Effect of coal mining subsidence fractures on source of water absorption of Artemisia Desertorum
-
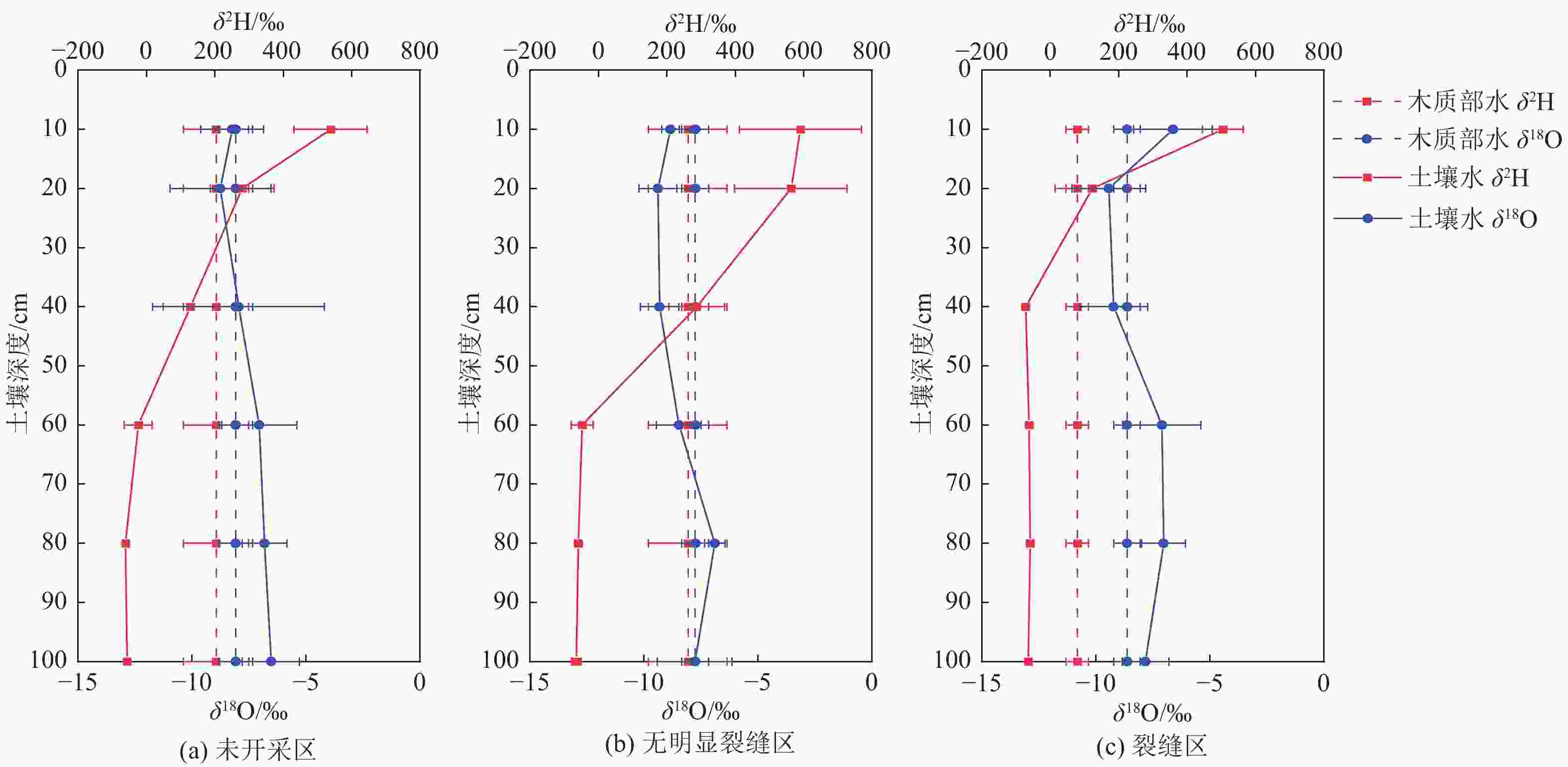
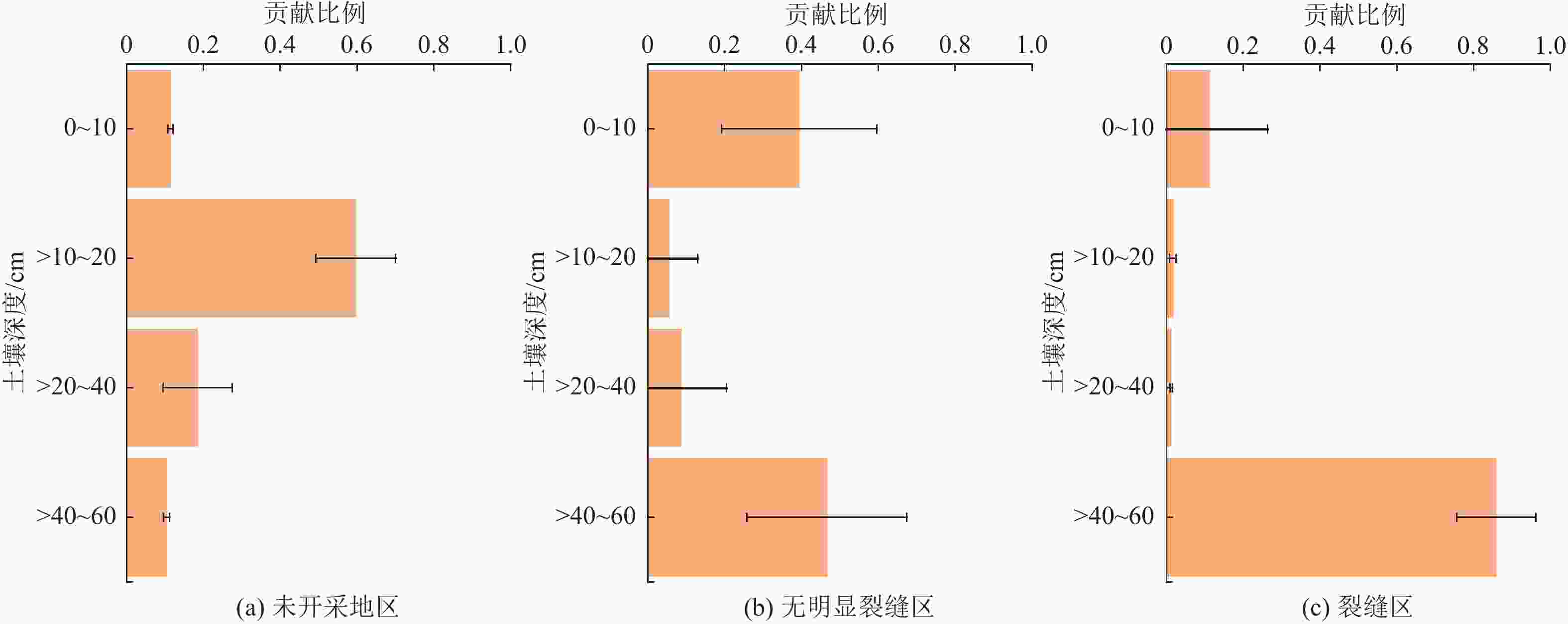
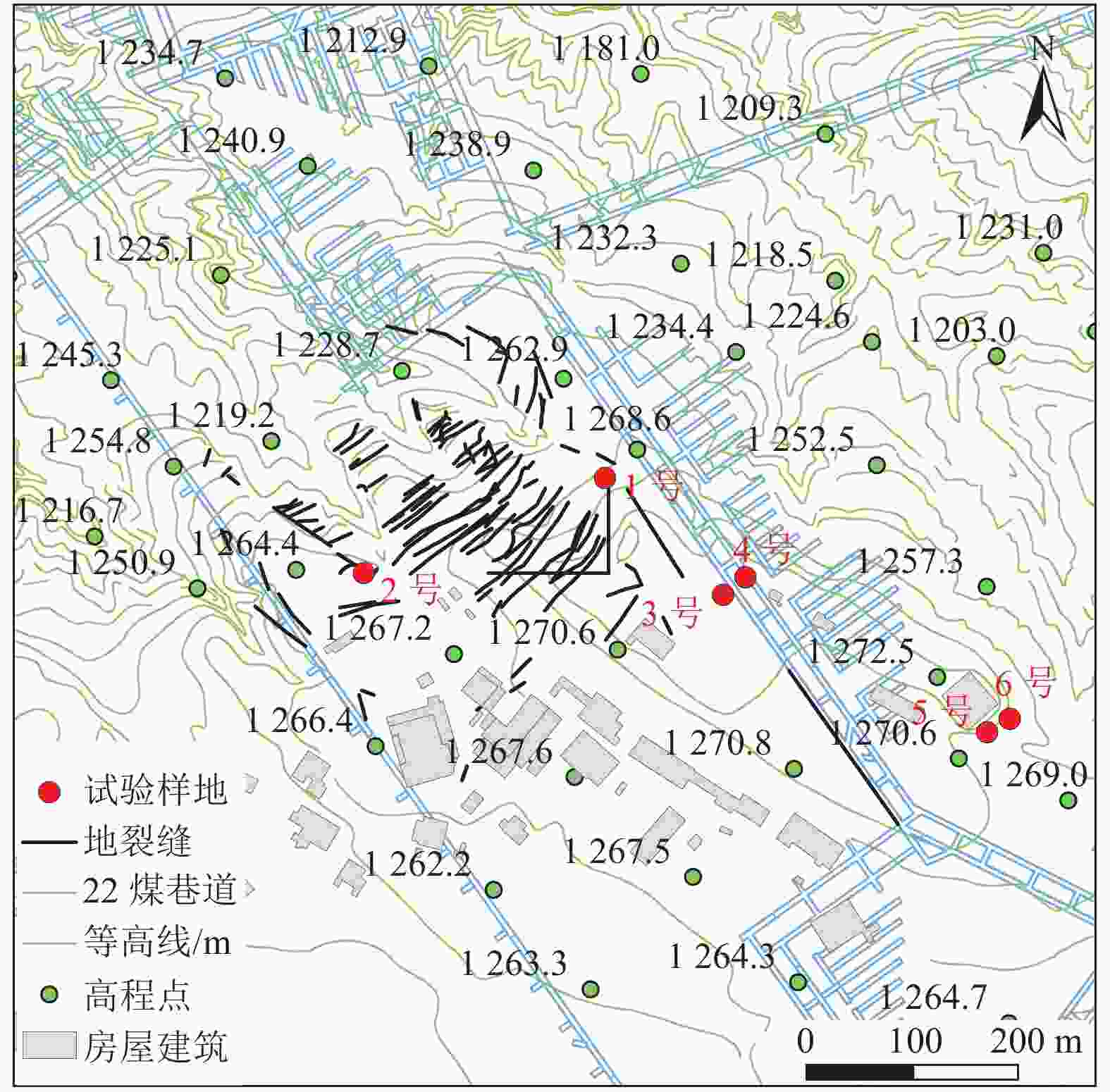
摘要: 采煤塌陷引起的地裂缝不仅造成地质灾害,还会影响矿区植被的生长发育,破坏矿区生态系统。为深入探讨采煤塌陷裂缝对沙蒿吸水来源的定量影响,在神东矿区活鸡兔井田22312工作面选取了受采煤塌陷裂缝影响程度不同的3个试验区进行同位素标记水模拟降水试验。3个试验区根据沙蒿与裂缝的距离不同划分,其采煤塌陷情况分别为未开采区(试验样地内沙蒿距离裂缝大于50 m)、受采煤塌陷影响但无明显裂缝区(简称无明显裂缝区,试验样地内沙蒿距离裂缝大于5 m)以及裂缝区(试验样地内分布有宽度15 cm左右的裂缝通过,且距离沙蒿0~20 cm)。本次试验选择6株沙蒿作为研究对象,划分6个土壤剖面,采用液态水同位素分析仪LGR和Isoprime 100同位素比值质谱仪IRMS分别计算不同土层土壤水和植物样本木质部水的δ18O和δ2H同位素含量,并利用R脚本的MixSIAR贝叶斯混合模型量化降水后不同土层对沙蒿吸水的贡献,探讨土壤水分补给机制和植物水分来源。结果表明:(1) 裂缝区的优先流比例为18.2%;(2) 在未开采区,沙蒿吸收的59.7%的水分来自10~20 cm的土层;(3) 在无裂缝区,沙蒿主要从40~60 cm土层(46.6%)和0~10 cm土层(39.4%)吸水;(4) 在裂缝区,沙蒿吸收的85.9%的水分主要来自40~60 cm的土层。研究结果对揭示采煤塌陷裂缝区土壤水补给机制以及沙蒿吸水模式具有重要意义。Abstract: Ground fissures caused by coal mining subsidence are not only a serious geological hazard, but also affect the growth and development of vegetation in the mining area and damage the mining ecosystem. To investigate the quantitative influence of coal mining subsidence fractures on the source of water uptaken by Artemisia Desertorum, the simulated precipitation tests of isotopically-labeled water were conducted in three test areas influenced by coal mining subsidence fractures to different degrees on 22312-working face of Huojitu mine field in Shendong mining area. The three test areas were divided according to the distance between Artemisia Desertorum and the fractures, where the coal mining subsidence conditions were classified as the virgin zone (where the Artemisia Desertorum was over 50 m away from the cracks in the test area), the zone affected by coal mining subsidence without obvious fractures (hereinafter referred to as fracture-free zone, where Artemisia Desertorum was more than 5 m away from the fractures in the test area) and the fracture zone (where the fractures with a width of about 15 cm passed through the test area at 0-20 cm away from Artemisia Desertorum). In this test, six pieces of Artemisia Desertorum were selected as the research objects and divided into six soil profiles. Then, the δ18O and δ2H isotope contents of soil water and xylem water of plant samples in different soil layers were calculated with LGR liquid water isotope analyzer and Isoprime 100 isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS) respectively. In addition, the contribution of different soil layers to the water uptaken by Artemisia Desertorum after precipitation was quantified with the MixSIAR Bayesian mixture model of R script, and to explore the mechanism of soil water recharge and the source of plant water. The results show that: (1) The proportion of preferential flow in the subsidence fracture zone is 18.2%, (2) 59.7% of water uptaken by Artemisia Desertorum comes from the 10‒20 cm soil layer in the virgin area, (3) 46.6% and 39.4% of water comes from the 40‒60 cm and 0‒10 cm soil layers in the fracture-free zone, respectively, and (4) 85.9% of water uptaken by Artemisia Desertorum is mainly derived from the 40-60 cm soil layer in the subsidence fracture zone. The research results are significant to reveal the mechanism of soil water recharge and the water uptake pattern of plants in subsidence fracture zone of coal-mining areas.
-
表 1 试验样地内沙蒿植被参数
Table 1 Vegetation parameters of Artemisia Desertorum in the sample area
cm 样地序号 样地西侧 样地东侧 株高 冠幅 株高 冠幅 1号 30.31 42.11 32.12 39.57 2号 29.28 39.68 28.26 38.27 3号 32.15 45.27 35.24 46.88 4号 28.45 46.62 27.63 41.28 5号 31.22 40.58 30.85 40.63 6号 33.53 44.34 33.62 45.32 -
[1] 胡振琪,袁冬竹. 黄河下游平原煤矿区采煤塌陷地治理的若干基本问题研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1392−1403.HU Zhenqi,YUAN Dongzhu. Research on several fundamental issues of coal mining subsidence control in plain coal mining area of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(5):1392−1403. [2] BI Yinli,ZHANG Jian,SONG Ziheng,et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate root damage stress induced by simulated coal mining subsidence ground fissures[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,652:398−405.. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.249 [3] DANG Hongzhong,ZHANG Lizhen,YANG Wenbin,et al. Severe drought strongly reduces water use and its recovery ability of mature Mongolian Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv. ) in a semi−arid sandy environment of northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Land,2019,11(6):880−891.. doi: 10.1007/s40333-019-0029-2 [4] LIU Ying,LEI Shaogang,CHEN Xiaoyang,et al. Disturbance mechanism of coal mining subsidence to typical plants in a semiarid area using O–J–I–P chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis[J]. Photosynthetica,2020,58(5):1178−1187.. doi: 10.32615/ps.2020.072 [5] WANG Jianhua,LU Chuiyu,SUN Qingyan,et al. Simulating the hydrologic cycle in coal mining subsidence areas with a distributed hydrologic model[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:39983.. doi: 10.1038/srep39983 [6] YU Xiaona,HUANG Yongmei,LI Engui,et al. Effects of vegetation types on soil water dynamics during vegetation restoration in the Mu Us Sandy Land,northwestern China[J]. Journal of Arid Land,2017,9(2):188−199.. doi: 10.1007/s40333-017-0054-y [7] 雷少刚,肖浩宇,郄晨龙,等. 开采沉陷对关键土壤物理性质影响的相似模拟实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(2):300−307.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.6006LEI Shaogang,XIAO Haoyu,QIE Chenlong,et al. Similar simulation experiment on the influence of mining subsidence on the key physical properties of soil[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(2):300−307.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.6006 [8] 彭苏萍,毕银丽. 黄河流域煤矿区生态环境修复关键技术与战略思考[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(4):1211−1221.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.0444PENG Suping,BI Yinli. Strategic consideration and core technology about environmental ecological restoration in coal mine areas in the Yellow River Basin of China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(4):1211−1221.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.0444 [9] 杜华栋,曹祎晨,聂文杰,等. 黄土沟壑区采煤塌陷地人工与自然植被恢复下土壤性质演变特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1641−1649.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.st20.1784DU Huadong,CAO Yichen,NIE Wenjie,et al. Evolution of soil properties under artificial and natural revegetation in loess gully coal mining subsidence area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(5):1641−1649.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.st20.1784 [10] 苗春光,杨惠惠,毕银丽,等. 丛枝菌根真菌与沙棘对露天矿排土场的联合改良效应[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):202−206.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.025MIAO Chunguang,YANG Huihui,BI Yinli,et al. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Hippophae rhamnoides on the improvement of the dump of open–pit coal mine in the eastern grassland[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(2):202−206.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.025 [11] 张雁,黄选明,陈实,等. 露天煤矿草原区植被指数与气象水文要素关系[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(4):94−101.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.014ZHANG Yan,HUANG Xuanming,CHEN Shi,et al. Relationship between NDVI and hydromet factors in grassland area of open–pit coal mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(4):94−101.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.014 [12] 李琪. 石羊河流域民勤盆地表生生态与地下水关系研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2021.LI Qi. Study on the relationship of supergene ecology and groundwater in Minqin Basin of Shiyang River Basin[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2021. [13] 李欣颖,张萌,郭洋楠,等. 采煤沉陷区林下植物多样性与土壤因子的关系[J]. 水土保持学报,2022,36(1):268−276.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2022.01.035LI Xinying,ZHANG Meng,GUO Yangnan,et al. Relationship between understory plant diversity and soil factors in coal mining subsidence area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,36(1):268−276.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2022.01.035 [14] 李斐,孙明伟,钟尚志,等. 不同光合类型牧草对干旱–复水的光合生理响应及生长适应策略[J]. 植物生态学报,2022,46(1):74−87.. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0203LI Fei,SUN Mingwei,ZHONG Shangzhi,et al. Photosynthetic physiology and growth adaptation of herbages with different photosynthetic pathways in response to drought−rehydration[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2022,46(1):74−87.. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0203 [15] 赵明,王文科,王周锋,等. 半干旱区沙地沙蒿生物量及根系分布特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理,2018,41(4):786−792.. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2018.04.14ZHAO Ming,WANG Wenke,WANG Zhoufeng,et al. Biomass of Artemisia Ordosica in sand land and its root system distribution characteristics in the semiarid regions[J]. Arid Land Geography,2018,41(4):786−792.. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2018.04.14 [16] 刘嘉伟. 黑沙蒿根系受损自修复后力学特性的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019.LIU Jiawei. Study on mechanical properties of self−healed Artemisia Ordosica Krasch. roots after erosional force damage[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. [17] 王博,包玉海,刘静,等. 半干旱矿区侵蚀营力对黑沙蒿根系生长特性的影响及其自修复[J]. 生态学杂志,2022,41(2):263−269.. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202202.006WANG Bo,BAO Yuhai,LIU Jing,et al. Effects of erosive agent on root growth and self−healing of Artemisia Ordosica in semi−arid mining site[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2022,41(2):263−269.. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202202.006 [18] 王成龙. 四种植物根系剪拉组合力损伤自修复后固土特性[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021.WANG Chenglong. Study on the soil reinforcement of four plants roots damaged by shear−tensile combination[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. [19] 郑双科,司炳成,张志强,等. 黄土塬区苹果园降雨入渗机制[J]. 应用生态学报,2017,28(9):2870−2878.ZHENG Shuangke,SI Bingcheng,ZHANG Zhiqiang,et al. Mechanism of rainfall infiltration in apple orchards on Loess Tableland,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2017,28(9):2870−2878. [20] 巩国丽,陈辉,段德玉. 利用稳定氢氧同位素定量区分白刺水分来源的方法比较[J]. 生态学报,2011,31(24):7533−7541.GONG Guoli,CHEN Hui,DUAN Deyu. Comparison of the methods using stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope to distinguish the water source of Nitraria Tangutorum[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(24):7533−7541. [21] ROTHFUSS Y,JAVAUX M. Reviews and syntheses:Isotopic approaches to quantify root water uptake:A review and comparison of methods[J]. Biogeosciences,2017,14(8):2199−2224.. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-2199-2017 [22] 苏文旭,贾德彬,冯蕴,等. 浑善达克沙地杨树水分利用特征[J]. 干旱区研究,2020,37(2):357−363.SU Wenxu,JIA Debin,FENG Yun,et al. Analysis of water use characteristics of poplar trees in Otindag Sandy Land[J]. Arid Zone Research,2020,37(2):357−363. [23] 刘柯渝,司炳成,张志强. 黄土高原不同林龄苹果树根系吸水策略对降水的响应[J]. 水土保持学报,2018,32(4):88−94.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2018.04.014LIU Keyu,SI Bingcheng,ZHANG Zhiqiang. Responses of water uptake pattern of apple trees with different stand ages to precipitation on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(4):88−94.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2018.04.014 [24] 吴友杰,魏镇华,杜太生. 交替沟灌条件下土壤水稳定氢氧同位素分布特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2014,33(4/5):251−255.. doi: 10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2014.04/05.055WU Youjie,WEI Zhenhua,DU Taisheng. Characteristics of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in soil water under alternate partial root−zone furrow irrigation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2014,33(4/5):251−255.. doi: 10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2014.04/05.055 [25] 李荣磊,黄来明,裴艳武,等. 毛乌素沙地圪丑沟小流域沙柳水分利用来源研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2021,35(2):122−130.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.02.017LI Ronglei,HUANG Laiming,PEI Yanwu,et al. Water use source of Salix psammophila in Gechougou small watershed of Mu Us Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,35(2):122−130.. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.02.017 [26] GUO Hui,ZHAO Ying. Using isotopic labeling to investigate root water uptake in an alley cropping system within Taklimakan Desert Oasis,China[J]. Agroforestry Systems,2021,95(5):907−918.. doi: 10.1007/s10457-020-00527-0 [27] 冯蕴,贾德彬,李雪松,等. 基于稳定同位素的干旱半干旱地区杨树水分来源研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2019,27(4):27−31.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2019.04.006FENG Yun,JIA Debin,LI Xuesong,et al. Study on water sources of poplar in arid and semi–arid regions based on stable isotopes[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2019,27(4):27−31.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2019.04.006 [28] ZHANG Mengman,WU Xiuqin. The rebound effects of recent vegetation restoration projects in Mu Us Sandy Land of China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2020,113:106228.. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106228 [29] 侯恩科,首召贵,徐友宁,等. 无人机遥感技术在采煤地面塌陷监测中的应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(6):102−110.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.06.017HOU Enke,SHOU Zhaogui,XU Youning,et al. Application of UAV remote sensing technology in monitoring of coal mining−induced subsidence[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2017,45(6):102−110.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.06.017 [30] 柳琳秀. 毛乌素沙地三种植物根系垂直分布研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2015.LIU Linxiu. Study on root vertical distribution of three kinds of Shrubs in Mu Us Sandy Land[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2015. [31] 岳艳鹏,孙迎涛,庞营军,等. 毛乌素沙地沙丘活化过程中油蒿(Artemisia Ordosica)根系特征[J]. 中国沙漠,2020,40(3):177−184.YUE Yanpeng,SUN Yingtao,PANG Yingjun,et al. Root characteristics of Artemisia Ordosica in the process of sand dunes activation in the Mu Us Sand Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2020,40(3):177−184. [32] 杜俊杉,马英,胡晓农,等. 基于双稳定同位素和MixSIAR模型的冬小麦根系吸水来源研究[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(18):6611−6622.DU Junshan,MA Ying,HU Xiaonong,et al. Applying dual stable isotopes and a MixSIAR model to determine root water uptake of winter wheat[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(18):6611−6622. [33] 曾祥明,徐宪立,钟飞霞,等. MixSIAR和IsoSource模型解析植物水分来源的比较研究[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(16):5611−5619.ZENG Xiangming,XU Xianli,ZHONG Feixia,et al. Comparative study of MixSIAR and IsoSource models in the analysis of plant water sources[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(16):5611−5619. [34] YANG Yonggang,FU Bojie. Soil water migration in the unsaturated zone of semiarid region in China from isotope evidence[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2017,21(3):1757−1767.. doi: 10.5194/hess-21-1757-2017 [35] ZHANG Jing,LEI Tingwu,QU Liqin,et al. Method to quantitatively partition the temporal preferential flow and matrix infiltration in forest soil[J]. Geoderma,2019,347:150−159.. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.03.026 [36] 王强民,董书宁,王皓,等. 西部风沙区采煤塌陷地裂缝影响下的土壤水分运移规律及调控方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1532−1540.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.st21.0267WANG Qiangmin,DONG Shuning,WANG Hao,et al. Influence of mining subsidence on soil water movement law and its regulation in blown−sand area of western China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(5):1532−1540.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.st21.0267 [37] 杜华栋,宋世杰,张勇,等. 彬长矿区不同地表沉陷类型下植物群落特征[J]. 生态学杂志,2019,38(5):1520−1527.. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201905.003DU Huadong,SONG Shijie,ZHANG Yong,et al. Characteristics of plant community in different types of coal mining subsidence in Binchang mining area[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2019,38(5):1520−1527.. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201905.003 [38] 胡振琪,龙精华,王新静. 论煤矿区生态环境的自修复、自然修复和人工修复[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(8):1751−1757.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.9029HU Zhenqi,LONG Jinghua,WANG Xinjing. Self–healing,natural restoration and artificial restoration of ecological environment for coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(8):1751−1757.. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.9029 -








 下载:
下载: