Critical drilling and completion techniques for deep coalbed methane in the Shenfu block and their applications
-
摘要:目的
深部煤层具有高地应力、中高温度、特低渗透、强压缩性、强非均质性等特点,目前尚未形成成熟的开发技术体系,复杂的地质特征为钻井与完井工程带来了新的技术难题与挑战,亟需开展针对深部煤储层地质特征的钻完井理论与技术攻关,助力油气增储上产,保障国家能源战略安全。
方法基于鄂尔多斯盆地东缘神府区块深部煤层气开发先导性试验,研发了一套高效钻完井关键技术。
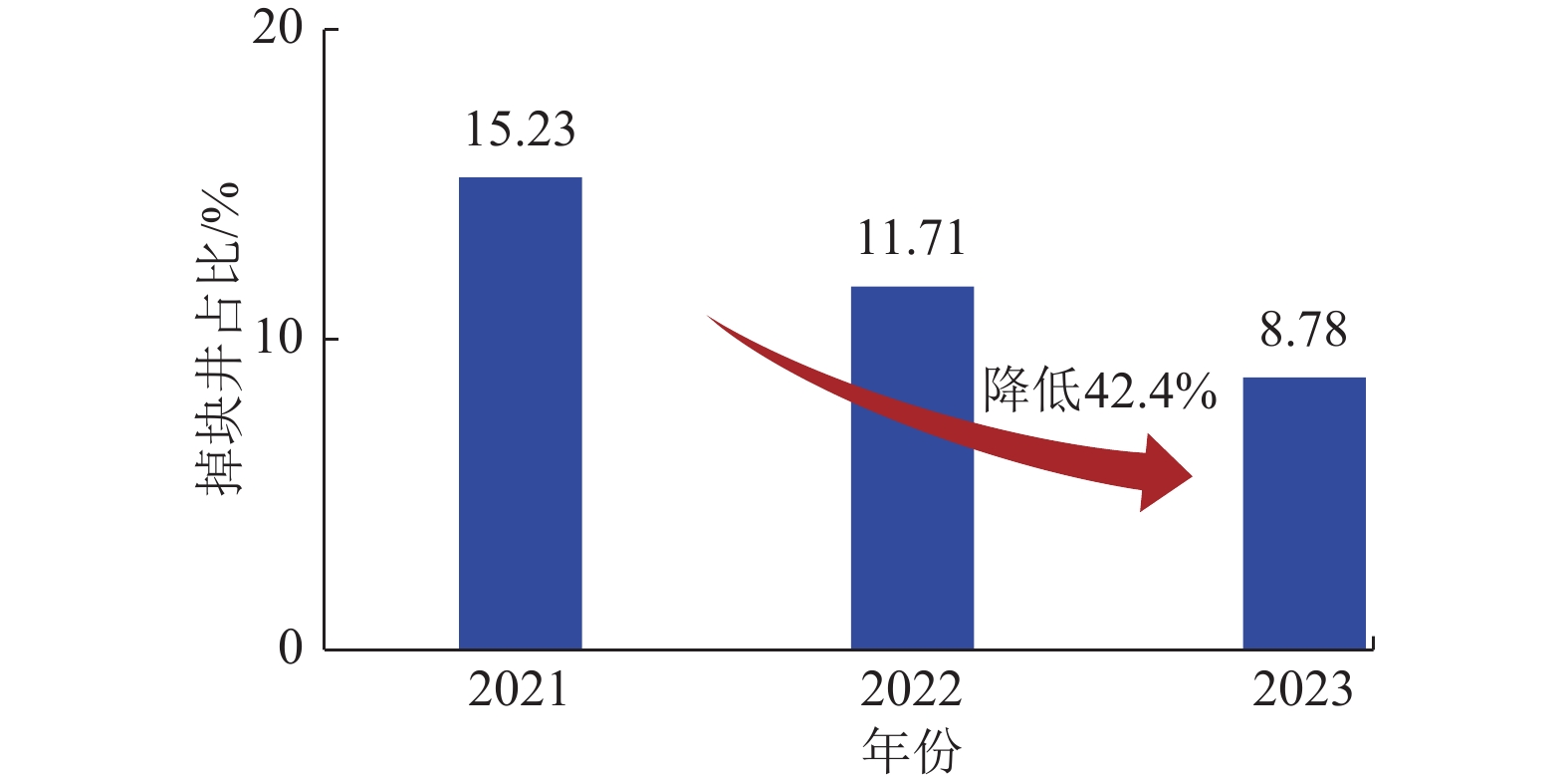
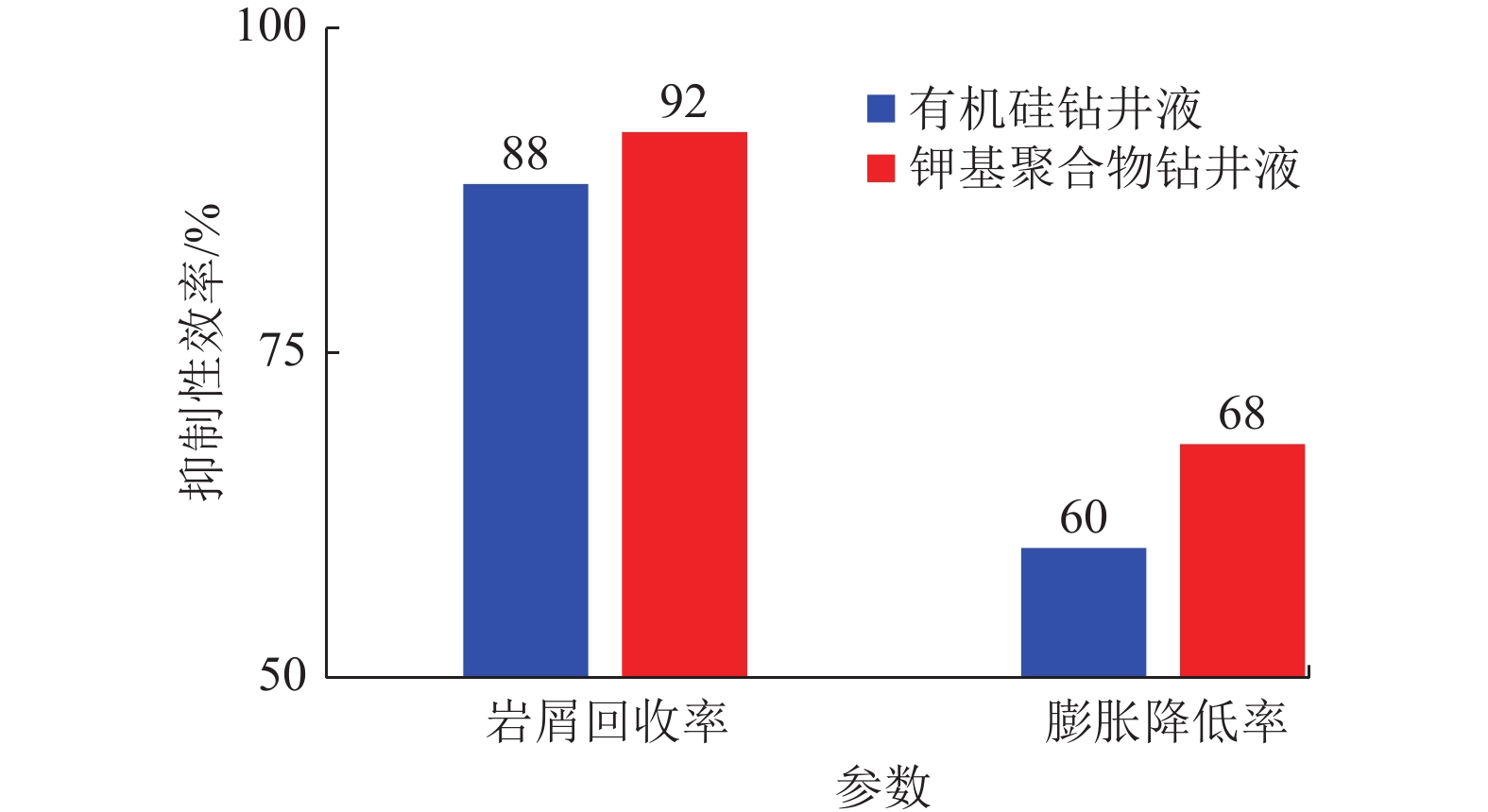
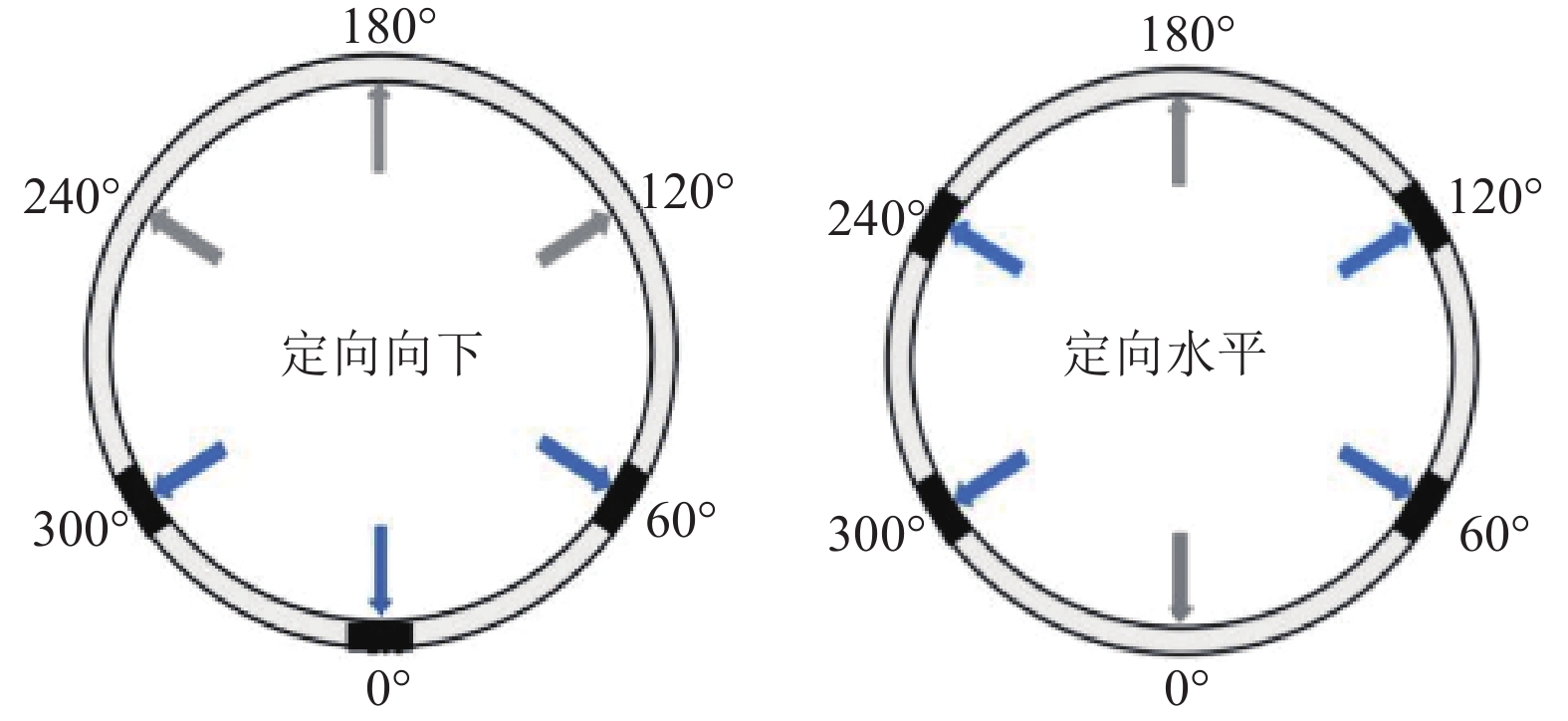
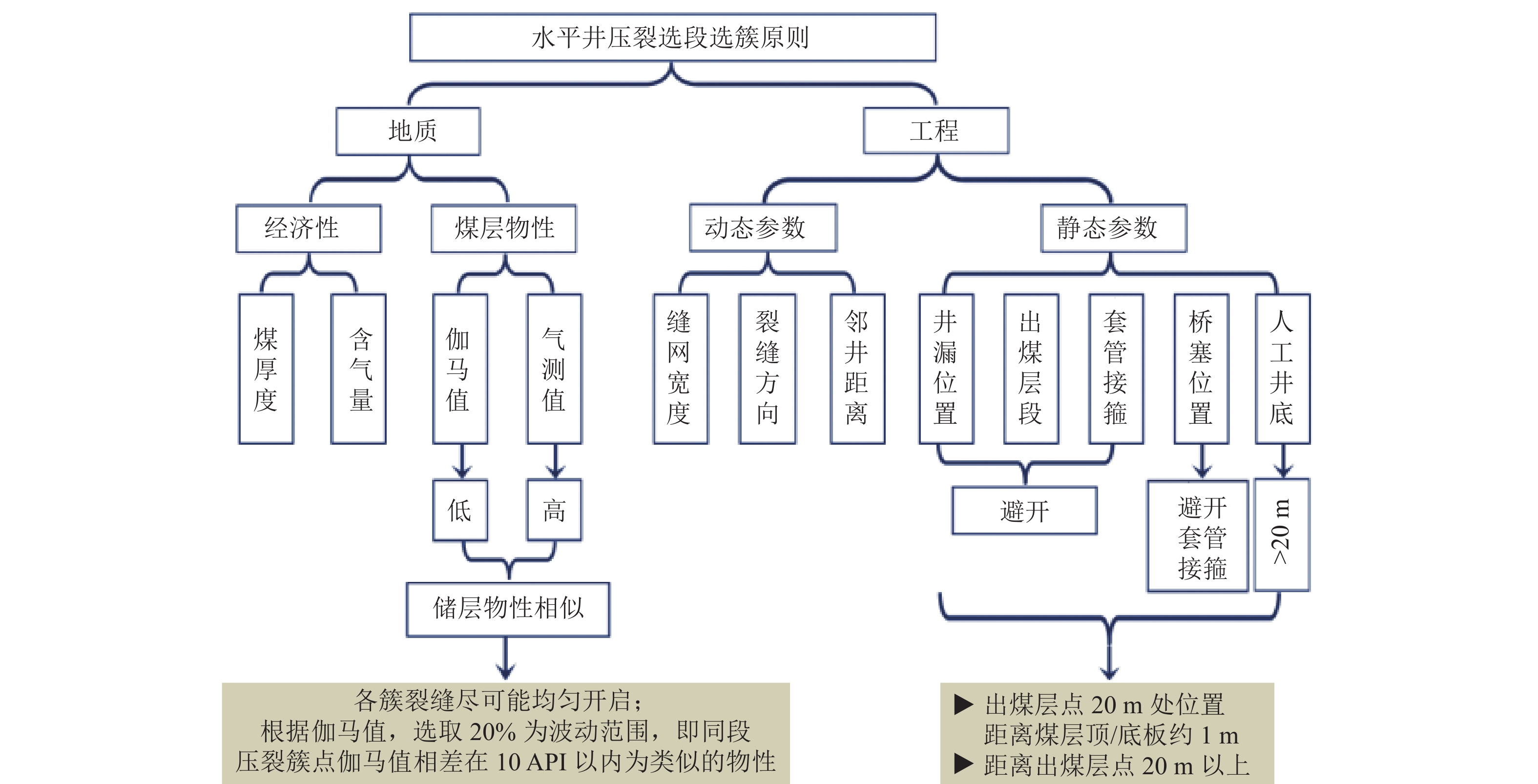
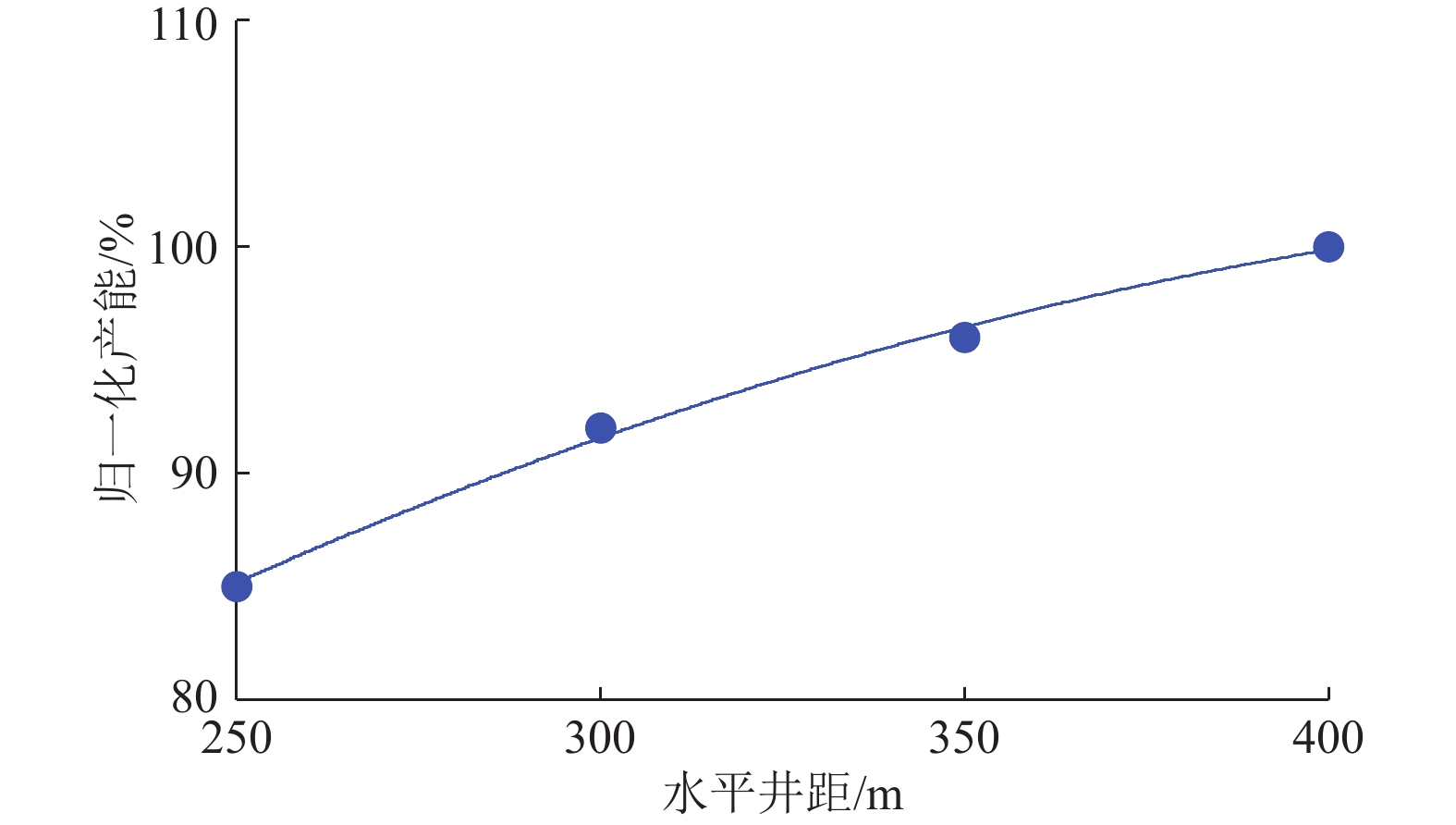
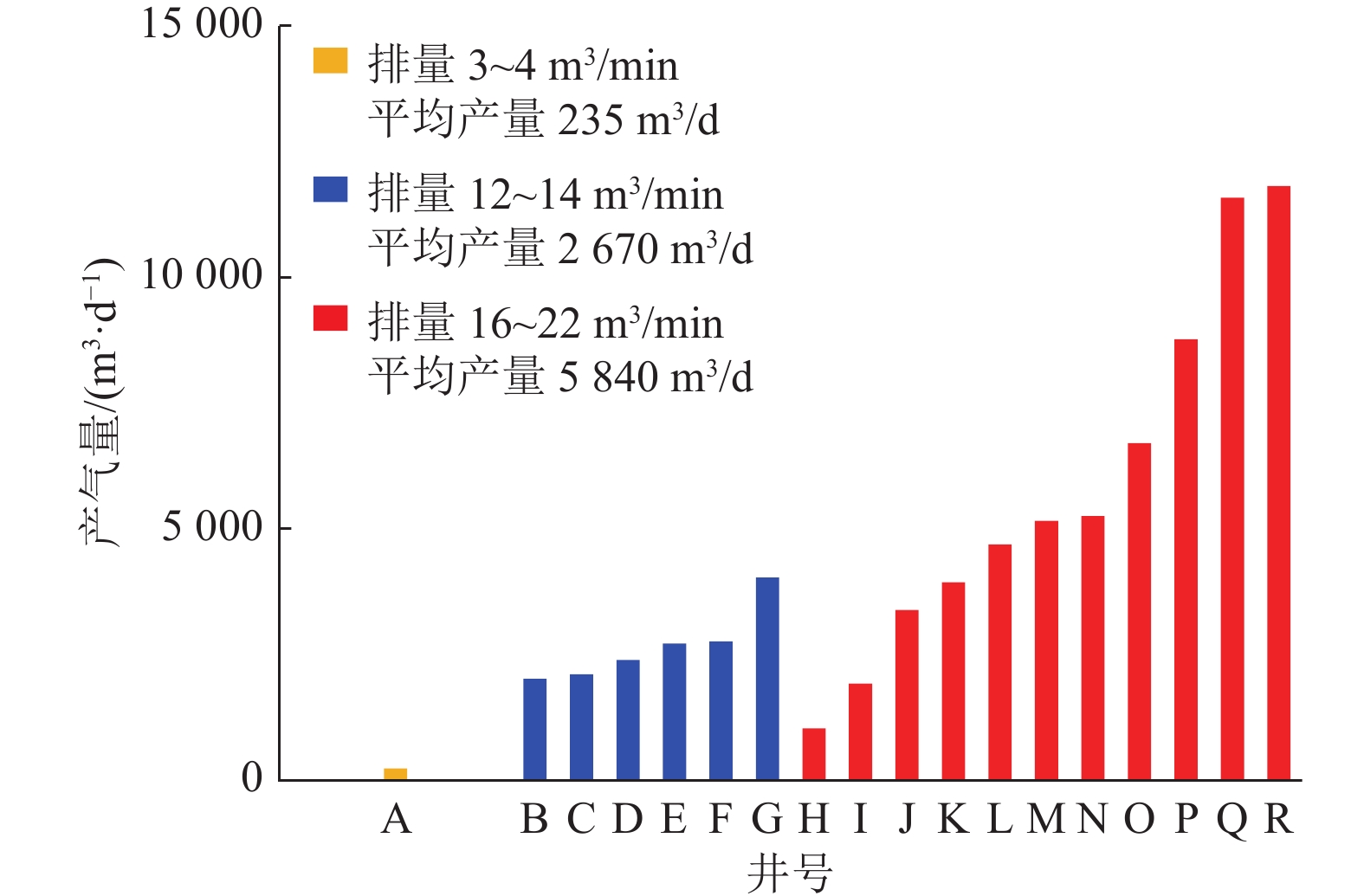
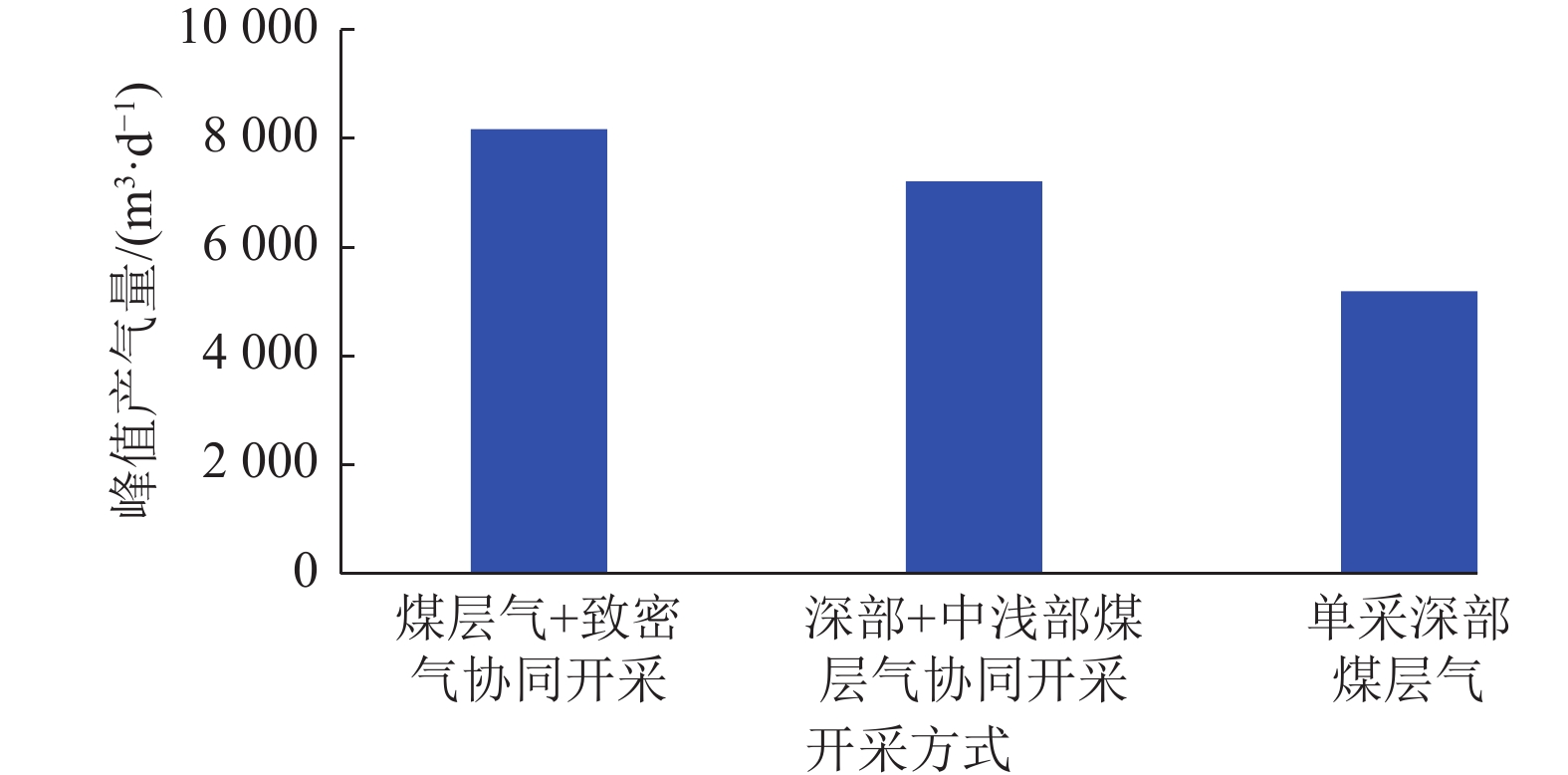
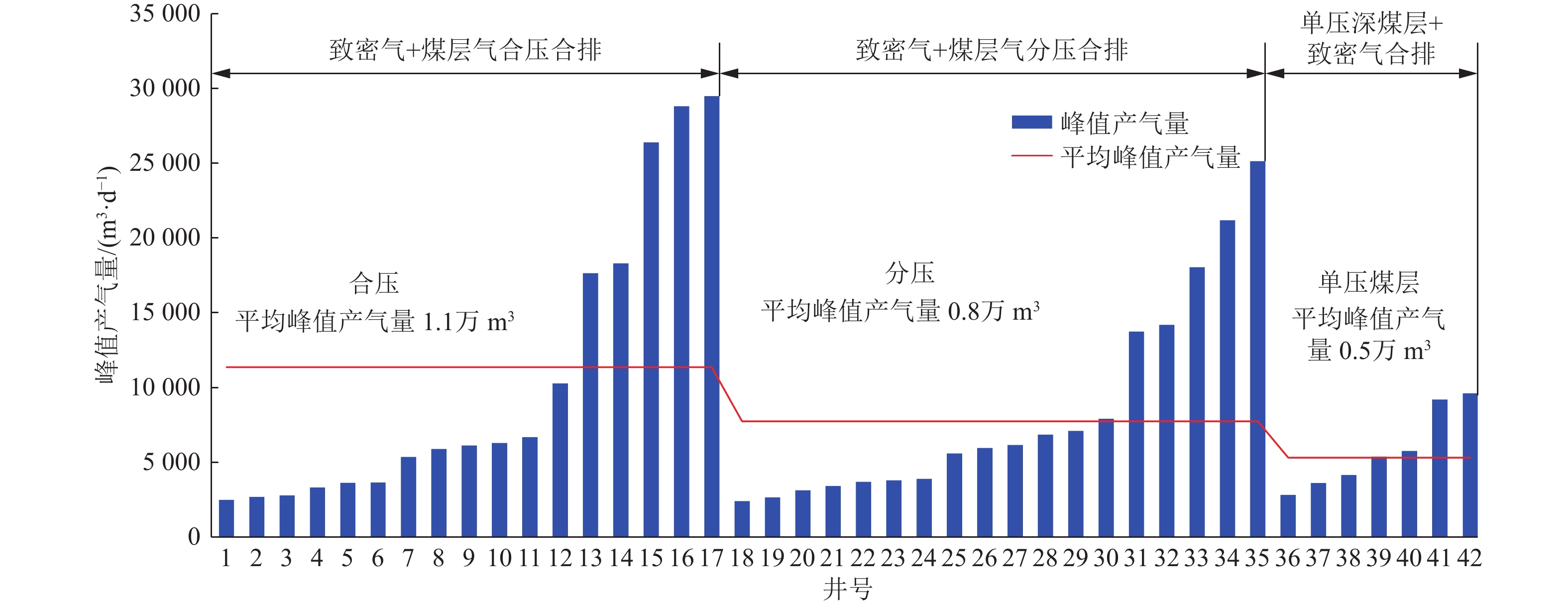
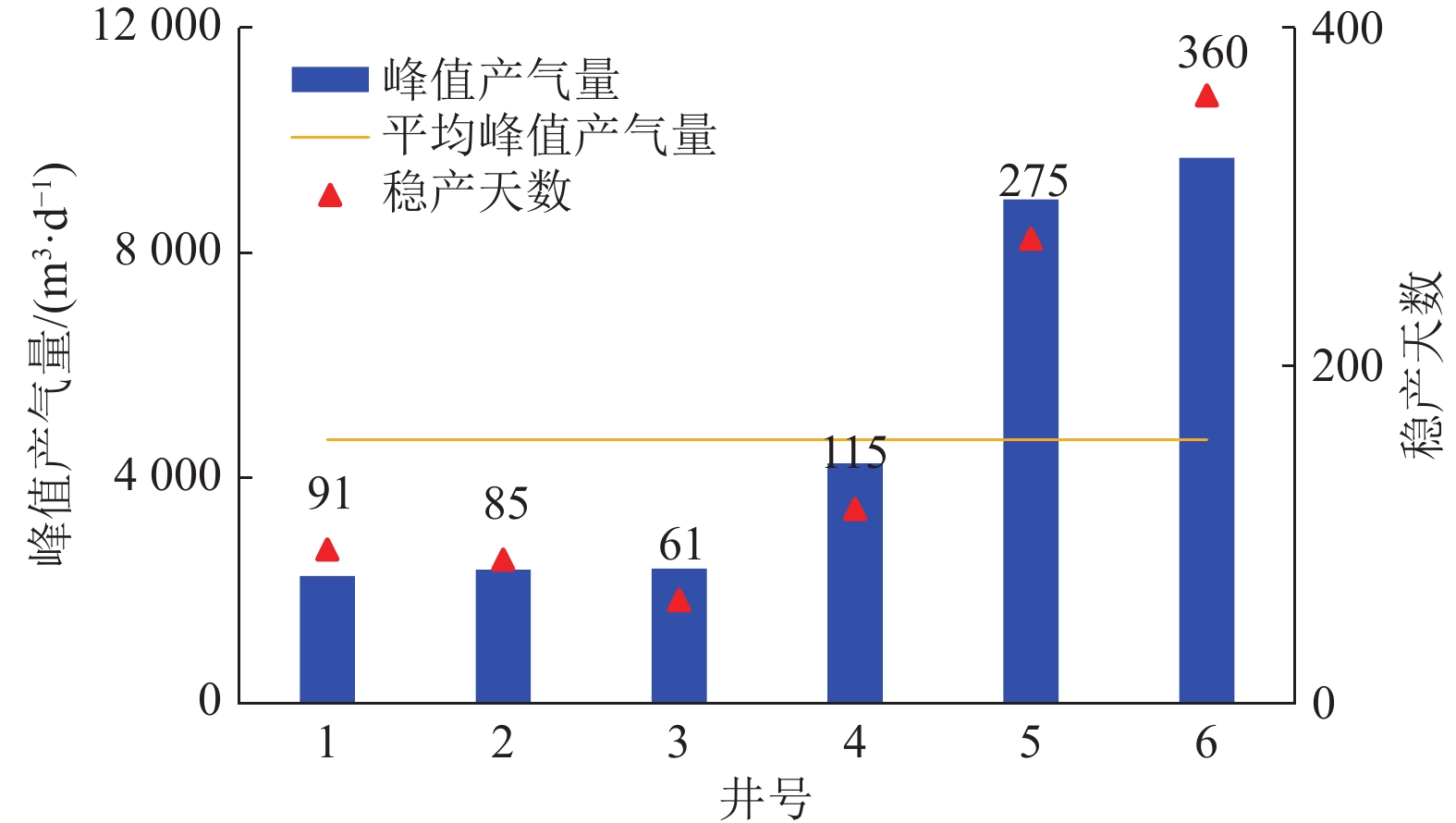
结果和结论(1)针对深部煤层井壁稳定性差、钻速低、钻井周期长,通过优化二开井身结构、优选钻井液体系与“一趟钻”技术,并结合井眼轨迹精细化控制,实现了深部煤层一体化高效钻进,助力“新优快”井台建设落地。(2)针对深部煤层地质特征复杂、采用常规压裂规模产量低,形成了以“定向射孔+前置酸液降破压+段内多簇密切割+高排量大规模+一体化变黏滑溜水+暂堵转向+多粒径组合支撑剂”为核心的复合极限规模化压裂技术体系。(3)基于“一区一策+全局寻优”的工作理念,设计立体井网工厂化钻完井作业模式,最优水平井距为350 m时,“拉链式”压裂模式效果最佳。(4)“深部煤层气+致密气”协同开采,获得了更高的工业气流,多气合采是提升鄂尔多斯盆地东缘非常规天然气开发效益的重要措施。研究结果有望为鄂尔多斯盆地深部煤层高效钻完井技术提供理论指导与实践经验。
Abstract:ObjectiveDeep coal seams exhibit high in-situ stress, moderate to high temperatures, ultra-low permeability, high compressibility, and significant heterogeneity, leading to the absence of mature technical systems for their exploitation presently. The complex geological characteristics of deep coal seams pose new technical challenges to their drilling and completion engineering, rendering it urgent to tackle theoretical and technical challenges in drilling and completion tailored to the geological characteristics of deep coal seam reservoirs. The purpose is to achieve the reserve growth and production addition of hydrocarbons in order to guarantee China’s strategic energy security.
MethodsBased on the pilot tests for deep coalbed methane (CBM) production in the Shenfu block along the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, a set of critical techniques have been developed for efficient drilling and completion.
Results and Conclusions(1) Given the low wellbore stability, low drilling rates, and prolonged drilling cycles of deep coal seams, integrated and efficient drilling of deep coal seams has been achieved by optimization using a second-spud-in casing program, the optimal drilling fluid system, and “one-trip drilling” technique, combined with fine-scale control of borehole trajectories. Such technology can boost the construction of innovative, optimized, and efficient well platforms. (2) To address the challenge posed by the complex geological characteristics and low hydrocarbon production through conventional fracturing of deep coal seams, a composite extremely large-scale fracturing technology system has been developed, which centers on directional perforation, pre-acid to reduce fracturing pressure, multi-cluster closely spaced fracturing within intervals, large-scale fracturing at high injection rates of fracturing fluids, integrated viscosity-variable slickwater, temporary plugging and diverting, and proppants with multiple grain sizes. (3) Following the work philosophy of one strategy for one block and global optimization, a factory drilling and completion operation mode for a stereoscopic well pattern has been designed, with the zipper fracturing mode manifesting the best performance at an optimal horizontal well spacing of 350 m. (4) The high industrial gas flow from the commingled production of deep CBM and tight gas proves that multi-gas commingled production serves as a significant measure to enhance the production efficiency of unconventional natural gas along the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin. It is expected that the findings of this study will provide theoretical guidance and practical experience for the efficient drilling and completion techniques for deep coal seams in the Ordos Basin.
-
-
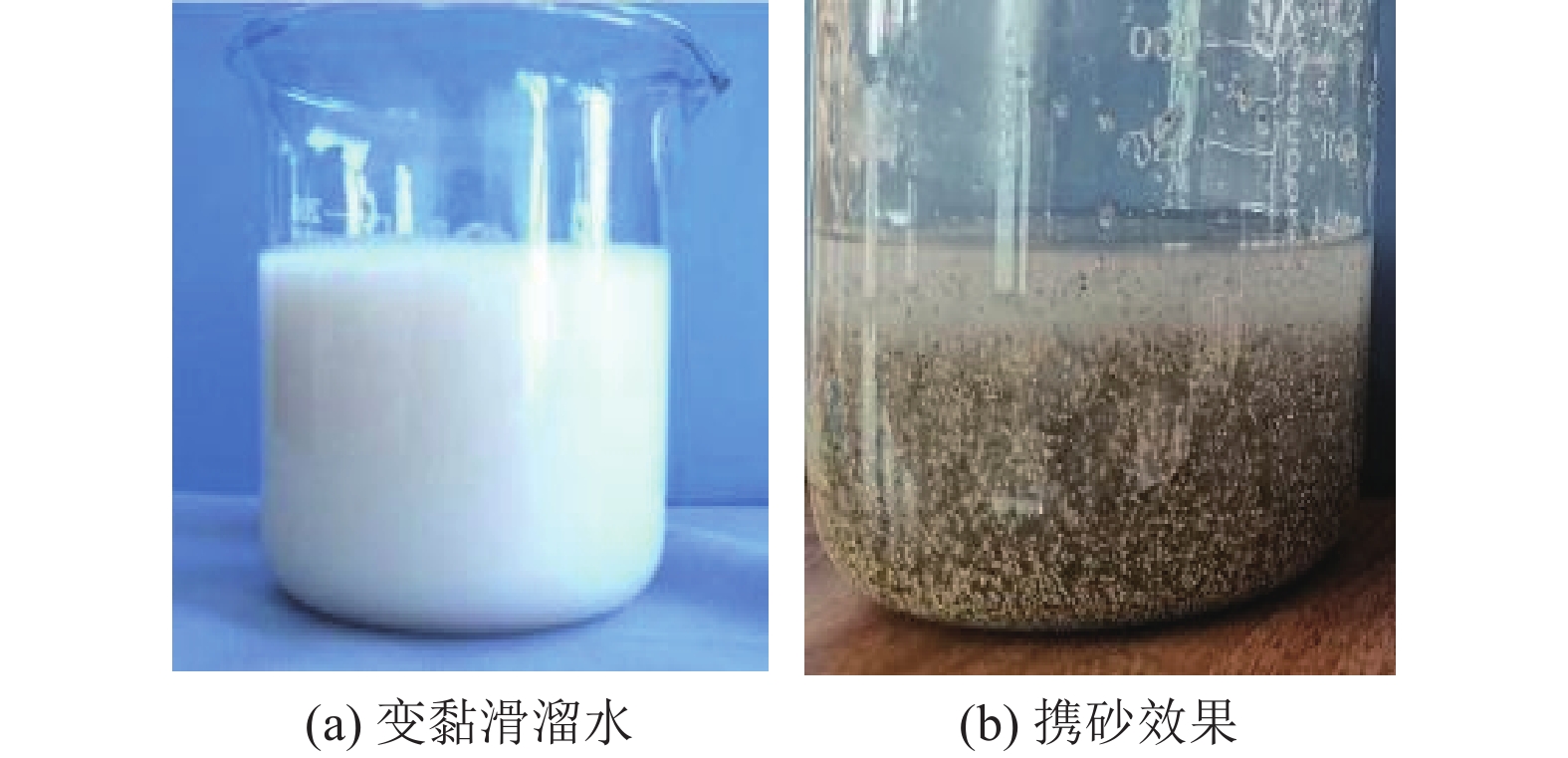
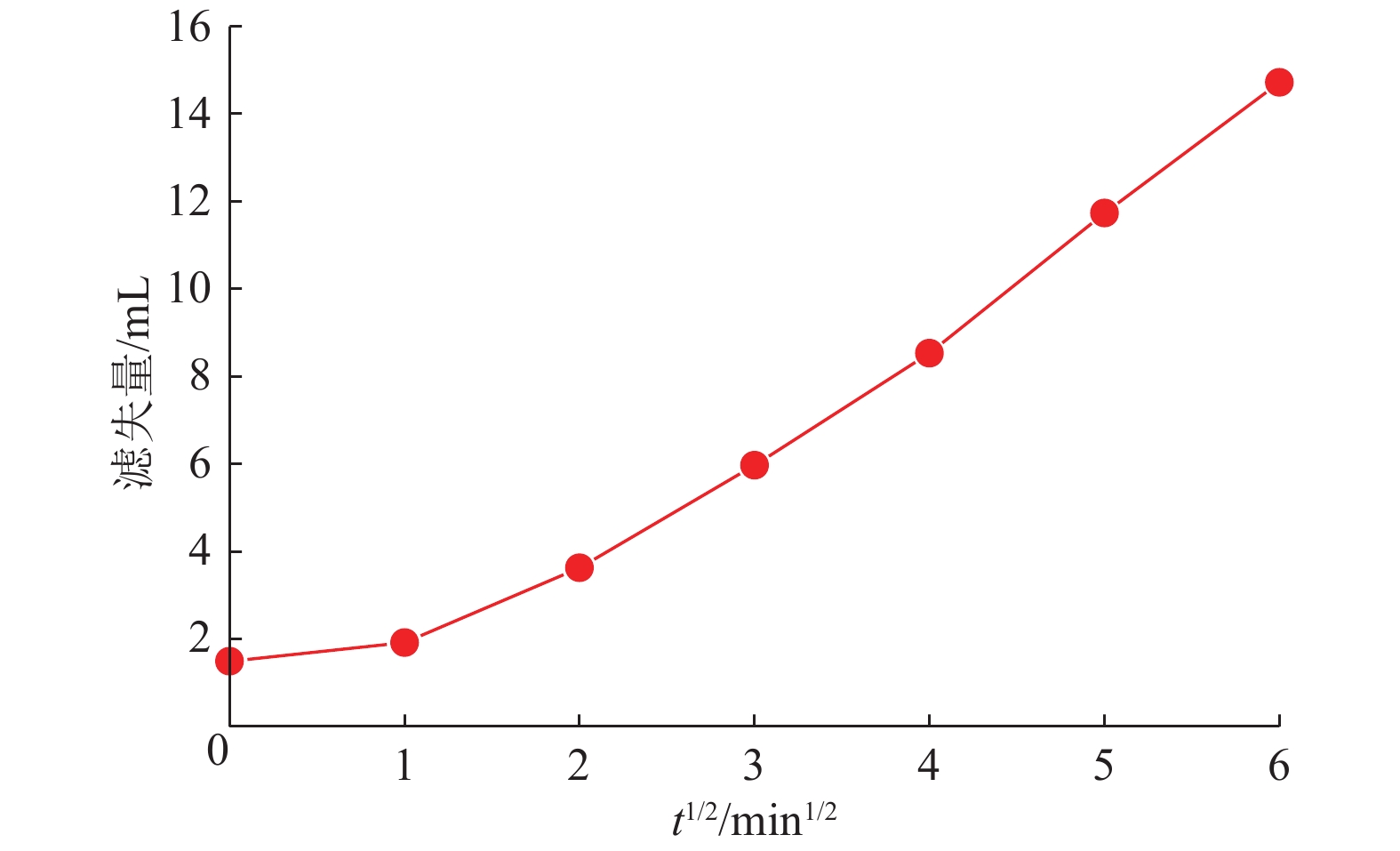
表 1 一体化变黏滑溜水性能参数
Table 1 Performance parameters of integrated viscosity-variable slickwater
序号 参数 指标/要求 数值 1 pH 6~9 7 2 表观黏度/
(mPa·s)低黏 (1,10] 3 中黏 (10,20] 15 高黏 (20,40] 28 3 降阻率/% 低黏 ≥70 83.4 中黏 80.1 高黏 78.2 4 增黏速率/% ≥80% 88.7 5 基质渗透
损害率/%≤15% 11.2 6 破胶时间/min ≤120 60 7 结垢趋势 无 无 8 破胶后表面
张力/(mN·m−1)≤28 22.4 9 破胶后表观
黏度/(mPa·s)<5 1.0 10 破胶液
防膨率/%≥60 87.1 11 CST比值 <1.5 1.06 12 配伍性 室温和储层温度下
均无絮凝现象,
无沉淀产生(清水)室温和储层温度下
均无絮凝现象,
无沉淀产生(清水)注:CST为滑溜水和卷心粉混合物扩散到滤纸时间比。 表 2 模型基本参数
Table 2 Fundamental parameters of the model
类别 参数 数值 地层参数 目标层位 8号煤层 垂深/m 1800 弹性模量/GPa 8~14 泊松比 0.29~0.39 最小水平主应力/MPa 40~44 水平两向应力差/MPa 5.5~6.7 储隔层应力差/MPa 5~9 压裂参数 水平段长/m 1000 施工排量/(m3·min−1) 18 压裂液类型 变黏滑溜水 支撑剂类型 组合粒径石英砂 表 3 微地震监测结果参数
Table 3 Parameters for microseismic monitoring results
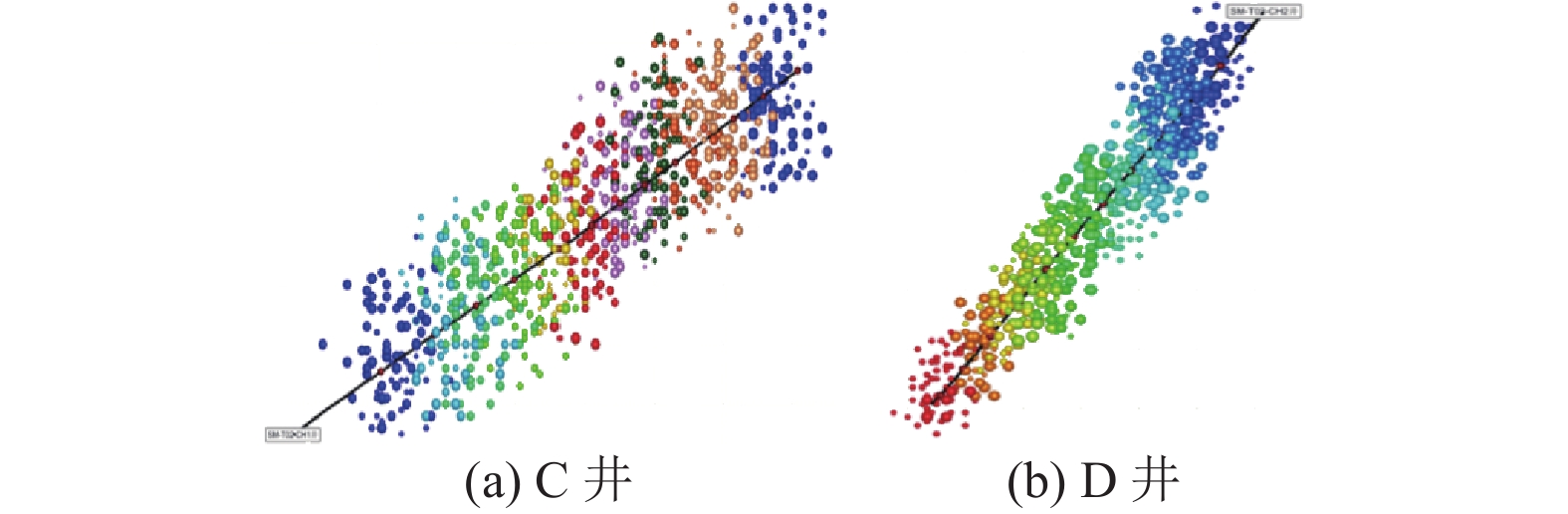
井号 累积产气
量/104 m3缝长/m 缝宽/m 缝高/m SRV/m3 C 264.39 290~390 170~242 20~30 19261000 D 116.52 253~351 112~191 20~30 16229437 注:SRV为储层改造体积。 -
[1] 国家能源局. 张星:2023年,煤层气产量达到117.7亿立方米,同比增长20.5% [EB/OL]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-0 1/25/c_1310761983.htm.2024-01-25. [2] 吴裕根,门相勇,娄钰. 我国“十四五” 煤层气勘探开发新进展与前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探,2024,29(1):1−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2024.01.001 WU Yugen,MEN Xiangyong,LOU Yu. New progress and prospect of coalbed methane exploration and development in China during the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2024,29(1):1−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2024.01.001
[3] JOHNSON R C,FLORES R M. Developmental geology of coalbed methane from shallow to deep in Rocky Mountain Basins and in Cook Inlet–Matanuska Basin,Alaska,U. S. A. and Canada[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,1998,35(1/2/3/4):241−282.
[4] 李勇,徐立富,张守仁,等. 深煤层含气系统差异及开发对策[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(2):900−917. LI Yong,XU Lifu,ZHANG Shouren,et al. Gas bearing system difference in deep coal seams and corresponded development strategy[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(2):900−917.
[5] ZHANG Songhang,TANG Shuheng,QIAN Zheng,et al. Evaluation of geological features for deep coalbed methane reservoirs in the Dacheng Salient,Jizhong Depression,China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2014,133:60−71. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2014.09.002
[6] 聂志宏,徐凤银,时小松,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气开发先导试验效果与启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):1−12. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0645 NIE Zhihong,XU Fengyin,SHI Xiaosong,et al. Outcomes and implications of pilot tests for deep coalbed methane production on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):1−12. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0645
[7] 徐凤银,闫霞,李曙光,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部(层)煤层气勘探开发理论技术难点与对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):115−130. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.06.0503 XU Fengyin,YAN Xia,LI Shuguang,et al. Theoretical and technological difficulties and countermeasures of deep CBM exploration and development in the eastern edge of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):115−130. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.06.0503
[8] 郑毅. 中国煤层气钻完井技术的发展现状及趋势分析[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2017,37(5):51−52. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.05.024 ZHENG Yi. Development status and trend analysis of coalbed methane drilling and completion technology in China[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality,2017,37(5):51−52. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.05.024
[9] 刘行. 深煤层煤层气井低伤害完井液研究[D]. 成都:西南石油大学,2015. LIU Xing. Study on low-damage completion fluid for coalbed methane wells in deep coal seam[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Petroleum University,2015.
[10] 朱光辉,李本亮,李忠城,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘非常规天然气勘探实践及发展方向:以临兴−神府气田为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2022,34(4):16−29. DOI: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.04.002 ZHU Guanghui,LI Benliang,LI Zhongcheng,et al. Practices and development trend of unconventional natural gas exploration in eastern margin of Ordos Basin:Taking Linxing-Shenfu gas field as an example[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2022,34(4):16−29. DOI: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.04.002
[11] 李国璋. 煤系气合采产层贡献及其预测模型[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. LI Guozhang. Contribution and prediction model of gas production layer in coal measures[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[12] 刘建忠,朱光辉,刘彦成,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气勘探突破及未来面临的挑战与对策:以临兴—神府区块为例[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1827−1839. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311006 LIU Jianzhong,ZHU Guanghui,LIU Yancheng,et al. Breakthrough,future challenges and countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin:A case study of Linxing-Shenfu Block[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1827−1839. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311006
[13] 付金华,魏新善,任军峰. 伊陕斜坡上古生界大面积岩性气藏分布与成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2008,35(6):664−667. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.06.004 FU Jinhua,WEI Xinshan,REN Junfeng. Distribution and genesis of large-scale Upper Palaeozoic lithologic gas reservoirs on Yi-Shaan Slope[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(6):664−667. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.06.004
[14] 杨帆,李斌,王昆剑,等. 深部煤层气水平井大规模极限体积压裂技术:以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴区块为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2024,51(2):389−398. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20230513 YANG Fan,LI Bin,WANG Kunjian,et al. Extreme massive hydraulic fracturing in deep coalbed methane horizontal wells:A case study of the Linxing Block,eastern Ordos Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2024,51(2):389−398. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20230513
[15] 安琦,杨帆,杨睿月,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神府区块深部煤层气体积压裂实践与认识[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(5):2376−2393. AN Qi,YANG Fan,YANG Ruiyue,et al. Practice and understanding of deep coalbed methane massive hydraulic fracturing in Shenfu Block,Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024,49(5):2376−2393.
[16] 王红岩,段瑶瑶,刘洪林,等. 煤层气水平井开发的理论技术初探:兼论煤层气和页岩气开发条件对比[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(4):47−59. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0794 WANG Hongyan,DUAN Yaoyao,LIU Honglin,et al. Preliminarily exploring the theories and technologies for coalbed methane production using horizontal wells:Comparison of conditions for coalbed methane and shale gas exploitation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(4):47−59. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0794
[17] 韩军昌. 寿阳区块煤层气井排采影响因素分析[J]. 中国煤层气,2018,15(2):13−16. HAN Junchang. Analysis of influence factors of CBM wells in Shouyang Block[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2018,15(2):13−16.
[18] 赵凌云,易同生. 煤层气水平井井型结构分析及钻完井技术优化[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(3):221−226. ZHAO Lingyun,YI Tongsheng. Analysis on well type structure and optimization of associated drilling technology of CBM horizontal wells[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(3):221−226.
[19] 张聪,李梦溪,胡秋嘉,等. 沁水盆地南部中深部煤层气储层特征及开发技术对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):122−133. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0624 ZHANG Cong,LI Mengxi,HU Qiujia,et al. Moderately deep coalbed methane reservoirs in the Southern Qinshui Basin:Characteristics and technical strategies for exploitation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):122−133. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0624
[20] 刘克强. “一趟钻” 关键工具技术现状及发展展望[J]. 石油机械,2019,47(11):13−18. LIU Keqiang. Technology status and development prospect of the key tools of one-trip drilling[J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2019,47(11):13−18.
[21] 吴鹏程,汪瑶,付利,等. 深层页岩气水平井“一趟钻” 技术探索与实践[J]. 石油机械,2023,51(8):26−33. WU Pengcheng,WANG Yao,FU Li,et al. Exploration and practice of “one trip” technology for deep shale gas horizontal wells[J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2023,51(8):26−33.
[22] 曾波,王星皓,黄浩勇,等. 川南深层页岩气水平井体积压裂关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(5):77−84. DOI: 10.11911/syztjs.2020073 ZENG Bo,WANG Xinghao,HUANG Haoyong,et al. Key technology of volumetric fracturing in deep shale gas horizontal wells in Southern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques,2020,48(5):77−84. DOI: 10.11911/syztjs.2020073
[23] 蒋廷学. 非常规油气藏新一代体积压裂技术的几个关键问题探讨[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(4):184−191. DOI: 10.11911/syztjs.2023023 JIANG Tingxue. Discussion on several key issues of the new-generation network fracturing technologies for unconventional reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques,2023,51(4):184−191. DOI: 10.11911/syztjs.2023023
[24] 范宇恒,周丰,蒋廷学,等. 页岩气环保变黏压裂液的研究与应用[J]. 特种油气藏,2023,30(2):147−152. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.02.021 FAN Yuheng,ZHOU Feng,JIANG Tingxue,et al. Research and application of environmentally friendly variable-viscosity fracturing fluid for shale gas[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2023,30(2):147−152. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.02.021
[25] 刘雨舟,张志坚,王磊,等. 国内变黏滑溜水研究进展及在川渝非常规气藏的应用[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2022,51(3):76−81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2022.03.012 LIU Yuzhou,ZHANG Zhijian,WANG Lei,et al. Research progress of variable viscosity slick water in China and its application in unconventional gas reservoirs in Sichuan and Chongqing[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas,2022,51(3):76−81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2022.03.012
[26] 顾燕凌,樊红旗,刘运强,等. 前置酸压裂工艺在低渗砂岩储层中的试验与评价[J]. 油气田地面工程,2008,27(8):4−5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2008.08.002 GU Yanling,FAN Hongqi,LIU Yunqiang,et al. Experimentation and evaluation of pad acid fracturing process in low-permeability sandstone reservior[J]. Oil-Gasfield Surface Engineering,2008,27(8):4−5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2008.08.002
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王羽扬,李剑,李元林,张勇,刘勇,张毅,韩连昌. 岩溶区顶板沉降特点及覆岩裂隙分形维数变化研究. 采矿与安全工程学报. 2023(04): 679-690 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)







 下载:
下载: