Mechanism of coal fine-bubble coupling in the unsaturated flow stage of coalbed methane drainage
-
摘要:
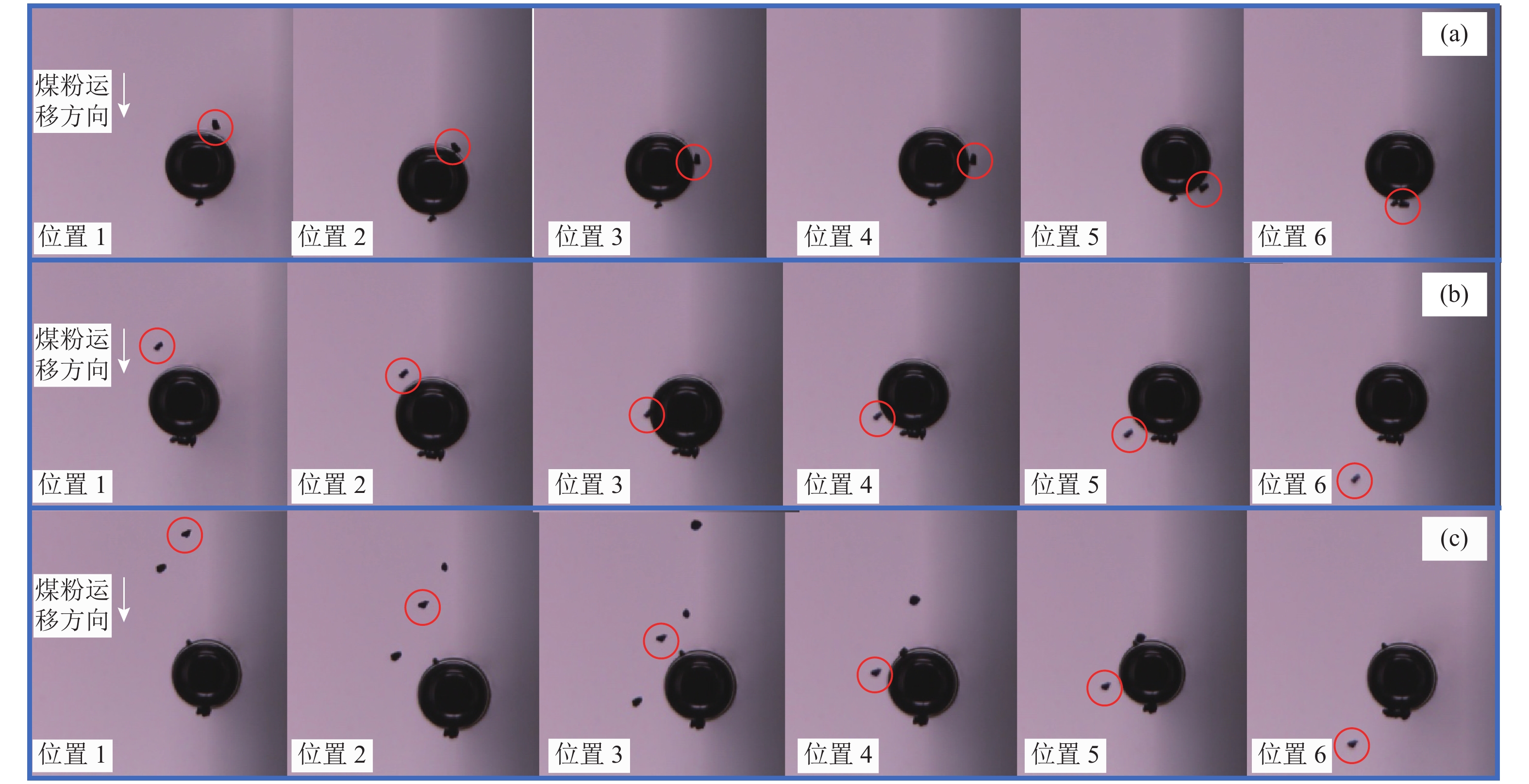
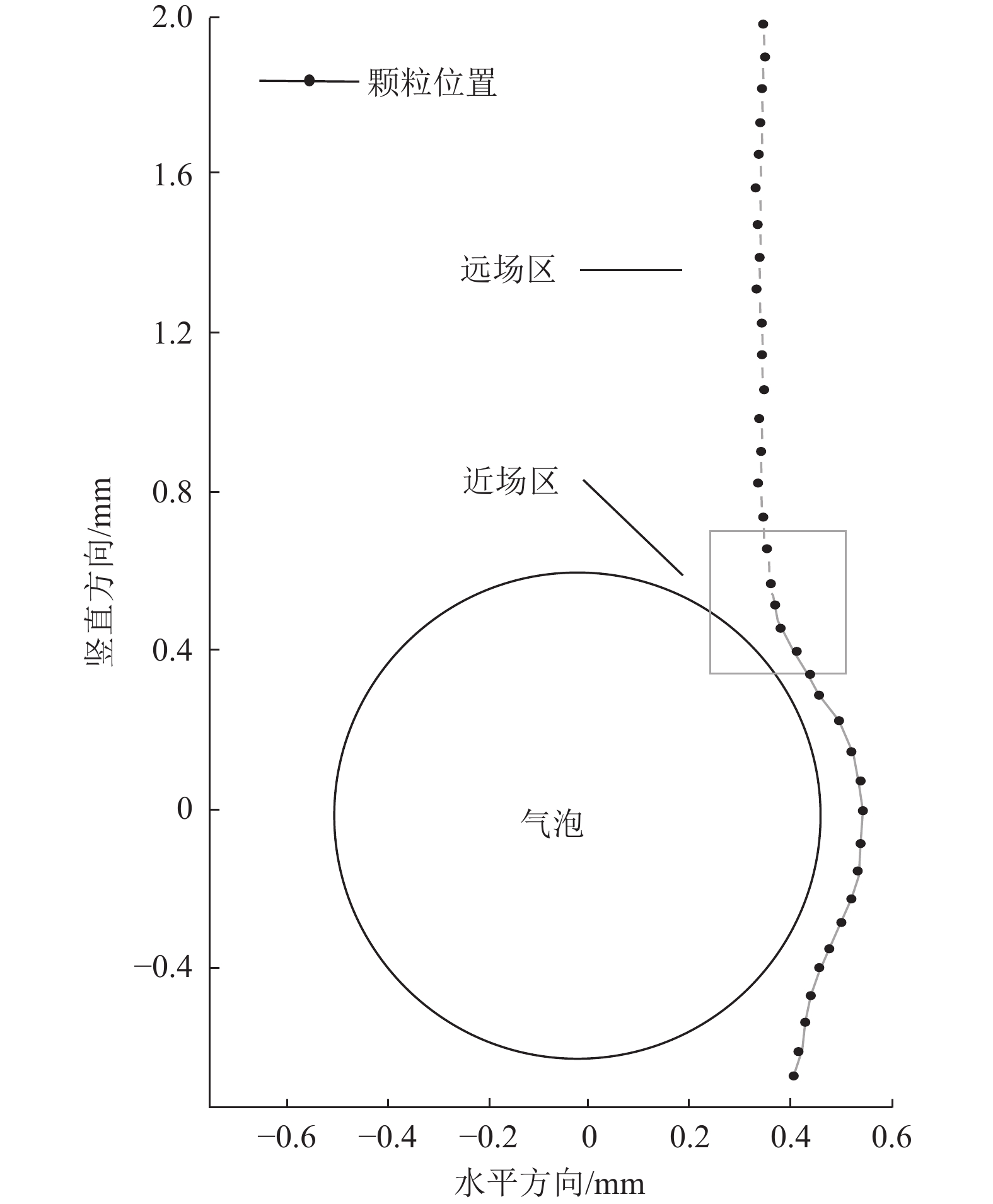
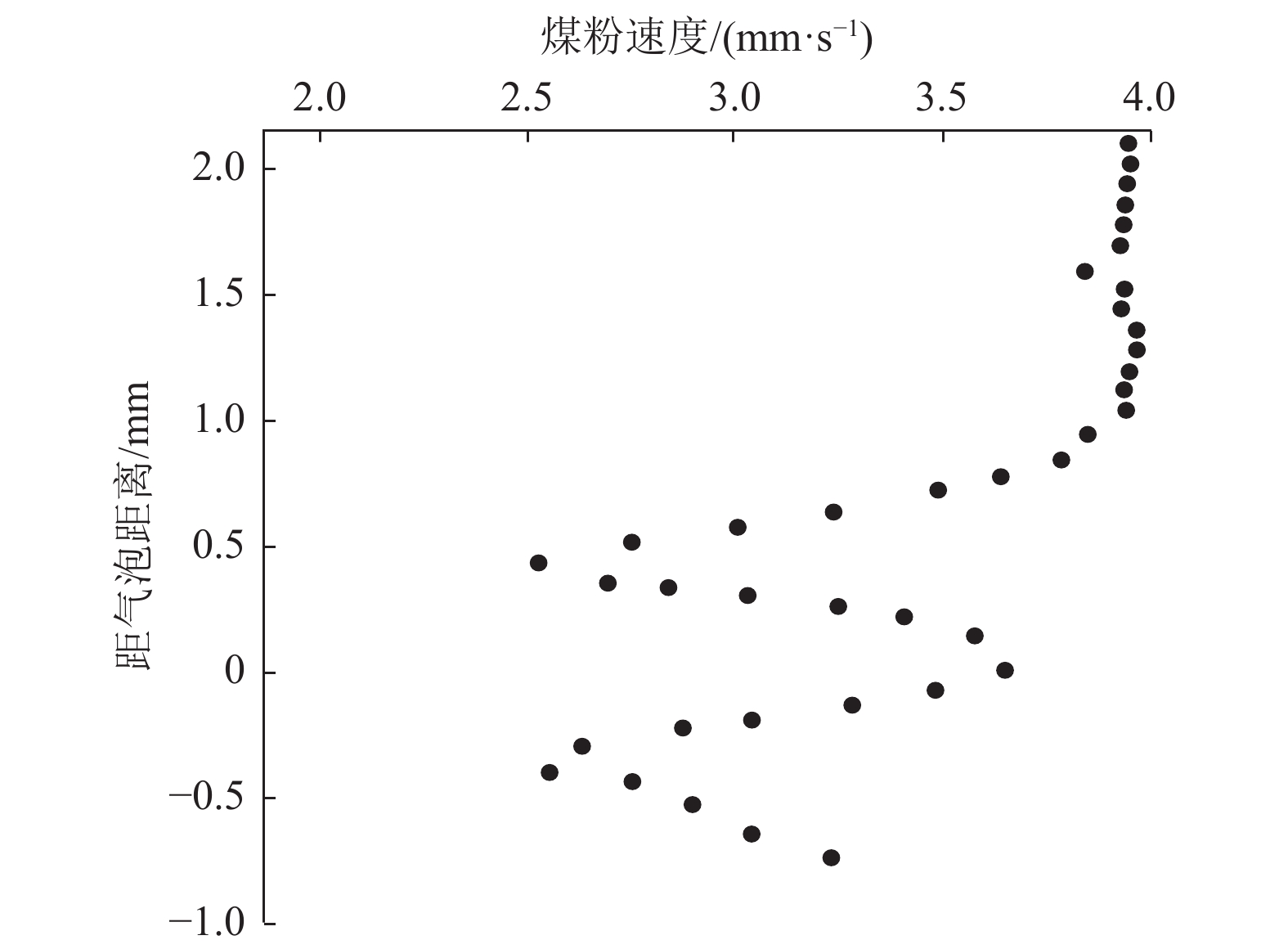
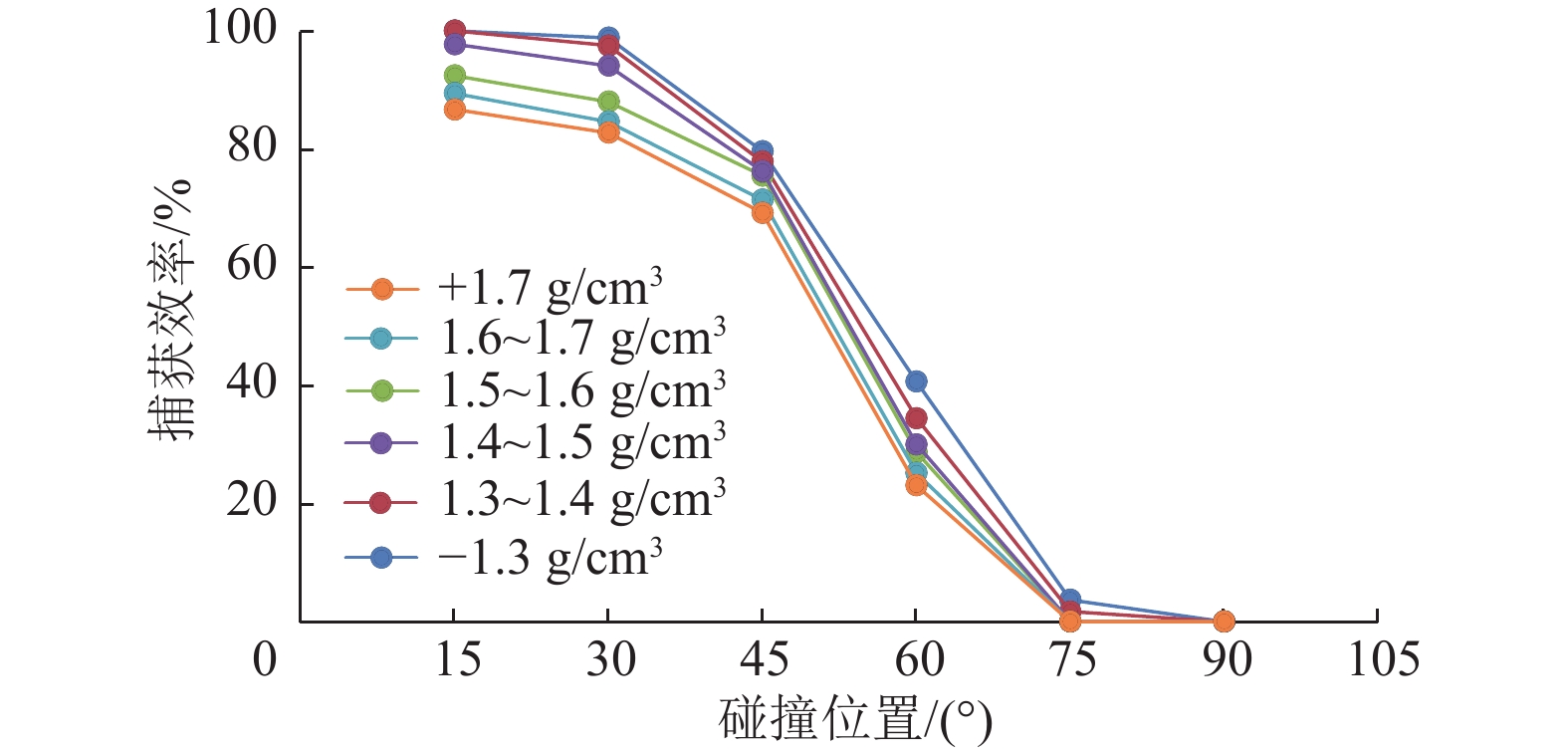
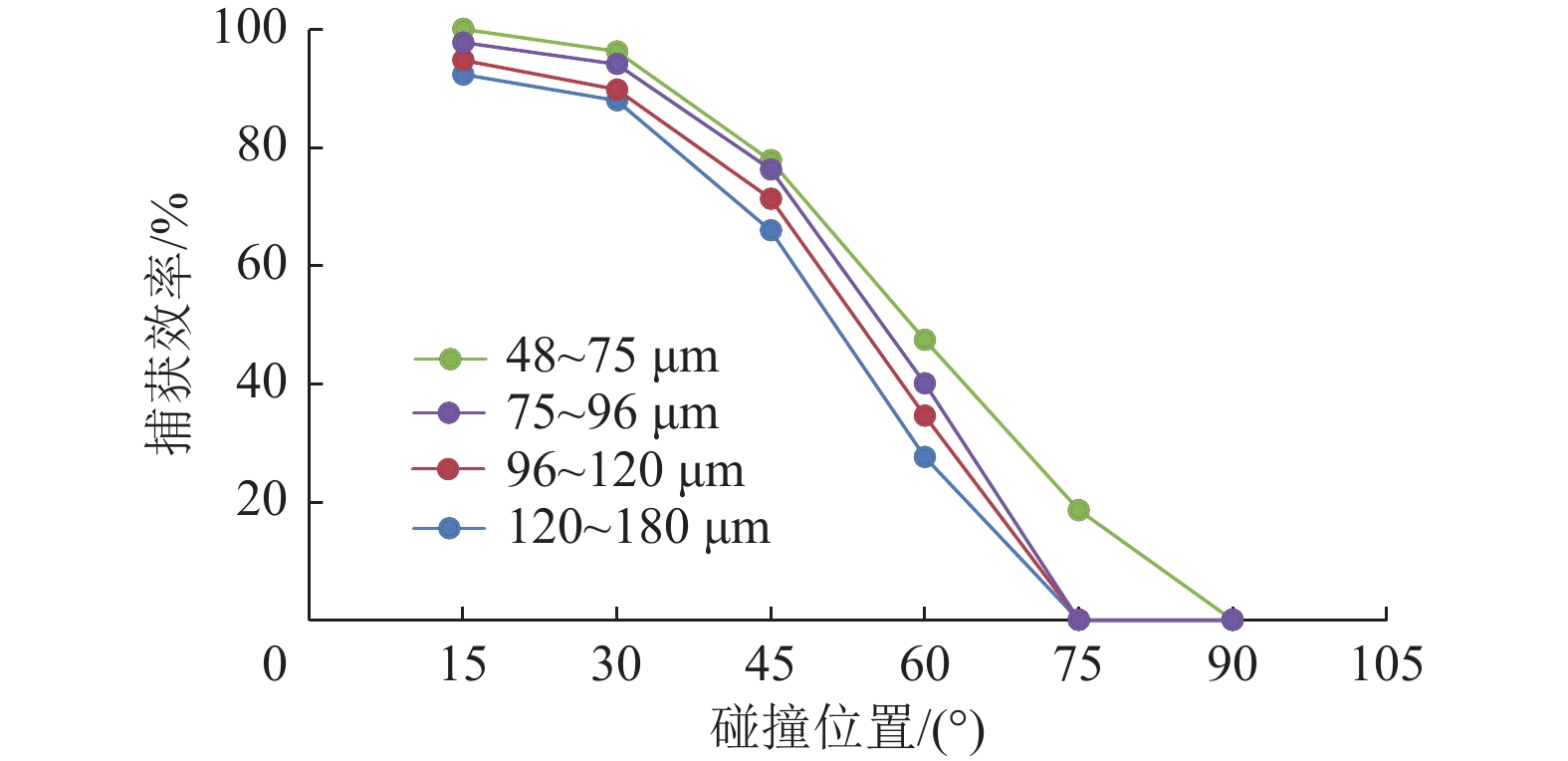
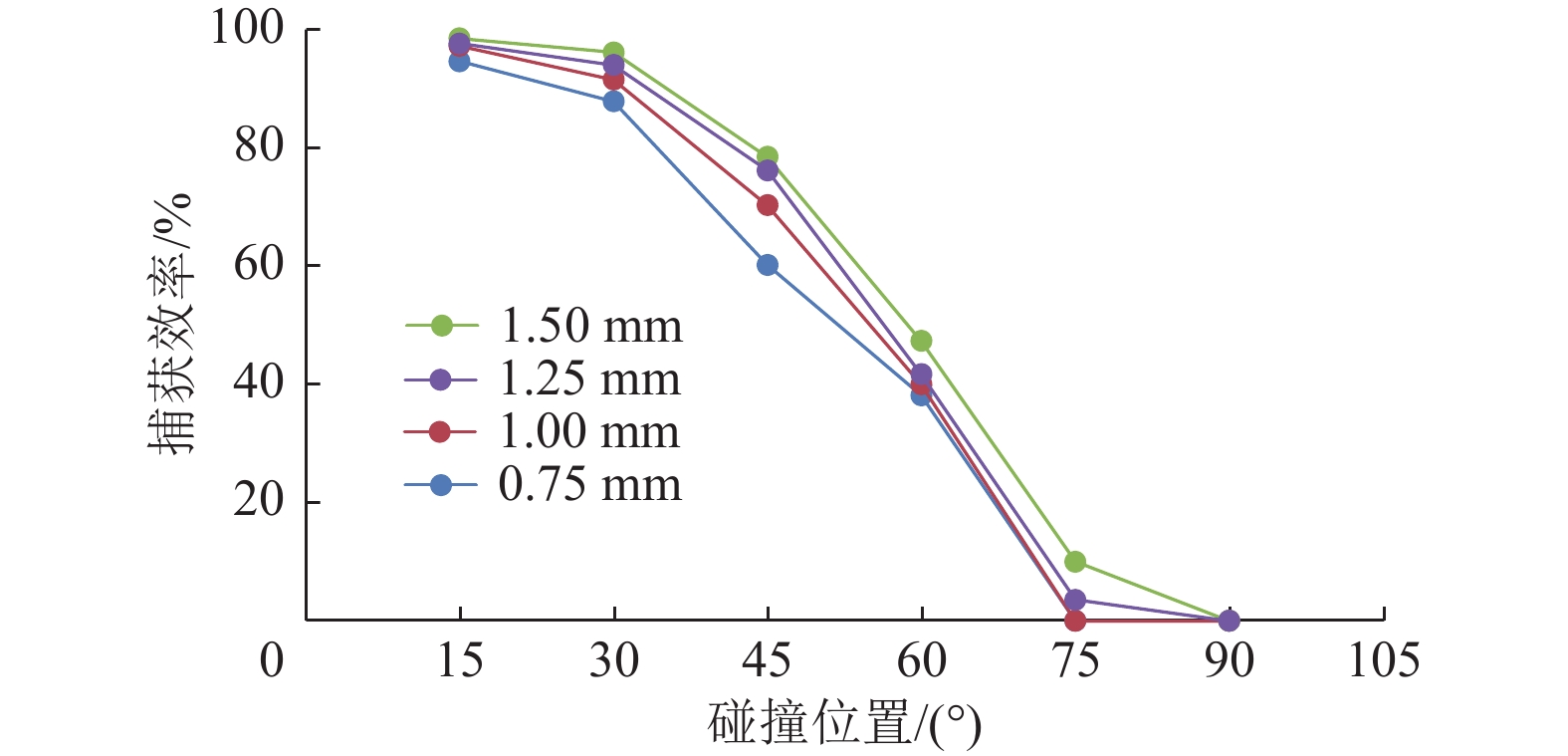
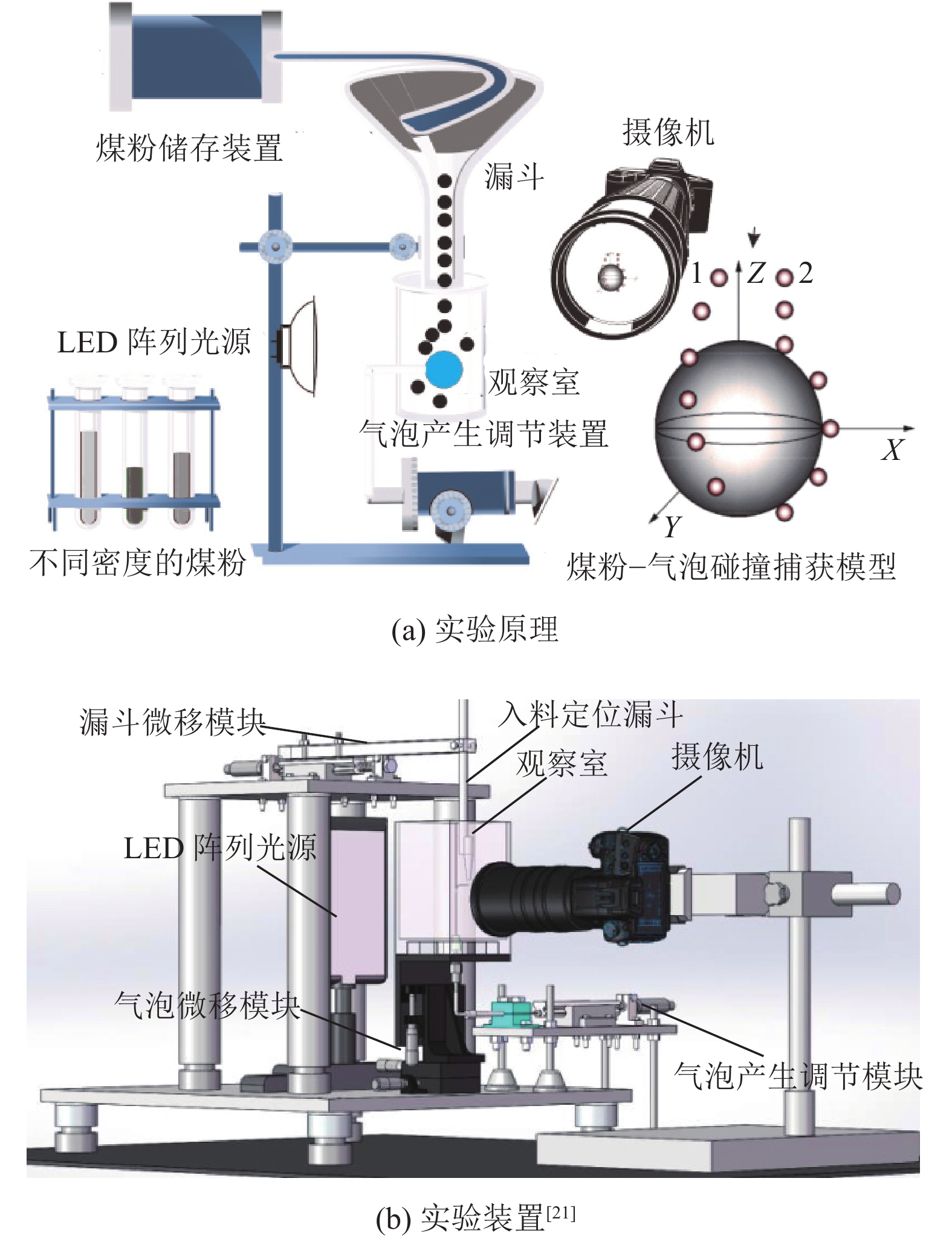
揭示煤层气排采储层非饱和流阶段煤粉与气体相互作用机理,对制定排采制度和提高产气量具有重要意义。通过气泡–煤粉微观作用实验装置,系统开展了不同直径大小的气泡对不同粒度和密度煤粉的作用实验,分析了气泡对煤粉运移轨迹和速度的影响及捕获煤粉特征。结果表明,气泡产出能够影响煤粉的运移轨迹,甚至能够捕获煤粉;煤粉通过气泡时会产生3种运动类型:沿着气泡表面运移到气泡底部最后被捕获、沿着气泡表面运移到气泡底部最后脱落及接近气泡时被排斥而轨迹发生偏转。煤粉若被气泡捕捉,则运动速度呈现出减小–增大–减小的变化特征;若未被气泡捕获,速度呈现出减小–增大–减小–增大的变化特征。不同条件下气泡对煤粉的捕获效率高达64.38%~86.64%;在气泡表面最高点附近发生碰撞煤粉被捕获的概率最大,并且随着偏离角度的增大,气泡捕获效率均呈现出逐渐减小的趋势;在相同的碰撞位置下,气泡对煤粉的捕获效率随着煤粉密度、煤粉粒径的增大而减小,随着气泡直径的增大而增大。煤层气产气初期应根据储层的实际导流能力合理控制降压速率,若储层导流能力较强,应加大排采速率,增大气体解吸对煤粉的扰动和捕获作用,促使大量煤粉随地下水或气泡产出;若储层导流能力较弱,应该适当降低排采速率,以防气体快速解吸而引起大量煤粉启动运移;同时,可应用大气泡携煤粉能力强的特性,促使近井地带的煤粉产出以增大储层导流能力。
Abstract:To reveal the mechanism of interaction between coal fines and gas in the unsaturated flow stage of coalbed methane (CBM) drainage, it is essential to formulate the drainage system and improve the gas production. The effect of air bubbles with different diameters on coal fines with different particle sizes and densities was systematically experimented through the experiment device for microscopic interaction between the air bubble and the coal fines. Meanwhile, the influence of air bubbles on the migration trajectory and velocity of coal fines and the characteristics of coal fine capturing by air bubbles were also analyzed. The results show that the production of air bubbles could affect the migration trajectory of coal fines, and even capture and carry coal fines. Typically, three types of motion are generated in the coal fines through the air bubbles: the coal fines may migrate along the surface of the air bubble to the bottom to be captured or fall off at last, or be repelled upon its approaching to the air bubble with the migration trajectory deflected. If the coal fines are captured by air bubbles, the velocity will decrease at first, then increase, and finally decrease. If the coal fines are not captured by air bubbles, the velocity will decrease at first, followed by increase and decrease successively, and increase finally. The capture efficiency of air bubbles to coal fines under different conditions ranges from 64.38% to 86.64%. The maximum capture probability occurs near the highest point of the bubble surface, and with the increase of the deviation angle, the capture efficiency of bubble shows a decreasing trend. At the same collision position, the capture efficiency of air bubbles on coal fines decreases with the increase of coal fines in density and particle size, but increases with the increase of bubble diameter. In the initial stage of CBM production, the depressurization rate should be reasonably controlled according to the actual conductivity of the reservoir. In case of large reservoir conductivity, the drainage rate should be increased to increase the disturbance and capture of gas desorption to coal fines, so that a large amount of coal fines will be produced with groundwater or air bubbles. In case of small reservoir conductivity, the drainage rate should be appropriately reduced to prevent the migration of a large amount of coal fines due to the rapid desorption of gas. At the same time, the production of coal fines in the near-wellbore area may be stimulated with the great carrying capability of air bubbles for coal fines, so as to increase the conductivity of the reservoir.
-
Keywords:
- coalbed methane /
- unsaturated flow /
- coal fine /
- bubble /
- migration
-
-
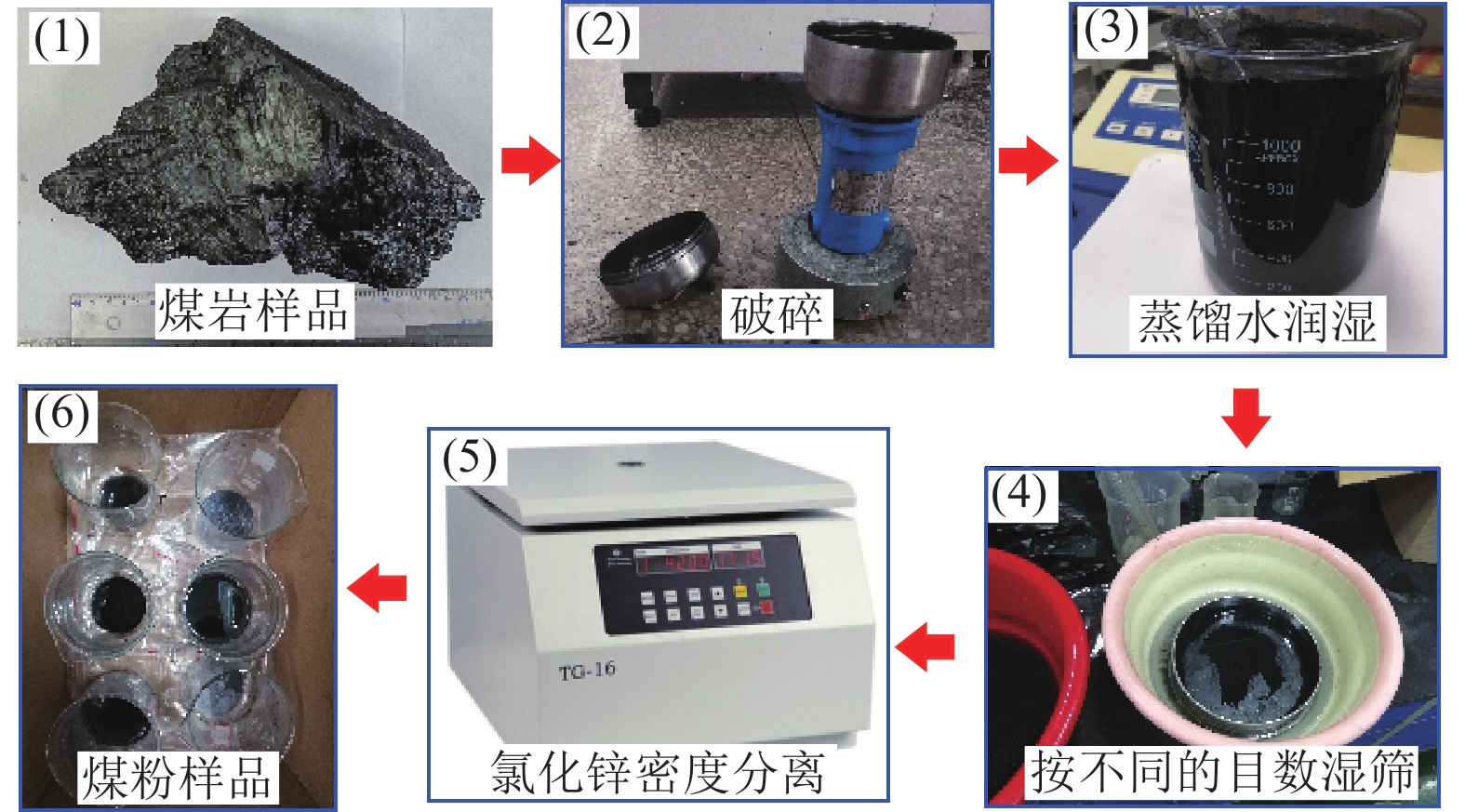
表 1 实验方案
Table 1 Experimental program
编号 煤粉粒径/μm 煤粉密度/(g·cm−3) 气泡直径/mm 1 75~96 −1.3,1.3~1.4,1.4~1.5,1.5~1.6,1.6~1.7,+1.7 1 2 120~180,96~120,48~75 1.4~1.5 1 3 75~96 1.4~1.5 0.75,1.25,1.50 -
[1] 朱庆忠,杨延辉,左银卿,等. 中国煤层气开发存在的问题及破解思路[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(4):96−100. ZHU Qingzhong,YANG Yanhui,ZUO Yinqing,et al. CBM development in China:Challenges and solutions[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(4):96−100.
[2] 刘岩,苏雪峰,张遂安. 煤粉对支撑裂缝导流能力的影响特征及其防控[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(3):687−693. LIU Yan,SU Xuefeng,ZHANG Sui’an. Influencing characteristics and control of coal powder to proppant fracture conductivity[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(3):687−693.
[3] 李勇,韩文龙,王延斌,等. 基于煤层气高效开发的煤粉凝聚–沉降机制研究进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):1−12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.001 LI Yong,HAN Wenlong,WANG Yanbin,et al. Progress of coal fines agglomeration and settlement mechanism based on high efficiency coalbed methane drainage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(2):1−12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.001
[4] 綦耀光,张芬娜,刘冰,等. 煤层气井产气通道内煤粉运动特征分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(9):1627−1633. QI Yaoguang,ZHANG Fenna,LIU Bing,et al. Calculation on discharge flow of pulverized coal in gas production channel for coalbed methane well[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(9):1627−1633.
[5] 刘升贵,涂坤,彭智高,等. 三交区块煤层气井煤粉产出动态规律及管控措施[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2016,35(8):785−790. DOI: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2016.08.001 LIU Shenggui,TU Kun,PENG Zhigao,et al. Pulverized coal output dynamic laws and control measures of CBM wells in Sanjiao Block[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science),2016,35(8):785−790. DOI: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2016.08.001
[6] 刘春花,刘新福,周超. 煤层气井排采过程中煤粉运移规律研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2015,43(5):23−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2015.05.006 LIU Chunhua,LIU Xinfu,ZHOU Chao. Migration patterns of coal powder in coal reservoirs during the well drainage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2015,43(5):23−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2015.05.006
[7] 魏迎春,张傲翔,王孝亮,等. 临汾区块煤层气井排采过程中煤粉产出规律[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2016,35(7):673−678. WEI Yingchun,ZHANG Aoxiang,WANG Xiaoliang,et al. Output laws of pulverized coal concentration during the CBM well drainage in Linfen Block[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science),2016,35(7):673−678.
[8] 韩文龙,王延斌,刘度,等. 煤层气直井产气曲线特征及其与储层条件匹配性[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(3):97−104. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.03.016 HAN Wenlong,WANG Yanbin,LIU Du,et al. The matching of gas production curve characteristic and reservoir conditions in vertical coalbed methane wells[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(3):97−104. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.03.016
[9] BAI Tianhang,CHEN Zhongwei,AMINOSSADATI S M,et al. Experimental investigation on the impact of coal fines generation and migration on coal permeability[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2017,159:257−266. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.09.035
[10] 刘岩,张遂安,曹立虎,等. 煤粉在支撑裂缝中的运移与沉积规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(7):1333−1337. LIU Yan,ZHANG Sui’an,CAO Lihu,et al. Rules of coal powder migration and deposition in the proppant fracture[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(7):1333−1337.
[11] 吴昊镪,彭小龙,朱苏阳,等. 煤层气井煤粉成因、运移和防控研究进展[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2020,10(4):70−80. WU Haoqiang,PENG Xiaolong,ZHU Suyang,et al. Research progress of coal fine formation,migration and control in CBM well[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development,2020,10(4):70−80.
[12] 刘泉声,崔先泽,张程远. 基于变孔隙率的多孔介质中悬浮颗粒沉积渗透率衰减模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(Sup.1):3308−3314. LIU Quansheng,CUI Xianze,ZHANG Chengyuan. Permeability reduction model of particles deposit in porous medium considering changeable porosity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(Sup.1):3308−3314.
[13] 胡胜勇,郝勇鑫,陈云波,等. 煤粉运移与沉积对支撑裂缝渗透率动态影响规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(4):1288−1296. HU Shengyong,HAO Yongxin,CHEN Yunbo,et al. Dynamic influence law of coal powder migration and deposition on propped fracture permeability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(4):1288−1296.
[14] HAN Wenlong,WANG Yanbin,FAN Jingjing,et al. An experimental study on coal fines migration during single phase water flow[J]. Geofluids,2020,2020:1−13.
[15] 曹代勇,姚征,李小明,等. 单相流驱替物理模拟实验的煤粉产出规律研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(4):624−628. CAO Daiyong,YAO Zheng,LI Xiaoming,et al. Rules of coal powder output under physical simulation experiments of single–phase water flow displacement[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(4):624−628.
[16] HAN Wenlong,WANG Yanbin,LI Yong,et al. Coal fines migration,deposition,and output simulation during drainage stage in coalbed methane production[J]. Energy & Fuels,2021,35:4901−4913.
[17] ZOU Yushi,ZHANG Shicheng,ZHANG J. Experimental method to simulate coal fines migration and coal fines aggregation prevention in the hydraulic fracture[J]. Transport in Porous Media,2014,101(1):17−34. DOI: 10.1007/s11242-013-0228-9
[18] 张傲翔. 煤岩润湿性对煤层气渗流的影响机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2021. ZHANG Aoxiang. Study of the influence mechanism of coal wettability on coalbed methane seepage[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2021.
[19] 韩文龙. 沁水盆地柿庄煤层气区块煤粉赋存及运移产出机制[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2021. HAN Wenlong. Occurrence and production mechanism of coal fines in coalbed methane wells of Shizhuang Block, Qinshui Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2021.
[20] 慕甜,马东民,陈跃,等. 煤层气井多相流条件下不同粒径煤粉启动–运移规律[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(5):188−196. MU Tian,MA Dongmin,CHEN Yue,et al. Start–migration law of coal powder with different particle sizes under multi–phase flow conditions in coalbed methane wells[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(5):188−196.
[21] ZHUO Qiming,LIU Wenli,XU Hongxiang,et al. The effect of collision angle on the collision and adhesion behavior of coal particles and bubbles[J]. Processes,2018,6(11):218. DOI: 10.3390/pr6110218
[22] 卓启明,刘文礼,刘伟,等. 煤颗粒与气泡黏附行为的试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(7):2029−2035. ZHUO Qiming,LIU Wenli,LIU Wei,et al. Experimental study on the attachment behavior of coal particles and bubbles[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(7):2029−2035.







 下载:
下载: