Reservoir properties and gas production difference between No.15 coal and No.3 coal in Zhengzhuang Block, southern Qinshui Basin
-
摘要:
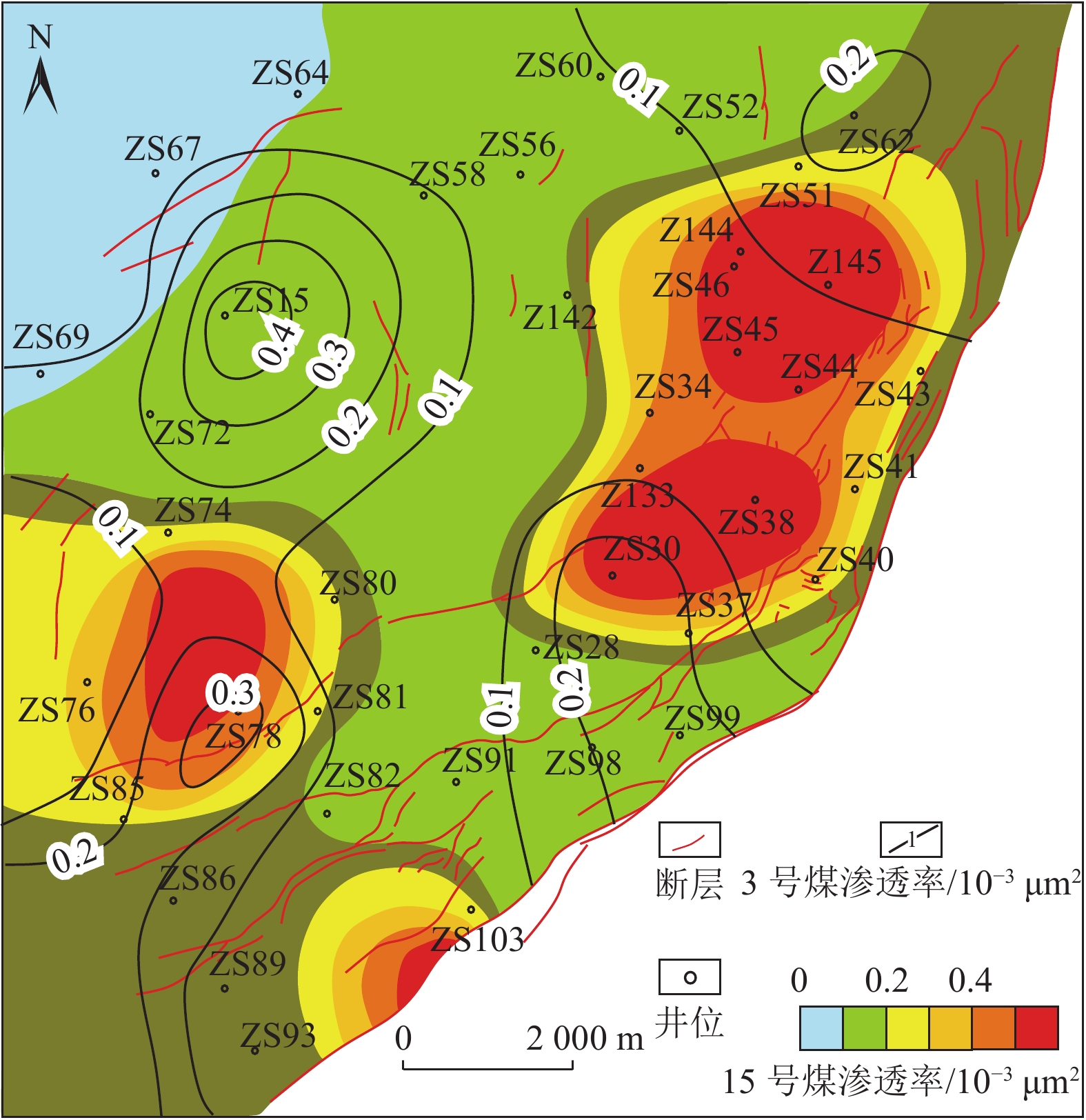
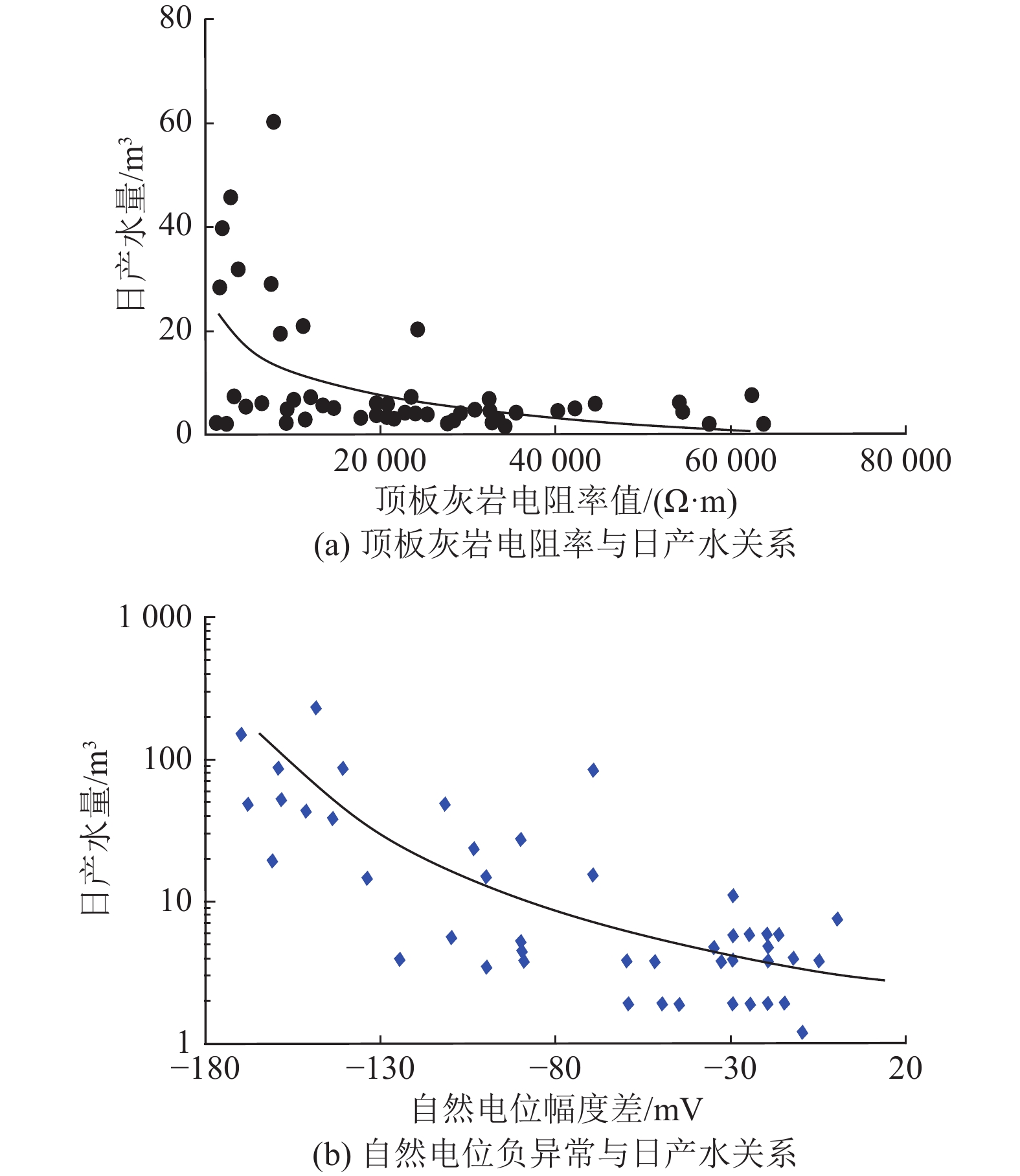
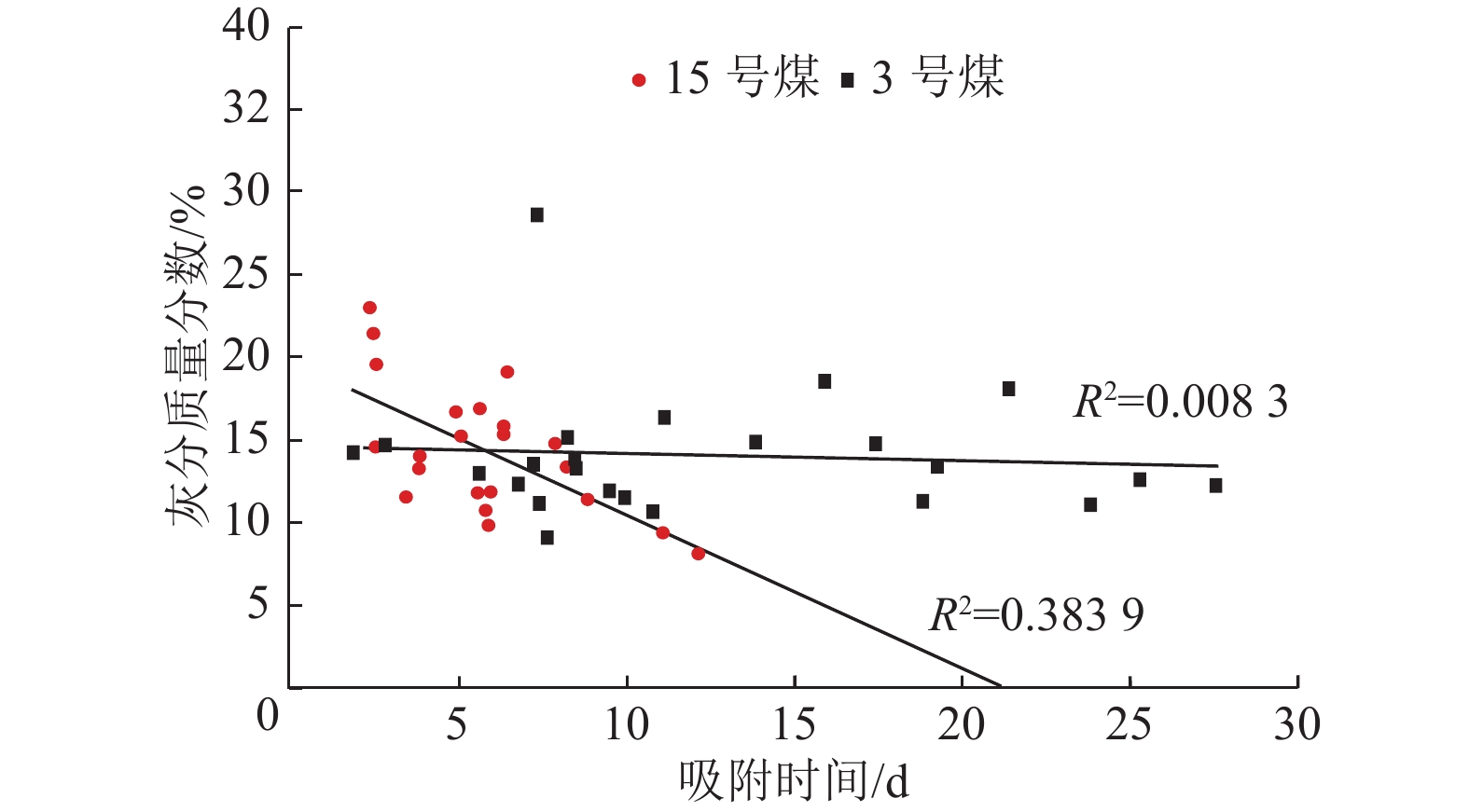
随着煤层气勘探开发的深入,同一区域不同层系开发差异逐步呈现,深化储层认识对开发策略的制定显得尤为重要,以沁水盆地南部郑庄区块为例,以往重点关注主力层3号煤资源,根据区块增产需求,需要逐步多层系开采。本研究重点剖析15号煤层气资源,采取与开发较为成熟的3号煤层气资源对比分析的方法,得出储层差异和分区差异,并推测其成因机制,指导针对性开发策略的制定。通过钻井岩心描述及镜下观察,结合分析化验、地震勘探、测井及生产等资料,对比研究了郑庄区块15号煤层与3号煤层在煤厚、物性和含气性等方面的差异。结果表明:与3号煤层相比,15号煤层厚度较薄,且平面分布不稳定,存在局部分叉现象;总体上,15号煤层含气量与3号煤层相当,一般为10~29 m3/t,但在区块内部呈现出具有一定规律的分区差异;15号煤层的吸附时间较3号煤层明显缩短,表明其较为有利的开发潜力。研究认为,沉积环境差异和构造影响程度不同是导致两套煤储层物性和含气性差异的主要原因,太原组障壁海相沉积环境水体变化大导致15号煤层沉积厚度平面变化大,强还原沉积环境造成15号煤层镜质组分含量较高;相比于3号煤层,局部地段太原组15号煤层受基底构造、断层、褶皱等地质构造影响更为明显。根据煤储层参数特征,将15号煤有利区划分为三类,指出开发“甜点区”;试采结果表明,I类区15号煤层套管压裂水平井日产气量突破10 000 m3,3号、15号煤层直井合采较单采3号煤层产量翻番;Ⅱ类区15号煤层套管压裂水平井获得高产,为区域增产、规模扩建起到技术支撑作用。
Abstract:With the in-depth exploration and development of coalbed methane (CBM), the development differences between different strata in the same region are gradually emerging. Deepening the understanding of reservoir is crucial to formulate development strategies. Taking the Zhengzhuang Block in the southern Qinshui Basin as an example, in the past, the focus was on the main No.3 coal resources. With the stimulation demand in this block, the CBM needs to be gradually recovered in multiple layers. In this paper, the CBM resource of No.15 coal is analyzed. Comparative analysis with well developed No.3 CBM resources is carried to probe into the cause of reservoir differences and regional differences. Furthermore, the genesis mechanism is speculated to guide the formulation of targeted development strategies. Based on the description of drilling cores and observation under microscope, combined with the indoor test, seismic exploration, logging and production data, the differences in coal thickness, physical properties and gas-bearing properties between the No.15 and the No.3 coal seams in Zhengzhuang Block are investigated. The results show that compared with the No.3 coal, No.15 coal is thinner and the plane distribution is unstable with local bifurcation phenomenon. In general, the gas content of No.15 coal is equivalent to that of No.3 coal, ranging from 10 m3/t to 29 m3/t, although there are regular regional differences within the block. The adsorption time of No.15 coal is significantly shorter than that of No.3 coal, indicating its favorable development potential. The distinction in sedimentary environment and tectonic influence are the main reasons for the difference in petrophysical properties and gas-bearing properties between the two seams. Specifically, because of the barrier coast sedimentary of Taiyuan Formation, the water turbulence and strong reducing environment lead to a varying coal thickness in plane and a higher vitrinite content of the No.15 coal. Tectonically, compared with the No.3 coal, partial No.15 coal is more obviously affected by geological structures such as basement structure, faults and folds. According to the characteristics of coal reservoir parameters, the favorable area of No.15 coal is divided into three categories, and the “sweet spot” is identified. Pilot production suggests that the daily production of casing fractured horizontal wells in No.15 coal in category I area exceeds 10 000 m3 and the production of vertical wells in No.3 and No.15 coal seams has doubled than that of single-mining No.3 coal seam. In category Ⅱ area the output of casing fractured horizontal well developing No.15 coal achieves high yield. This research provides technical supports for regional production increase and scale expansion.
-
-
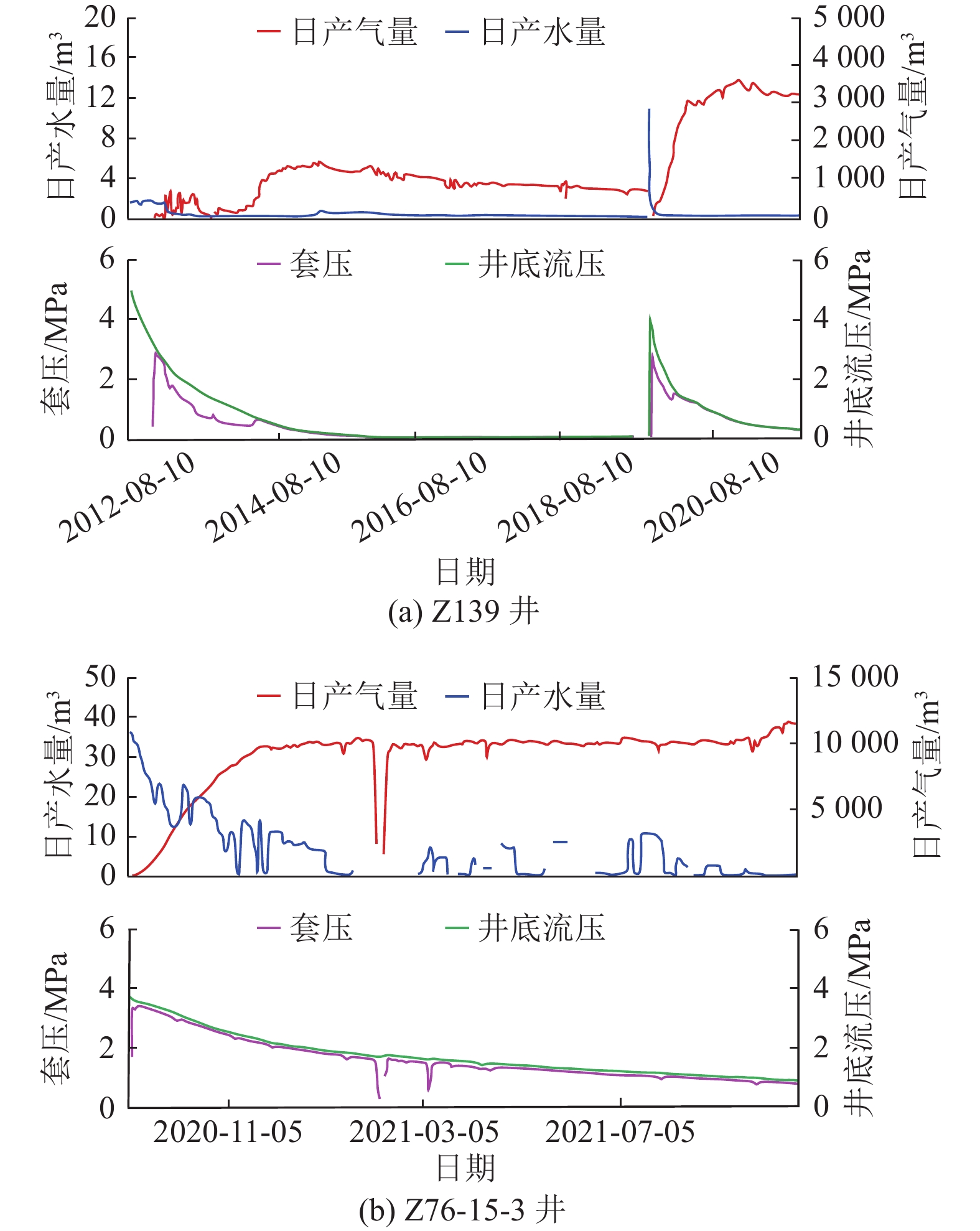
表 1 Z76水平井组生产数据汇总
Table 1 Summary of production data of Z76 horizontal well group
井号 煤层 进尺/m 埋深/m 初始井底流压/MPa 解吸压力/MPa 稳产气量/(m3·d−1) 日产水量/m3 井底流压/MPa Z76-3-1 3号 700 460 3.7 2.0 6 000 2 0.07 Z76-3-2 725 458 4.2 2.2 6 000 0.2 0.13 Z76-3-3 885 461 4.6 1.9 5 000 0.2 0.3 Z76-15-1 15号 683 552 3.5 2.8 10 600 13 1.1 Z76-15-2 648 548 3.5 2.9 8 000 10 1.4 Z76-15-3 755 544 2.5 3.1 11 000 12 1.1 Z76-15-4 680 544 2.2 2.7 10 000 15 1.6 -
[1] 姚艳斌,王辉,杨延辉,等. 煤层气储层可改造性评价:以郑庄区块为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(1):119−129. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.012 YAO Yanbin,WANG Hui,YANG Yanhui,et al. Evaluation of the hydro–fracturing potential for coalbed methane reservoir:A case study of Zhengzhuang CBM field[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(1):119−129. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.012
[2] 叶建平,彭小妹,张小朋. 山西沁水盆地煤层气勘探方向和开发建议[J]. 中国煤层气,2009,6(3):7−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2009.03.002 YE Jianping,PENG Xiaomei,ZHANG Xiaopeng. Exploration orientation and development proposal of coalbed methane in Qinshui Basin of Shanxi Province[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2009,6(3):7−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2009.03.002
[3] 贾慧敏,胡秋嘉,樊彬,等. 沁水盆地郑庄区块北部煤层气直井低产原因及高效开发技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):34−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.005 JIA Huimin,HU Qiujia,FAN Bin,et al. Causes for low CBM production of vertical wells and efficient development technology in northern Zhengzhuang block in Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(2):34−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.005
[4] 李梦溪,李仰民,谷文彬,等. 沁水盆地煤储层非均质性控制因素研究[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2009(16):17−20. LI Mengxi,LI Yangmin,GU Wenbin,et al. Controlled factors of heterogeneity on coal reservoir in Qinshui Basin[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2009(16):17−20.
[5] 徐凤银,肖芝华,陈东,等. 我国煤层气开发技术现状与发展方向[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(10):205−215. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019.10.027 XU Fengyin,XIAO Zhihua,CHEN Dong,et al. Current status and development direction of coalbed methane exploration technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(10):205−215. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019.10.027
[6] 朱庆忠,鲁秀芹,杨延辉,等. 郑庄区块高阶煤层气低效产能区耦合盘活技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(8):2547−2555. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.KJ19.0428 ZHU Qingzhong,LU Xiuqin,YANG Yanhui,et al. Coupled activation technology for low−efficiency productivity zones of high−rank coalbed methane in Zhengzhuang block,Shanxi,China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(8):2547−2555. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.KJ19.0428
[7] 李忠城. 沁水盆地南部高产水煤储层煤层气开发机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012. LI Zhongcheng. The coalbed methane development mechanism of the high–water–yield reservoir in south of Qinshui Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
[8] 倪小明,苏现波,李广生. 樊庄地区3#和15#煤层合层排采的可行性研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2010,21(1):144−149. NI Xiaoming,SU Xianbo,LI Guangsheng. Feasibility of multi–layer drainage for No.3 and No.15 coal seams in the Fanzhuang area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2010,21(1):144−149.
[9] 尹帅,单钰铭,王磊,等. 沁水盆地东北部地区15号煤储层物性特征分析[J]. 地质与资源,2013,22(4):318−325. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.04.012 YIN Shuai,SHAN Yuming,WANG Lei,et al. Analysis of the physical characteristics of No. 15 coal reservoir in northeastern Qinshui Basin[J]. Geology and Resources,2013,22(4):318−325. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.04.012
[10] 许启鲁,黄文辉,刘贝,等. 沁水盆地南部15号煤储层物性特征分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2015,46(3):160−163. DOI: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2015.03.047 XU Qilu,HUANG Wenhui,LIU Bei,et al. Physical characteristics analysis of No.15 coal reservoir in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2015,46(3):160−163. DOI: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2015.03.047
[11] 许启鲁,黄文辉,杨延绘,等. 柿庄地区15号煤层低渗透率影响因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(11):141−146. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2016.11.027 XU Qilu,HUANG Wenhui,YANG Yanhui,et al. Analysis on factors affected to low permeability of No. 15 seam in Shizhuang area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(11):141−146. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2016.11.027
[12] 孟贵希,贺小黑,周国文,等. 沁水盆地和顺区块15号煤储层特征及试采效果分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2013,25(1):12−15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2013.01.03 MENG Guixi,HE Xiaohei,ZHOU Guowen,et al. No. 15 coal reservoir characteristics and production testing result analysis in Heshun block,Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology of China,2013,25(1):12−15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2013.01.03
[13] 路芳芳. 胡底井田15号煤层气储层物性及特征分析[J]. 山东煤炭科技,2017(10):144−146. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2017.10.060 LU Fangfang. Physical properties and characteristics of coalbed methane reservoir in No. 15,Hudi minefield,southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Shandong Coal Science and Technology,2017(10):144−146. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2017.10.060
[14] 李梦溪,崔新瑞,王立龙,等. 郑村井区15号煤煤层气开发实践与认识[J]. 中国煤层气,2013,10(6):18−23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2013.06.005 LI Mengxi,CUI Xinrui,WANG Lilong,et al. Practice and cognition for CBM development in No.15 coal seam of Zhengcun wellblock[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2013,10(6):18−23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2013.06.005
[15] 刘一楠,侯岩波,胡秋萍. 沁南潘河区块15号煤煤层气高效开发技术[J]. 中国煤层气,2020,17(1):9−14. LIU Yinan,HOU Yanbo,HU Qiuping. Efficient CBM development technology of No.15 coal seam in Qinnan Panhe block[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2020,17(1):9−14.
[16] 陆小霞,黄文辉,敖卫华,等. 沁水盆地南部3号和15号煤层产气量差异因素[J]. 石油天然气学报:江汉石油学院学报,2013,35(3):30−35. LU Xiaoxia,HUANG Wenhui,AO Weihua,et al. The factors of yield differences between No.3 and No.15 coal seams in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology(J. JPI),2013,35(3):30−35.
[17] 王保玉,胡斌,白建平,等. 山西沁水盆地东南部上石炭统–下二叠统太原组聚煤环境[J]. 古地理学报,2015,17(5):677−688. DOI: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.05.056 WANG Baoyu,HU Bin,BAI Jianping,et al. Coal–accumulating environments of the Upper Carboniferous–Lower Permian Taiyuan formation in southeastern Qinshui Basin,Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2015,17(5):677−688. DOI: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.05.056
[18] 岳立孝,石彦强. 沁水煤田玉溪井田煤系沉积环境及聚煤规律[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2017,29(12):50−54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.12.10 YUE Lixiao,SHI Yanqiang. Coal measures sedimentary environment and coal accumulation pattern in Yuxi minefield,Qinshui coalfield[J]. Coal Geology of China,2017,29(12):50−54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.12.10
[19] 杨克兵,严德天,郭建东,等. 沁水盆地南部煤系地层层序及聚煤控制因素[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2014,37(3):24−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2014.03.006 YANG Kebing,YAN Detian,GUO Jiandong,et al. Sequence and factors affecting accumulation in coal series,southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development,2014,37(3):24−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2014.03.006
[20] 孟艳军,汤达祯,许浩,等. 煤层气解吸阶段划分方法及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(5):612−617. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.14 MENG Yanjun,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. Division of coalbed methane desorption stages and its significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014,41(5):612−617. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.14
[21] 刘峻杉. 煤储层渗透率影响因素探讨[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2014,31(2):100−104. LIU Junshan. The influencing factors of coal reservoir permeability[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science),2014,31(2):100−104.
[22] 刘贝,黄文辉,敖卫华,等. 沁水盆地南部煤中矿物赋存特征及其对煤储层物性的影响[J]. 现代地质,2014,28(3):645−652. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.03.023 LIU Bei,HUANG Wenhui,AO Weihua,et al. Occurrence characteristics of minerals and their influences on physical properties of coal reservoirs in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Geoscience,2014,28(3):645−652. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.03.023
[23] 李忠城,吴建光,王建中,等. 沁水盆地南部15号煤层和顶板K2灰岩水文地球化学演化特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(3):75−80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.03.011 LI Zhongcheng,WU Jianguang,WANG Jianzhong,et al. Hydrogeochemical evolution of No.15 coal seam and limestone K2 in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(3):75−80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.03.011
[24] 孙粉锦,王勃,李梦溪,等. 沁水盆地南部煤层气富集高产主控地质因素[J]. 石油学报,2014,35(6):1070−1079. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201406004 SUN Fenjin,WANG Bo,LI Mengxi,et al. Major geological factors controlling the enrichment and high yield of coalbed methane in the southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2014,35(6):1070−1079. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201406004
[25] 孙粉锦, 王勃, 王玫珠, 等. 煤层气富集高产理论进展与定量化评价[C]//全国天然气学术年会论文集. 银川: 中国石油学会天然气专业委员会, 2016. [26] 王勃,姚红星,王红娜,等. 沁水盆地成庄区块煤层气成藏优势及富集高产主控地质因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2018,39(2):366−372. DOI: 10.11743/ogg20180215 WANG Bo,YAO Hongxing,WANG Hongna,et al. Favorable and major geological controlling factors for coalbed methane accumulation and high production in the Chengzhuang block,Qinshui Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2018,39(2):366−372. DOI: 10.11743/ogg20180215
[27] 刘贝,黄文辉,敖卫华,等. 高阶煤的吸附性能及其影响因素:以沁水盆地柿庄区块为例[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,29(5):31−37. LIU Bei,HUANG Wenhui,AO Weihua,et al. Adsorption capacity of high−rank coal and its influencing factors:Taking Shizhuang block of Qinshui Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition),2014,29(5):31−37.
[28] 秦勇,汤达祯,刘大锰,等. 煤储层开发动态地质评价理论与技术进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(1):80−88. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2014.01.020 QIN Yong,TANG Dazhen,LIU Dameng,et al. Geological evaluation theory and technology progress of coal reservoir dynamics during coalbed methane drainage[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2014,42(1):80−88. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2014.01.020
[29] 张强. 沁水盆地郑庄区块15#煤L型水平井钻完井关键技术[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(11):61−66. ZHANG Qiang. Key technologies for drilling and completion of No.15 coal L−shaped horizontal well in Zhengzhuang block,Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Engineering,2021,53(11):61−66.
-
期刊类型引用(20)
1. 李建林,薛杨,王心义,徐博博,郭水涛. 基于模糊综合评价的导水通道超前探查判识技术. 煤炭科学技术. 2024(07): 178-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 白怀东,范玉海,冯喜珍. 无线电波透视法在何家塔煤矿50106工作面的应用. 能源与节能. 2023(05): 1-5 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王铮,易洪春. 无线电波透视技术在工作面隐伏地质构造探测中的应用. 煤炭与化工. 2023(06): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王庆. 准格尔矿区煤矿井下水害综合防治技术. 煤矿安全. 2021(06): 104-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘卫卫. 定向钻探在工作面电法异常探查中的应用. 煤炭技术. 2021(07): 75-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 侯海龙. 无线电波坑道透视技术在煤矿综采工作面的应用. 能源与节能. 2021(09): 182-184+186 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙全业. 唐家会煤矿复杂地质条件下智能化建设探索与实践. 中国煤炭. 2021(S1): 69-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 宋永,覃觅觅. 电磁精细探测法在隐伏型导水地质裂缝勘探中的应用. 水利水电技术. 2020(02): 184-191 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 冀前辉,郝世俊,王程,刘卫卫. 复合勘探技术在煤矿工作面水害防治中的应用. 工矿自动化. 2020(03): 79-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 江微娜. 无线电波透视探查地质异常区的应用与分析. 能源与环保. 2020(03): 61-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张志伟. 短工作面陷落柱无线电波透视探测研究及应用. 能源与环保. 2020(04): 92-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 窦文武,卫金善,焦阳,杨高峰,吉泽宇. 矿井分布式地震超前探测系统研究与应用. 煤田地质与勘探. 2020(02): 228-234 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 王振环. 浅析复合勘探技术在煤矿工作面水害中的应用. 当代化工研究. 2020(14): 92-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 王龙成,杨高峰. YDT88坑透仪在回采工作面陷落柱探测中的应用. 煤炭科技. 2020(04): 116-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 杨高峰,卫金善,杨新亮,窦文武. YDT88无线电波透视仪在地质异常体探测中的应用. 陕西煤炭. 2020(06): 131-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 蒋庆丰,吴茂林. 无线电波透视法在张集煤矿1122(1)工作面探测中的应用. 绿色科技. 2019(02): 159-160+182 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 牟义. 综采工作面带压区域电磁波CT探测小构造技术. 煤矿安全. 2019(12): 69-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 郝海涛. 无线电波坑道透视仪在煤矿生产中的应用. 科学技术创新. 2018(08): 185-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 袁鹏. 井间电磁探测技术正演模拟计算. 科学技术创新. 2017(20): 62-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 李德山. 井间电磁波层析成像技术应用进展. 科学技术创新. 2017(20): 1-2 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)








 下载:
下载: