Typical coalbed methane (CBM) enrichment and production modes under the control of regional structure and evolution
-
摘要: 煤层气勘探开发对改善我国能源结构、解决煤矿灾害与生态环境问题意义重大。结合我国区域构造与演化过程及煤层气地质条件,将煤层气富集产气模式划分为4种主要类型:构造简单裂隙系统、褶皱系统(较浅向斜轴部、褶皱翼部、次级构造高部位)、冲断构造系统(褶皱冲断带、高陡冲断构造)和构造叠加系统模式。其中,(1) 构造简单裂隙系统模式发育在构造相对稳定的地区,煤层气以深成热成因为主,也可受岩浆热接触作用影响,在裂隙中等发育区形成高产富集区。(2) 褶皱系统模式中,较浅向斜轴部挤压应力利于煤层气保存从而富集产气;褶皱翼部压力分布均匀,封闭性较好,其含气量与渗透率匹配适中形成富集高产带;次级构造高部位模式主要是在构造作用下形成的伴生构造(背斜、鼻隆构造、断块等)高部位形成构造圈闭,生成“气顶”。(3) 冲断构造系统模式中,褶皱冲断带模式中逆冲断层阻止了煤层气的逸散,在靠近逆冲断层的相对构造高点富集产气;高陡冲断构造模式发育在复杂断裂区,深部煤层气在一定温压作用下,解吸游离至上部地层,重新被吸附或部分仍呈游离状态而富集产气。(4) 构造叠加系统模式形成于受多期构造活动共同作用的煤储层中,不同的应力方向和机制引起的构造叠加使含气量和渗透率相匹配,煤层气富集且有一定产量。因此,区域构造特征控制着煤层气富集产气的每个模式,构造演化过程决定了富集产气的不同模式。这些富集产气模式对系统认识中国煤层气富集规律,指导“十四五”煤层气勘探开发具有重要意义。Abstract: Coalbed methane (CBM) exploration and development is of great significance to optimize China’s energy structure and cope with coal mine disasters and ecological environment problems. In this paper, combined with regional structure and evolution and CBM geological conditions, the enrichment and recovery modes of CBM are innovatively divided into four categories: simple structural fracture system, fold system (shallower synclinal shaft, fold limb, secondary structural high position), thrust system (fault-thrust-fold belt, high-steep thrust structure) and structural superposition system. Among them, simple structural fracture system mode is often encountered in the areas with relatively stable structure, where the CBM is mainly derived from deep thermogenesis, and can also be reformed by magma thermal contact, forming high-yield enrichment zones with moderately developed fracture. In the fold system mode, the extrusion stress at the shallower synclinal shaft is conducive to the preservation of CBM. The fold limbs with uniform pressure distribution and superior sealing performance are compatible with both gas content and permeability, thus forming high-yield enrichment zones. The secondary structural high position mode refers to the structural traps formed in the high part of the associated structures (anticlines, nose-shaped uplift, fault blocks, etc.) under compression, which generate “gas cup”. In the fault-thrust-fold belt mode, the thrust fault prevents the escape of CBM, and captures gas at the relative structural high position close to the thrust fault. The high-steep thrust structure mode is developed in the complex fault area. Subjected to the specific temperature and pressure fields, the desorbed deep CBM migrates to the upper strata, and is re-adsorbed or partially still in a free state and accumulated. The structural superposition system mode, in contrast to single main control mode, is formed in the coal reservoirs affected by multi-stage tectonic movements. The structural superposition caused by different stress directions and mechanisms superposition achieves optimal matching of gas content and permeability, which is also favorable for CBM enrichment. Therefore, regional structural characteristics control the mode of CBM enrichment and recovery, which is fundamentally determined by tectonic evolution. Conclusions drawn in this study are of great reference value to systematically understanding the law of CBM enrichment in China and guiding the exploration and exploitation of CBM during the 14th Five-Year Plan.
-
表 1 煤层气富集产气模式及机理
Table 1 Mode and mechanism of CBM enrichment and production
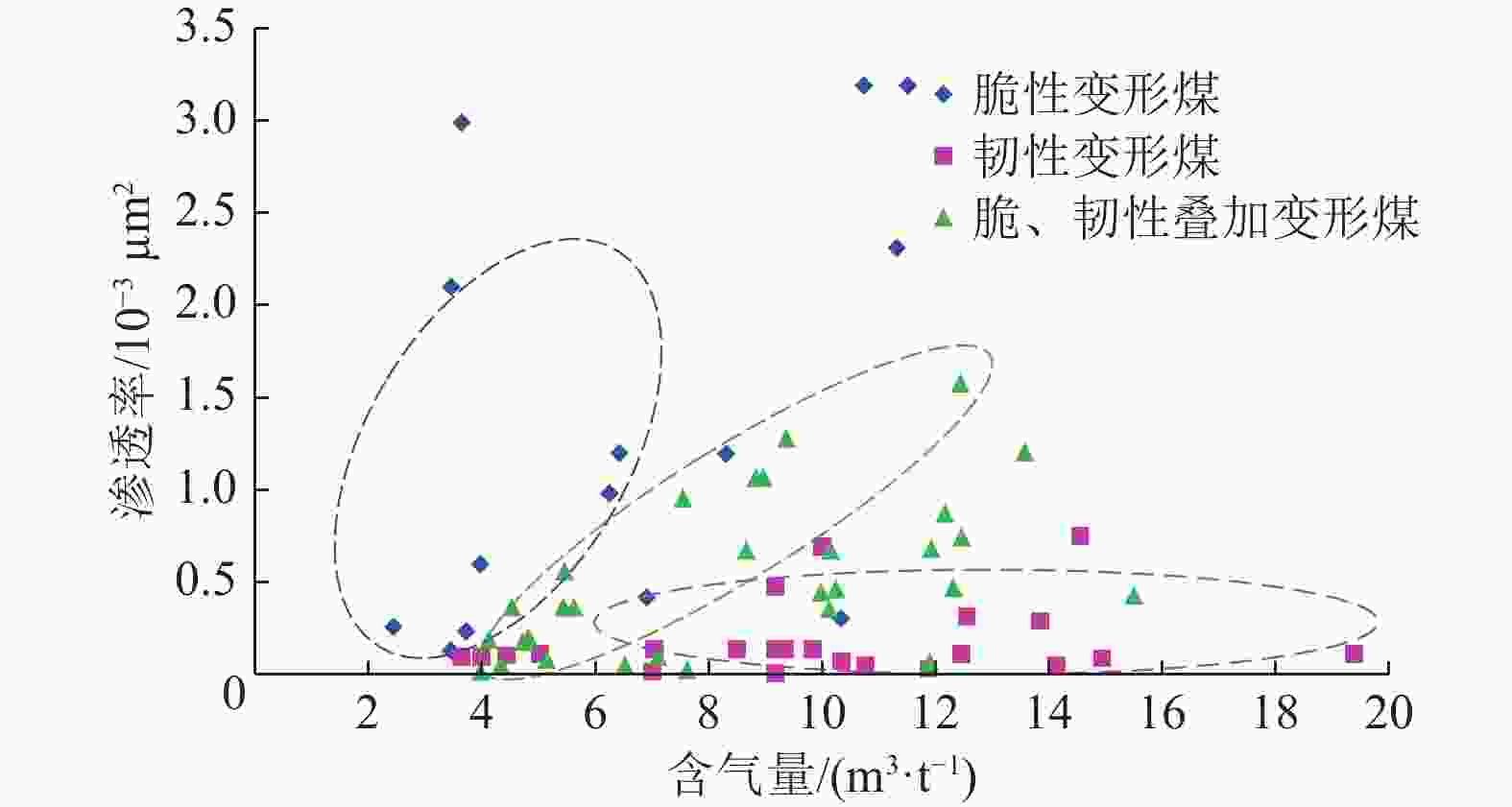
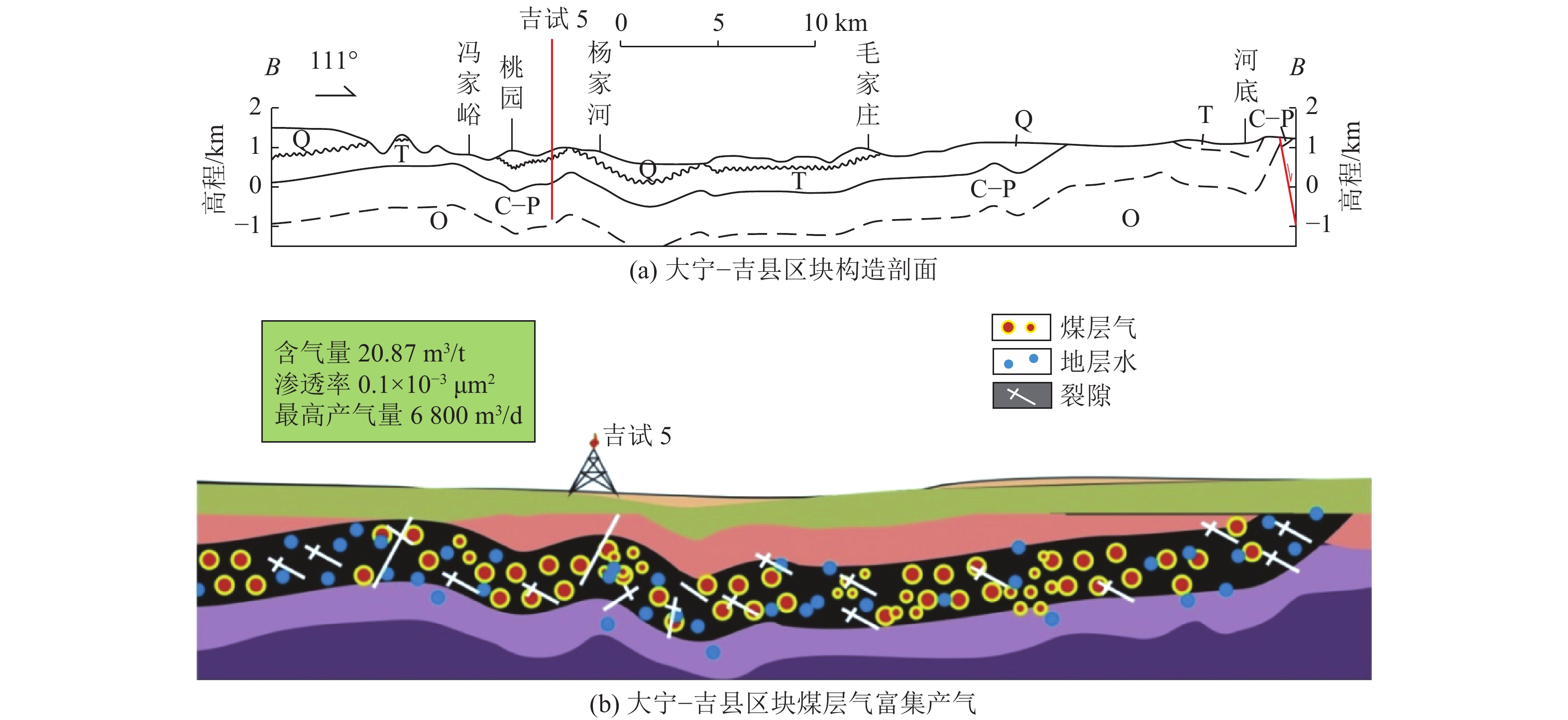
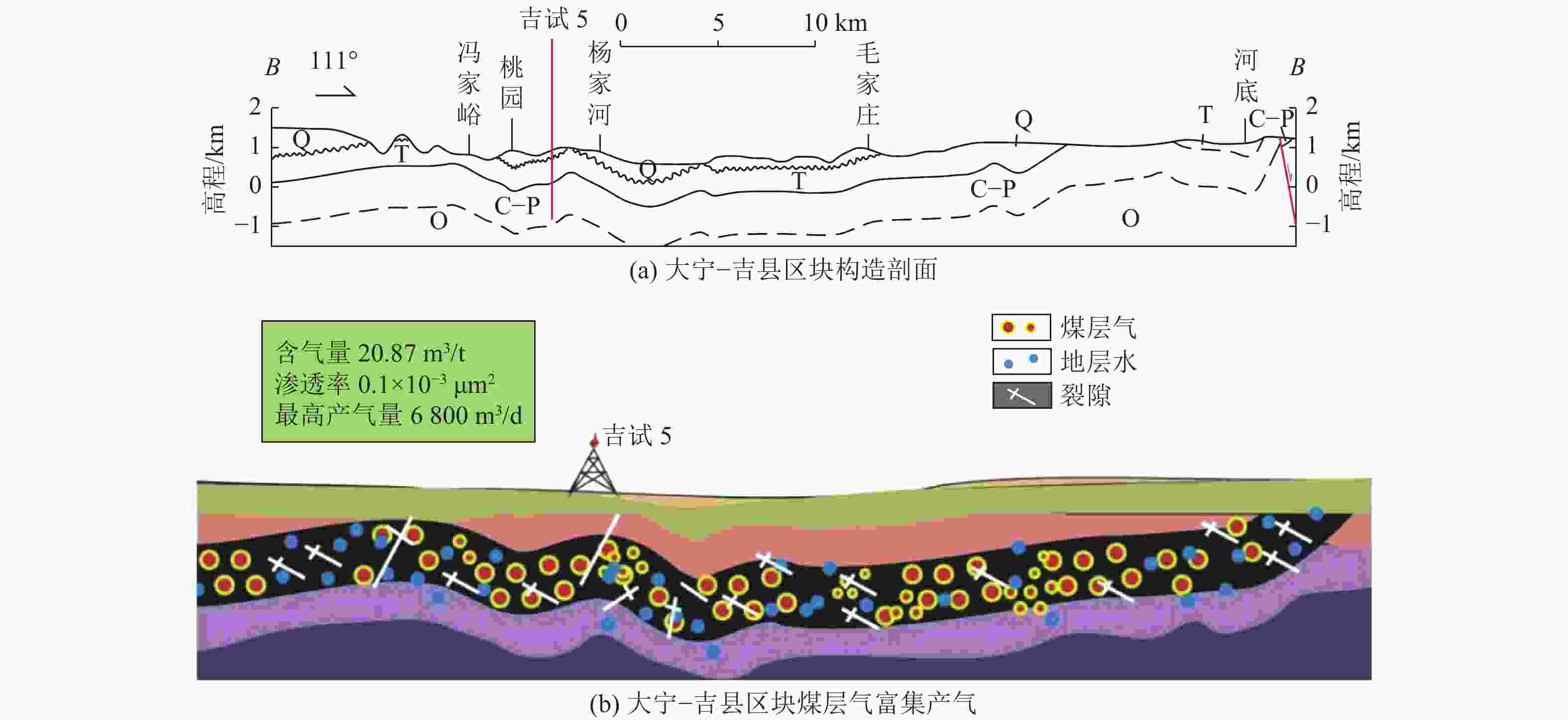
煤层气富集产气模式 构造形态 典型区块 富集产气机理 构造简单裂隙
模式
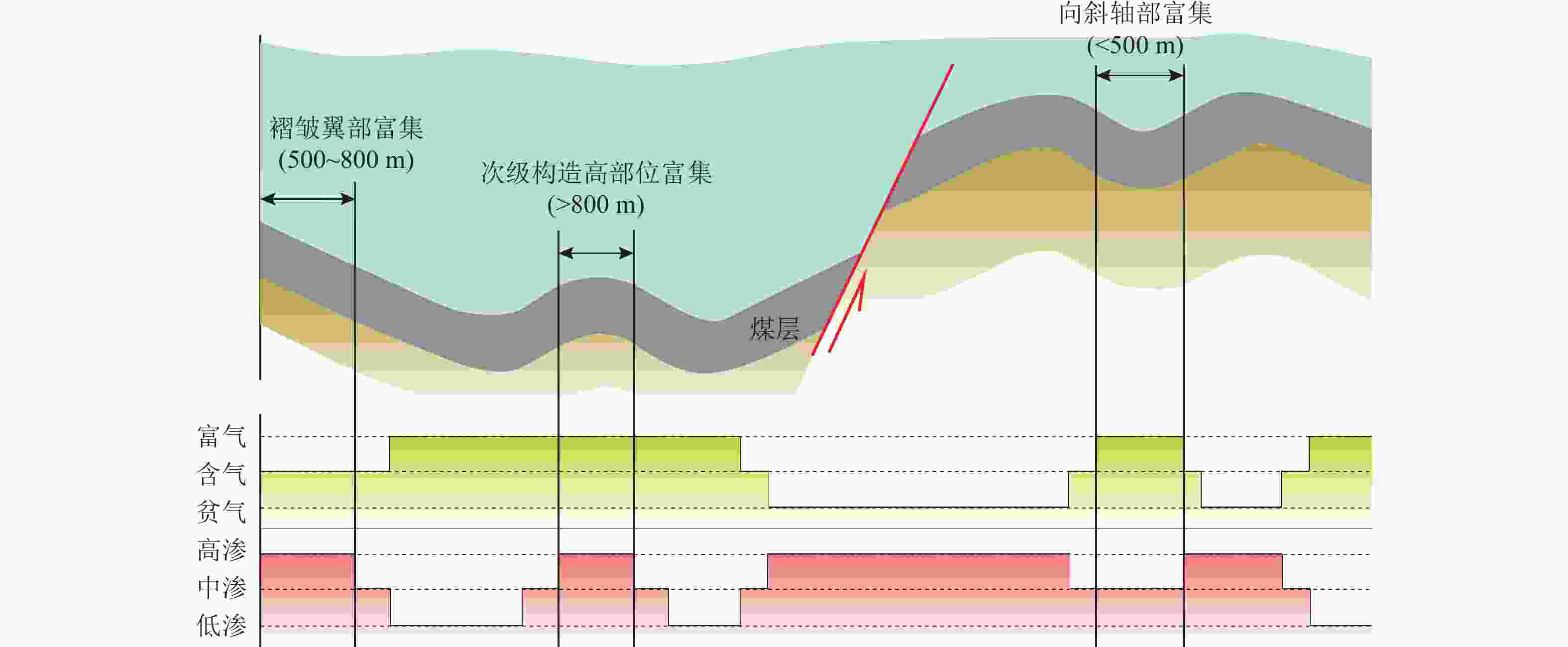
鄂尔多斯盆地东缘大宁−吉县区块 煤层含气性、渗透性、保存条件均适中。尽管裂隙发育,但上覆盖层封闭,含气量与渗透率相匹配 褶皱
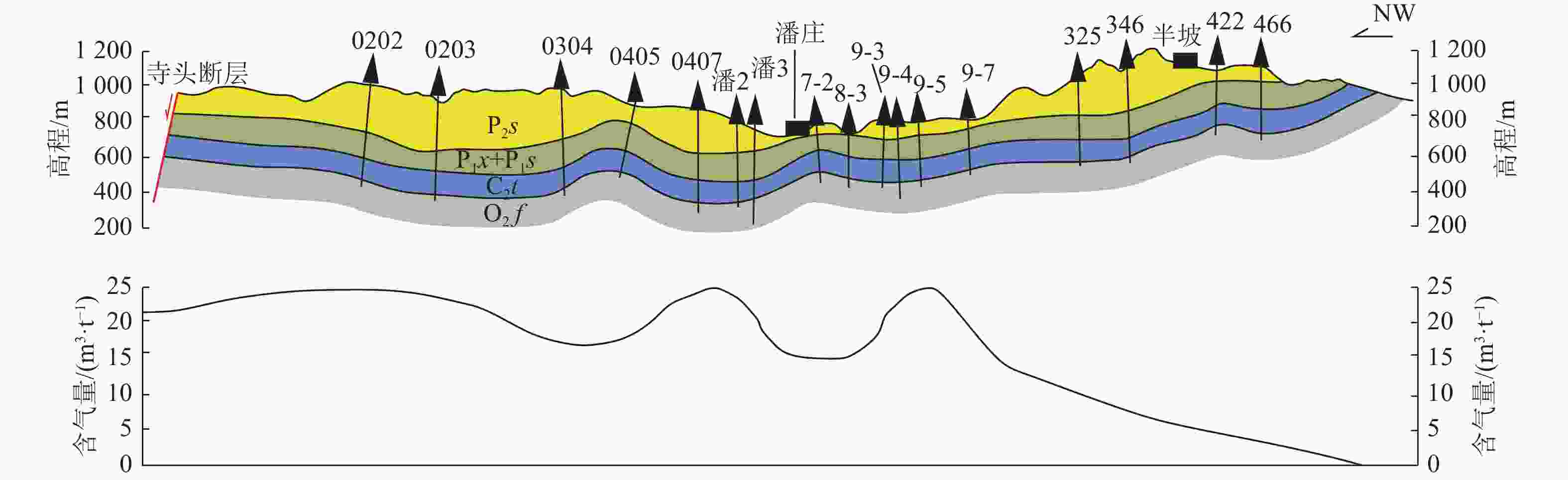
模式较浅向斜轴部 
沁水盆地南部潘庄、潘河区块;贵州西部六盘水矿区 仅适合煤层埋深较浅地区。压应力有利于煤层气吸附,两翼地下水补给形成水力封闭,富气的同时渗透率无明显减小 褶皱翼部 
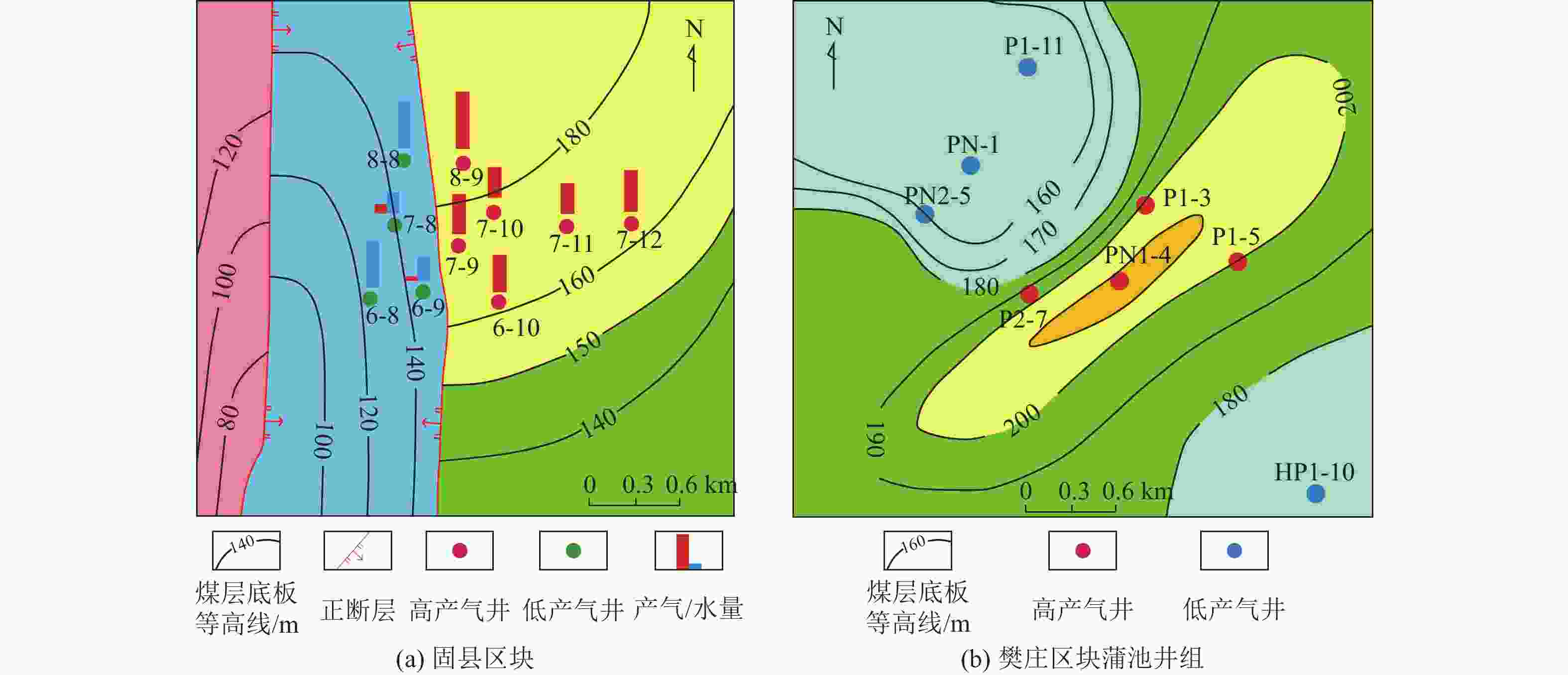
沁水盆地南部樊庄区块;鄂尔多斯盆地东缘延川南区块 受剪切应力作用,整体压力分布均匀,同时受到褶皱翼部至向斜轴部的水力封堵,封闭性较好,含气量和渗透率匹配较好 次级构造
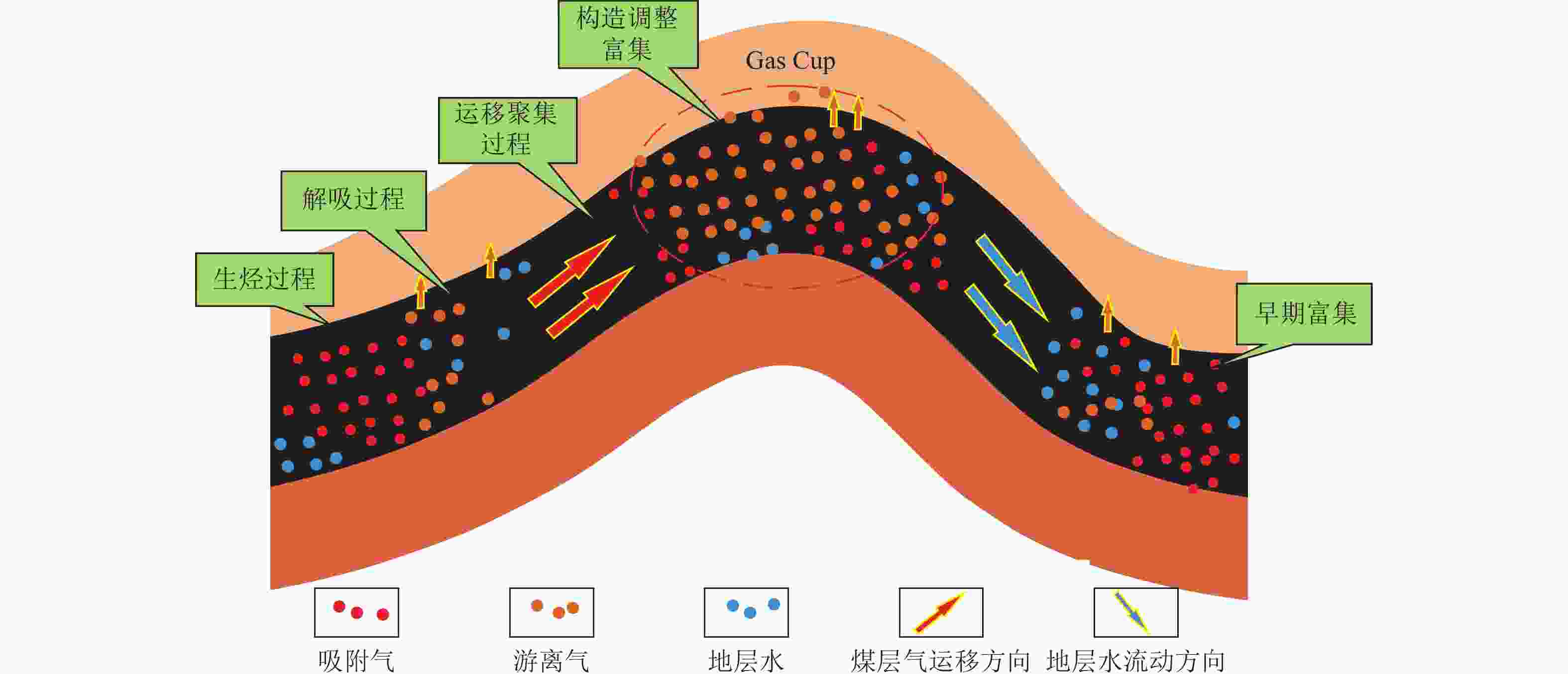
高部位
沁水盆地南部郑庄区块;鄂尔多斯盆地东缘延川南区块 局部应力拉张,裂隙发育使渗透率明显增加。储层压力下降,煤层气饱和度增高。部分吸附气转换为游离气向构造高点运移富集 冲断构造
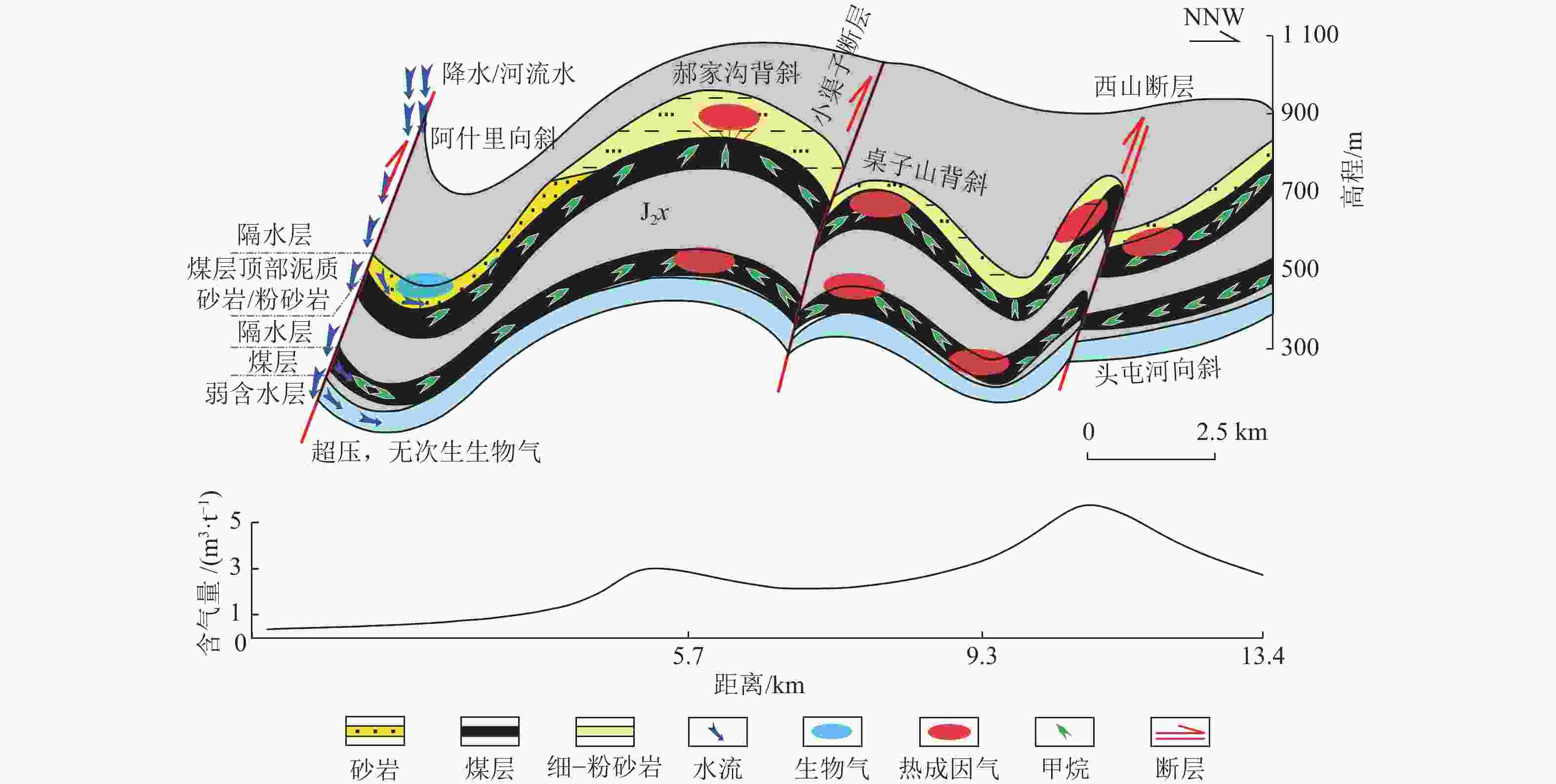
模式褶皱冲断带 
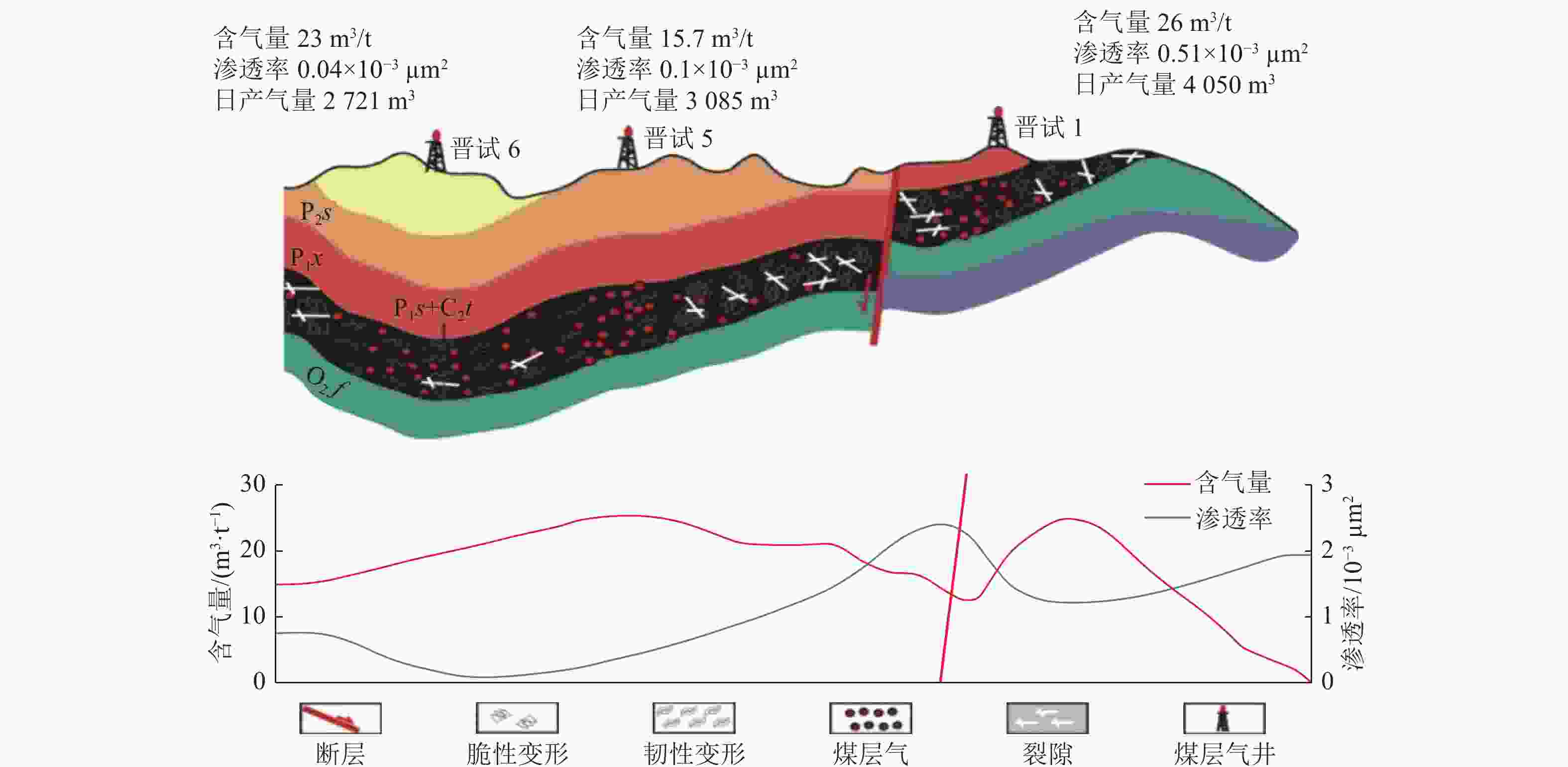
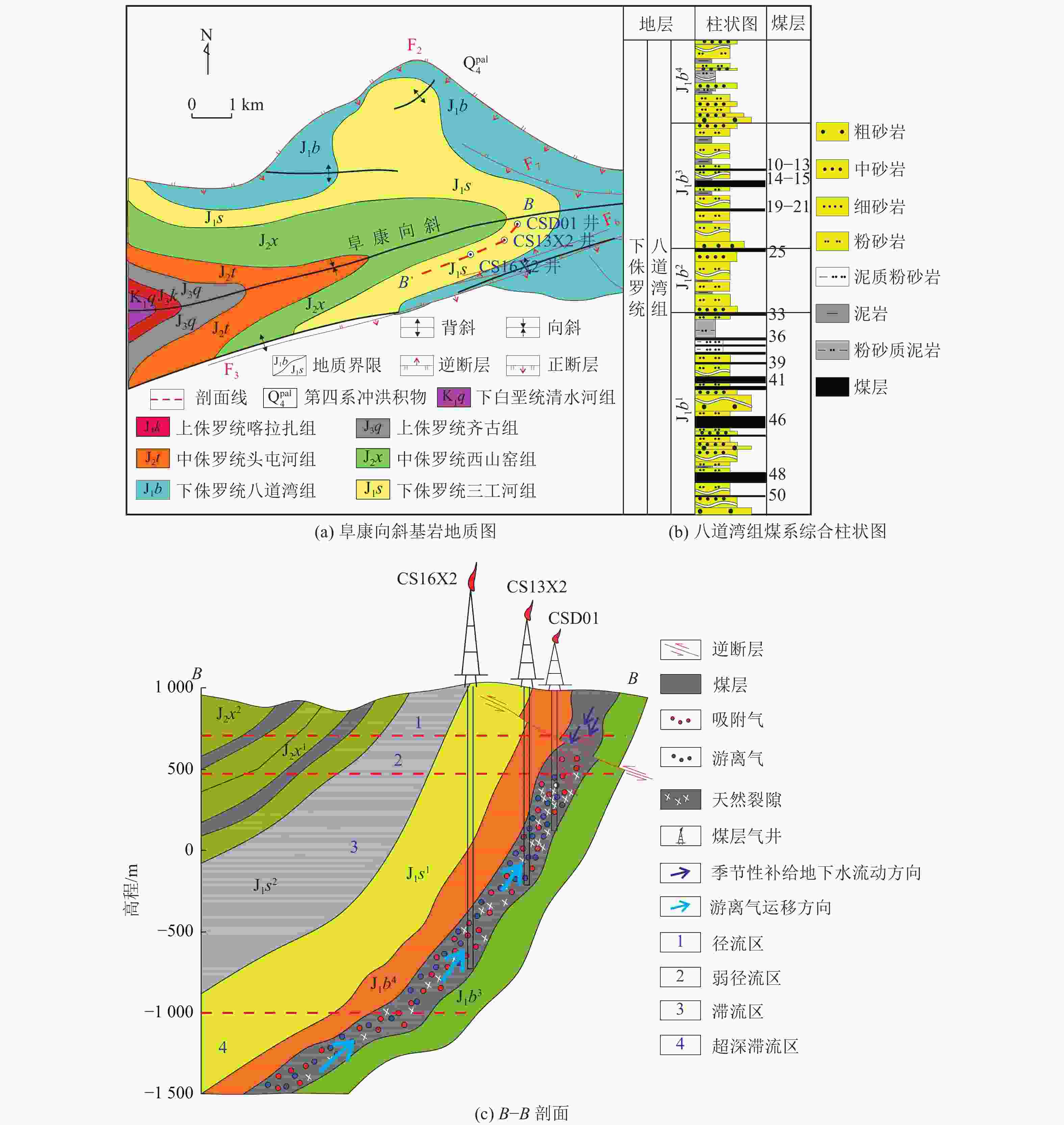
准噶尔盆地南缘头屯河−乌鲁木齐河区块 逆冲断层以煤层韧性变形为主,阻止了煤层气逸散并使煤层气吸附能力增强。深部的煤层气向浅部运移,在靠近断层的相对构造高点富集 高陡冲断带 
准噶尔盆地南缘阜康区块 超深部、深部煤层气在一定温度作用下,吸附气转变为游离气,向中深部煤层运移。仰起端地层倾角大,逆断层同煤层顶底板及煤层火烧区滞流段的水力封堵作用共同抑制了煤层气继续向外界逸散,从而富集并产气 构造叠加模式 
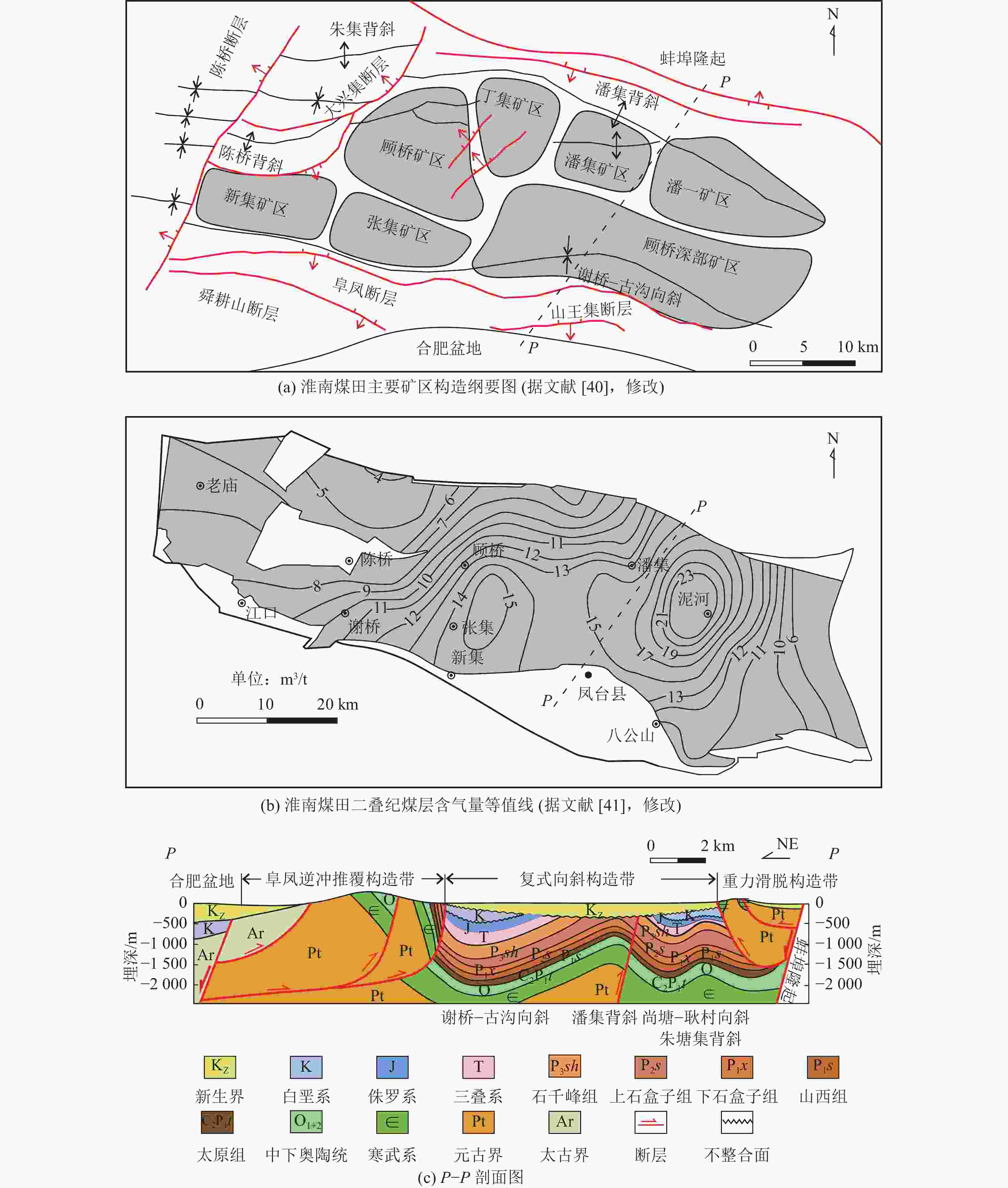
华北克拉通盆地南部淮南、淮北矿区 煤层早期受逆冲推覆向深部就位,生气的同时封闭性较好。后期岩浆岩侵入,生烃的同时改善了储层的渗透率。煤层早期韧性变形与后期脆性变形叠加,渗透率和含气量匹配较好 -
[1] 邹才能,熊波,薛华庆,等. 新能源在碳中和中的地位与作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(2):411−420.. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.02.18ZOU Caineng,XIONG Bo,XUE Huaqing,et al. The role of new energy in carbon neutral[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(2):411−420.. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.02.18 [2] MOORE T A. Coalbed methane:A review[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2012,101:36−81.. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.011 [3] 李鑫. 构造对深层煤层气井产能的控制研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2021,11(4):643−651.. doi: 10.13809/j.cnki.cn32-1825/te.2021.04.022LI Xin. Structural control on productivity of deep coalbed methane wells[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development,2021,11(4):643−651.. doi: 10.13809/j.cnki.cn32-1825/te.2021.04.022 [4] 刘大锰,李俊乾. 我国煤层气分布赋存主控地质因素与富集模式[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(6):19−24.LIU Dameng,LI Junqian. Main geological controls on distribution and occurence and enrichment patterns of coalbed methane in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2014,42(6):19−24. [5] 李勇,孟尚志,吴鹏,等. 煤层气成藏机理及气藏类型划分:以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘为例[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(8):22−30.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.08.003LI Yong,MENG Shangzhi,WU Peng,et al. Accumulation mechanisms and classification of CBM reservoir types:A case study from the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2017,37(8):22−30.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.08.003 [6] FLORES R M. Coal and coalbed gas: Fueling the future[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 2013. [7] SCOTT A R,KAISER W R,AYERS JR W B. Thermogenic and secondary biogenic gases,San Juan basin,Colorado and New Mexico:Implications for coalbed gas producibility[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1994,78(8):1186−1209. [8] SCOTT A R. Hydrogeologic factors affecting gas content distribution in coal beds[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2002,50(1/2/3/4):363−387.. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(02)00135-0 [9] RICE C A,FLORES R M,STRICKER G D,et al. Chemical and stable isotopic evidence for water/rock interaction and biogenic origin of coalbed methane,Fort Union formation,Powder River Basin,Wyoming and Montana USA[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2008,76(1/2):76−85. [10] MONTGOMERY S L. Powder River Basin,Wyoming:An expanding coalbed methane (CBM) play[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1999,83(8):1207−1222. [11] GILLILAND E S,RIPEPI N,CONRAD M,et al. Selection of monitoring techniques for a carbon storage and enhanced coalbed methane recovery pilot test in the Central Appalachian basin[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2013,118:105−112.. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.07.007 [12] LYONS P C. The central and northern Appalachian Basin:A frontier region for coalbed methane development[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,1998,38(1/2):61−87.. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(98)00033-0 [13] MILICI R C,HATCH J R,PAWLEWICZ M J. Coalbed methane resources of the Appalachian Basin,eastern USA[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2010,82(3/4):160−174. [14] JU Yiwen,YU Kun,WANG Guangzeng,et al. Coupling response of the Meso–Cenozoic differential evolution of the north China Craton to lithospheric structural transformation[J]. Earth–Science Reviews,2021,223:103859. [15] 琚宜文,卫明明,侯泉林,等. 华北含煤盆地构造分异与深部煤炭资源就位模式[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(9):1501−1505.JU Yiwen,WEI Mingming,HOU Quanlin,et al. The tectonic differentiation of the coal basins and the emplacement models of the deep coal in north China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(9):1501−1505. [16] 琚宜文,卫明明,薛传东. 华北盆山演化对深部煤与煤层气赋存的制约[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2011,40(3):390−398.JU Yiwen,WEI Mingming,XUE Chuandong. Control of basin–mountain evolution on the occurrence of deep coal and coalbed methane in north China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2011,40(3):390−398. [17] 刘成林,车长波,樊明珠,等. 中国煤层气地质与资源评价[J]. 中国煤层气,2009,6(3):3−6.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2009.03.001LIU Chenglin,CHE Changbo,FAN Mingzhu,et al. Coalbed methane resource assessment in China[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2009,6(3):3−6.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2009.03.001 [18] 接铭训. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘煤层气勘探开发前景[J]. 天然气工业,2010,30(6):1−6.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.06.001JIE Mingxun. Prospects in coalbed methane gas exploration and production in the eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2010,30(6):1−6.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.06.001 [19] 王琳琳,姜波,屈争辉. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘煤层含气量的构造控制作用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2013,41(1):14−19.WANG Linlin,JIANG Bo,QU Zhenghui. Structural control on gas content distribution in eastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2013,41(1):14−19. [20] 李登华,高煖,刘卓亚,等. 中美煤层气资源分布特征和开发现状对比及启示[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(1):252−261.LI Denghua,GAO Xuan,LIU Zhuoya,et al. Comparison and revelation of coalbed methane resources distribution characteristics and development status between China and America[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(1):252−261. [21] 李勇,王延斌,孟尚志,等. 煤系非常规天然气合采地质基础理论进展及展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(4):1406−1418.LI Yong,WANG Yanbin,MENG Shangzhi,et al. Theoretical basis and prospect of coal measure unconventional natural gas co−production[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(4):1406−1418. [22] QIN Yong,MOORE T A,SHEN Jian,et al. Resources and geology of coalbed methane in China:A review[J]. International Geology Review,2018,60(5/6):777−812.. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1408034 [23] 刘大锰,王颖晋,蔡益栋. 低阶煤层气富集主控地质因素与成藏模式分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(6):1−8.LIU Dameng,WANG Yingjin,CAI Yidong. Analysis of main geological controls on coalbed methane enrichment and accumulation patterns in low rank coals[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(6):1−8. [24] 王勃,巢海燕,郑贵强,等. 高、低煤阶煤层气藏地质特征及控气作用差异性研究[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(10):1396−1401.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.10.014WANG Bo,CHAO Haiyan,ZHENG Guiqiang,et al. Differences of coalbed methane geological characteristics and gas–controlling function between low rank coal and high rank coal[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2008,82(10):1396−1401.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.10.014 [25] 蔚远江,汪永华,杨起,等. 准噶尔盆地低煤阶煤储集层吸附特征及煤层气开发潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2008,35(4):410−416.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.04.003YU Yuanjiang,WANG Yonghua,YANG Qi,et al. Adsorption characteristics of low−rank coal reservoirs and coalbed methane development potential,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(4):410−416.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.04.003 [26] 李勇,曹代勇,魏迎春,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中低煤阶煤层气富集成藏规律[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(12):1472−1482.. doi: 10.7623/syxb201612003LI Yong,CAO Daiyong,WEI Yingchun,et al. Middle to low rank coalbed methane accumulation and reservoiring in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(12):1472−1482.. doi: 10.7623/syxb201612003 [27] 张群,葛春贵,李伟,等. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂煤层气高效抽采模式[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):150−159.ZHANG Qun,GE Chungui,LI Wei,et al. A new model and application of coalbed methane high efficiency production from broken soft and low permeable coal seam by roof strata–in horizontal well and staged hydraulic fracture[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(1):150−159. [28] 方良才,李贵红,李丹丹,等. 淮北芦岭煤矿煤层顶板水平井煤层气抽采效果分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(6):155−160.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.06.021FANG Liangcai,LI Guihong,LI Dandan,et al. Analysis on the CBM extraction effect of the horizontal wells in the coal seam roof in Luling coal mine in Huaibei[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(6):155−160.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.06.021 [29] 李彬刚. 淮北芦岭井田煤层气地面抽采技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2017,49(7):90−92.. doi: 10.11799/ce201707027LI Bingang. Research on surface CBM drainage technology in Luling coal field of Huaibei[J]. Coal Engineering,2017,49(7):90−92.. doi: 10.11799/ce201707027 [30] JU Yiwen,WANG Guangzeng,LI Sanzhong,et al. Geodynamic mechanism and classification of basins in the Earth system[J]. Gondwana Research,2022,102:200−228.. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.08.017 [31] 李勇,许卫凯,高计县,等. “源–储–输导系统”联控煤系气富集成藏机制:以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘为例[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(8):2440−2453.LI Yong,XU Weikai,GAO Jixian,et al. Mechanism of coal measure gas accumulation under integrated control of “source reservoir–transport system”:A case study from east margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(8):2440−2453. [32] 桑树勋,韩思杰,刘世奇,等. 高煤阶煤层气富集机理的深化研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):388−403.SANG Shuxun,HAN Sijie,LIU Shiqi,et al. Comprehensive study on the enrichment mechanism of coalbed methane in high rank coal reservoirs[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):388−403. [33] 王国强. 影响煤层气井生产特征的关键因素分析: 以沁水盆地南部潘河地区为例: 煤层气学术研讨会论文集[C]//北京: 地质出版社, 2008. [34] 赵少磊,朱炎铭,曹新款,等. 地质构造对煤层气井产能的控制机理与规律[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2012,40(9):108−111.. doi: 10.13199/j.cst.2012.09.114.zhaoshl.001ZHAO Shaolei,ZHU Yanming,CAO Xinkuan,et al. Control mechanism and law of geological structure affected to production capacity of coal bed methane well[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2012,40(9):108−111.. doi: 10.13199/j.cst.2012.09.114.zhaoshl.001 [35] 刘飞. 山西沁水盆地煤岩储层特征及高产富集区评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2007.LIU Fei. The characteristics of coal reservoirs and evaluation of coalbed methane enrichment and high–productivity in Qinshui Basin of Shanxi Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2007. [36] 汪新伟,汪新文,马永生. 准噶尔盆地南缘褶皱–冲断带的构造变换带特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2007,28(3):345−354.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.03.007WANG Xinwei,WANG Xinwen,MA Yongsheng. Characteristics of structure transform zones in the fold–thrust belts on the southern margin of Junggar Basin,northwest China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2007,28(3):345−354.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.03.007 [37] 陈建平,王绪龙,邓春萍,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘油气生成与分布规律:烃源岩地球化学特征与生烃史[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(7):767−780.. doi: 10.7623/syxb201507001CHEN Jianping,WANG Xulong,DENG Chunping,et al. Geochemical features of source rocks in the southern margin,Junggar Basin,northwestern China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2015,36(7):767−780.. doi: 10.7623/syxb201507001 [38] 陈书平,漆家福,于福生,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘构造变形特征及其主控因素[J]. 地质学报,2007,81(2):151−157.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.02.002CHEN Shuping,QI Jiafu,YU Fusheng,et al. Deformation characteristics in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin and their controlling factors[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(2):151−157.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.02.002 [39] LI Xin,FU Xuehai,YANG Xuesong,et al. Coalbed methane accumulation and dissipation patterns:A case study of the Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,160:13−26.. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.003 [40] YU Kun,JU Yiwen,QIAN Jin,et al. Burial and thermal evolution of coal−bearing strata and its mechanisms in the southern north China basin since the Late Paleozoic[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,198:100−115.. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.09.007 [41] LIU Dameng,YAO Yanbin,TANG Dazhen,et al. Coal reservoir characteristics and coalbed methane resource assessment in Huainan and Huaibei coalfields,southern north China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2009,79(3):97−112.. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.05.001 -








 下载:
下载: