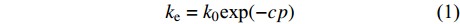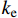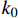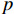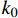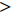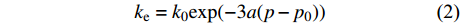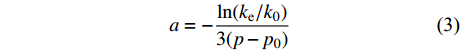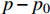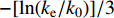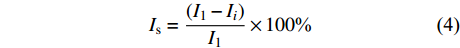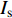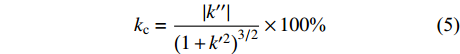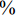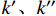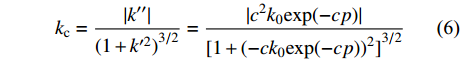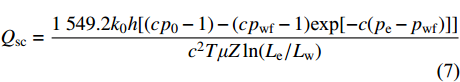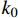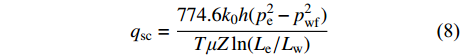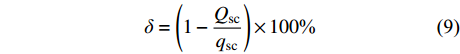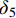Stress sensitivity characteristics of deep coal reservoirs and its influence on coalbed methane productivity
-
摘要: 深部煤储层处于高地应力环境中,其渗透率变化特征与浅部存在较大差异,为研究有效应力对深部煤储层渗透率的差异性影响,以及应力敏感性各向异性特征,以沁水盆地横岭区块15号煤层为研究对象,采样深度1 200~1 700 m,采用覆压孔渗实验,开展平行层理和垂直层理样品在不同有效应力下的渗透率变化规律研究,探究其应力敏感性特征及其对煤层气产能的影响。结果表明:渗透率随有效应力的增加呈幂指函数降低,平行层理面渗透率总体高于垂直层理面,且在2个方向上渗透率变化规律呈正相关性。选取储层孔裂隙压缩系数、渗透率损害率和渗透率曲率3个参数作为煤储层应力敏感性评价指标,其中,孔裂隙压缩系数随有效应力增加,以5 MPa为界限先后呈现正相关性和负相关性,渗透率损害率和渗透率曲率分别与有效应力呈指数上升和下降的规律。基于应力敏感性参数,推导出煤层气井产能模型,模型显示,不考虑应力敏感性的气井产量高于考虑应力敏感性,揭示了应力敏感性对煤层气产量的影响程度,即在5 MPa生产压差下,气井的产量降低幅度随应力敏感性系数的增大整体呈增高趋势。针对应力敏感性的阶段划分,研究区目标煤层在煤层气排采过程中应采用小–中–大的排采方案来控制生产流量。Abstract: Deep coal reservoirs are in a high in-situ stress environment, and their permeability change characteristics are quite different from those of shallow ones. In order to study the effect of the effective stress on the permeability difference of deep coal reservoirs and the characteristics of stress sensitivity anisotropy, the samples from 1 200 m to 1 700 m of the No.15 coal seam in the Hengling block in the Qinshui Basin are taken as the research objects. The overburden porosity and permeability experiments are used to study the permeability changes of parallel and vertical bedding samples under different effective stress conditions to explore their stress sensitivity characteristics and the impact on CBM productivity. The results show that the permeability decreases in a power exponential function with the increase of effective stress. The permeability of the parallel bedding surface in the study area is generally higher than that of the vertical bedding surface, and the permeability changes in the two directions show a positive correlation. The three parameters of reservoir pore and fracture compressibility, permeability stress damage rate, and permeability curvature are selected as the stress sensitivity evaluation indexes of coal reservoirs. Among them, the pore and fracture compressibility coefficient shows a positive correlation and a negative correlation with the increase of the effective stress, with 5 MPa as the limit. The permeability damage rate and permeability curvature increase and decrease exponentially with the effective stress. Based on the study of stress sensitivity parameters, the CBM well productivity model was derived. It was found that the productivity of gas wells without stress sensitivity was higher than that with stress sensitivity. That is to say, under the same production pressure of 5 MPa, the production reduction rate of the gas well production shows an overall increasing trend with the increase of the stress sensitivity coefficient. According to the phase division, the target coal seam in the study area should adopt a small-medium-large displacement scheme to control the production flow during the CBM extraction process.
-
当前我国煤层气勘探开发正逐渐由浅层向深层发展,仅沁水盆地和鄂尔多斯盆地埋深1 000~3 000 m的煤层气资源量就达到33万亿m3,勘探开发前景十分可观[1-3]。深部煤层气资源由于埋深大、盖层厚,保存条件较好,其含气量往往较高。但是埋深较高的同时也存在地应力高、渗透率低的不利因素,而渗透率是决定煤层气开采成败的关键参数之一,其高低直接影响煤层气井产能和开发效益[4-6]。因此,探讨渗透率的关键影响因素成为深部煤层气资源勘探开发的热点问题。
众多学者从不同角度开展了渗透率的影响因素研究,认为应力是影响煤层渗透性的关键因素[7-10]。排水降压初期,储层压力逐渐降低(导致有效应力增加),裂缝孔隙闭合,煤储层渗透率随着有效应力的增加而降低。M. A. Biot[11]1941年首次提出渗透率随有效应力呈指数下降。随后,Zeng Kaihua等[12]讨论和分析了煤在三轴压缩条件下的渗透率变化,认为裂隙的演化是影响煤渗透率变化的重要因素;陈世达[13]、黄强[14]等探究有效应力对中高阶煤储层渗透率的控制作用及其应力敏感性;马如英等[15]研究了低阶煤储层孔隙率和渗透率特征及储层应力敏感性对煤层气开采的影响。程鸣[16]、孟雅[17]、孟召平[18]等开展煤系“三气”覆压孔渗对比实验研究,分析不同煤系的应力敏感性特征,得出煤层应力敏感性随不同有效应力阶段而发生动态变化。Li Jianhua[19]、王攀[20]等基于煤体的应力应变关系及煤体裂缝与基质的相互作用,构建了考虑不同应力条件的各向异性渗透率模型。同时,也有部分学者开展了有效应力与不同方向煤岩渗透率的关系研究[21-24],结果表明,割理中部分充填了方解石和黏土矿物,水平层理面方向的渗透率比垂直层理面方向的渗透率大约高2.5倍,但上述主要通过物理模拟实验测试温度、围压、饱和度及有效应力等对渗透率的总体影响趋势,并未详细阐述各向异性随有效应力增大应力敏感性的变化和相应阶段孔裂隙变化特征,且研究对象主要为中、浅部煤层。
因此,笔者选取深部煤层气勘探开发的热点区域——沁水盆地东北部横岭区块,以15号煤层为研究对象,通过覆压孔渗试验,对目标煤层在有效应力增加过程中,应力敏感性变化趋势开展阶段划分,并分析平行层理面和垂直层理面方向上渗透率以及应力敏感性的各向异性特征,以期揭示深部煤储层应力敏感性变化规律,为研究区煤层气高效勘探开发提供理论支撑。
1 样品与实验设计
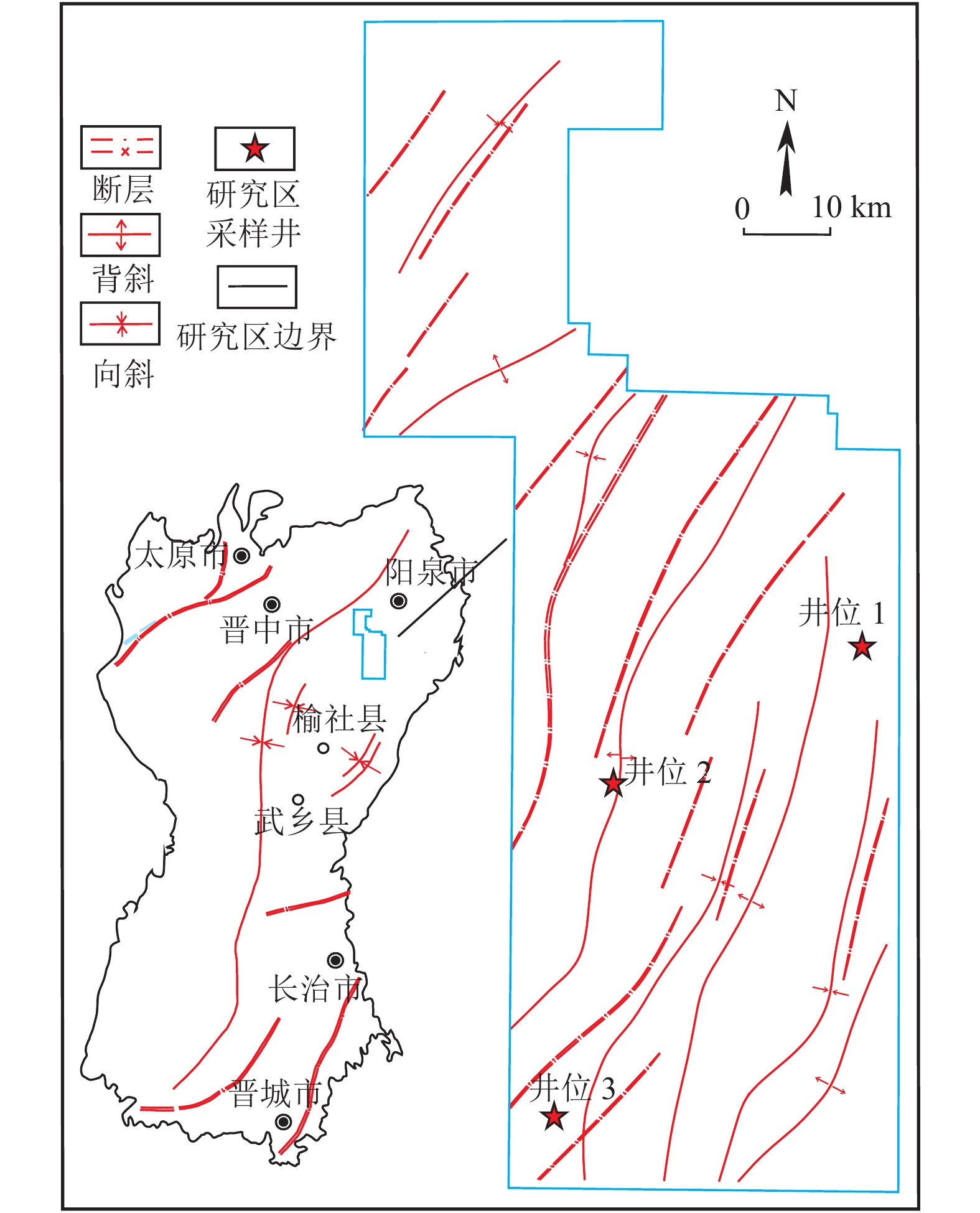
沁水盆地为中生代以来形成的构造盆地,先后历经海西、印支、燕山和喜马拉雅4期构造运动叠加影响,盆地主体为一轴向呈NNE展布的大型宽缓复向斜。盆地构造应力场以东西向挤压应力为主,构造变形强度由盆缘向内逐渐减弱,边缘多发育断裂构造。横岭区块位于沁水盆地东北部,沁水复向斜东翼沾尚–武乡–阳城褶皱带内,区内以正断层为主,倾角大于70°,褶皱两翼宽缓,倾角小于6°,构造线方向受区域构造应力控制,呈NNE向(图1)。样品采自横岭区块3口煤层气井的15号煤。15号煤形成于晚石炭–早二叠世太原组潮坪环境中,为区内稳定可采煤层,埋深大于1 200 m,煤厚2.02~9.90 m,平均5.20 m,含1~3层夹矸,煤阶为贫煤,宏观煤岩类型为半亮煤。
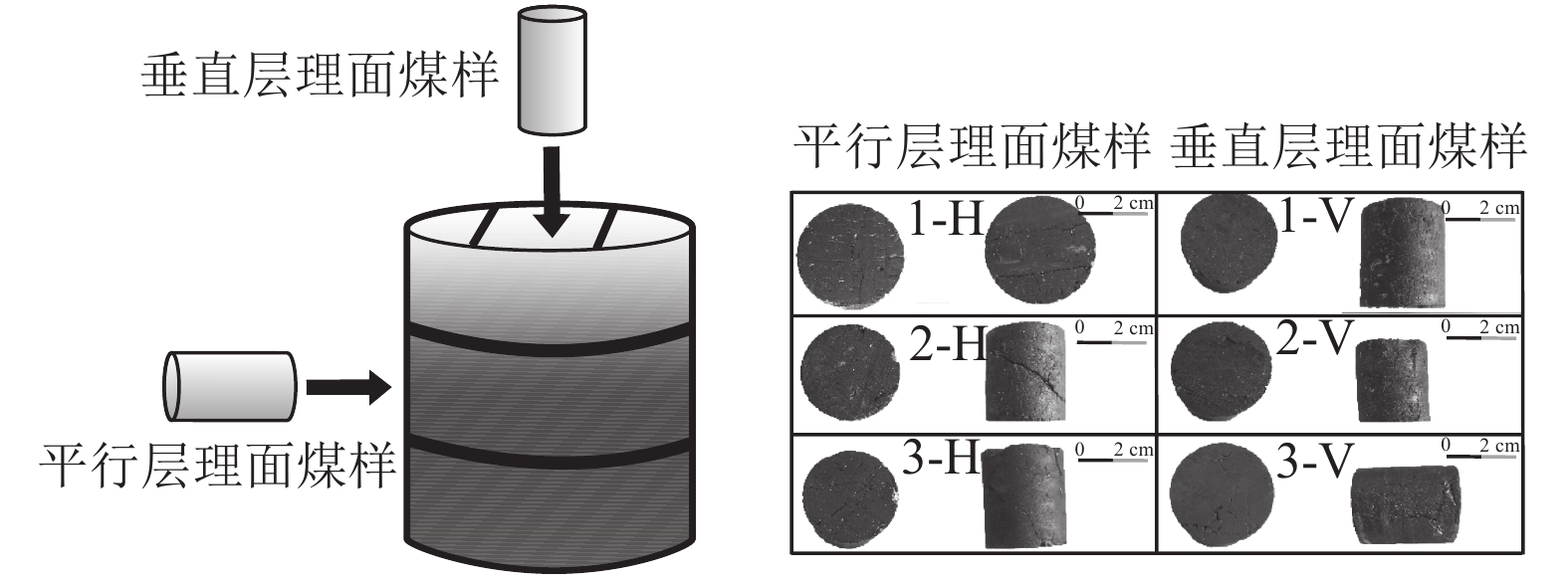
为研究有效应力对渗透率各向异性的影响,分别对3块煤样沿平行层理和垂直层理方向钻取直径为25 mm的柱状样品(图2)。平行层理面样品编号为1-H、2-H和3-H,垂直层理面样品编号为1-V、2-V和3-V,为保证样品原始孔裂隙结构,未对柱状样进行特殊的烘干处理(表1)。
表 1 煤样基本特征Table 1. Basic properties of coal samples样品编号 深度/m 直径/mm 长度/mm 1-H 1 692 25.49 29.18 1-V 25.47 29.35 2-H 1 249 25.45 28.36 2-V 25.08 27.44 3-H 1 622 25.48 29.92 3-V 25.38 29.68 实验采用覆压孔隙率−渗透率测试仪AP-608,非稳态脉冲衰减法,执行中国石油天然气行业标准SY/T 6385—2016《覆压下岩石孔隙度和渗透率测定方法》,以He为测试介质。实验过程中保持进口压力不变,利用平流泵逐步增加样品的围压值,依据研究区煤层埋深情况共设计7个压力点(3.5~15.0 MPa),压力点平衡时间控制在30 min以上,分别测定各压力点的渗透率。
2 实验及结果分析
2.1 渗透率与有效应力关系
渗透率是评价煤层气可采性的关键参数之一,反映煤储层的渗流能力,是非常规天然气资源开发的关键影响因素。对实验数据进行回归分析,获得煤样的渗透率随有效应力的增大呈幂指数函数规律衰减,满足下式:
$$ {k_{\rm{e}}} = {k_0}\exp ( - cp) $$ (1) 式中:
$ {k_{\rm{e}}} $ 为已知应力条件下的渗透率,10−3 μm2;$ {k_0} $ 为初始有效应力为0时的渗透率,10−3 μm2;$ p $ 为有效应力,MPa;c为衰减系数,MPa−1。初始渗透率
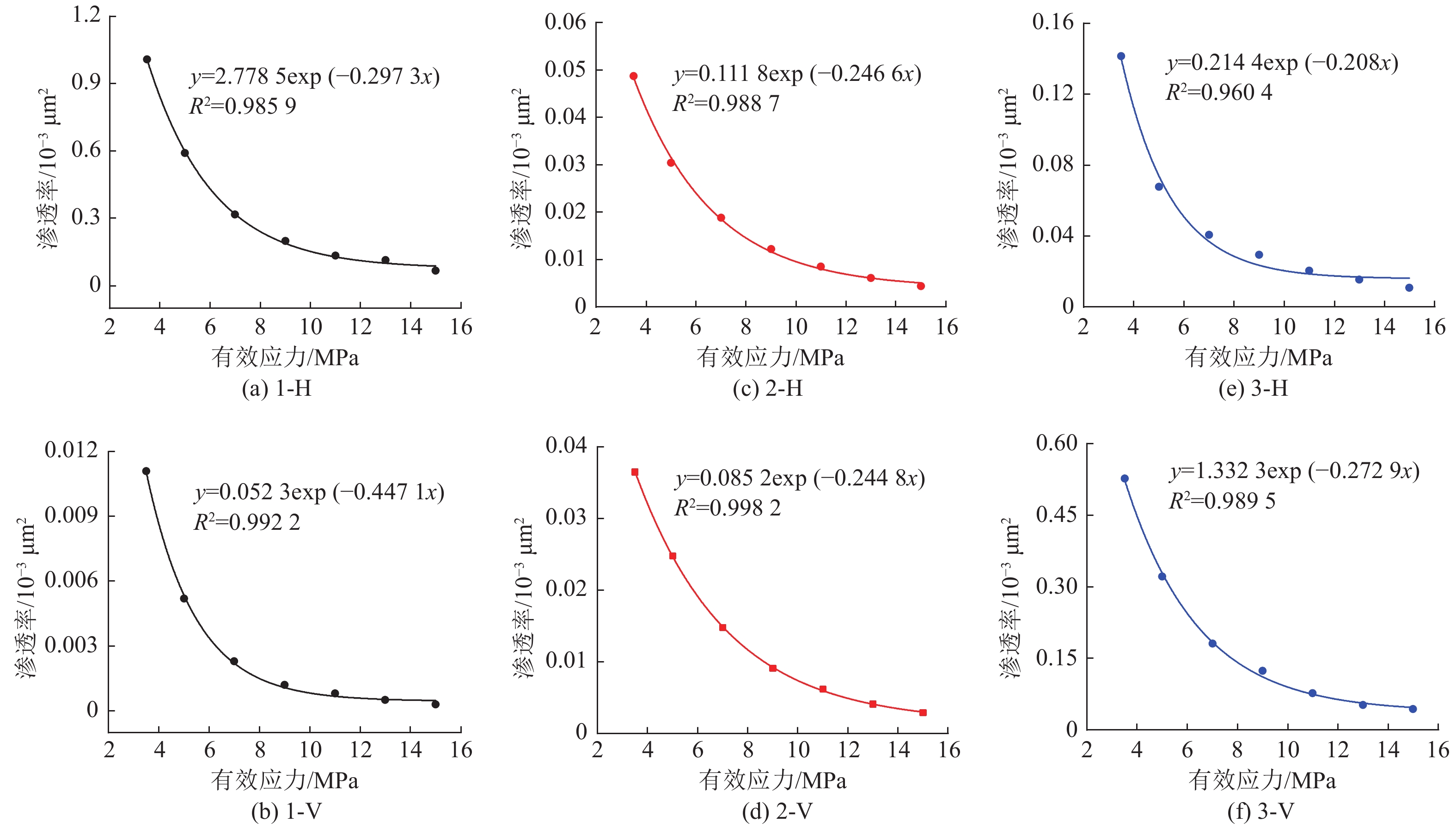
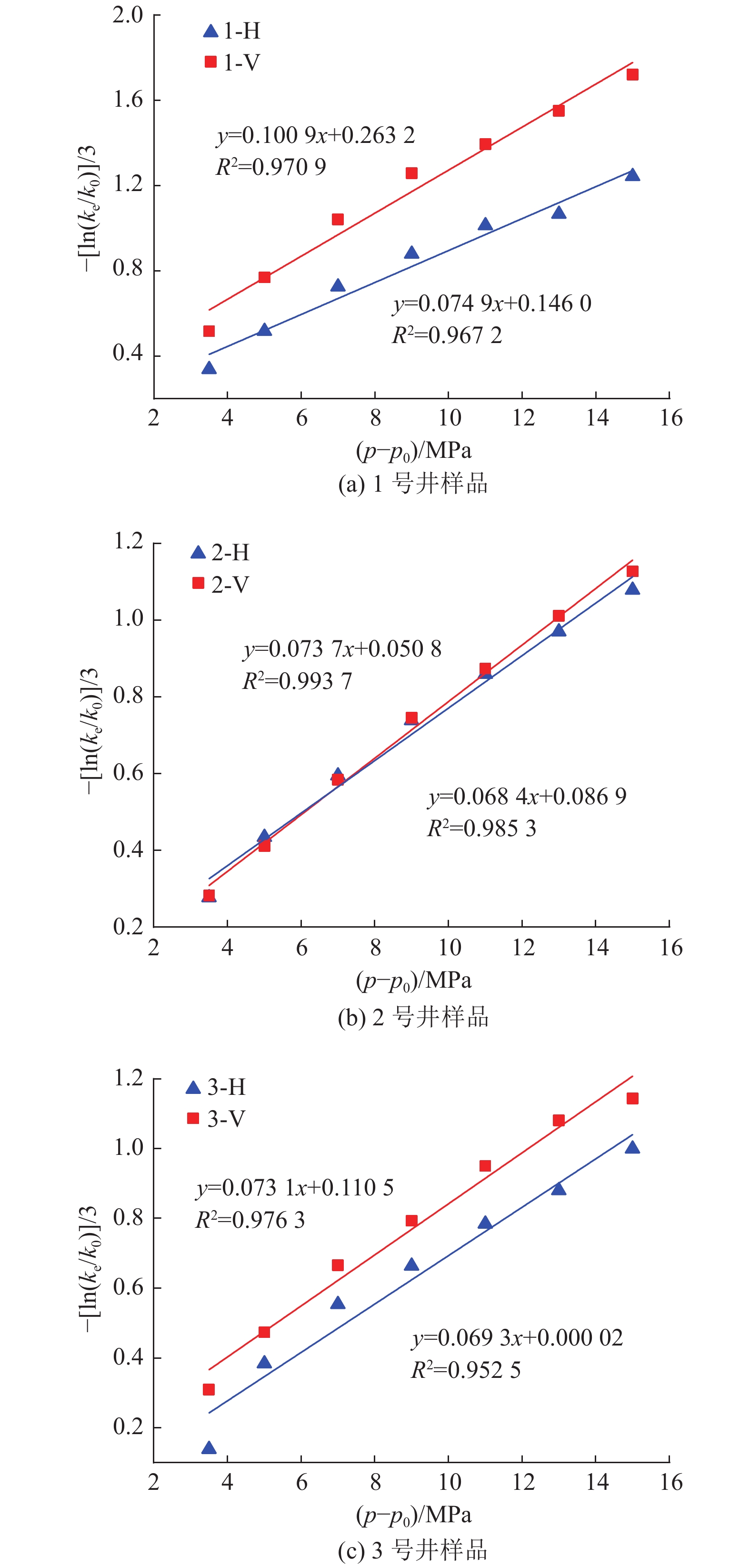
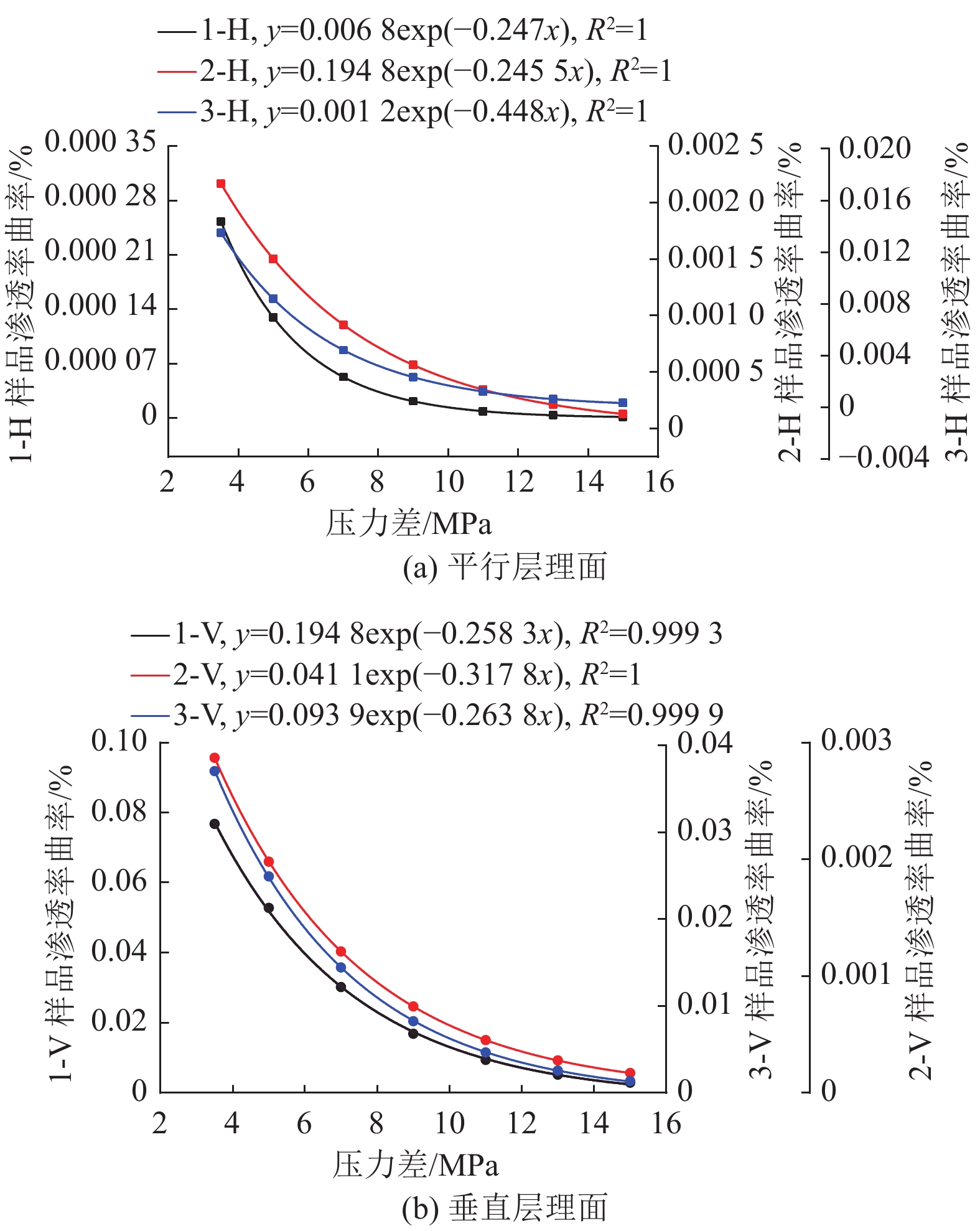
$ {k_0} $ 是煤样脱离原位储层,不受任何外部应力和不考虑基质吸附变形时的渗透率,无法通过实验测得,可以通过式(1)进行回归分析拟合得出。6个样品的初始渗透率如图3所示(相关系数R2$ \gt $ 0.9604)。由图中可知,平行层理面初始渗透率大小为1-H>3-H>2-H,分别为2.778 5×10−3、0.2144×10−3和0.1118×10−3 μm2;垂直层理面初始渗透率3-V>2-V>1-V,分别为1.3323×10−3、0.0852×10−3和0.0523×10−3 μm2。因此依据现有数据分析,研究区1号井位附近平行层理面渗透率具有优势,而3号井位附近垂直层理面渗透率具有优势。对比分析同一样品平行层理面和垂直层理面渗透率发现,除3号样品外,其余2个样品平行层理面渗透率均大于垂直层理面渗透率。表明沉积物在沉积过程中形成的层理面是渗透率大小的优势方向。2.2 不同方向渗透率特征
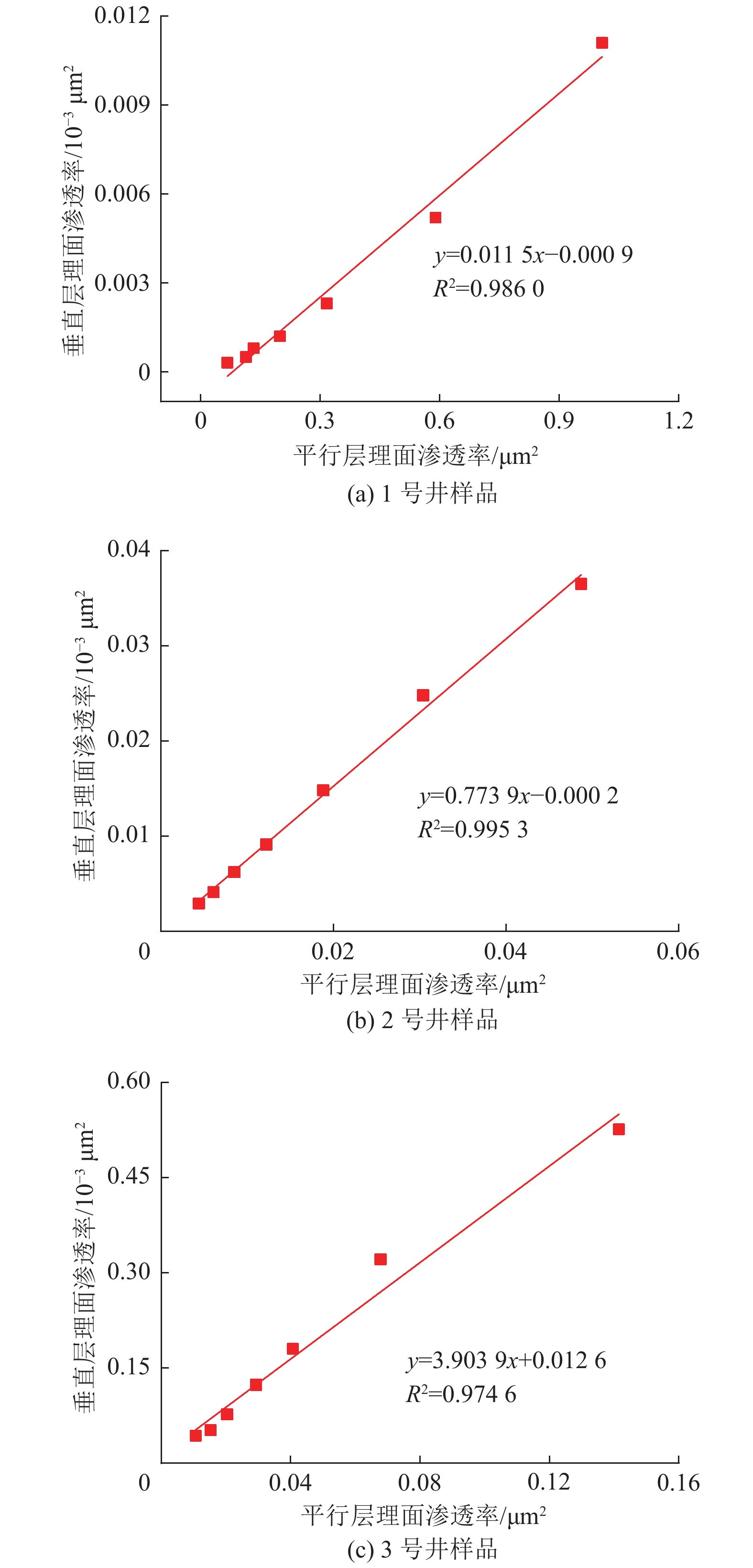
进一步分析平行层理面和垂直层理面渗透率随有效应力变化规律,并进行线性拟合,二者呈正相关性(R2>0.974 6,图4)。从图中可以看出,在不同方向上渗透率随有效应力的增加,呈一定比例系数增大。样品1—样品3平行层理面与垂直层理面渗透率比例系数分别为0.01,0.77和3.90。从比例系数来看,由于煤样个体存在差异性导致变化系数差别较大,并无特定比例关系,但比例系数提供了预测不同方向上渗透率的方法,对煤层气勘探开发具有较强的现实指导意义。
2.3 储层应力敏感性分析
煤层气开采过程中随着孔隙流体的排出,有效应力不断增加,使得储层岩体发生变形,产生应力敏感现象,导致渗透率降低。本文选取储层孔裂隙压缩系数、渗透率损害率和渗透率曲率3个参数开展深部煤储层应力敏感性阶段划分和各向异性特征研究。
2.3.1 孔裂隙压缩系数
煤储层孔裂隙随有效应力的增加逐渐被压缩,导致渗透率急剧下降,其变化范围可达2~3个数量级。孔裂隙压缩系数是定量表征渗透率随有效应力变化的程度,是最直观反映储层应力敏感性参数。C. R. Mckee等[25](1988)给出了渗透率、有效应力与孔裂隙压缩系数的关系式,即:
$$ {k}_{{\rm{e}}}={k}_{0}\mathrm{exp}(-3a(p-{p}_{0})) $$ (2) 式中:a为孔裂隙压缩系数,MPa−1;p0为初始有效应力,MPa。
由式(2)可推导出孔裂隙压缩系数:
$$ a = - \frac{{\ln ({k_{\rm{e}}}/{k_0})}}{{3(p - {p_0})}} $$ (3) 由式(3)可知,a是参数
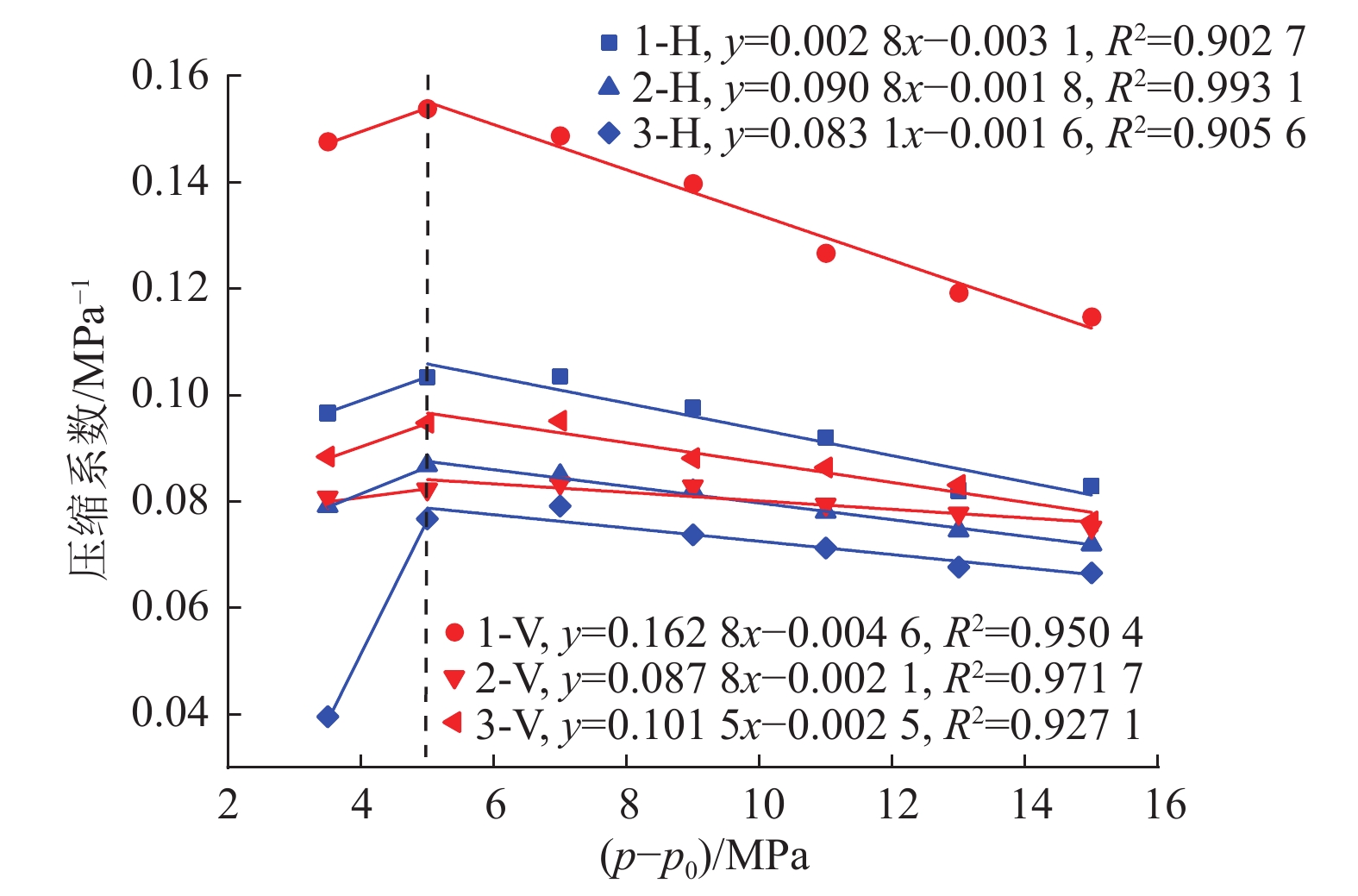
${p}-{{p}}_{0}$ 和$ -[\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}(k_{\rm{e}}/{k}_{0})]/3 $ 的线性函数系数,以二者为横坐标和纵坐标进行线性拟合,直线的斜率即为孔裂隙压缩系数(图5)。孔裂隙压缩系数的差异导致应力敏感性具有各向异性。由图5可知,垂直层理面孔裂隙压缩系数为0.073 1~0.100 9 MPa−1,平均0.082 6 MPa−1;平行层理面孔裂隙压缩系数为0.068 4~0.0749 MPa−1,平均0.070 9 MPa−1。无论是单个样品结果还是平均值,在相同压差的条件下,垂直层理面压缩系数均大于平行层理面,表明储层在垂直层理面方向上具有更高的应力敏感性。研究区15号煤层两个方向上的应力敏感性比例平均值为1.17∶1。
进一步分析孔裂隙压缩系数与有效应力差值之间关系,发现压缩系数以压差5 MPa为界限分为2段(图6),前段呈正相关性,后段则表现出显著的负相关性。从图中可知,孔裂隙压缩系数为一动态参数,并非定值,在有效应力增加初期,由于煤中宏观裂隙具有大量可压缩的空间,其压缩系数逐渐增大;之后,随着压差不断增加,储层转入显微孔裂隙压缩阶段,可压缩空间不断降低,压缩难度越来越大,因此压缩系数呈现降低趋势。
2.3.2 渗透率损害率
渗透率损害率是反映储层应力敏感性的又一重要参数,可表征渗透率在有效应力增加情况下样品受损伤的程度,用百分数表示。该值越大,表明储层渗透率受有效应力损害程度越严重,对应的应力敏感性越高,其表达式为:
$$ {I_{{\rm{s}}}} = \frac{{({I_1} - {I_i})}}{{{I_1}}} \times 100{\text{%}} $$ (4) 式中:
$ {I}_{\mathrm{s}} $ 为渗透率损害率,%;I1为第1个应力点下的渗透率,10−3 μm2;Ii为第i个应力点下的渗透率,10−3 μm2。由图7可知,渗透率损害率与有效应力之间呈指数关系(R2>0.9855),有3个变化区间:当有效应力达到5 MPa时,渗透率损害率为68.38%~90.06%,平均76.13%,渗透率损害率近似呈线性关系快速增加;当有效应力达到12 MPa时,渗透率损害率为91.81%~98.87%,平均94.99%,样品的渗透率损害率增加程度放缓,与上一阶段平均值差为19%,整体程度低于第一阶段;当压力达到15 MPa时,渗透率损害率达到最大值,介于95.01%~99.43%,平均96.91%,渗透率降低程度有限,与上一阶段平均值差仅为2%。
2.3.3 渗透率曲率
在数学上通常用曲率来描述物体的弯曲程度,曲率越大,表明物体在该点处弯曲变形程度越高。渗透率曲率可以更有效地表征渗透率随有效应力增大而降低的速率,即渗透率曲率越大,渗透率的应力敏感性就越强;反之越弱[22]。因此,本次通过引入渗透率曲率来对比分析渗透率受应力的影响程度,进一步揭示渗透率对应力的敏感程度。
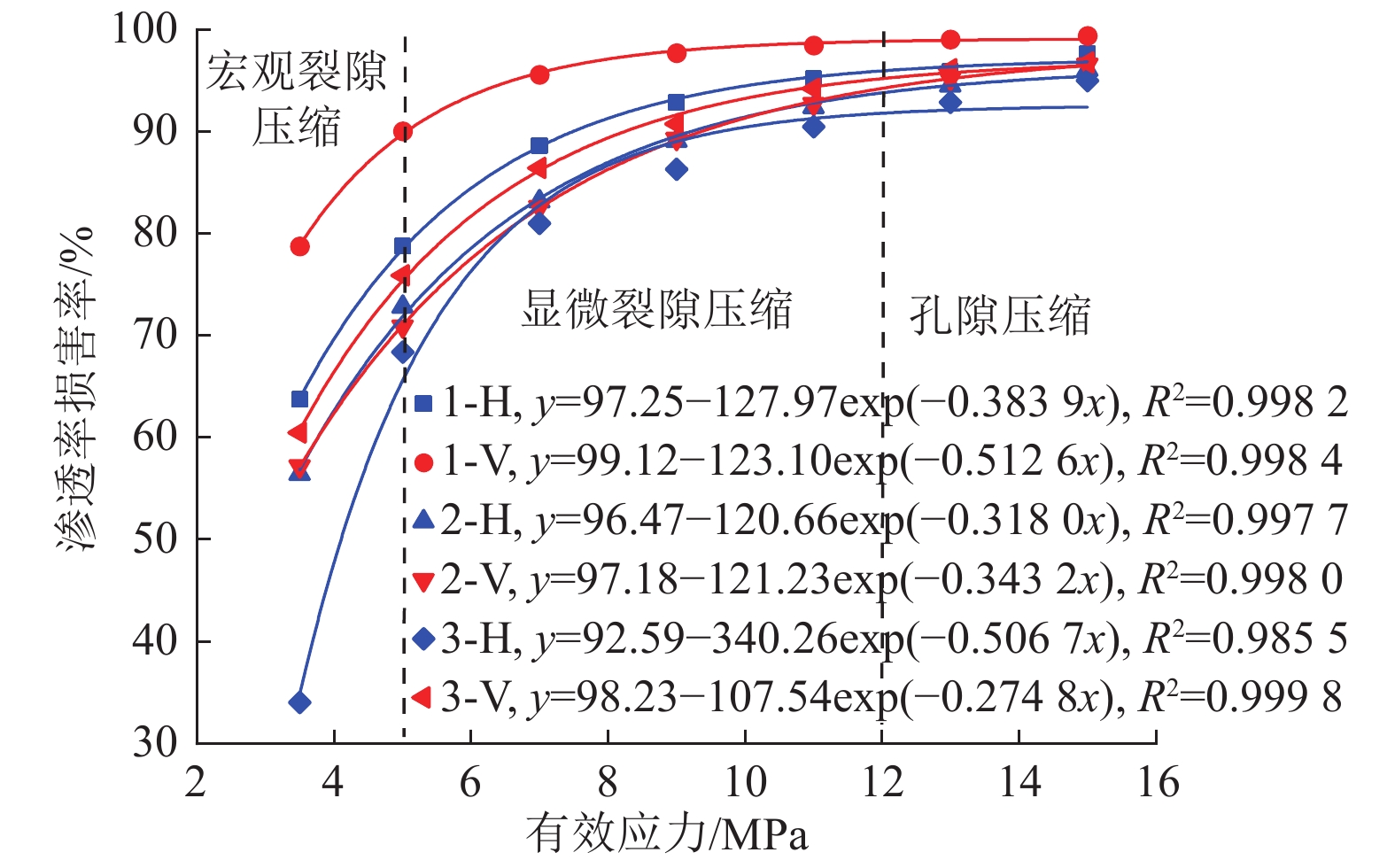
$$ k_{{\rm{c}}}=\frac{\left|k^{\prime\prime}\right|}{\left(1+k^{\prime2}\right)^{3 / 2}} \times 100{\text{%}}$$ (5) 式中:kc为渗透率曲率,
${\text{%}}$ ;${k^\prime }、{k}^{\prime\prime}$ 分别为渗透率对有效应力的一阶、二阶导数。渗透率曲率为:
$$ {k_{\rm{c}}} = \frac{{\left| {{k^{\prime\prime}}} \right|}}{{{{(1 + {k^{\prime 2}})}^{3/2}}}} = \frac{{|{c^2}{k_0}{\rm{exp}}( - cp)|}}{{{{[1 + {{( - c{k_0}{\rm{exp}}( - cp))}^2}]}^{3/2}}}} $$ (6) 式中:c为应力敏感系数,MPa−1。
由图8可知,6个样品渗透率曲率随有效应力的增加呈负指数规律降低(R2>0.9999),当有效应力小于5 MPa时,渗透率曲率随有效应力的增加快速下降,表明该阶段储层中孔裂隙的压缩速率下降极快,渗透率快速降低;当有效应力为5~12 MPa时,随有效应力的增大,渗透率曲率下降趋势逐渐变缓,表明孔裂隙的可压缩空间已经降低,渗透率下降程度变缓;当有效应力大于12 MPa时,渗透率变化程度微弱。
综上所述,同时结合渗透率损害率和渗透率曲率的变化程度,可将研究区样品相应划分为宏观裂隙压缩、显微裂隙压缩和孔隙压缩3个阶段(图7)。
平行层理面和垂直层理面上,其渗透率曲率具有显著差异(表2):其中,平行层理面样品其渗透率曲率大小为3-H>2-H>1-H,而垂直层理面其渗透率曲率大小为1-V>3-V>2-V,由此可知,3号样品在平行层理方向上、1号样品在垂直层理面方向上具有较高的应力敏感性。
进一步对每个样品在两个方向上的渗透率曲率开展分析发现,研究区垂直层理面渗透率曲率均大于平行层理面方向,表明储层的渗透率在垂向上受有效应力影响更大,具有更强的应力敏感性。
表 2 储层应力敏感性评价参数Table 2. Stress sensitivity evaluation parameters of coal reservoirs煤样编号 裂隙压缩
系数/MPa−1渗透率损害率/% 渗透率曲率/% 5 MPa 12 MPa 15 MPa 1-H 0.074 9 78.77 95.97 97.60 0.000 001~0.000 253 1-V 0.100 9 90.06 98.87 99.43 0.002 840~0.076 750 2-H 0.068 4 72.80 93.81 96.06 0.000 130~0.002 170 2-V 0.073 7 70.89 94.25 96.60 0.000 168~0.002 870 3-H 0.069 3 68.38 91.81 95.01 0.000 348~0.013 510 3-V 0.073 1 75.87 95.21 96.76 0.002 840~0.037 08 3 煤储层应力敏感性对煤层气排采的影响
3.1 煤层气产能计算
煤层气排采经历解吸–扩散–渗流3个阶段,包括排水、降压和产气过程。假定储层水平等厚,煤层气以达西平面径向流的方式流向井底,考虑应力敏感性但不考虑表皮系数的影响,标准条件下气井的产能公式[26]:
$$\begin{split} &\\ &{Q_{{{\rm{sc}}}}} = \frac{{1\;549.2{k_0}h[(c{p_0} - 1) - (c{p_{{{\rm{wf}}}}} - 1){{\exp} {[ - c({p_{{\rm{e}}}} - {p_{{{\rm{wf}}}}})]}}]}}{{{c^2}T\mu Z\ln ({L_{{\rm{e}}}}/{L_{{\rm{w}}}})}} \end{split} $$ (7) 式中:Qsc为标准状态下的产气量,m3/d;h为煤层的有效厚度,m;μ为气体黏度,MPa·s;Z为压缩因子;T为煤储层温度,K;pwf为井底流压,MPa;pe为原始储层压力,MPa;Le为泄压半径,m;Lw为井筒直径,m;其中,标准状态下的压力、温度和偏差系数依次取:0.101 328 MPa、293 K和1。
当完全不考虑煤储层应力敏感性的影响时,则气体的渗流是渗透率为
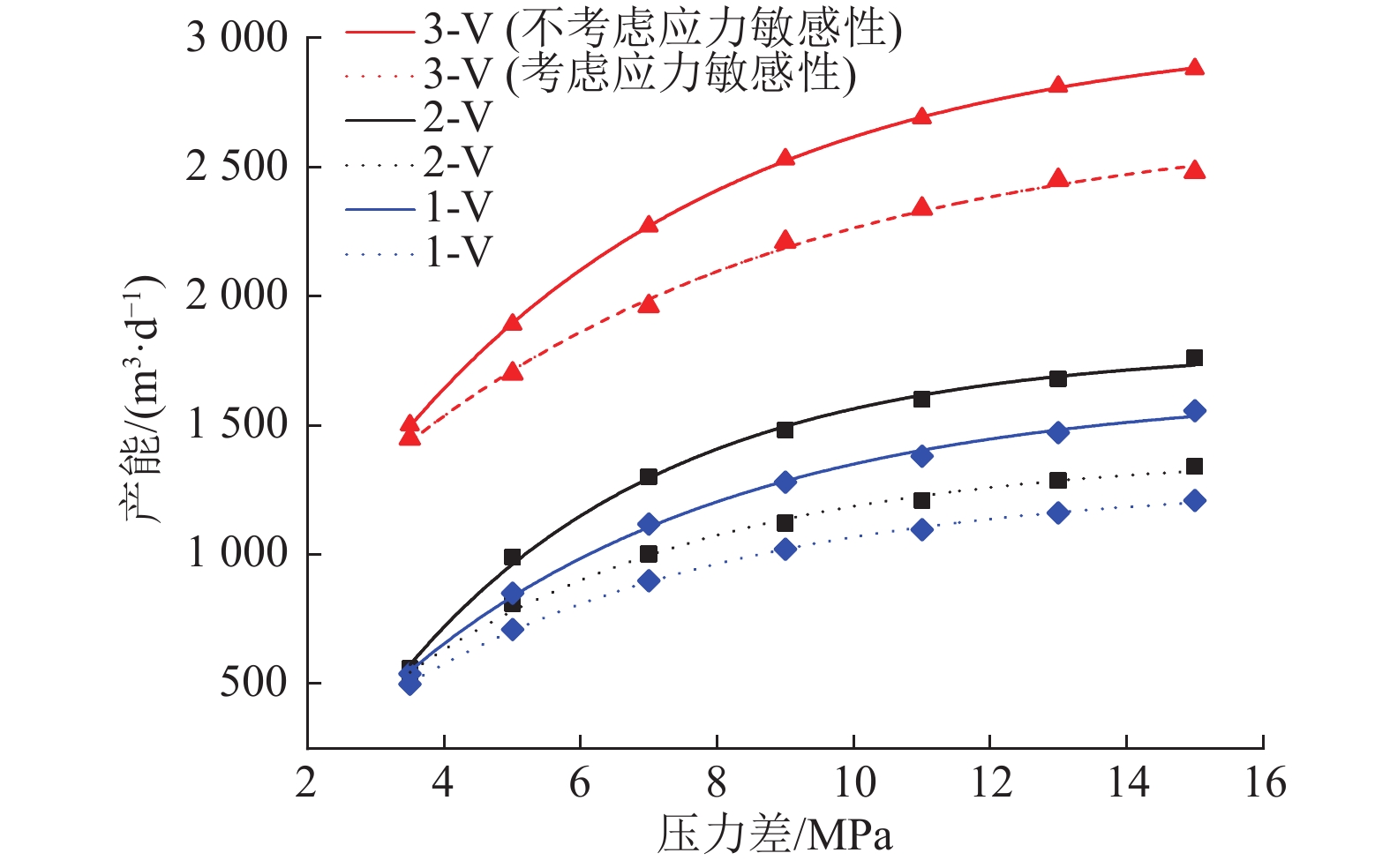
$ {k_0} $ 条件下的达西渗流[26],其气井产气量qsc为:$$ {q_{{\rm{sc}}}} = \frac{{774.6{k_0}h(p_{\rm{e}}^2 - p_{{\rm{wf}}}^2)}}{{T\mu Z\ln ({L_{\rm{e}}}/{L_{\rm{w}}})}} $$ (8) 为分析煤储层应力敏感性对本研究区产气井的影响,对采样点3口井在不同生产压差、分别考虑和不考虑应力敏感性条件下,通过式(7)和式(8)进行产能理论对比分析,煤层气井相关参数见表3。由图9可知,煤储层不考虑应力敏感性的气井产量要高于考虑应力敏感性的气井产量,且随着生产压差不断增大,受到的有效应力逐渐增加,煤储层渗透率指数降低,影响其气井产能。应力敏感性对气井产能有显著影响,煤层气排采过程中,随着生产压力的增加,气井的产量增加幅度变小,并逐渐趋向稳定,说明单纯依靠增大生产压差并不能获得最大产量[25]。
表 3 煤层气井参数Table 3. Parameters of CBM wells参数 数值 煤层厚度/m 4.8~5.2 煤储层渗透率/10−3 μm2 0.052 3~2.778 5 原始储层压力/MPa 8.52~13.80 井底半径/m 0.09 泄压半径/m 200 衰减系数 0.244~0.318 储层温度/K 313.55 压缩因子 0.89 3.2 应力敏感性对煤层气井产量的影响程度
为了反映应力敏感性对煤层气产量的影响程度,可定义产量降低幅度为δ:
$$ \delta = \left(1 - \frac{{{Q_{{{\rm{sc}}}}}}}{{{q_{{{\rm{sc}}}}}}}\right) \times 100{\text{%}}$$ (9) 取井位1、2、3的6个样品裂隙压缩系数作为应力敏感性系数。为便于对比分析,统一生产压差为5 MPa,表征应力敏感性对气井产能的影响,由式(9)定义生产压差为5 MPa的产量降低幅度为
$ {\delta _5} $ 。计算结果如图10所示,在同一生产压差下可以看出,气井的产量降低幅度
$ {\delta _5} $ 随应力敏感性系数a的增大整体呈增高趋势。究其原因,排水降压阶段随着孔隙流体不断采出,煤储层的有效应力逐渐增大,造成孔裂隙开度降低甚至发生闭合,而排采过程中的压力波动会造成孔裂隙的永久缩小,导致其渗透率急剧降低及渗透率损害率逐渐增大,进而影响煤层气产量。3.3 煤储层开发建议
有效应力增加的实质是由于排水降压导致储层压力降低引起,从而使渗透率发生动态变化。因此,渗透率与有效应力之间关系反映了煤层气井排采过程中储层渗透率与生产压差之间的关系[27]。生产压差是储层压力与井底流压之间的差值,因而煤层气井排采需要制定合理的动液面高度(生产流量)来改变生产压差。同时既要保证较高产量,又要避免生产压差过大导致煤储层产生明显的应力敏感性,减少其对煤储层伤害程度,确保气井的高产和稳产。因此,通过对研究区储层应力敏感性的阶段划分,可以把握关键压力点,更有效控制煤层气的产出过程。
结合研究区3口煤层气井的应力敏感性特征,给出以下建议:
(1) 当有效应力小于5 MPa时,渗透率随有效应力的增加迅速下降,应力敏感性最强,横岭区块平均储层压力梯度为0.7 MPa/hm,因此,生产中动液面下降区间为0~500 m,此阶段应采用小排量来控制生产流量。
(2) 当有效应力为5~12 MPa时,生产中对应的动液面下降区值大于500 m,渗透率随有效应力的增加降低速度变缓,应力敏感性减弱,应采取中等排量方案来控制流量。
(3) 当有效应力大于12 MPa时,渗透率下降速度极其缓慢,应力敏感性最弱,可将有效应力12 MPa作为研究区渗透率动态变化的理论临界值,大于此临界值时采用大排量来控制生产流量。
4 结 论
a. 深部煤储层渗透率随有效应力的增大呈指数函数规律降低,平行层理面的渗透率与垂直层理面的呈正相关性。对比分析同一样品2个方向上的渗透率,除3号样品外,其余2个样品平行层理面渗透率均大于垂直层理面渗透率,表明沉积物在沉积过程中形成的层理面是渗透率大小的优势方向。
b. 储层应力敏感性各向异性特征研究表明:在相同压差的条件下,垂直层理面方向上孔裂隙压缩系数要高于平行层理面方向;渗透率损害率随有效应力增加呈指数函数规律增加,相反,渗透率曲率相应减少;同时垂直层理面方向上的渗透率损害率和渗透率曲率均大于平行层理面方向,表明研究区垂直层理面方向上应力敏感性更高。
c. 基于应力敏感性参数研究,通过煤层气气井产能模型,分析得出,不考虑应力敏感性条件下气井产量偏高,结合应力敏感性对煤层气产量影响程度,可将研究区15号煤储层应力敏感性变化划分为3个阶段,相应地在煤层气排采过程中可采取小–中–大的排量方案来控制生产流量。
d. 沁水盆地横岭区块目前为煤层气勘探开发的新区块,3号样品所在位置储层渗透率要高于另外两个,因此,下一步进行深部煤层气勘探开发过程中,可以考虑将新井位部署在渗透率相对较高的3号井区附近。同时,由于垂直层理面方向应力敏感性高于平行层理面,且平行层理面为渗透率的优势方向,因此,在研究区煤储层压裂改造过程中,应注重孔裂隙在平行层理面方向上的扩展,从而激发其主导作用。
-
表 1 煤样基本特征
Table 1 Basic properties of coal samples
样品编号 深度/m 直径/mm 长度/mm 1-H 1 692 25.49 29.18 1-V 25.47 29.35 2-H 1 249 25.45 28.36 2-V 25.08 27.44 3-H 1 622 25.48 29.92 3-V 25.38 29.68 表 2 储层应力敏感性评价参数
Table 2 Stress sensitivity evaluation parameters of coal reservoirs
煤样编号 裂隙压缩
系数/MPa−1渗透率损害率/% 渗透率曲率/% 5 MPa 12 MPa 15 MPa 1-H 0.074 9 78.77 95.97 97.60 0.000 001~0.000 253 1-V 0.100 9 90.06 98.87 99.43 0.002 840~0.076 750 2-H 0.068 4 72.80 93.81 96.06 0.000 130~0.002 170 2-V 0.073 7 70.89 94.25 96.60 0.000 168~0.002 870 3-H 0.069 3 68.38 91.81 95.01 0.000 348~0.013 510 3-V 0.073 1 75.87 95.21 96.76 0.002 840~0.037 08 表 3 煤层气井参数
Table 3 Parameters of CBM wells
参数 数值 煤层厚度/m 4.8~5.2 煤储层渗透率/10−3 μm2 0.052 3~2.778 5 原始储层压力/MPa 8.52~13.80 井底半径/m 0.09 泄压半径/m 200 衰减系数 0.244~0.318 储层温度/K 313.55 压缩因子 0.89 -
[1] 贾慧敏,胡秋嘉,樊彬,等. 沁水盆地郑庄区块北部煤层气直井低产原因及高效开发技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):34−42. JIA Huimin,HU Qiujia,FAN Bin,et al. Causes for low CBM production of vertical wells and efficient development technology in northern Zhengzhuang block in Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(2):34−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.005 JIA Huimin, HU Qiujia, FAN Bin, et al. Causes for low CBM production of vertical wells and efficient development technology in northern Zhengzhuang block in Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(2): 34–42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.005
[2] 穆福元,仲伟志,赵先良,等. 中国煤层气产业发展战略思考[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(6):110−116. MU Fuyuan,ZHONG Weizhi,ZHAO Xianliang,et al. Strategies for the development of CBM gas industry in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2015,35(6):110−116. MU Fuyuan, ZHONG Weizhi, ZHAO Xianliang, et al. Strategies for the development of CBM gas industry in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(6): 110–116.
[3] 宋慧波,安红亮,刘顺喜,等. 沁水盆地武乡南煤层气赋存主控地质因素及富集区预测[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(12):3974−3978. SONG Huibo,AN Hongliang,LIU Shunxi,et al. Controlling geological factors and coalbed methane enrichment areas in southern Wuxiang block, Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(12):3974−3978. SONG Huibo, AN Hongliang, LIU Shunxi, et al. Controlling geological factors and coalbed methane enrichment areas in southern Wuxiang block, Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(12): 3974-3978
[4] JIN Yi,DONG Jiabin,LI Xiang,et al. Kinematical measurement of hydraulic tortuosity of fluid flow in porous media[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C,2015,26(2):1550017. DOI: 10.1142/S0129183115500175
[5] ZHANG Lei,YE Zhiwei,HUANG Mengqian,et al. Characteristics of bituminous coal permeability response to the pore pressure and effective shear stress in the Huaibei coalfield in China[J]. Geofluids,2019(2):1−12.
[6] 秦勇,吴建光,张争光,等. 基于排采初期生产特征的煤层气合采地质条件分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(1):241−257. QIN Yong,WU Jianguang,ZHANG Zhengguang,et al. Analysis of geological conditions for coalbed methane co–production based on production characteristics in early stage of drainage[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(1):241−257. QIN Yong, WU Jianguang, ZHANG Zhengguang, et al. Analysis of geological conditions for coalbed methane co–production based on production characteristics in early stage of drainage[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 241–257.
[7] ZHANG Xiaoyang,WU Caifang,WANG Ziwei. Experimental study of the effective stress coefficient for coal permeability with different water saturations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2019,182:106282. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106282
[8] MENG Ya,LI Zhiping,LAI Fengpeng. Influence of effective stress on gas slippage effect of different rank coals[J]. Fuel,2021,285:119207. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119207
[9] 薛培,高潮. 有效应力对保德区块煤储层渗透率影响研究[J]. 地质与勘探,2016,52(2):334−339. XUE Pei,GAO Chao. Study on influence of effective stress on coal reservoir permeability in the Baode block[J]. Geology and Exploration,2016,52(2):334−339. XUE Pei, GAO Chao. Study on influence of effective stress on coal reservoir permeability in the Baode block[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(2): 334–339.
[10] ZHAO Mengyu,JIN Yi,LIU Xianhe,et al. Characterizing the complexity assembly of pore structure in a coal matrix:Principle,methodology,and modeling application[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2020,125(e2020JB020110):1−18.
[11] BIOT M A. Theory of deformation of a porous viscoelastic anisotropic solid[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,1956,27(5):459−467. DOI: 10.1063/1.1722402
[12] ZENG Kaihua,XU Jiaxiong,HE Pengfei,et al. Experimental study on permeability of coal sample subjected to triaxial stresses[J]. Procedia Engineering,2011,26:1051−1057. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2273
[13] 陈世达,汤达祯,高丽军,等. 有效应力对高煤级煤储层渗透率的控制作用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(4):76−80. CHEN Shida,TANG Dazhen,GAO Lijun,et al. Control of effective stress on permeability in high–rank coal reservoirs[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2017,45(4):76−80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.04.013 CHEN Shida, TANG Dazhen, GAO Lijun, et al. Control of effective stress on permeability in high–rank coal reservoirs[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2017, 45(4): 76–80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.04.013
[14] 黄强,傅雪海,张庆辉,等. 沁水盆地中高煤阶煤储层覆压孔渗试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(6):164−170. HUANG Qiang,FU Xuehai,ZHANG Qinghui,et al. Experimental study on overburden pore permeability of medium and high rank coal reservoirs in Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(6):164−170. HUANG Qiang, FU Xuehai, ZHANG Qinghui, et al. Experimental study on overburden pore permeability of medium and high rank coal reservoirs in Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(6): 164–170.
[15] 马如英,王猛,阿斯亚•巴克,等. 准东南低阶煤覆压孔渗试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2020,49(6):1182−1192. MA Ruying,WANG Meng,ASIYA B,et al. Experimental study of overburden pore porosity and permeability of low–rank coal reservoirs in southeastern Junggar[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2020,49(6):1182−1192. MA Ruying, WANG Meng, ASIYA B, et al. Experimental study of overburden pore porosity and permeability of low–rank coal reservoirs in southeastern Junggar[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(6): 1182–1192.
[16] 程鸣,傅雪海,张苗,等. 沁水盆地古县区块煤系“三气”储层覆压孔渗实验对比研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(8):1163−1171. CHENG Ming,FU Xuehai,ZHANG Miao,et al. Comparative study on porosity and permeability in net confining stress of three natural gases in coal series reservoirs in Guxian County,Qinshui Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2018,29(8):1163−1171. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.05.013 CHENG Ming, FU Xuehai, ZHANG Miao, et al. Comparative study on porosity and permeability in net confining stress of three natural gases in coal series reservoirs in Guxian County, Qinshui Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(8): 1163–1171. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.05.013
[17] 孟雅,李治平. 覆压下煤的孔渗性实验及其应力敏感性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(1):154−159. MENG Ya,LI Zhiping. Experimental study on the porosity and permeability of coal in net confining stress and its stress sensitivity[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(1):154−159. MENG Ya, LI Zhiping. Experimental study on the porosity and permeability of coal in net confining stress and its stress sensitivity[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(1): 154–159.
[18] 孟召平,侯泉林. 煤储层应力敏感性及影响因素的试验分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(3):430−437. MENG Zhaoping,HOU Quanlin. Experimental research on stress sensitivity of coal reservoir and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2012,37(3):430−437. MENG Zhaoping, HOU Quanlin. Experimental research on stress sensitivity of coal reservoir and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(3): 430–437.
[19] LI Jianhua,LI Bobo,WANG Zhihe,et al. A permeability model for anisotropic coal masses under different stress conditions[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,198:108197. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.108197
[20] 王攀,杜文凤,冯飞胜. 基于影响因素优选的煤层瓦斯渗透率预测模型[J]. 煤矿安全,2017,48(11):21−25. WANG Pan,DU Wenfeng,FENG Feisheng. Prediction model of coalbed gas permeability based on optimization of influencing factors[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2017,48(11):21−25. WANG Pan, DU Wenfeng, FENG Feisheng. Prediction model of coalbed gas permeability based on optimization of influencing factors[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(11): 21–25.
[21] WANG Shugang,ELSWORTH D,LIU Jishan. Permeability evolution in fractured coal:The roles of fracture geometry and water–content[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2011,87:13−25.
[22] LI Huoyin,SHIMADA S,ZHANG Ming. Anisotropy of gas permeability associated with cleat pattern in a coal seam of the Kushiro coalfield in Japan[J]. Environmental Geology,2004,47:45−50. DOI: 10.1007/s00254-004-1125-x
[23] 刘帅帅,杨兆彪,张争光,等. 有效应力对煤储层不同方向渗透率影响的差异性[J]. 天然气地球科学,2019,30(10):1422−1429. LIU Shuaishuai,YANG Zhaobiao,ZHANG Zhengguang,et al. Study on the differences of effective stress on coal reservoirs permeability in different directions[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2019,30(10):1422−1429. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.10.006 LIU Shuaishuai, YANG Zhaobiao, ZHANG Zhengguang, et al. Study on the differences of effective stress on coal reservoirs permeability in different directions[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(10): 1422–1429. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.10.006
[24] WANG L L,VANDAMME M,PEREIRA J M,et al. Permeability changes in coal seams:The role of anisotropy[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,199:52−64. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.09.014
[25] MCKEE C R,BUMB A C,KOENLG R A. Stress–dependent permeability and porosity of coal and other geologic formations[J]. SPE Formation Evaluation,1988,3:81−91. DOI: 10.2118/12858-PA
[26] 孟召平,张纪星,刘贺,等. 考虑应力敏感性的煤层气井产能模型及应用分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(4):593−599. MENG Zhaoping,ZHANG Jixing,LIU He,et al. Productivity model of CBM wells considering the stress sensitivity and its application analysis[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(4):593−599. MENG Zhaoping, ZHANG Jixing, LIU He, et al. Productivity model of CBM wells considering the stress sensitivity and its application analysis[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(4): 593–599.
[27] 朱维耀,马东旭,朱华银,等. 页岩储层应力敏感性及其对产能影响[J]. 天然气地球科学,2016,27(5):892−897. ZHU Weiyao,MA Dongxu,ZHU Huayin,et al. Stress sensitivity of shale gas reservoir and its influence on productivity[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2016,27(5):892−897. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.05.0892 ZHU Weiyao, MA Dongxu, ZHU Huayin, et al. Stress sensitivity of shale gas reservoir and its influence on productivity[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(5): 892–897. DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.05.0892
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 聂志宏,徐凤银,时小松,熊先钺,宋伟,张雷,刘莹,孙伟,冯延青,刘世瑞,闫霞,孙潇逸,吴满生. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气开发先导试验效果与启示. 煤田地质与勘探. 2024(02): 1-12 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 赵航,罗腾跃,贺沛,孙建峰,李涛. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部山西组致密储层的分形特征及其影响因素分析. 非常规油气. 2024(02): 37-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 白江. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区延长组长6段储层特征研究. 非常规油气. 2024(02): 46-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张彬,孙蓓蕾,王德璋,康天合,马鑫,张晓雨,李立功,李昊洋,梁晓敏,朱文庆,张俊爽. 矿物对无烟煤力学非均质性影响的分子动力学研究——以沁水盆地南部主要黏土矿物高岭石为例. 煤炭学报. 2024(09): 3896-3906 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 熊鹏辉,范张磊,马壮,张东升,李强,吕扬,蒋超,孔梓涵. 破碎颗粒堆积方式对渗透率应力敏感性的影响机制. 科学技术与工程. 2024(27): 11648-11654 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘春春,张聪,贾慧敏,吴定泉,霸振,王琪,毛生发. 流体产出特征评价方法预测高阶煤储层产能. 石油钻采工艺. 2024(02): 189-198 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 徐舜,杨菲菲. 煤层气储层的不同多相流因素对渗透率影响. 粘接. 2024(11): 128-131 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 苏现波,王乾,于世耀,赵伟仲,王小明,毕彩芹,陈明,王一兵,孙长彦,伏海蛟,邹成龙,张双斌,黄津,谢相军. 基于低负碳减排的深部煤系气一体化开发技术路径. 石油学报. 2023(11): 1931-1948 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)







 下载:
下载: