Quantitative study of 3D numerical simulation on optimizing borehole layout spacing of gas drainage
-
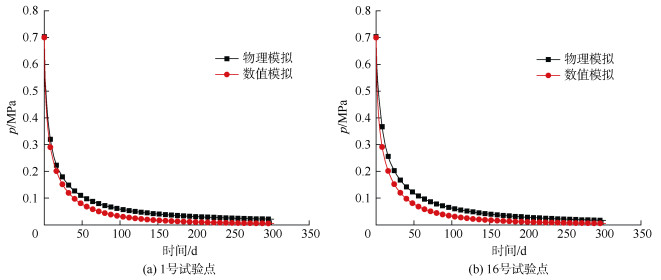
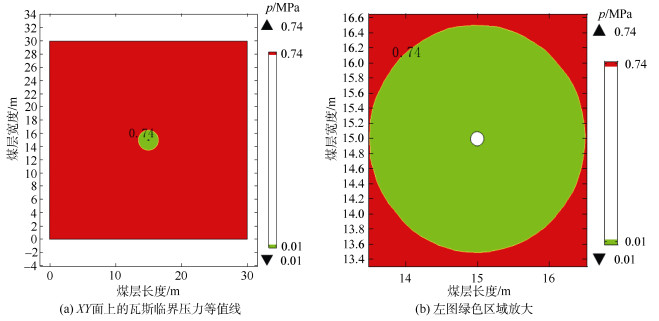
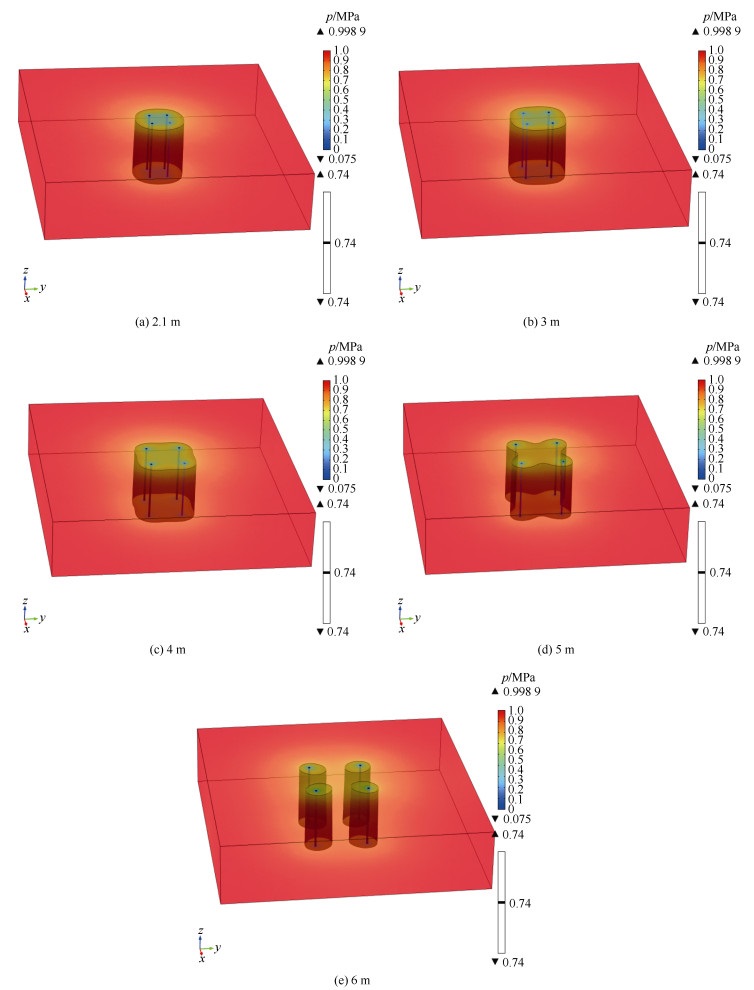
摘要: 为了识别钻孔间距对煤层瓦斯抽采的影响及如何实现高效抽采,基于流固耦合模型,建立三维几何模型,使其更接近现场实际,借助COMSOL软件模拟某煤矿钻孔不同间距的瓦斯抽采过程,利用瓦斯压力为0.74 MPa等压面三维立体图使有效抽采区域可视化,通过计算有效抽采区域体积大小,量化分析钻孔间距对抽采效果的影响。结果表明:单一钻孔抽采120 d时,有效抽采半径约为1.5 m;当布置多个钻孔且钻孔间距d为5 m,抽采120 d时,瓦斯压力为0.74 MPa的等压面围绕所有钻孔近似呈圆柱状但向内部凹陷(即出现空白带);钻孔间距d为2.1、3、4、5、6 m时,有效抽采区域体积V的大小顺序随着时间的增长而改变,抽采120 d时,Vd=5 m>Vd=4 m>Vd=3 m>Vd=2.1 m>Vd=6 m。综合分析瓦斯压力等压面三维立体图和有效抽采区域体积的大小顺序,确定该矿钻孔的较优间距为4 m。研究提出的以有效抽采半径、叠加效应、三维瓦斯压力等压面的形状及有效抽采区域体积大小为指标的钻孔间距数值计算考察方法,可为煤矿井下钻孔间距优化布置提供参考。Abstract: In order to optimize the spacing of boreholes and realize efficient drainage, based on the fluid solid coupling model, a three-dimensional geometric model was established to make it closer to the field reality, the gas drainage processes of a coal mine with different borehole spacing were simulated using COMSOL software. The results show that: the effective drainage area was visualized by the three-dimensional diagram of the isobaric surface with gas pressure of 0.74 MPa, and the influence of borehole spacing on the extraction efficiency was discussed. The results show that: the effective extraction radius is about 1.5 m during gas extraction with single borehole at 120 days; when the borehole spacing d was 5 m during gas extraction with multiple boreholes at 120 days, the isobaric surface with gas pressure of 0.74 MPa was approximately cylindrical around all the boreholes, but it was sunken to the interior(there is a blanking zone); when the borehole spacing were 2.1 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m and 6 m respectively, the order of the volumes of the effective drainage area V changed with the growth of time; at 120 days, the order was Vd=5 m>Vd=4 m>Vd=3 m>Vd=2.1 m>Vd=6 m. According to the three-dimensional diagram of gas pressure isobaric surface and the order of effective drainage area volumes, the optimal borehole spacing is determined to be 4 m. In this paper, a numerical investigation method for borehole spacing based on effective extraction radius, superposition effect, shape of isobaric surface of three-dimension of gas pressure and volume of effective extraction area was presented, providing reference for optimizing layout of borehole spacing in underground coal mines.
-
-
表 1 模型参数取值
Table 1 The values of the model parameters
参数 数值 弹性模量E/Pa 2.8×109 煤基质弹性模量ES/ Pa 8.4×109 泊松比υ 0.3 煤基质密度s/(kg·m–3) 1.35×103 煤层初始孔隙率${\phi _0}$ 0.037 煤层裂隙初始渗透率k0/m2 8.6×10–17 瓦斯动力黏度g/(Pa·s) 1.08×10–5 初始瓦斯压力p0/Pa 1.0×106 Langmuir压力常数pL/Pa 3.03×106 Langmuir体积应变常数${\varepsilon _{\rm{L}}}$ 0.026 -
[1] ZHANG Chaolin, WANG Enyuan, XU Jiang, et al. A new method for coal and gas outburst prediction and prevention based on the fragmentation of ejected coal[J]. Fuel, 2021, 287: 119493. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119493
[2] YANG Chunli, LI Xiangchun, REN Yanbin, et al. Statistical analysis and countermeasures of gas explosion accident in coal mines[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 84: 166-171. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.10.422
[3] SHI Juntai, WANG Shan, WANG Ke, et al. An accurate method for permeability evaluation of undersaturatedcoalbed methane reservoirs using early dewatering data[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2019, 202: 147-160. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.12.008
[4] 王晶, 姚团琪, 程斌. 基于煤矿"先抽后建"及资源开发的煤层气地面井位抽采部署及应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(4): 28-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.04.005 WANG Jing, YAO Tuanqi, CHENG Bin. Research and application of CBM surface extraction based on coal mine with "gas drainage first, construction later" and resource development[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(4): 28-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.04.005
[5] 方佳伟, 韩保山, 周加佳, 等. 基于工作面全覆盖的地面瓦斯高效抽采模式研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(3): 81-85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.03.012 FANG Jiawei, HAN Baoshan, ZHOU Jiajia, et al. Surface efficient gas extraction mode based on full coverage of working face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(3): 81-85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.03.012
[6] 刘永茜, 张书林, 舒龙勇. 吸附-解吸状态下煤层气运移机制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(4): 12-18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.04.003 LIU Yongqian, ZHANG Shulin, SHU Longyong. Coalbed methane migration mechanism under adsorption-desorption condition in coal[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(4): 12-18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.04.003
[7] 李宏, 马金魁. 顶板大直径定向长钻孔参数优化与优势分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20200212.2018.008.html. LI Hong, MA Jinkui. Parameter optimization and advantage analysis of large diameter directional long hole in roof[J]. Coal Science and Technology. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20200212.2018.008.html
[8] 齐黎明, 祁明, 陈学习. 抽采钻孔周围煤层瓦斯压力分布理论分析及应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(7): 102-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201807017.htm QI Liming, QI Ming, CHEN Xuexi. Theoretical analysis of coal seam gas pressure distribution around drainage hole and its application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(7): 102-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201807017.htm
[9] LIU Zhengdong, CHENG Yuanping, JIANG Jingyu, et al. Interactions between coal seam gas drainage boreholes and the impact of such on borehole patterns[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 38: 597-607. DOI: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.01.015
[10] 李波, 孙东辉, 张路路. 煤矿顺层钻孔瓦斯抽采合理布孔间距研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(8): 121-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201608021.htm LI Bo, SUN Donghui, ZHANG Lulu. Study on rational space between gas drainage boreholes passing through seam in coal mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(8): 121-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201608021.htm
[11] 王兆丰, 李炎涛, 夏会辉, 等. 基于COMOSOL的顺层钻孔有效抽采半径的数值模拟[J]. 煤矿安全, 2012, 43(10): 4-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ201210001.htm WANG Zhaofeng, LI Yantao, XIA Huihui, et al. Numerical simulation on effective drainage radius of drill hole along coal seam based on COMSOL[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2012, 43(10): 4-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ201210001.htm
[12] 马耕, 苏现波, 魏庆喜. 基于瓦斯流态的抽放半径确定方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(4): 501-504. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.04.014 MA Geng, SU Xianbo, WEI Qingxi. The determination method of coal gas drainage radius based on methane flow state[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(4): 501-504. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.04.014
[13] 刘三钧, 马耕, 卢杰, 等. 基于瓦斯含量的相对压力测定有效半径技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(10): 1715-1719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201110020.htm LIU Sanjun, MA Geng, LU Jie, et al. Relative pressure determination technology for effective radius found on gas content[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(10): 1715-1719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201110020.htm
[14] 郝富昌, 刘明举, 孙丽娟. 基于多物理场耦合的瓦斯抽放半径确定方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(增刊1): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2013S1018.htm HAO Fuchang, LIU Mingju, SUN Lijuan. Determination method of gas drainage radius based on multi-physics coupling[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(Sup. 1): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2013S1018.htm
[15] 郝富昌, 刘明举, 孙丽娟. 瓦斯抽采半径确定方法的比较及存在问题研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2012, 40(12): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201212014.htm HAO Fuchang, LIU Mingju, SUN Lijuan. Study on comparison of methods to determine gas drainage radius and existed problems[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2012, 40(12): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201212014.htm
[16] 梁冰, 袁欣鹏, 孙维吉, 等. 分组测压确定瓦斯有效抽采半径试验研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2013, 30(1): 132-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSYL201301024.htm LIANG Bing, YUAN Xinpeng, SUN Weiji, et al. Grouped pressure test to determine effective gas drainage radius[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2013, 30(1): 132-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSYL201301024.htm
[17] 李润芝, 梁冰, 孙维吉, 等. 顺层钻孔瓦斯抽采半径及布孔间距试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(10): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201610026.htm LI Runzhi, LIANG Bing, SUN Weiji, et al. Experimental study on both gas drainage radius and bedding borehole space[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(10): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201610026.htm
[18] 林柏泉, 宋浩然, 杨威, 等. 基于煤体各向异性的煤层瓦斯有效抽采区域研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(6): 139-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201906021.htm LIN Baiquan, SONG Haoran, YANG Wei, et al. Study on effective gas drainage area based on anisotropic coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(6): 139-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201906021.htm
[19] ZHANG Chaolin, XU Jiang, PENG Shoujian, et al. Experimental study of drainage radius considering borehole interaction based on 3D monitoring of gas pressure in coal[J]. Fuel, 2019, 239: 955-963. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236118319884
[20] 许江, 宋肖徵, 彭守建, 等. 顺层钻孔布置间距对煤层瓦斯抽采效果影响的物理模拟试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(12): 4581-4589. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201912004.htm XU Jiang, SONG Xiaozheng, PENG Shoujian, et al. Physical simulation experiment on influence of borehole spacing along the seam on effect of gas drainage[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(12): 4581-4589. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201912004.htm
[21] XIA Tongqiang, GAO Feng, KANG Jianhong, et al. A fully coupling coal-gas model associated with inertia and slip effects for CBM migration[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(7): 582. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-016-5378-y
[22] ZHANG Hongbin, LIU Jishan, ELSWORTH D. How sorption-induced matrix deformation affects gas flow in coal seams: A new FE model[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2008, 45(8): 1226-1236. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1365160907001876
[23] PALMER I, MANSOORI J. How permeability depends on stress and pore pressure in coalbeds: A new model[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 1998, 1(6): 539-544. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/250089489_How_Permeability_Depends_on_Stress_and_Pore_Pressure_in_Coalbeds_A_New_Model
[24] CHEN Yuexia, XU Jiang, CHU Tingxiang, et al. The evolution of parameters during CBM drainage in different regions[J], Transport in Porous Media, 2017, 120(113): 83-100. DOI: 10.1007/s11242-017-0910-4
[25] CHEN Yuexia, XU Jiang, PENG Shoujian, et al. A gas-solid-liquid coupling model of coal seams and the optimization of gas drainage boreholes[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(3): 560. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/doaj/19961073/2018/00000011/00000003/art00081







 下载:
下载: