Characteristics of roof water hazard of coal seam in Huanglong Coalfield and key technologies for prevention and control
-
摘要:
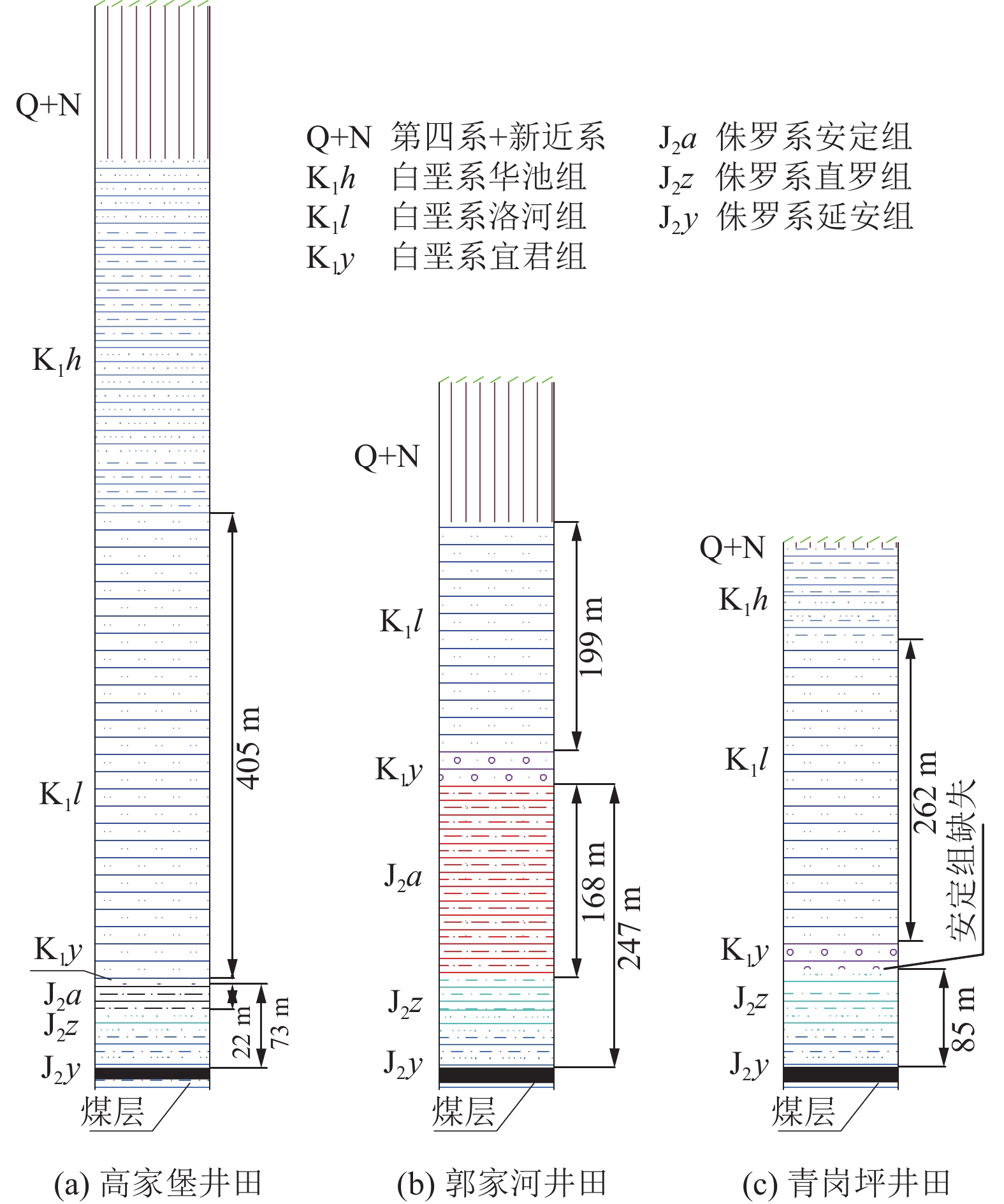
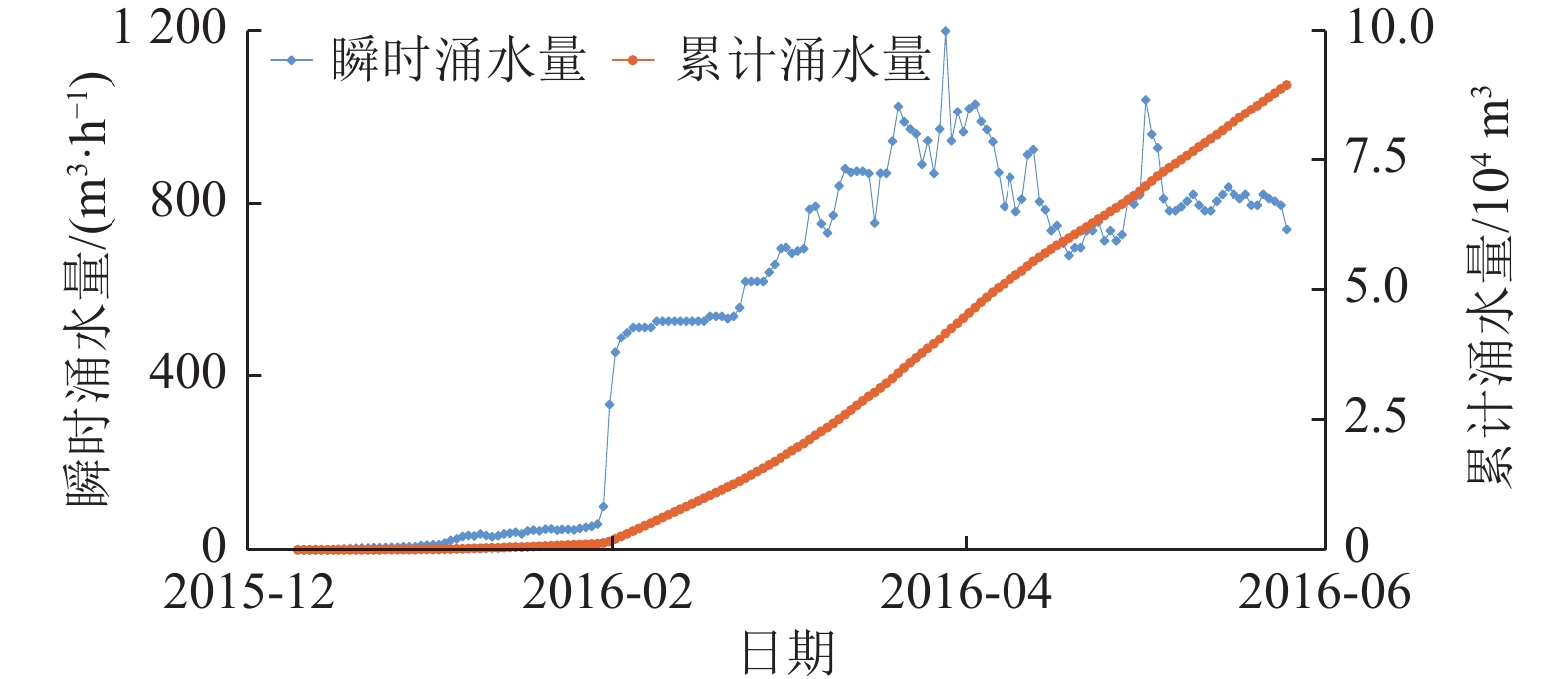
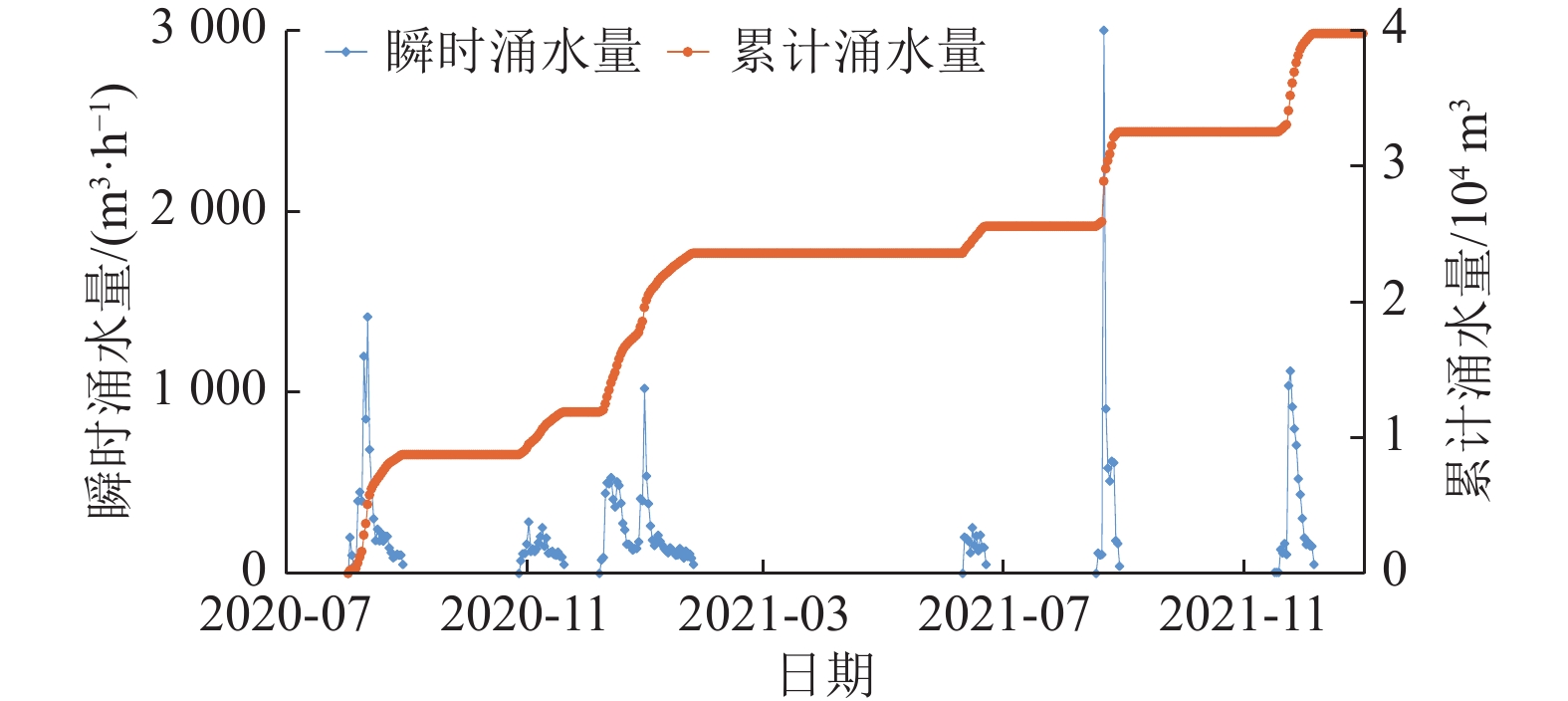
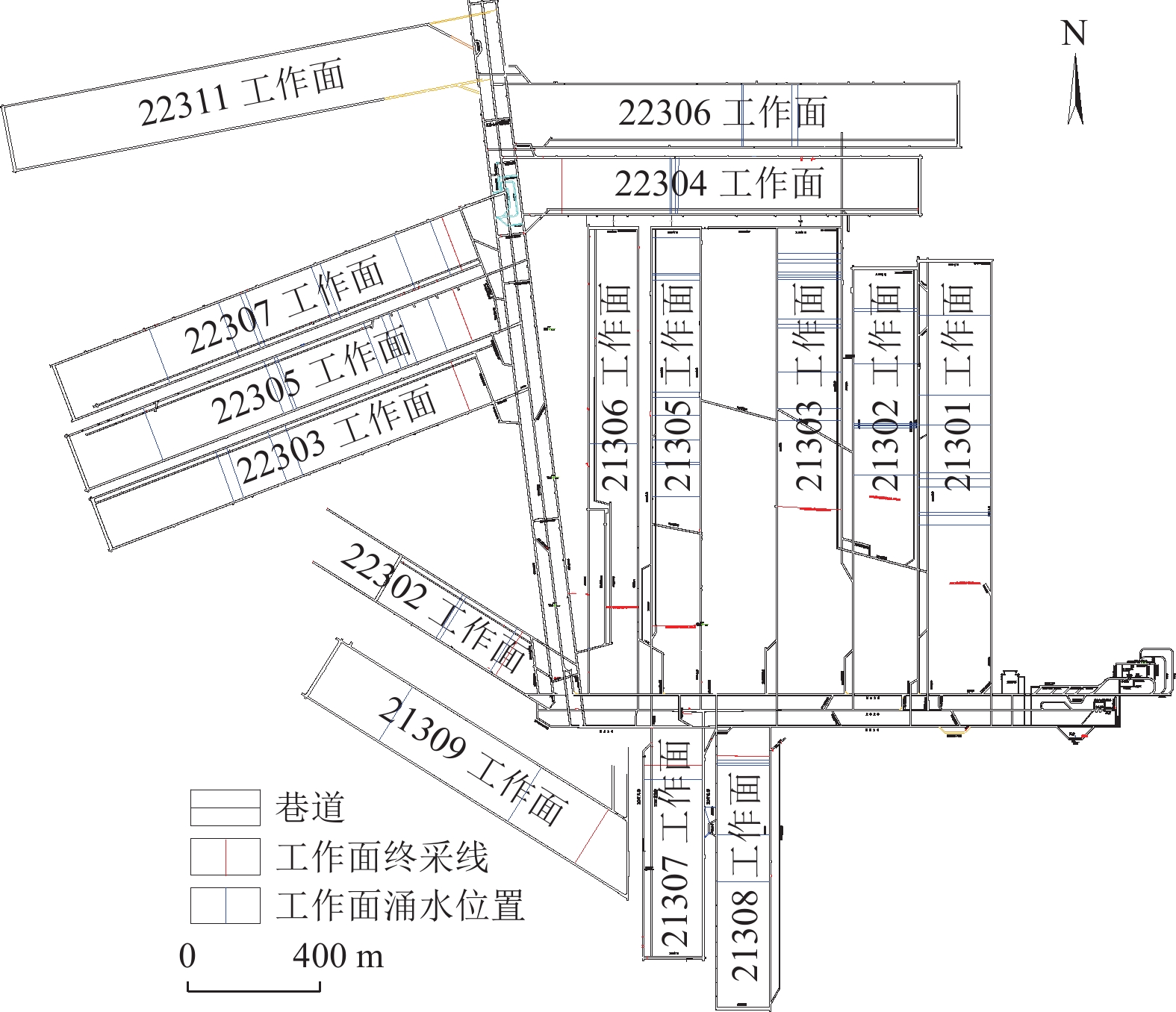
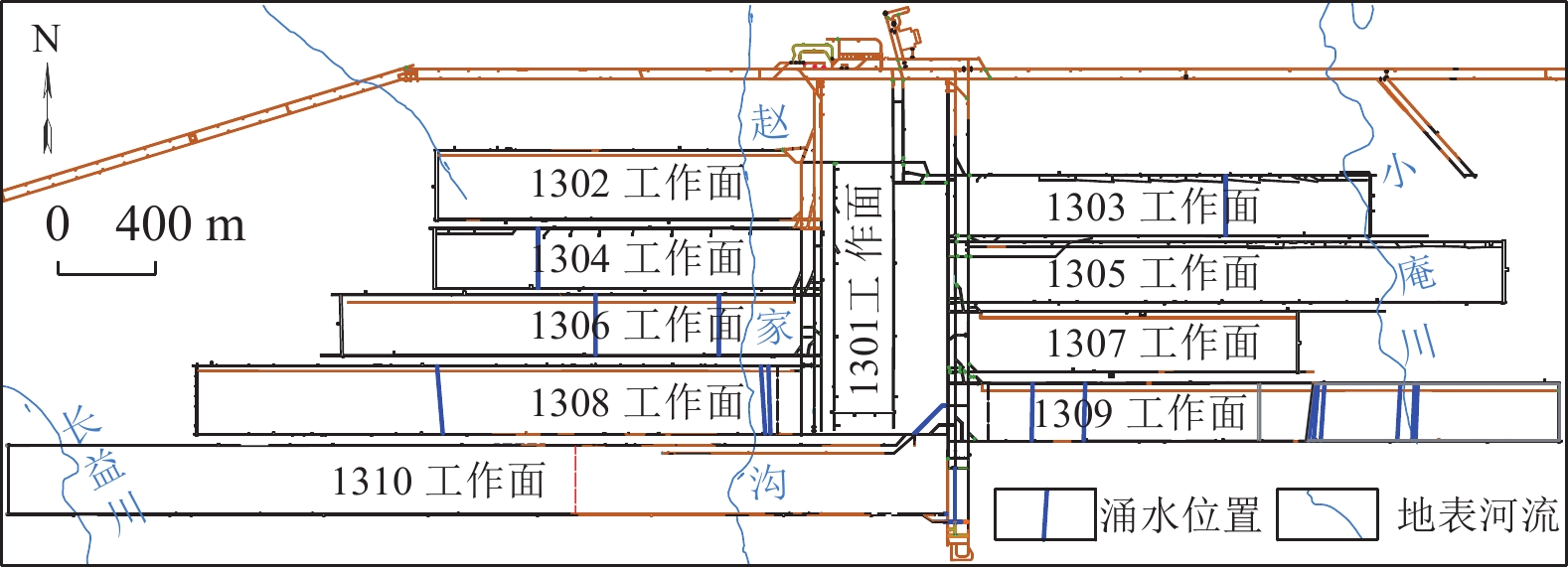
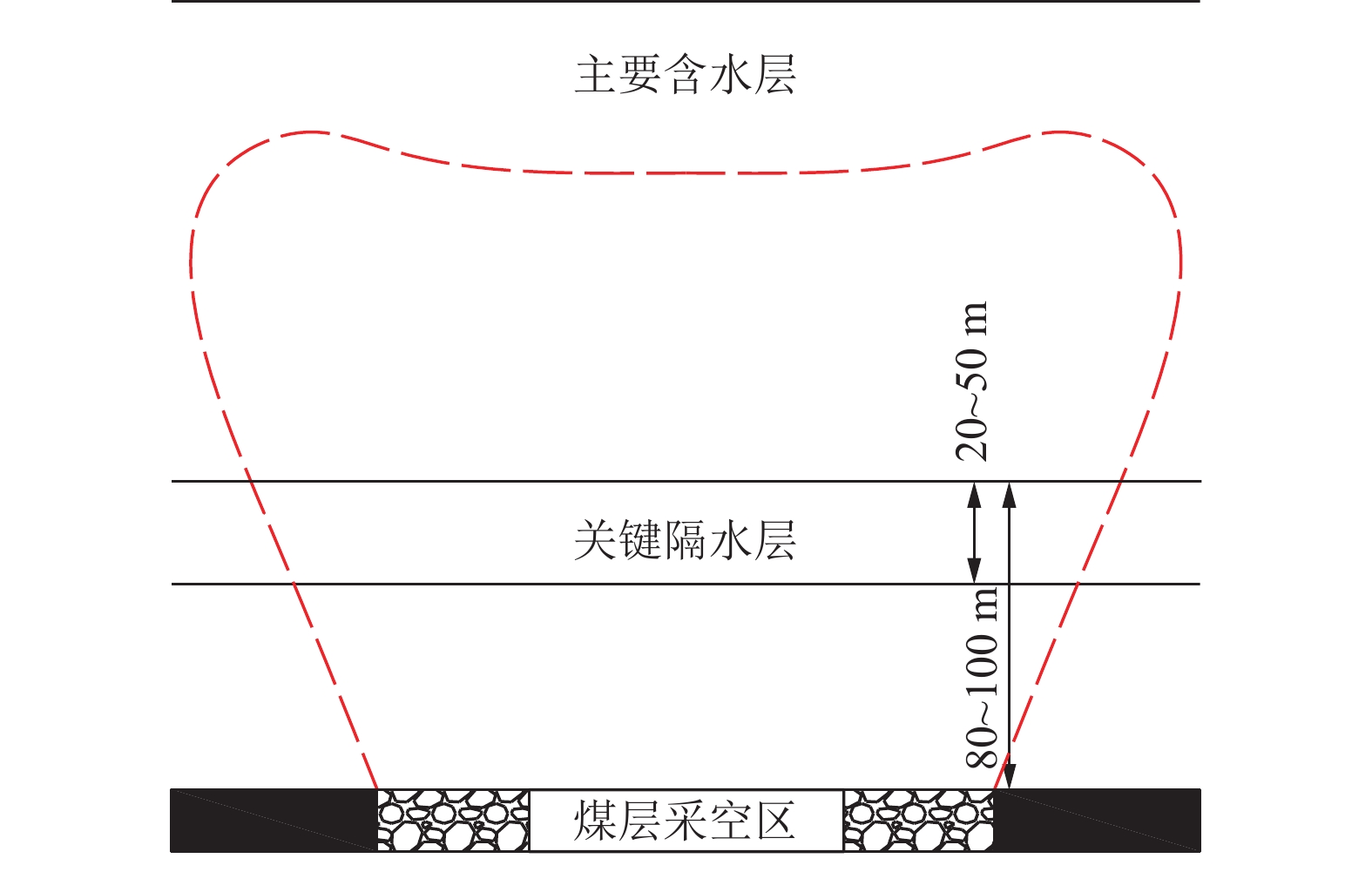
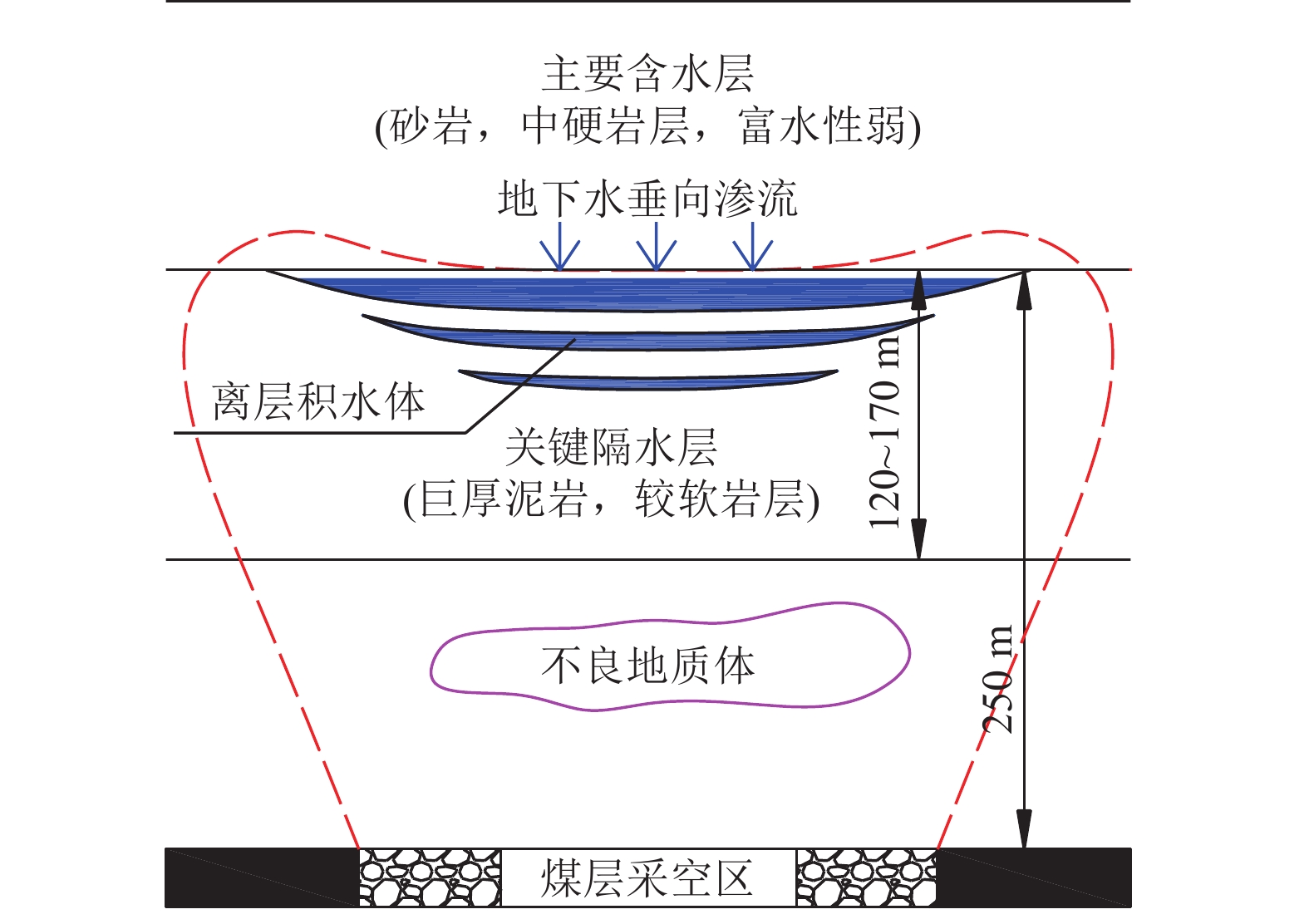
陕西黄陇煤田是我国主要产煤基地之一,煤层开采主要受顶板巨厚洛河组砂岩水威胁,水害防控形势严峻,分析顶板涌水特征、研究水害防控关键技术对于煤矿安全生产具有重大意义。在收集该区域典型煤矿工作面涌水量资料的基础上,分析顶板水害类型及其主控因素,总结工作面涌水量变化规律,并研究顶板巨厚砂岩含水层水害形成机理,进而提出顶板水害防控关键技术。结果表明:(1)黄陇煤田顶板含水层充水可分为持续涌水式、非持续涌水式和泥砂溃涌式3类,持续涌水式包括可控持续型和高强度持续型,非持续涌水式分为离层涌水型(包括偶发离层涌水型和频发离层涌水型)和脉冲式涌水型,以及泥砂溃涌型共6型。(2)关键隔水层厚度、煤层与洛河组砂岩间距、洛河组砂岩的富水性共同决定顶板涌水形式:当关键隔水层厚度较小甚至缺失,洛河组砂岩富水性弱且与煤层间距较小时,发生脉冲式涌水;当关键隔水层厚度较大且分布稳定,洛河组砂岩富水性中等至强且与煤层间距较小时发生持续涌水;当关键隔水层巨厚,洛河组砂岩富水性弱且与煤层间距巨大时发生离层涌水;当煤层顶板导水裂隙带范围内的侏罗系地层发育胶结不良地质体或煤层出现冒顶现象,容易形成水砂溃涌灾害。(3)地下水位监测预警技术、地面钻孔疏放离层积水技术、井下泄水巷集中排水技术、排水系统建设与维护技术、减水开采技术等是黄陇煤田水害防治的关键技术;工作面精细管理制度、工作面水情日分析制度、专家会诊及对标学习制度等是做好水害防治工作的配套管理对策。
Abstract:Huanglong Coalfield in Shaanxi is one of the main coal production bases in China. Coal mining is usually affected by the sandstone water of the thick Luohe Formation on the roof, resulting a significant difficulty in the prevention and control of water hazards. It is therefore of great importance to correctly analyze the characteristics of water inflow from the roof and successfully develop the key technologies for water hazard prevention and control, ensuring the safe production of coal mines. The types of roof water hazard and its main controlling factors were appropriately analyzed by collecting the information on water inflow at the working face of a typical coal mine. The variation of water inflow in the working face was identified. The formation mechanism of water hazard in the thick sandstone aquifer of the roof was then studied, and the key technologies were developed for the prevention and control of water hazard on the roof. The results show that: (1) Water filling in the roof aquifer of Huanglong Coalfield can be divided into 3 categories (the continuous water inflow, discontinuous water inflow and mud-sand burst) consisting of 6 types. Definitely, the continuous water inflow contains the controllable continuous type and the high-intensity continuous type. The discontinuous water inflow involves the separated layer water inflow (including the occasional and frequent types) and the pulsed water inflow. Besides, the mud-sand burst type is also included. (2) The form of water inflow in the roof is dependent on the thickness of the key aquiclude, the distance between the coal seam and the sandstone of Luohe Formation, and the water abundance of sandstone in Luohe Formation. Specifically, pulsed water inflow is likely to occur under the conditions of thin or little key aquiclude, weak water abundance of sandstone in Luohe Formation and small distance between sandstone and coal seam. Continuous water inflow will occur when the controlling conditions are thick key aquiclude that is distributed stably, medium to strong water abundance of sandstone in Luohe Formation and small distance between sandstone and coal seam. Separated layer water inflow will occur at a coalfield with very thick key aquiclude, weak water abundance of sandstone in Luohe Formation and very large distance between sandstone and coal seam. In addition, it is prone to form water-sand burst in case that poorly cemented geological bodies were developed in the Jurassic strata within the water-conducting fracture zone of the coal seam roof or roof fall appears in coal seams. (3) Successful water hazard prevention and control in Huanglong Coalfield needs the key techniques for monitoring and early warning of the groundwater level, separated layer water drainage by surface drilling, centralized water drainage through underground drainage tunnel, construction and maintenance of drainage systems, water-reducing mining, etc. In addition, the supporting management counter-measures for water hazard prevention and control include the fine management system of working face, daily analysis system of working face water situation, expert consultation, benchmarking learning system and so forth.
-
-
表 1 高家堡井田三、四盘区洛河组垂向水文地质特征
Table 1 Vertical hydrogeological characteristics of Luohe Formation in the third and fourth panels of Gaojiabao mine field
含水层段 厚度/m
(最小~
最大值/平均值)岩性 水文地质参数 地下水位
/m富水性 备注 渗透系数/
(m·d−1)涌水量/
(L·s−1·m−1)上段 14.38~106.08
/51.09泥岩类、细粒砂岩以及中粒砂岩 0.071 5 0.021 0 827.037 弱 弱含水层段 中上段 106.05~143.88
/125.53中粒砂岩、细粒砂岩、粗粒砂岩以及泥岩类 0.671 2~0.789 9 0.018 5~0.516 4 727.991~820.447 弱至
中等最主要含水层段 中下段 97.97~151.22
/124.84中粒砂岩、细粒砂岩、粗粒砂岩以及泥岩类 0.126 4~0.239 1 0.020 6~0.184 7 705.751~817.207 弱至
中等主要含水层段 下段 57.60~91.19
/79.51泥岩类、细粒砂岩、中粒砂岩以及粗粒砂岩 0.005 8~0.010 2 0.001 0~0.005 8 696.611~802.515 弱 弱含水层段 -
[1] 武强,崔芳鹏,赵苏启,等. 矿井水害类型划分及主要特征分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(4):561−565. WU Qiang,CUI Fangpeng,ZHAO Suqi,et al. Type classification and main characteristics of mine water disasters[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(4):561−565.
[2] 虎维岳,赵春虎. 基于充水要素的矿井水害类型三线图划分方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(5):1−8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.001 HU Weiyue,ZHAO Chunhu. Trilinear chart classification method of mine water hazard type based on factors of water recharge[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(5):1−8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.001
[3] 董书宁,姬亚东,王皓,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪煤田典型顶板水害防控技术与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2367−2375. DONG Shuning,JI Yadong,WANG Hao,et al. Prevention and control technology and application of roof water disaster in Jurassic coal field of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2367−2375.
[4] 李超峰. 煤层顶板含水层涌水危险性评价方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(增刊1):384−392. LI Chaofeng. Method for evaluating the possibility of water inrush from coal seam roof aquifer[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(Sup.1):384−392.
[5] 武强,许珂,张维. 再论煤层顶板涌(突)水危险性预测评价的“三图–双预测法”[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(6):1341−1347. WU Qiang,XU Ke,ZHANG Wei. Further research on“three maps–two predictions”method for prediction on coal seam roof water bursting risk[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(6):1341−1347.
[6] 曹海东. 煤层顶板次生离层水体透水机理及防治技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(6):90−95. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.06.015 CAO Haidong. Mechanism and control technology of water inrush from secondary separated bed on coal seam roof[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2017,45(6):90−95. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.06.015
[7] 乔伟,李文平,李小琴. 采场顶板离层水“静水压涌突水”机理及防治[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2011,28(1):96−104. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2011.01.019 QIAO Wei,LI Wenping,LI Xiaoqin. Mechanism of“hydrostatic water–inrush”and countermeasures for water inrush in roof bed separation of a mining face[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2011,28(1):96−104. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2011.01.019
[8] 郭小铭,董书宁,刘英锋,等. 深埋煤层开采顶板泥砂溃涌灾害形成机理[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(5):889−897. GUO Xiaoming,DONG Shuning,LIU Yingfeng,et al. Formation mechanism of mud and sand inrush disaster during the mining of deep–buried coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2019,36(5):889−897.
[9] 李文平,朱厅恩,王启庆,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地巨厚白垩系下煤层开采突泥溃砂物源及成灾模式[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):360−370. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.yg21.1859 LI Wenping,ZHU Ting’ en,WANG Qiqing,et al. Material source and disaster model of mud–sand inrush in coal mining under extremely thick Cretaceous in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):360−370. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.yg21.1859
[10] 靳德武,刘英锋,王甜甜. 巨厚砂岩含水层下厚煤层综放减水开采技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(9):88−95. JIN Dewu,LIU Yingfeng,WANG Tiantian. Water−reducing mining technology for fully–mechanized top–coal caving mining in thick coal seams under ultra–thick sandstone aquifer[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(9):88−95.
[11] 尹尚先,徐斌,徐慧,等. 综采条件下煤层顶板导水裂缝带高度计算研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2013,41(9):138−142. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2013.09.032 YIN Shangxian,XU Bin,XU Hui,et al. Study on height calculation of water conducted fractured zone caused by fully mechanized mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2013,41(9):138−142. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2013.09.032
[12] 许延春,李俊成,刘世奇,等. 综放开采覆岩“两带”高度的计算公式及适用性分析[J]. 煤矿开采,2011,16(2):4−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2011.02.002 XU Yanchun,LI Juncheng,LIU Shiqi,et al. Calculation formula of“two–zone”height of overlying strata and its adaptability analysis[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2011,16(2):4−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2011.02.002
[13] 张玉军,申晨辉,张志巍,等. 我国厚及特厚煤层高强度开采导水裂缝带发育高度区域分布规律[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(5):38−48. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2022-0050 ZHANG Yujun,SHEN Chenhui,ZHANG Zhiwei,et al. Regional distribution law of water–conducting fractured zone height in high−strength mining of thick and extra−thick coal seams in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(5):38−48. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2022-0050
[14] 李超峰. 黄陇煤田综放采煤顶板导水裂缝带高度发育特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(2):129−136. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.02.020 LI Chaofeng. Characteristics of height of water flowing fractured zone caused during fully−mechanized caving mining in Huanglong Coalfield[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(2):129−136. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.02.020
[15] 李超峰,虎维岳,王云宏,等. 煤层顶板导水裂缝带高度综合探查技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(1):101−107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.01.018 LI Chaofeng,HU Weiyue,WANG Yunhong,et al. Comprehensive detection technique for coal seam roof water flowing fractured zone height[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(1):101−107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.01.018
[16] 许家林. 煤矿绿色开采20年研究及进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(9):1−15. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.09.001 XU Jialin. Research and progress of coal mine green mining in 20 years[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(9):1−15. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.09.001
[17] 许家林,倪建明,轩大洋,等. 覆岩隔离注浆充填不迁村采煤技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(12):8−11. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2015.12.002 XU Jialin,NI Jianming,XUAN Dayang,et al. Coal mining technology without village relocation by isolated grout injection into overburden[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(12):8−11. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2015.12.002
[18] 许家林,轩大洋,朱卫兵,等. 部分充填采煤技术的研究与实践[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(6):1303−1312. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.3055 XU Jialin,XUAN Dayang,ZHU Weibing,et al. Study and application of coal mining with partial backfilling[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(6):1303−1312. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.3055
[19] 董书宁,杨志斌,姬中奎,等. 神府矿区大型水库旁烧变岩水保水开采技术研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(3):709−717. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.6028 DONG Shuning,YANG Zhibin,JI Zhongkui,et al. Study on water–preserved mining technology of burnt rock aquifer beside the large reservoir in Shenfu mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(3):709−717. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.6028
[20] 李超峰. 采煤工作面顶板巨厚层状含水层涌水量预测研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2019. LI Chaofeng. Prediction theory and method of water inflow from roof thick layered aquifer of coal mining face[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2019.








 下载:
下载: