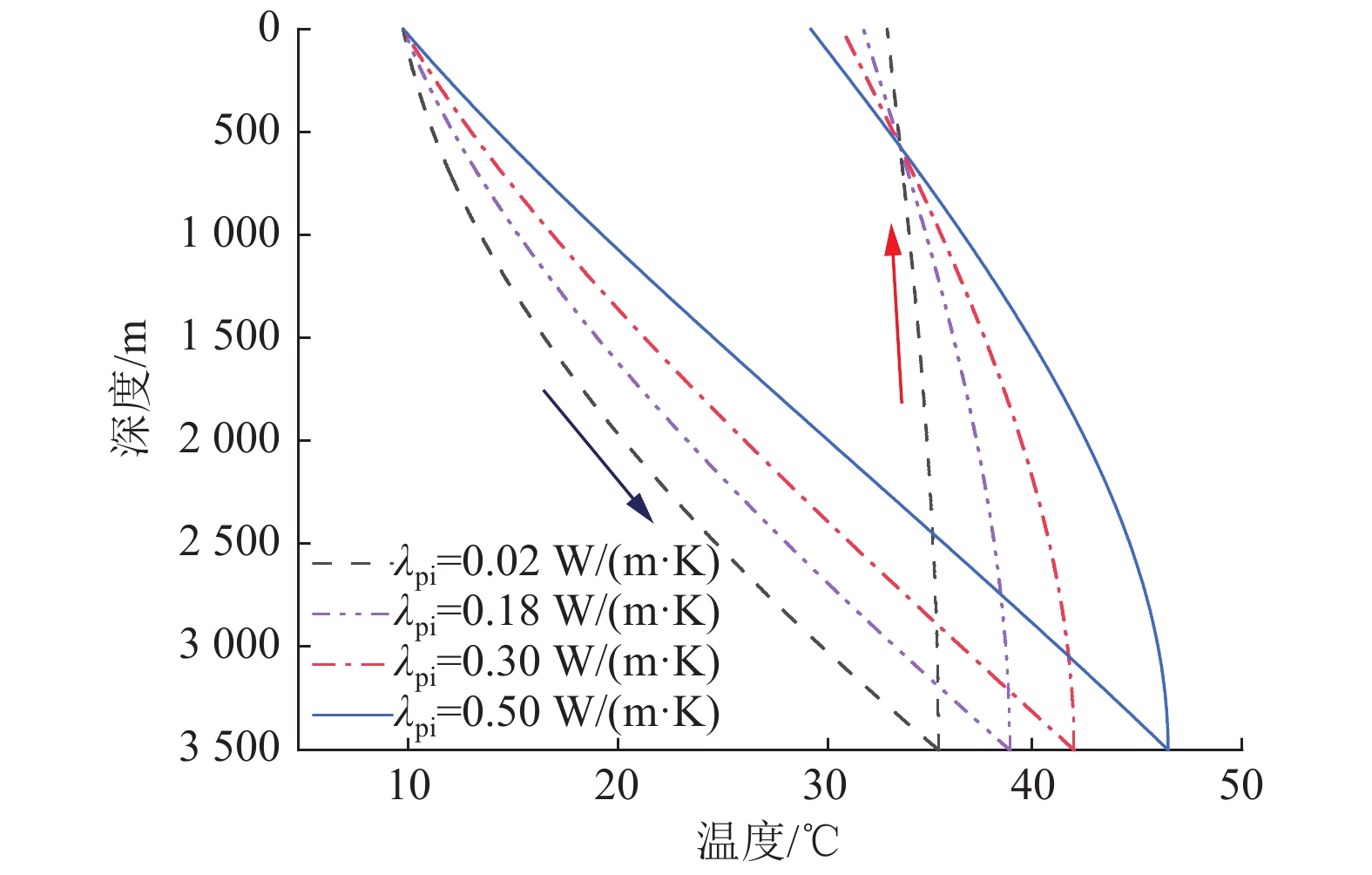
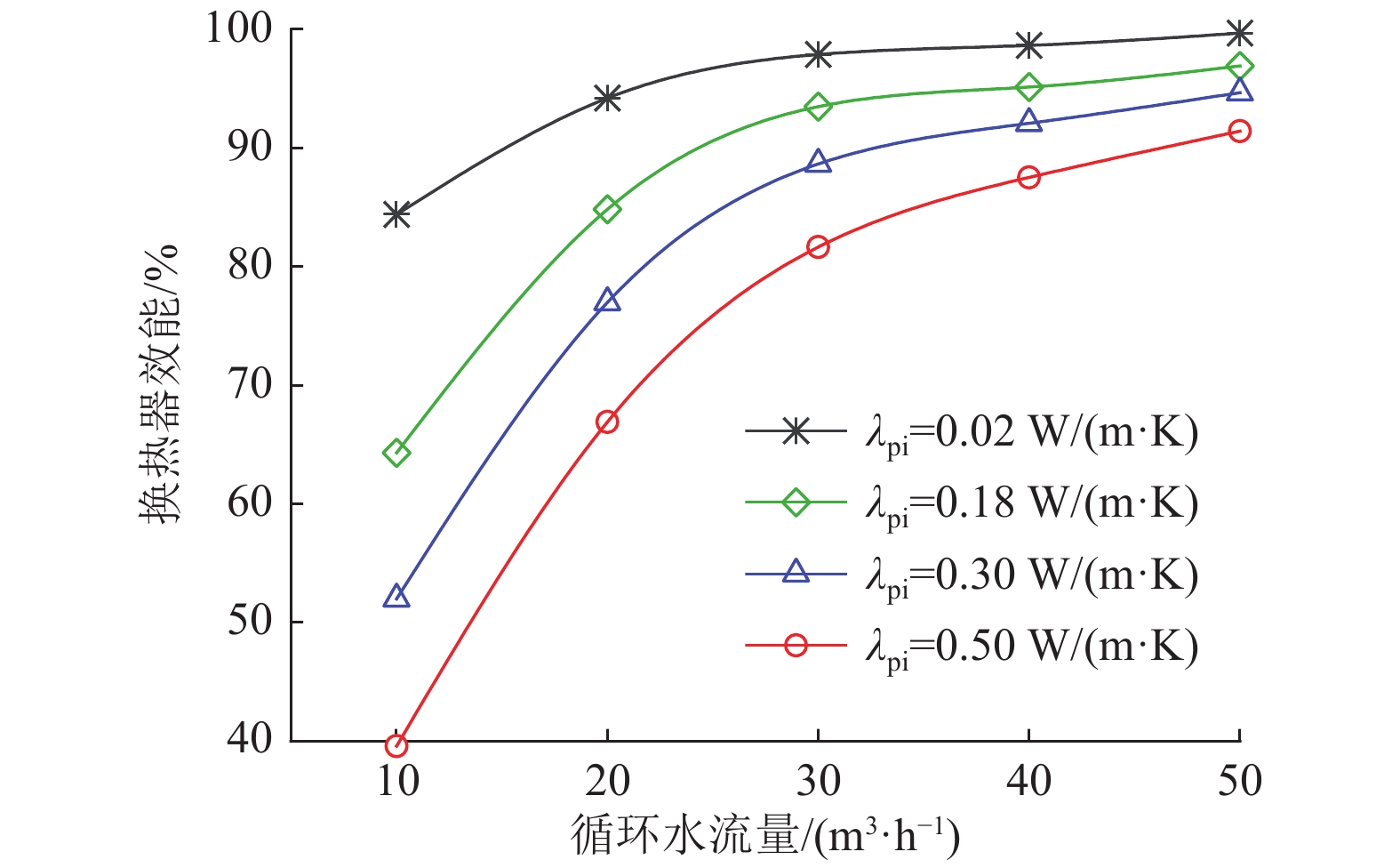
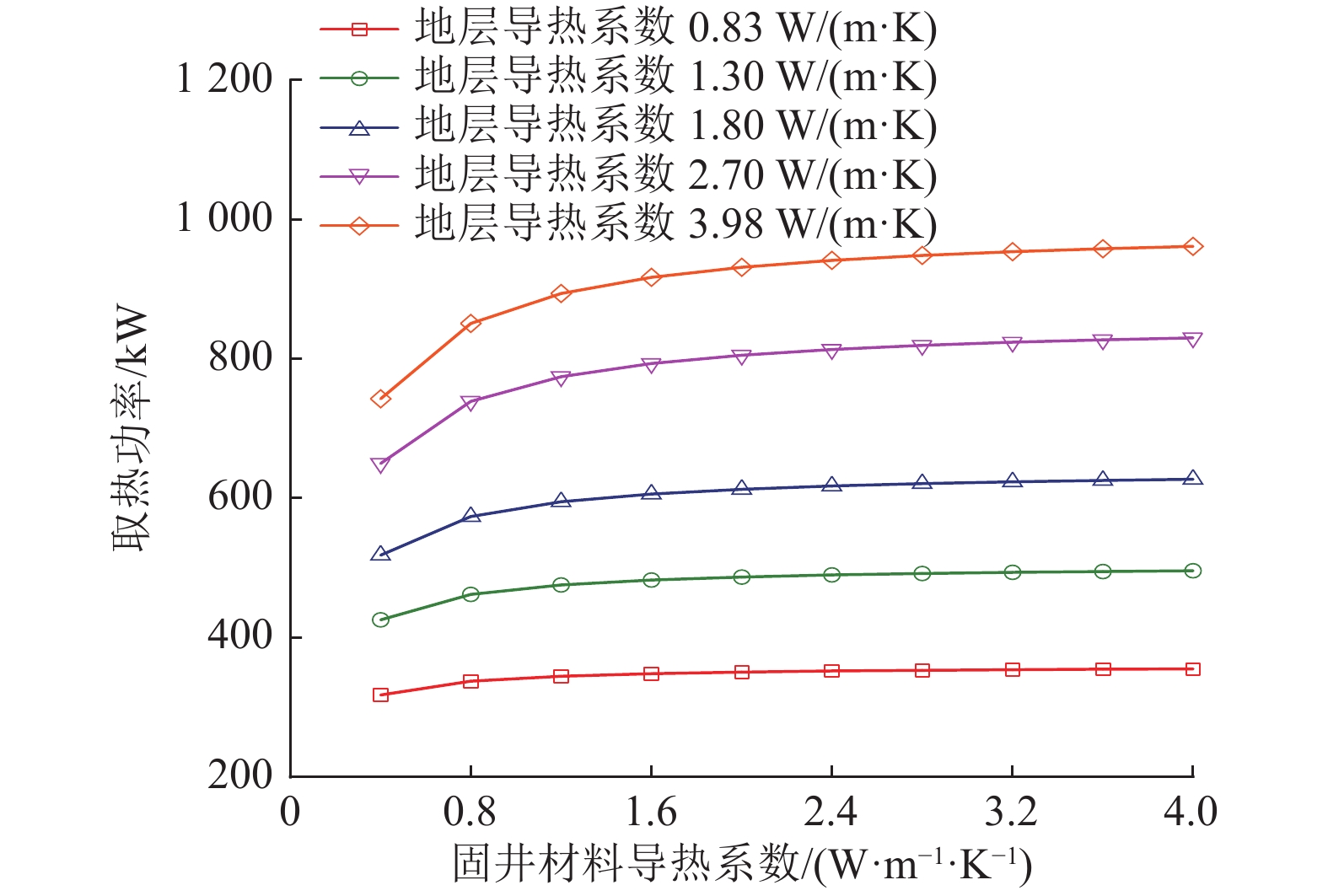
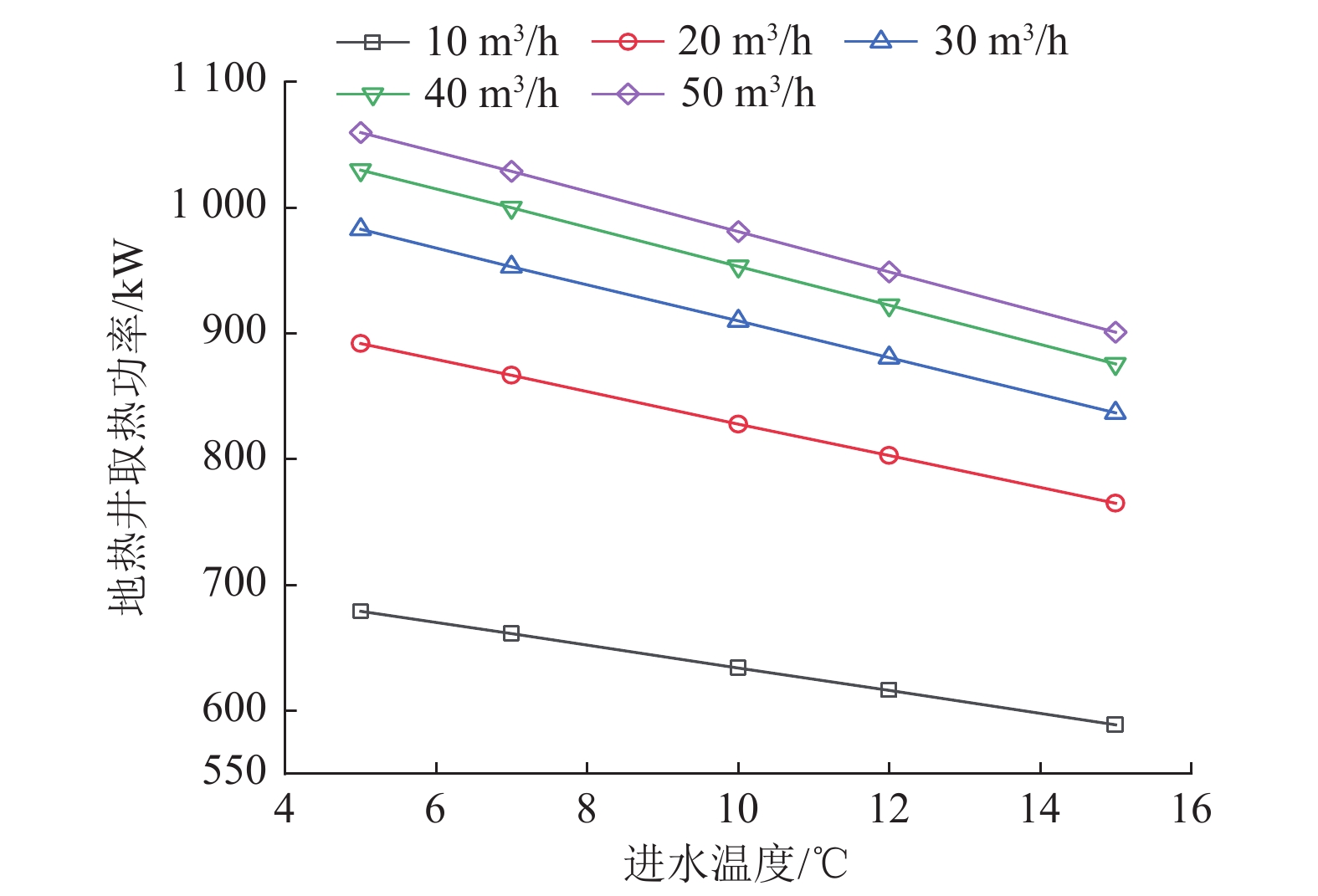
Influencing patterns of multiple factors on the heat transfer performance of moderately deep geothermal wells
-
摘要:
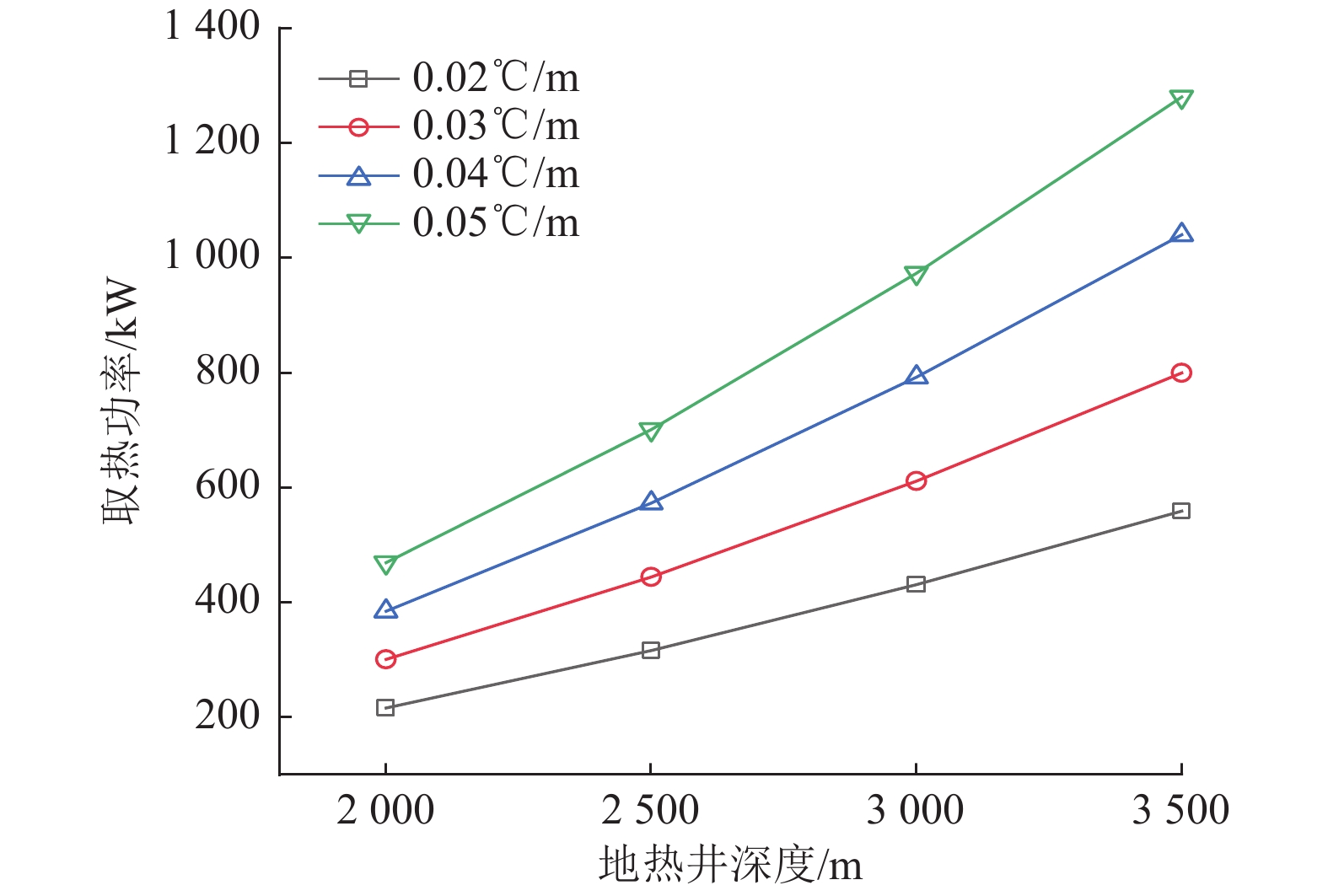
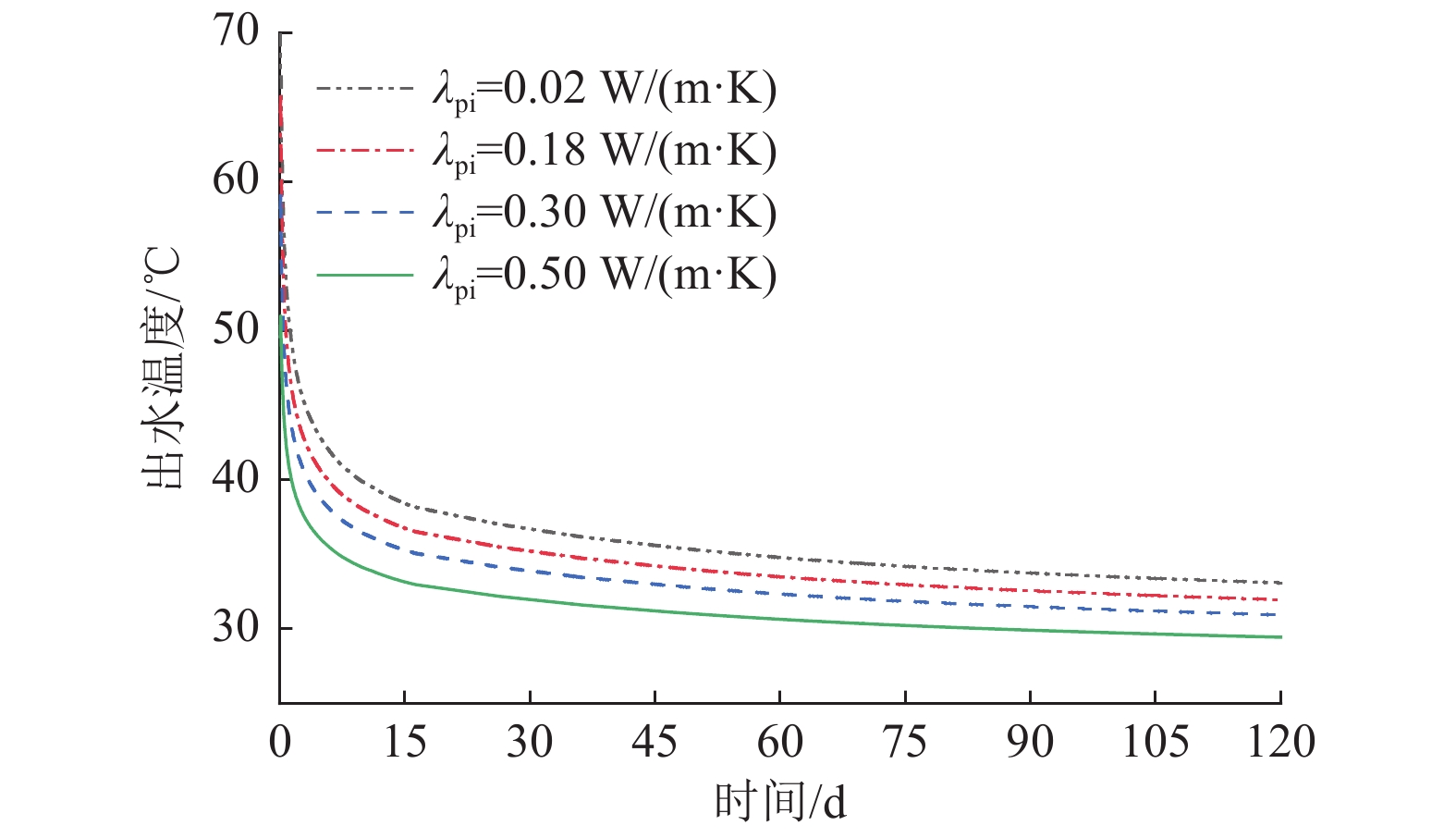
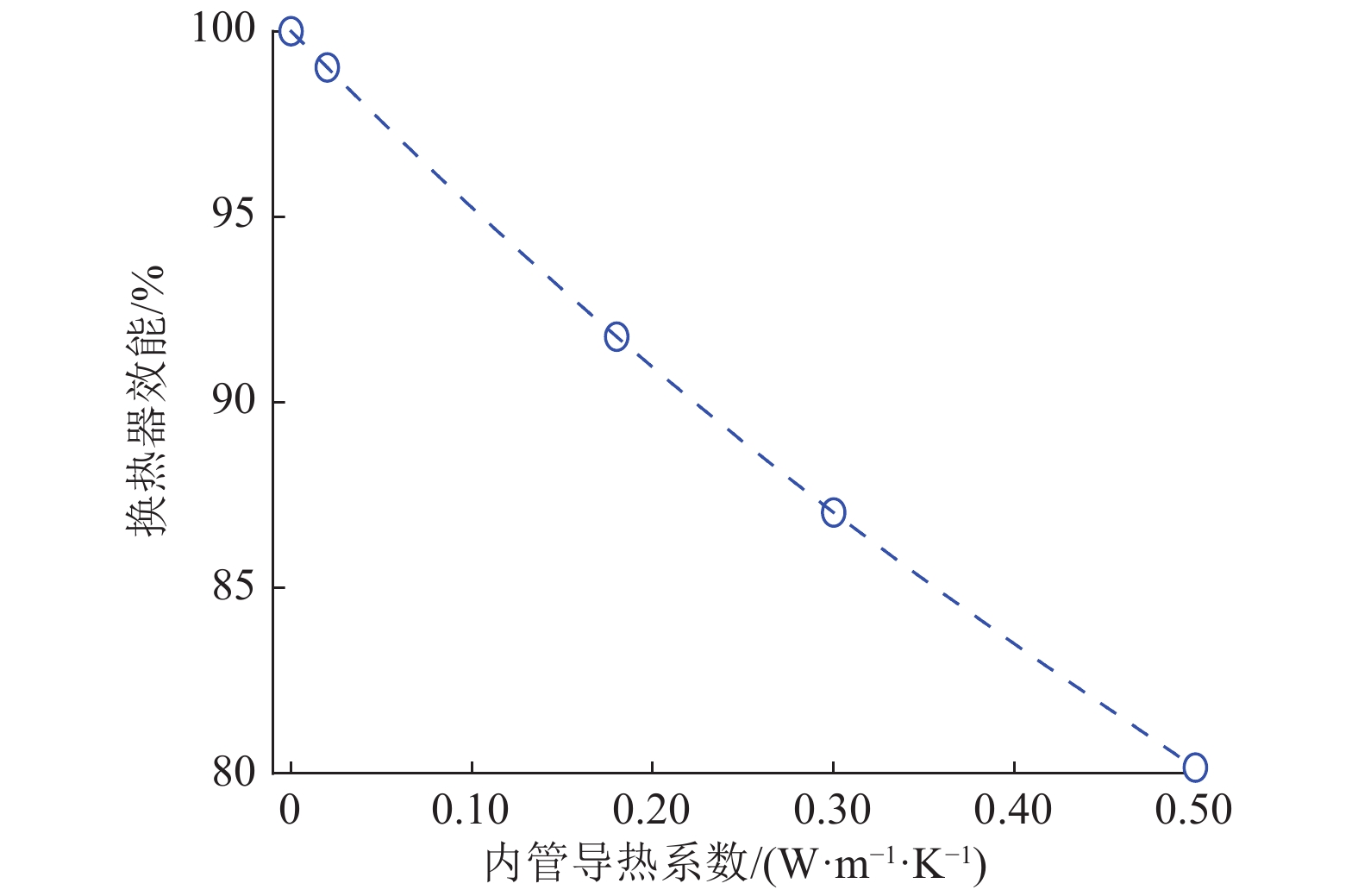
积极推进中深层地热能供暖技术,是践行国家碳达峰碳中和“双碳”目标的重要举措。中深层同轴套管式换热系统可避免对地下水资源和环境造成损害,且影响要素之间存在着复杂的非线性相互作用。基于中深层同轴套管式换热器的理论分析和数学描述,建立地热井分层换热模型,并验证其可靠性;以陕西关中盆地某中深层地热井为依托,采用数值模拟方法对各项因素影响下的地热井换热性能及连续运行过程的取热能力进行系统分析。结果表明:采用均质模型、分层模型计算地热井出水温度与实测值最大相对误差分别为14.08%、11.50%,平均误差分别为7.29%、6.93%,分层模型较均质模型具有较高的计算精度;影响因素中地热井深度、地温梯度及地层导热系数对取热功率影响最为显著,在一定程度上取热功率与地温梯度、进水温度、内管导热系数基本呈线性关系,且固井材料导热系数对传热过程具有热阻效应;中深层地热井取热量随运行年限的增加而降低,前5个供暖季取热量降幅较大,之后取热量降幅减缓,经过50个供暖季,年平均取热功率下降15.59%,将地温下降值超过1℃视为地温场受到影响,地温场平均受影响半径约为65 m,此外,由于地层的差异性,地热井周围地层温度下降及恢复等值线在地层交界面处出现了“阶梯式”变化,岩石导热系数较大的地层在地层交界面附近造成的温度扰动距离更远。研究成果可应用于中深层地热井取热换热能力的评估,同时为中深层同轴套管式换热系统的设计提供借鉴。
Abstract:Vigorously promoting the technology for heating using moderately deep geothermal energy serves as an important measure for China’s pursuit of carbon neutrality and peak carbon dioxide emissions. A coaxial double-pipe heat transfer system for moderately deep geothermal wells can avoid damage to groundwater resources and the environment. Furthermore, the influencing factors of the wells exhibit complicated and nonlinear interactions. Based on the theoretical analysis and mathematical description of a moderately deep well with a coaxial double-pipe heat exchanger, this study established a layered heat transfer model for the geothermal well and verified its reliability. This study investigated a moderately deep geothermal well in the Guanzhong Basin in Shaanxi Province. Through numerical simulations, it systematically analyzed the heat transfer performance of the geothermal well, as well as its heat extraction capacity during continuous operation, under the influence of various factors. The results show that compared to the measured values, the outlet water temperatures calculated using the homogeneous and layered models exhibited maximum relative errors of 14.08% and 11.50%, respectively, and average errors of 7.29% and 6.93%, respectively. Therefore, the layered model enjoyed a higher calculation accuracy than the homogeneous model. Among all influencing factors, geothermal well depth, geothermal gradient, and the thermal conductivity of strata exerted the most significant influence on the heat extraction power of the geothermal well. There existed roughly linear relationships of the heat extraction power with the geothermal gradient, inlet water temperature, and the thermal conductivity of the inner tube. Moreover, the thermal conductivity of well cementing materials produced thermal resistance effects on the heat transfer process. The heat amount extracted from the moderately deep geothermal well decreased with the operating years, with the decreasing amplitude being high in the first five heating seasons and then decreasing. After 50 heating seasons, the annual average heat extraction power decreased by 15.59%. Assuming that a geothermal field is influenced if the geotemperature decreases by more than 1℃, the average influence radius of the geothermal field was about 65 m. In addition, due to the differences in strata, the contour lines illustrating the drop and recovery of formation temperature around the geothermal well exhibited stepped changes at the interface of the strata. Strata with higher thermal conductivity of rocks corresponded to a greater distance of temperature disturbance near the interfaces of strata. The results of this study can be applied to the evaluation of the heat extraction and transfer capacities of moderately deep geothermal wells and also serve as a reference for the design of coaxial double-pipe heat transfer systems for moderately deep geothermal wells.
-
-
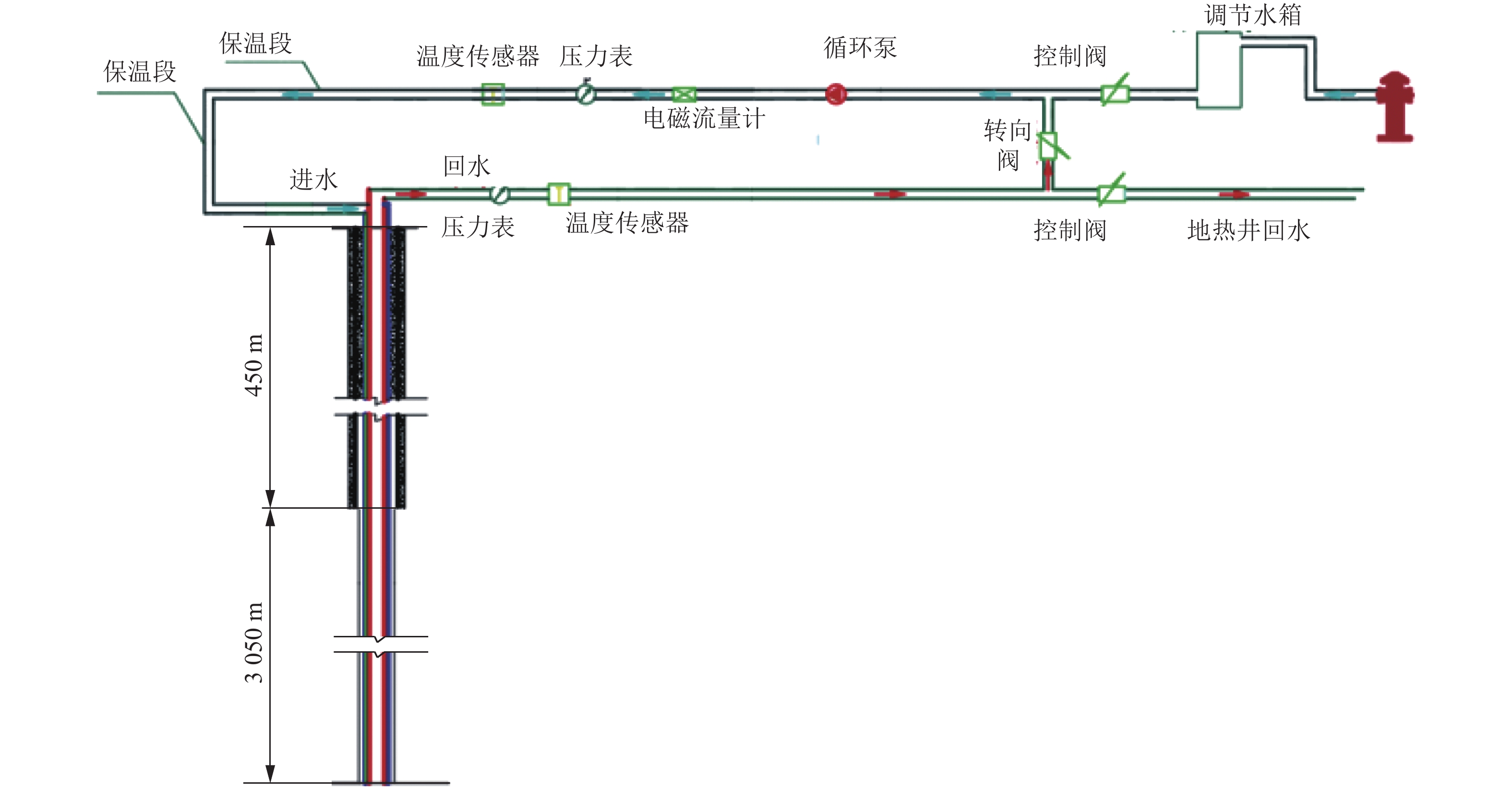
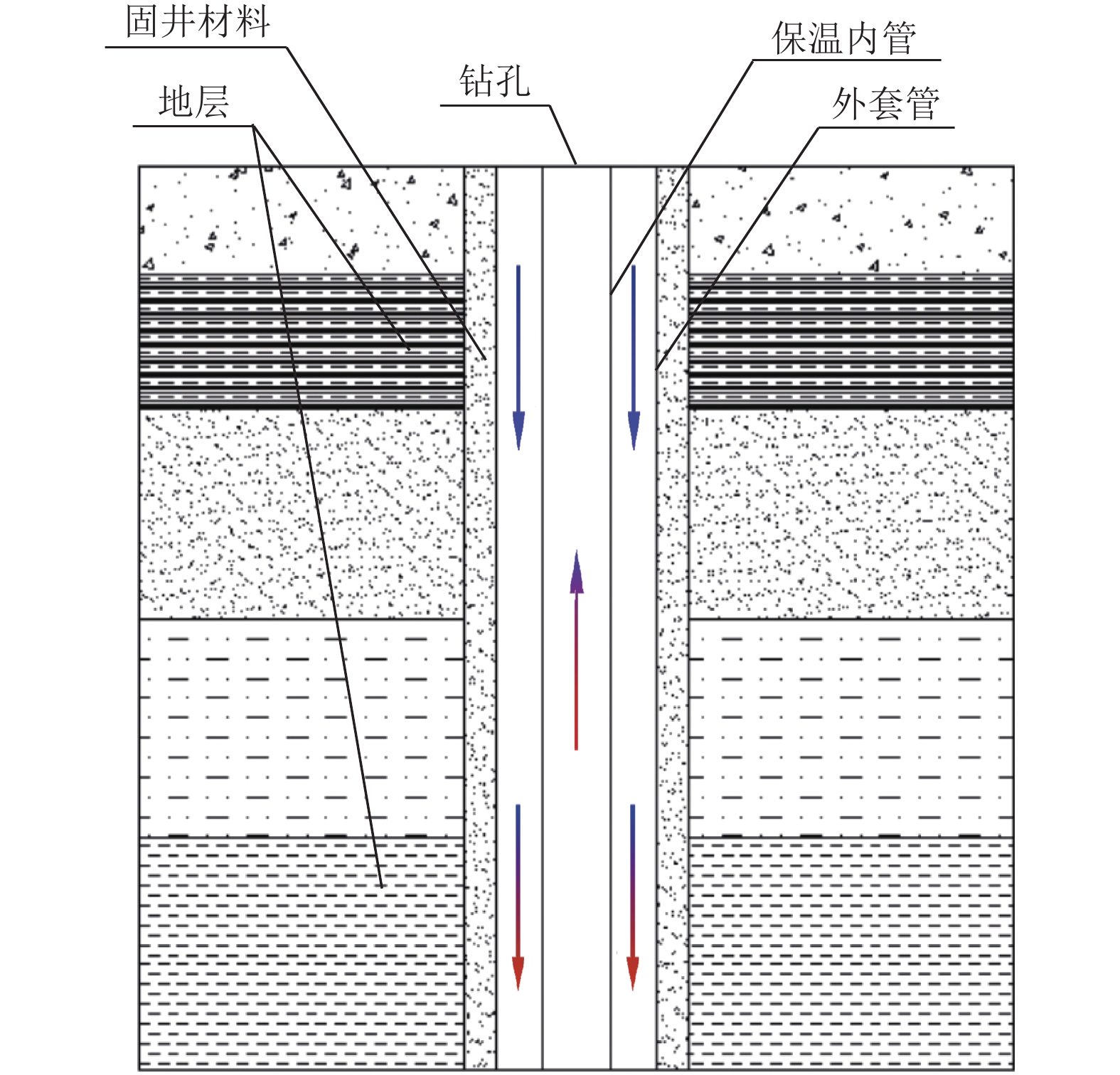
表 1 地热井井身结构设计
Table 1 Structural design of the casing program of a geothermal well
开钻次序 井段/m 钻头尺寸/
mm套管尺寸/
mm水泥返深/m 一开 0~450 374.7 273.1 0 二开 450~3500 241.3 177.8 0 表 2 套管式换热器分析的相关计算参数
Table 2 Calculation parameters for the analysis of the double-pipe heat exchanger
参数 数值 备注 钻孔直径/mm 241.3 内管直径/mm 114.3 外管直径/mm 177.8 内管厚度/mm 19.15 外管厚度/mm 9.19 外管导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 40 水的导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 0.63 水的比热容/(J·kg−1·K−1) 4.19×103 地层体积比热容/(MJ·m−3·K−1) 2.87×106 用于均质模型地层 地层导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 2.7 用于均质模型地层 水的密度/(kg·m−3) 996 表 3 分层模型地层参数
Table 3 Parameters of strata in the layered model
地层 深度范围/m 体积比热容/
(MJ·m−3·K−1)导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)秦川群 0~600.0 2.50 1.85 三门组 600.0~750.8 2.90 1.82 张家坡组 750.8~1 662.3 2.45 2.60 蓝田−灞河组 1 662.3~2 342.0 2.20 2.29 高陵群 2 342.0~3 500.0 2.30 2.22 表 4 现场试验参数
Table 4 Parameters of field tests
试验
类型实验
时间/d流量/
(m³·h−1)进水
温度/℃运行
方式备注 恒温恒流量 4 30 10 运行9 h
间歇15 h开式系统,
热水排出表 5 模拟方案
Table 5 Simulation schemes
方案
序号影响因素 备注 地热井
深度/m地温梯度/
(℃·m−1)地层导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)循环水流量/
(m³·h−1)固井水泥导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)内管导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)进水温度/℃ 1 2000、2500
3000、35000.02、0.03
0.04、0.052.70 30 1.8 0.02 10 2 3500 0.034 3.20 30 1.8 0.02、0.18
0.30、0.5010 3 3500 0.034 3.20 10、20、30、
40、501.8 0.02、0.18
0.30、0.5010 4 3500 0.034 0.83、1.30、
1.80、2.70、3.9830 0.4~4.0 0.02 10 固井水泥导热系数
每隔0.4 W/(m·K)设置
1个导热系数5 3500 0.034 3.20 10、20、30
40、501.8 0.02 5、7
10、12、156 2500×
(60%~160%)0.034×
(60%~160%)3.20×
(60%~160%)25×
(60%~160%)1.8×
(60%~160%)0.02×
(60%~160%)10×
(60%~160%)60%~160%变化率之间
每隔20%设置1个参数7 3500 0.034 30 1.8 0.02 5 地层导热系数见表2 -
[1] 蔺文静,刘志明,王婉丽,等. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质,2013,40(1):312−321. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021 LIN Wenjing,LIU Zhiming,WANG Wanli,et al. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China,2013,40(1):312−321. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
[2] 王贵玲,蔺文静,张薇. 我国主要城市浅层地温能利用潜力评价[J]. 建筑科学,2012,28(10):1−3. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8528.2012.10.001 WANG Guiling,LIN Wenjing,ZHANG Wei. Evaluation on utilization potential of shallow geothermal energy in major cities of China[J]. Building Science,2012,28(10):1−3. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8528.2012.10.001
[3] 国家发展改革委,国家能源局. 关于印发《“十四五”现代能源体系规划》的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-01-29) [2024-01-16]. http://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn.2022-01-29. [4] 国家能源局,科学技术部. 关于印发《“十四五”能源领域科技创新规划》的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-04-03) [2024-01-16]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1729337318997483867&;wfr=spider&for=pc. [5] 工业和信息化部. 关于印发《“十四五”工业绿色发展规划》的通知[EB/OL]. (2021-12-03) [2024-01-16]. https://www.miit.gov.cn/cms_files/filemanager/1226211233/attach/ 20224/99a5c254cd5a45c9896b0cb0b675ed03.pdf. [6] 国家发展改革委,国家能源局,财政部,等. 关于印发《“十四五”可再生能源发展规划》的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-06-01) [2024-01-16]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202206/t20220601_1326720.html. [7] 国务院. 关于印发《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》的通知[EB/OL]. (2021-10-26) [2024-01-16]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021–10/26/content_5644984.htm. [8] 王贵玲,刘彦广,朱喜,等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):1−9. WANG Guiling,LIU Yanguang,ZHU Xi,et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):1−9.
[9] 孔彦龙,陈超凡,邵亥冰,等. 深井换热技术原理及其换热量评估[J]. 地球物理学报,2017,60(12):4741−4752. DOI: 10.6038/cjg20171216 KONG Yanlong,CHEN Chaofan,SHAO Haibing,et al. Principle and capacity quantification of deep–borehole heat exchangers[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2017,60(12):4741−4752. DOI: 10.6038/cjg20171216
[10] HEPBASLI A,CANAKCI C. Geothermal district heating applications in Turkey:A case study of Izmir–Balcova[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2003,44(8):1285−1301. DOI: 10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00121-8
[11] 尚宏波,赵春虎,靳德武,等. 中深层地热单井换热数值计算[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(6):159−166. SHANG Hongbo,ZHAO Chunhu,JIN Dewu,et al. Numerical calculation of heat transfer in single medium–deep geothermal well[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(6):159−166.
[12] ABDELHAFIZ M M,OPPELT J,MAHMOUD O,HEGELE L A. Effect of drilling and wellbore geometry parameters on wellbore temperature profile: Implications for geothermal production[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2023,8(3):170−180.
[13] 鲍玲玲,徐豹,王子勇,等. 中深层同轴套管式地埋管换热器传热性能分析[J]. 地球物理学进展,2020,35(4):1217−1222. DOI: 10.6038/pg2020DD0335 BAO Lingling,XU Bao,WANG Ziyong,et al. Heat transfer performance analysis of the middle–deep coaxial casing ground heat exchanger[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2020,35(4):1217−1222. DOI: 10.6038/pg2020DD0335
[14] 吴晅,梁思源,郑明杰,等. 套管式地埋管换热器传热特性数值模拟[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2020,34(12):226−236. WU Xuan,LIANG Siyuan,ZHENG Mingjie,et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer characteristics of vertical double–pipe ground heat exchanger[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science),2020,34(12):226−236.
[15] 张东海. 分层和渗流条件下竖直地埋管换热器传热特性研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. ZHANG Donghai. Investigation on heat transfer behavior of vertical ground heat exchangers in a layered subsurface in the presence of groundwater advection[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining & Technology,2020.
[16] DU Dingshan,LI Yongqiang,WANG Kaipeng,et al. Experimental and numerical simulation research on heat transfer performance of coaxial casing heat exchanger in 3500 m–deep geothermal well in Weihe Basin[J]. Geothermics,2023,109:102658. DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2023.102658
[17] BEIER R A,ACUNA J,MOGENSEN P,et al. Transient heat transfer in a coaxial borehole heat exchanger[J]. Geothermics,2014,51:470−482. DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.02.006
[18] 付必伟,孙琳,张思. 同轴套管式深井换热器的换热性能分析[J]. 液压与气动,2021,45(10):95−103. DOI: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.10.014 FU Biwei,SUN Lin,ZHANG Si. Analysis of heat exchange performance of coaxial casing deep well heat exchanger[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics,2021,45(10):95−103. DOI: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.10.014
[19] 李奉翠,韩二帅,梁磊,等. 中深层地热井下同轴换热器长期换热性能研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):194−201. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.024 LI Fengcui,HAN Ershuai,LIANG Lei,et al. Long–term heat transfer performance of underground coaxial heat exchanger for medium–deep geothermal[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(2):194−201. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.024
[20] 刘俊,王沣浩,张育平,等. 中深层套管式换热器沿程传热与设计参数研究[J]. 工程热物理学报,2022,43(10):2770−2781. LIU Jun,WANG Fenghao,ZHANG Yuping,et al. Analysis on heat transfer along the pipe and design parameter significance of medium–deep coaxial heat exchanger[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2022,43(10):2770−2781.
[21] 沈浩. 关中地区中深层地热地埋管分层换热特性分析及试验研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2022. SHEN Hao. Analysis and experimental study on stratified heat transfer characteristics of medium–deep geothermal buried pipes in Guanzhong area[D]. Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2022.
[22] 唐晓音,程璐瑶,许威,等. 西安地区中深层套管式地埋管换热性能数值模拟[J]. 地质科学,2021,56(3):985−999. DOI: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.051 TANG Xiaoyin,CHENG Luyao,XU Wei,et al. Numerical study on factors that influence the heat transfer performance of mid–deep coaxial casing heat exchanger in the Xi’an area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2021,56(3):985−999. DOI: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.051
[23] 刘少勇,刘铮,陈永安. 井群排布形式对中深层地埋管换热器性能的影响[J]. 电力勘测设计,2022(12):5−11. LIU Shaoyong,LIU Zheng,CHEN Yong’an. Effects of well group arrangement on heat transfer performance of medium deep borehole heat exchanger[J]. Electric Power Survey & Design,2022(12):5−11.
[24] 王泽生,颜爱斌,郭进京. 地下层状结构土体中埋管换热器的传热分析[J]. 太阳能学报,2009,30(2):188−192. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2009.02.010 WANG Zesheng,YAN Aibin,GUO Jinjing. Heat transfer analysis of underground heat exchangers in multi–soil beds[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2009,30(2):188−192. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2009.02.010
[25] 李泽锟. 基于岩土分层和地下水渗流的竖直地埋管换热器设计优化研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2021. LI Zekun. Study on optimization of vertical ground heat exchanger based on geotechnical stratification and groundwater seepage[D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology,2021.
[26] 任战利,刘润川,任文波,等. 渭河盆地地温场分布规律及其控制因素[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(7):1938−1949. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.003 REN Zhanli,LIU Runchuan,REN Wenbo,et al. Distribution of geothermal field and its controlling factors in the Weihe Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(7):1938−1949. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.003
[27] 刘润川,任战利,任文波,等. 渭河盆地西安凹陷地热田热储特征及开发方式[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(10):3456−3474. LIU Runchuan,REN Zhanli,REN Wenbo,et al. Thermal storage characteristics and development mode of geothermal field in Xi’an Sag of the Weihe Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(10):3456−3474.
[28] 陕西省地矿局第一水文队. 西安地热普查报告[R]. 西安:陕西省地矿局第一水文队,1996. [29] 杜丁山,赵永哲,胡振阳,等. 隔热内管对中深层地热井同轴换热器换热性能的影响[J]. 煤炭工程,2023,55(2):164−170. DU Dingshan,ZHAO Yongzhe,HU Zhenyang,et al. Effect of insulated inner tube on performance of coaxial heat exchanger in medium–deep geothermal well[J]. Coal Engineering,2023,55(2):164−170.
[30] 杨世铭,陶文铨. 传热学(第四版)[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2006. [31] 李永强,徐拴海,张卫东,等. 套管式地埋管换热器热短路及换热性能[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):183−188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.024 LI Yongqiang,XU Shuanhai,ZHANG Weidong,et al. Thermal short–circuiting and heat transfer performance of coaxial borehole heat exchanger[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):183−188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.024







 下载:
下载: