2 ORB-SLAM3 本文方法 本文方法均方根误差降低百分比/% 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 均方根误差/m 平均值/m 相比ORB-SLAM2 相比ORB-SLAM3 f1_desk 0.019 0.015 0.017 0.013 0.013 0.010 31.57 23.52 f1_desk2 0.019 0.015 0.018 0.014 0.017 0.012 10.52 5.55 f1_floor --- --- --- --- 0.035 0.007 --- --- f1_room 0.022 0.016 0.022 0.015 0.012 0.009 45.45 45.45 f2_l_loop 0.058 0.034 0.055 0.032 0.053 0.031 8.62 3.63 f3_ns_far 0.076 0.052 0.089 0.056 0.052 0.035 31.57 41.57 f3_s_t_far 0.018 0.016 0.017 0.015 0.009 0.007 50 47.05 f3_s_t_near 0.013 0.011 0.012 0.009 0.008 0.007 38.46 33.33 注:“---”表示该算法在该序列中出现跟踪丢失,无法进行比较。 表 4 低照度条件下绝对轨迹误差和相对轨迹误差
Table 4 Absolute and relative trajectory errors under low illumination conditions
单位:m 序列名 绝对轨迹误差 相对轨迹误差 本文方法未使用图像增强 本文方法 本文方法未使用图像增强 本文方法 均方根误差 平均值 均方根误差 平均值 均方根误差 平均值 均方根误差 平均值 f1_desk 0.014 0.012 0.011 0.009 0.013 0.008 0.011 0.008 f1_desk2 0.029 0.024 0.022 0.020 0.015 0.011 0.013 0.010 f1_floor 0.169 0.134 0.146 0.126 0.042 0.007 0.024 0.005 f1_room 0.081 0.075 0.070 0.063 0.013 0.009 0.010 0.008 f2_l_loop 0.214 0.202 0.081 0.071 0.099 0.046 0.038 0.020 f3_ns_far 0.095 0.047 0.042 0.036 0.091 0.044 0.036 0.029 f3_s_t_far 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.005 0.009 0.008 0.006 0.005 f3_s_t_near 0.009 0.009 0.008 0.007 0.008 0.007 0.007 0.006 -
[1] 王国法,张建中,薛国华,等. 煤矿回采工作面智能地质保障技术进展与思考[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(2):12−26. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.02.0062 WANG Guofa,ZHANG Jianzhong,XUE Guohua,et al. Progress and reflection of intelligent geological guarantee technology in coal mining face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(2):12−26. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.02.0062
[2] 王海军,曹云,王洪磊. 煤矿智能化关键技术研究与实践[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):44−54. WANG Haijun,CAO Yun,WANG Honglei. Research and practice on key technologies for intelligentization of coal mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):44−54.
[3] CHEN Weifeng,ZHOU Chengjun,SHANG Guangtao,et al. SLAM overview:From single sensor to heterogeneous fusion[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(23):6033. DOI: 10.3390/rs14236033
[4] 葛世荣,胡而已,李允旺. 煤矿机器人技术新进展及新方向[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(1):54−73. GE Shirong,HU Eryi,LI Yunwang. New progress and direction of robot technology in coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(1):54−73.
[5] 胡博妮,陈霖,徐丙立,等. 基于无人机平台的地表环境实时稠密点云生成与数字模型构建[J]. 遥感学报,2024,28(5):1206−1221. HU Boni,CHEN Lin,XU Bingli,et al. Real–time dense point cloud generation and digital model construction of surface environment based on UAV platform[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2024,28(5):1206−1221.
[6] 高毅楠,姚顽强,蔺小虎,等. 煤矿井下多重约束的视觉SLAM关键帧选取方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(增刊1):472−482. GAO Yinan,YAO Wanqiang,LIN Xiaohu,et al. Visual SLAM keyframe selection method with multiple constraints in underground coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024,49(Sup.1):472−482.
[7] HUANG Zenghua,GE Shirong,HE Yonghua,et al. Research on the intelligent system architecture and control strategy of mining robot crowds[J]. Energies,2024,17(8):1834. DOI: 10.3390/en17081834
[8] LI Menggang,HU Kun,LIU Yuwang,et al. A multimodal robust simultaneous localization and mapping approach driven by geodesic coordinates for coal mine mobile robots[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(21):5093. DOI: 10.3390/rs15215093
[9] 薛光辉,张钲昊,张桂艺,等. 煤矿井下点云特征提取和配准算法改进与激光SLAM研究[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术,2024:1–12 [2024-07-23]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20240722.1557.003.html. XUE Guanghui,ZHANG Zhenghao,ZHANG Guiyi,et al. Improvement of point cloud feature extraction and alignment algorithms and LiDAR SLAM in coal mine underground[J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology,2024:1–12 [2024-07-23]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20240722.1557.003.html.
[10] YU Rui,FANG Xinqiu,HU Chengjun,et al. Research on positioning method of coal mine mining equipment based on monocular vision[J]. Energies,2022,15(21):8068. DOI: 10.3390/en15218068
[11] 王纪武,万伟鹏,尚学强,等. 基于图像增强和自适应阈值的语义视觉SLAM系统[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2024,30(12):4217−4232. WANG Jiwu,WAN Weipeng,SHANG Xueqiang,et al. Semantic visual SLAM system based on image enhancement and adaptive thresholding[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems,2024,30(12):4217−4232.
[12] 龚云,颉昕宇. 基于同态滤波方法的煤矿井下图像增强技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(3):241−250. GONG Yun,XIE Xinyu. Research on coal mine underground image recognition technology based on homomorphic filtering method[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(3):241−250.
[13] 占必超,吴一全,纪守新. 基于平稳小波变换和Retinex的红外图像增强方法[J]. 光学学报,2010,30(10):2788−2793. DOI: 10.3788/AOS20103010.2788 ZHAN Bichao,WU Yiquan,JI Shouxin. Infrared image enhancement method based on stationary wavelet transformation and Retinex[J]. Acta Optica Sinica,2010,30(10):2788−2793. DOI: 10.3788/AOS20103010.2788
[14] WANG Yifan,WANG Hongyu,YIN Chuanli,et al. Biologically inspired image enhancement based on Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing,2016,177:373−384. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.124
[15] 梅英杰,宁媛,陈进军. 融合暗通道先验和MSRCR的分块调节图像增强算法[J]. 光子学报,2019,48(7):0710005. DOI: 10.3788/gzxb20194807.0710005 MEI Yingjie,NING Yuan,CHEN Jinjun. Block–adjusted image enhancement algorithm combining dark channel prior with MSRCR[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica,2019,48(7):0710005. DOI: 10.3788/gzxb20194807.0710005
[16] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale–invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision,2004,60(2):91−110. DOI: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
[17] RUBLEE E,RABAUD V,KONOLIGE K,et al. ORB:An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona:IEEE,2011.
[18] 马艾强,姚顽强. 煤矿井下移动机器人多传感器自适应融合SLAM方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2024,50(5):107−117. MA Aiqiang,YAO Wanqiang. Multi sensor adaptive fusion SLAM method for underground mobile robots in coal mines[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2024,50(5):107−117.
[19] 张旭辉,杨红强,白琳娜,等. 基于改进RANSAC特征提取的掘进装备视觉定位方法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2022,43(12):168−177. ZHANG Xuhui,YANG Hongqiang,BAI Linna,et al. Research on the visual positioning method of tunneling equipment based on the improved RANSAC feature extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument,2022,43(12):168−177.
[20] GROMPONE VON GIOI R,JEREMIE J,JEAN–MICHEL M,et al. LSD:A fast line segment detector with a false detection control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2010,32(4):722−732. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.300
[21] 姚建均,李英朝,吴杨,等. 融合点线特征的视觉惯性同时定位及建图[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报,2024,45(4):771−778. YAO Jianjun,LI Yingzhao,WU Yang,et al. Visual–inertia simultaneous localization and mapping based on point–and–line features[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2024,45(4):771−778.
[22] 龚坤,徐鑫,陈小庆,等. 弱纹理环境下融合点线特征的双目视觉同步定位与建图[J]. 光学精密工程,2024,32(5):752−763. DOI: 10.37188/OPE.20243205.0752 GONG Kun,XU Xin,CHEN Xiaoqing,et al. Binocular vision SLAM with fused point and line features in weak texture environment[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering,2024,32(5):752−763. DOI: 10.37188/OPE.20243205.0752
[23] BIAN Jiawang,LIN Wenyan,LIU Yun,et al. GMS:Grid–based motion statistics for fast,ultra–robust feature correspondence[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision,2020,128(6):1580−1593. DOI: 10.1007/s11263-019-01280-3
[24] 王笛,胡辽林. 基于双目视觉的改进特征立体匹配方法[J]. 电子学报,2022,50(1):157−166. WANG Di,HU Liaolin. Improved feature stereo matching method based on binocular vision[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica,2022,50(1):157−166.
[25] CHEN Xinyu,YU Yantao. An unsupervised low–light image enhancement method for improving V–SLAM localization in uneven low–light construction sites[J]. Automation in Construction,2024,162:105404. DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105404
[26] 刘冬,于涛,丛明,等. 基于深度学习图像特征的动态环境视觉SLAM方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(6):156−163. LIU Dong,YU Tao,CONG Ming,et al. Visual SLAM method for dynamic environment based on deep learning image features[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(6):156−163.
[27] MUR–ARTAL R,TARDÓS J D. ORB–SLAM2:An open–source SLAM system for monocular,stereo,and RGB–D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2017,33(5):1255−1262. DOI: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103
[28] LAND E H. The Retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American,1978,237(6):108−128.
[29] HE Kaiming,SUN Jian,TANG Xiaoou. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,35(6):1397−1409. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213
[30] KOU Fei,CHEN Weihai,WEN Changyun,et al. Gradient domain guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2015,24(11):4528−4539. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2468183
[31] XU Xin,YU Zhibin. Low–light image enhancement based on Retinex theory[C]//2023 IEEE 6th International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT). Qingdao:IEEE,2023.
[32] AKINLAR C,TOPAL C. EDLines:A real–time line segment detector with a false detection control[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters,2011,32(13):1633−1642. DOI: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.06.001
[33] PUMAROLA A,VAKHITOV A,AGUDO A,et al. PL–SLAM:Real–time monocular visual SLAM with points and lines[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore:IEEE,2017.
[34] STURM J,ENGELHARD N,ENDRES F,et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB–D SLAM systems[C]//2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura–Algarve:IEEE,2012.
[35] CAMPOS C,ELVIRA R,RODRÍGUEZ J J G,et al. ORB–SLAM3:An accurate open–source library for visual,visual–inertial,and multimap SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2021,37(6):1874−1890. DOI: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 焦安军,田世祥,林华颖,许石青. 贵州三甲煤矿突出煤体结构参数及孔隙特征研究. 煤矿安全. 2023(02): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 石钰,刘洋,薛俊华,李树刚,张超. 基于LAMMPS的煤纳米孔隙中甲烷吸附/解吸和流动规律研究. 煤田地质与勘探. 2023(04): 37-45 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王龙伟. 基于低温液氮吸附法的长平井田3号煤孔隙结构特征研究. 山西煤炭. 2022(03): 65-73+87 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 牟全斌. 单一低渗煤层井下增透技术研究现状与展望. 能源与环保. 2022(09): 281-287+300 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈建,贾秉义,董瑞刚,孙四清,赵继展. 煤矿井下水力压裂加骨料增透瓦斯抽采技术应用. 煤炭工程. 2021(02): 90-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 贾秉义,陈冬冬,吴杰,孙四清,王建利,赵继展,张杰. 煤矿井下顶板梳状长钻孔分段压裂强化瓦斯抽采实践. 煤田地质与勘探. 2021(02): 70-76 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 陈月霞,褚廷湘,陈鹏,汤杨. 瓦斯抽采钻孔间距优化三维数值模拟量化研究. 煤田地质与勘探. 2021(03): 78-84+94 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 胡秋嘉,刘世奇,闫玲,王鹤,方辉煌,张庆,毛崇昊,贾慧敏. 樊庄-郑庄区块无烟煤储层气水赋存-运移-产出路径的研究. 煤矿安全. 2020(10): 218-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘大锰,刘正帅,蔡益栋. 煤层气成藏机理及形成地质条件研究进展. 煤炭科学技术. 2020(10): 1-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)







 下载:
下载: