The stability of long trench section in sand cobble stratum of mine water cutoff curtain
-
摘要:
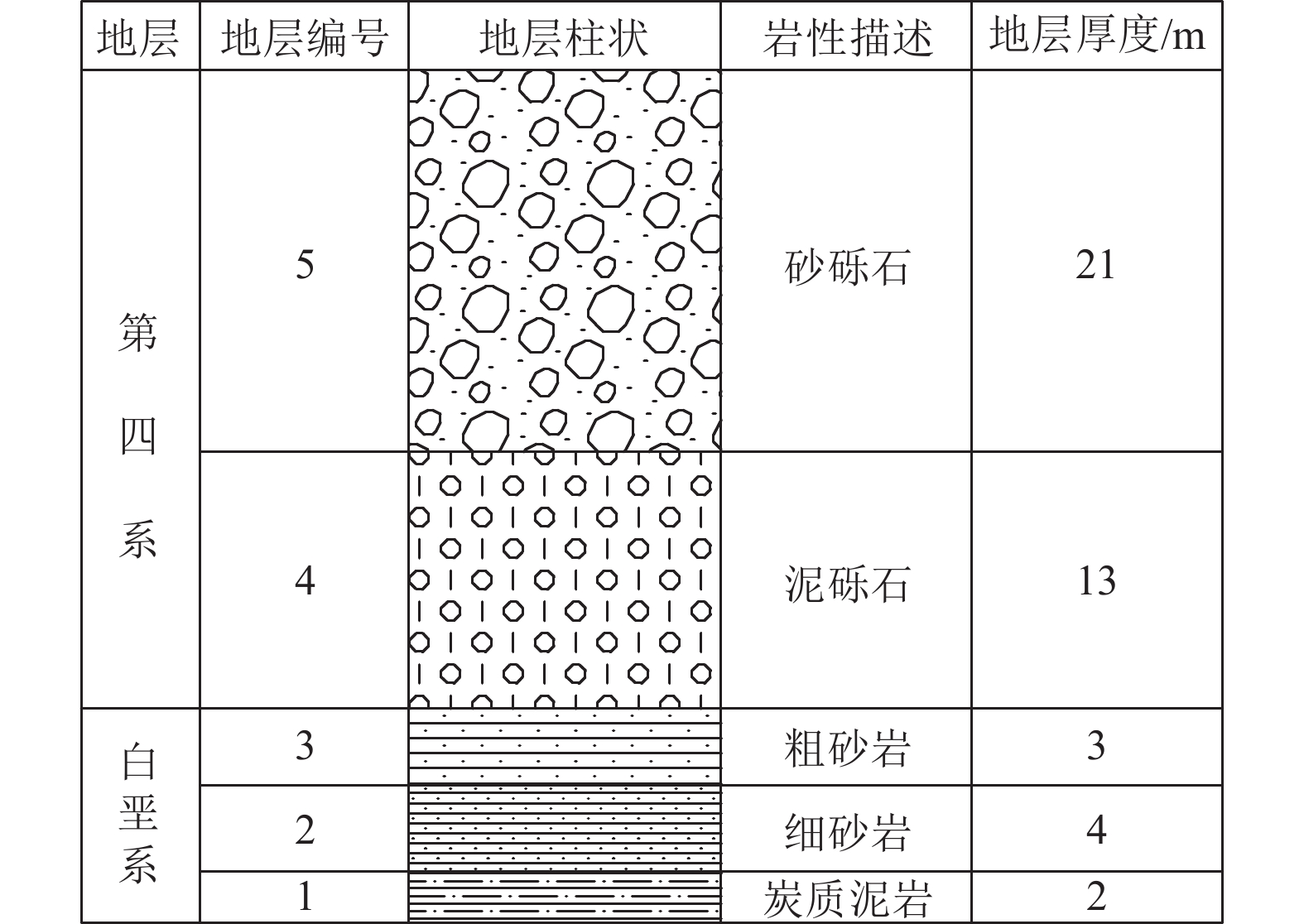
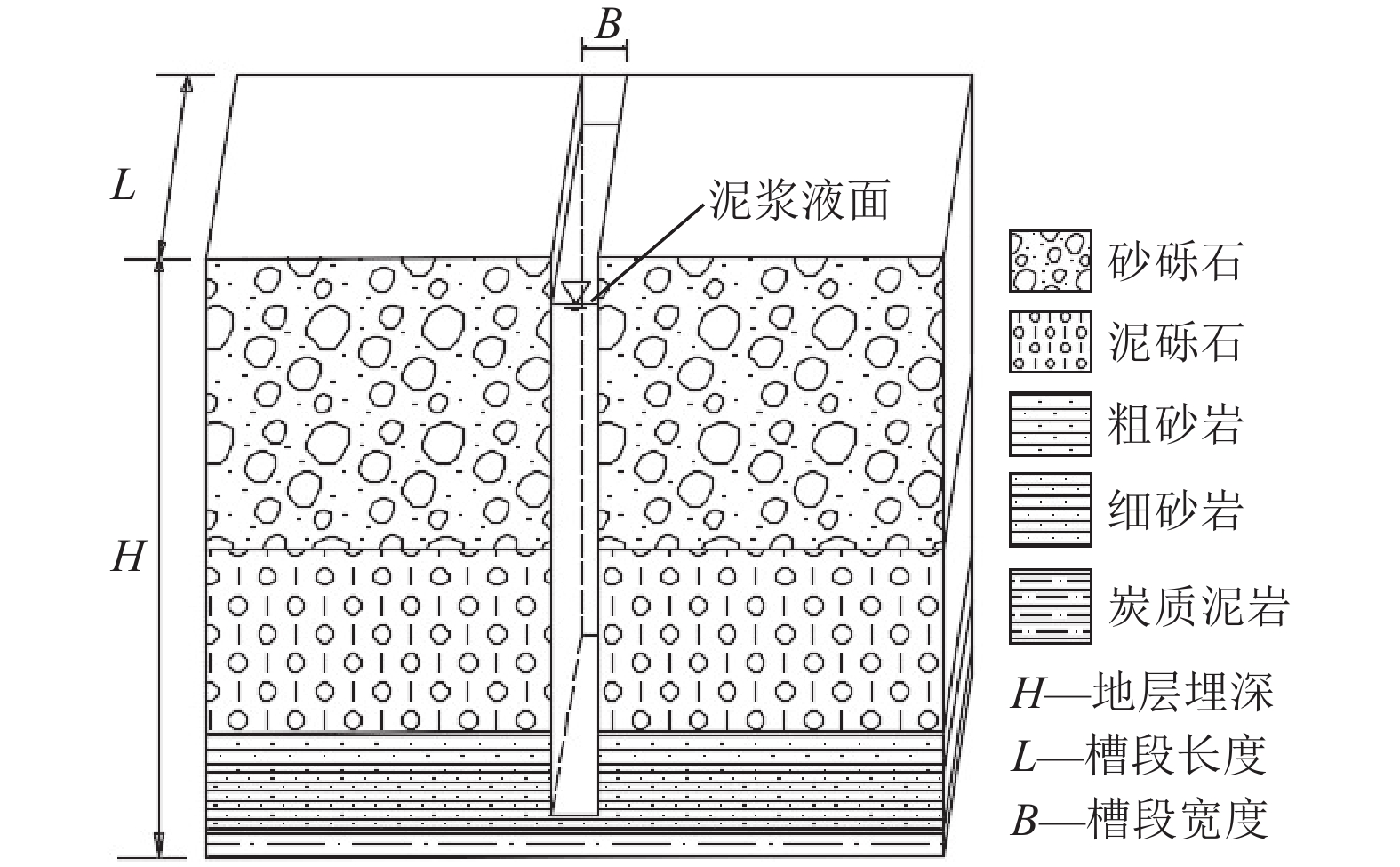
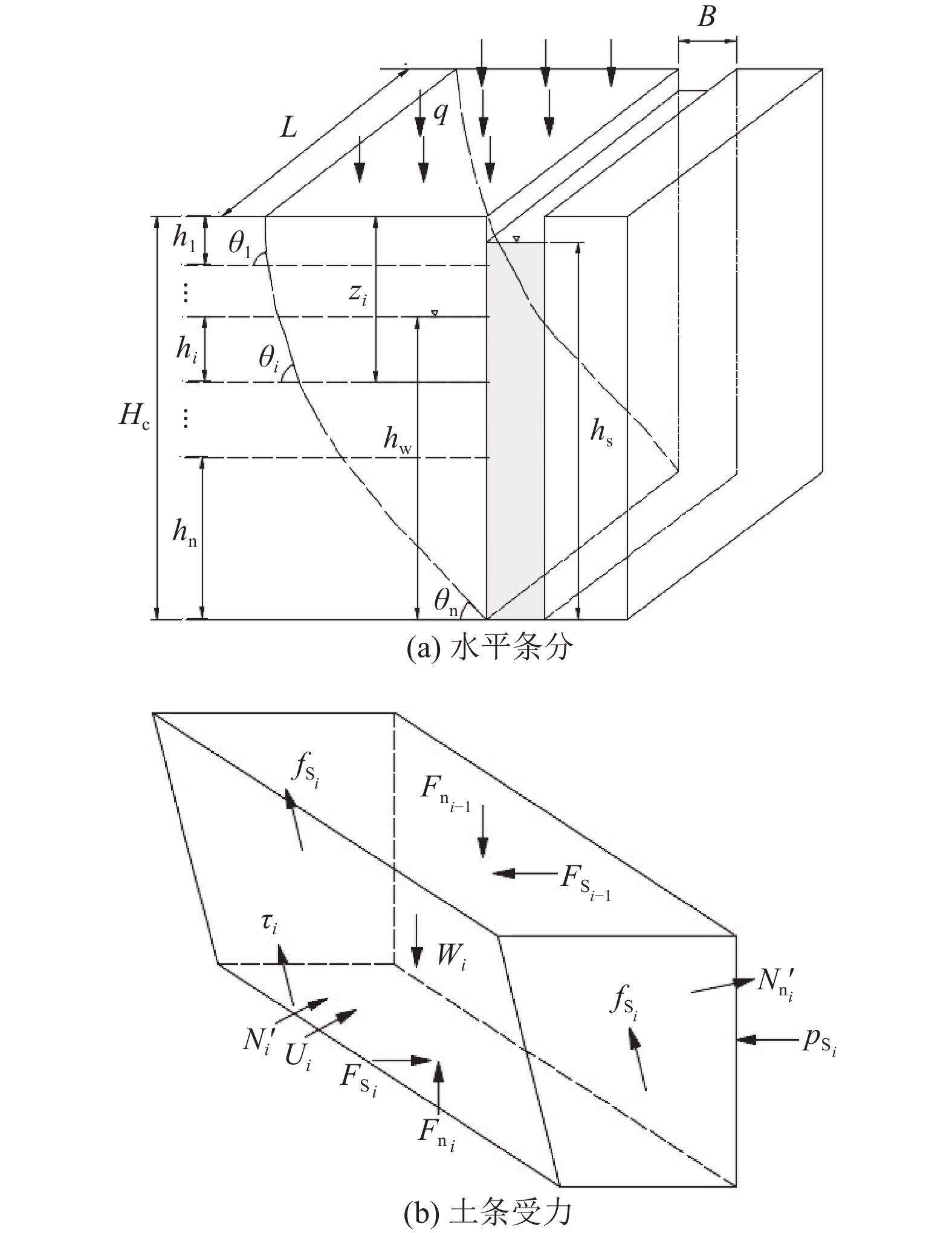
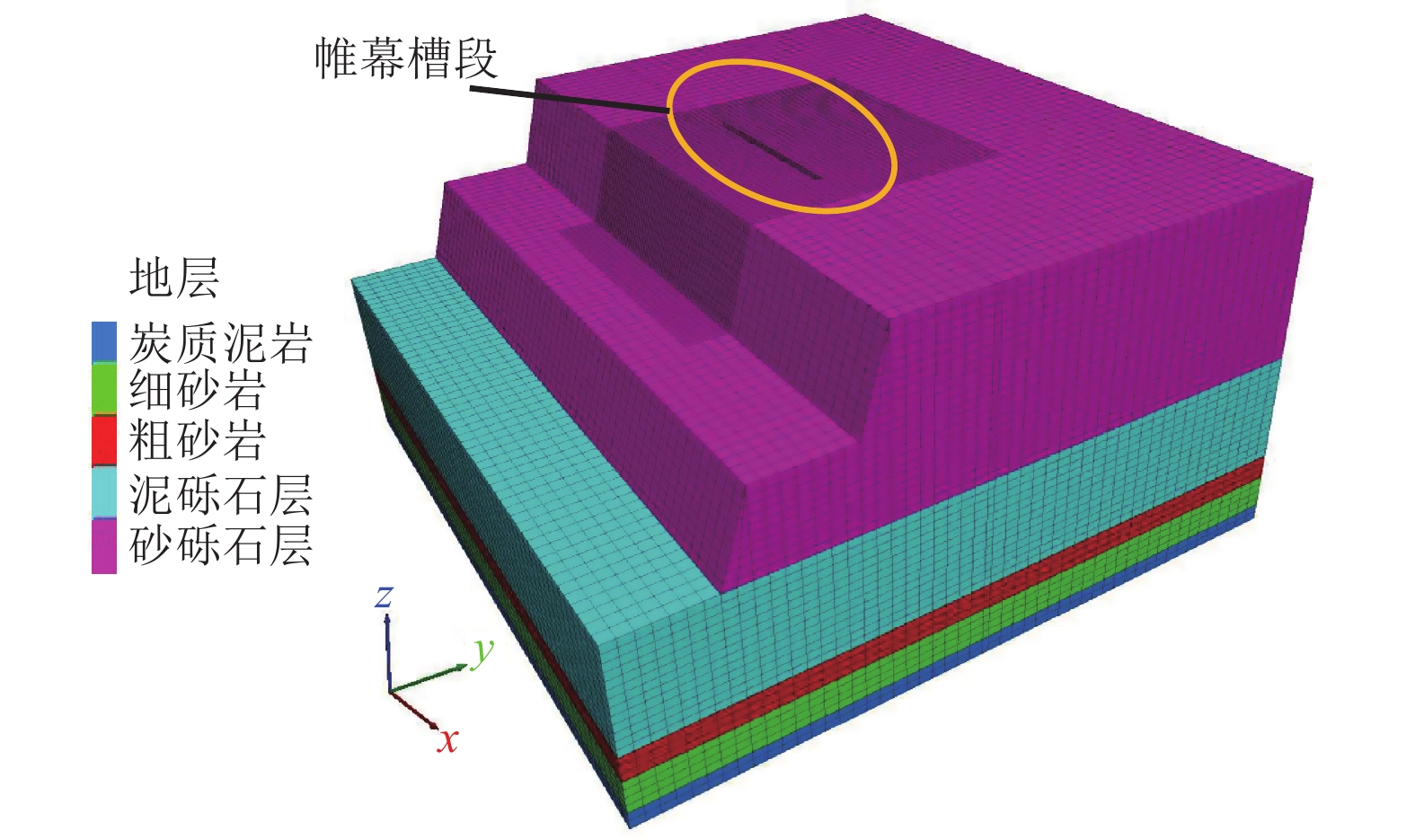
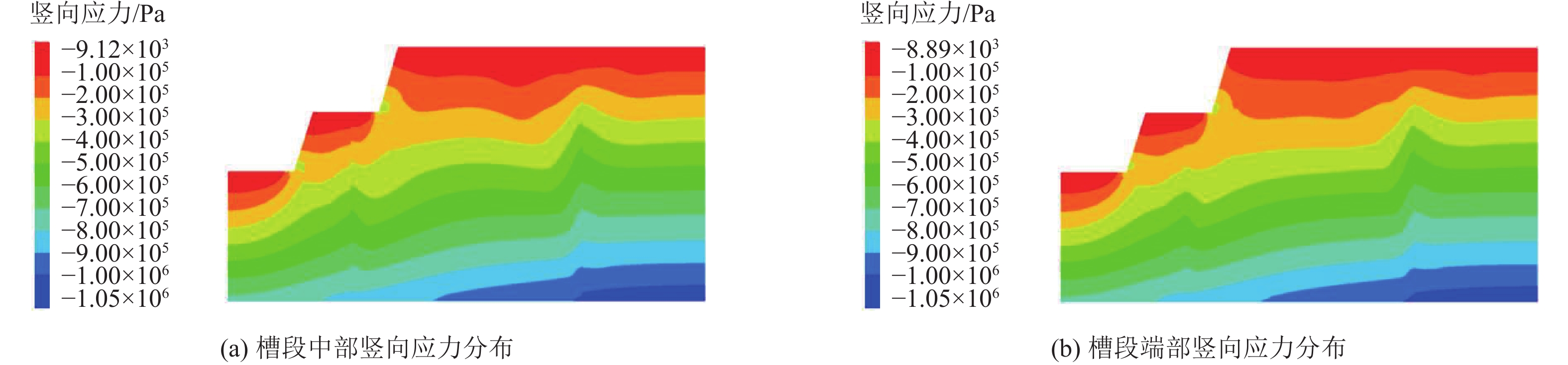
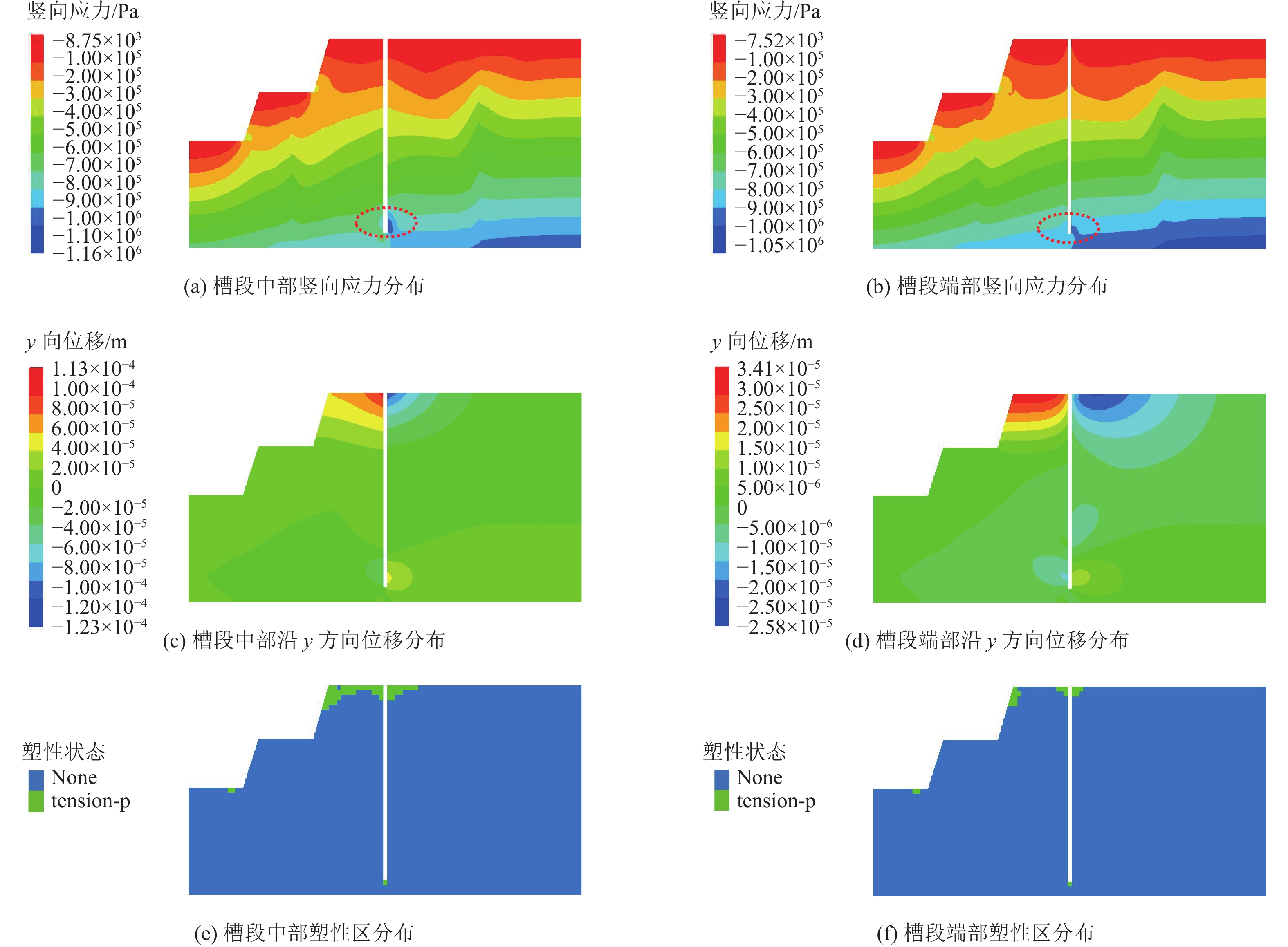
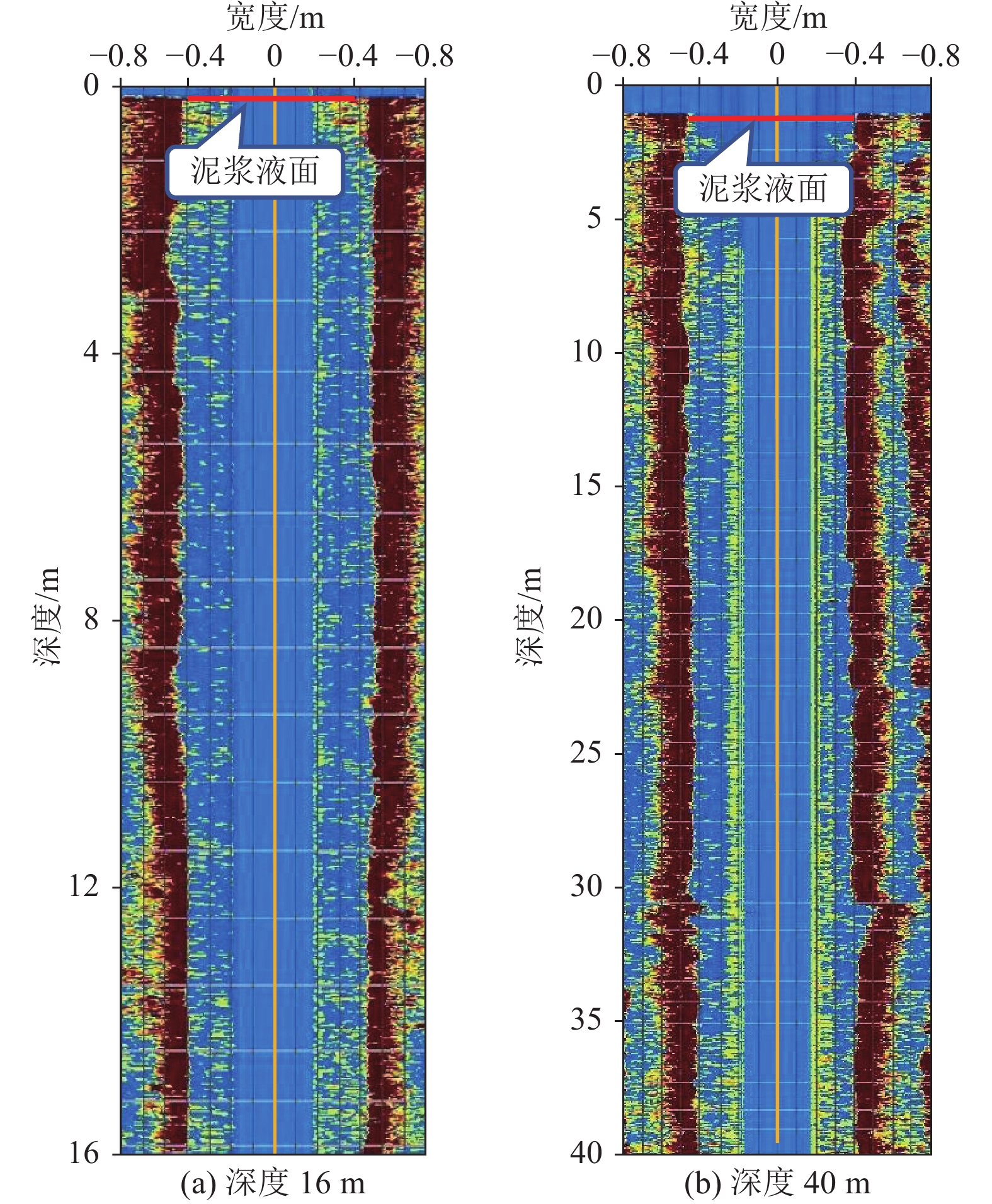
露天煤矿长时间大流量疏排降水导致矿区地下水资源严重浪费、井田周围生态环境急剧退化、生产运行成本大幅增加,截水帷幕技术为露天矿山地下水控制提供了新的思路。槽段稳定性直接关系到截水帷幕施工安全、成槽效率及防渗效果。为探讨矿山截水帷幕砂卵石地层在成槽时长幅槽段的稳定性,以我国内蒙古东部某露天煤矿为例,采用二维和三维水平条分法对砂卵石地层长幅槽段稳定性影响因素及规律进行研究,并对比分析二维与三维水平条分法在安全系数计算结果上的差异;借助FLAC3D软件模拟分析砂卵石地层分别开挖17.5、22.5 m 2种长度时槽段的稳定性;结合上述分析结果给出砂卵石地层长幅槽段稳定性控制措施;再通过超声波测试手段验证长幅槽段稳定性及控制效果。研究结果表明:影响槽段稳定性的主要因素有地层岩土体性质、槽段开挖深度、泥浆液面、泥浆密度、泥浆液面与地下水位高差及单幅槽段长度;调整泥浆参数、提高泥浆液面、降低地下水位、优化成槽次序及控制成槽时间等措施可以增加长幅槽段的稳定性;该地层条件下单幅槽段长度不超过21 m时,槽段可以保持直立稳定,长幅成槽技术可行。
Abstract:Long-term high flow rate drainage of precipitation in open-pit coal mines has led to serious waste of groundwater resources in the mine area, rapid degradation of the ecological environment around the mine field, and significant increase in production and operation costs. The curtain interception and emission reduction technology provides a new water control idea for the water control in open-pit mines. The stability of the trench section is directly related to the safety and efficiency of the water cutoff curtain during construction, at the same time, it also has a great influence on the anti-seepage effect. Taking an open-pit coal mine in the eastern Inner Mongolia of China as an example, we used the two-dimensional and three-dimensional horizontal slice method to study the factors and laws affecting the stability of the long trench section, in order to explore the stability of the trench section in sandy cobble stratum during construction. The differences between the two-dimensional and three-dimensional horizontal slice methods in the calculation of safety coefficient were compared and analyzed. The stability of the trench section was simulated and analyzed with the help of FLAC3D software for two lengths of 17.5 and 22.5 m for the sand cobble stratum respectively. Combined with the above analysis results, the stability control measures of the long trench section of sand cobble stratum were derived and verified by ultrasonic testing. The results of the study show that the main factors affecting the stability of the trench section are: the nature of the formation geotechnical body, the excavation depth of the trench section, the mud level, the mud density, the difference between the mud level and the groundwater level and the length of the single width trench section. The stability of the long trench section can be increased by adjusting the mud parameters, increasing the mud level, lowering the groundwater level, optimizing the trenching sequence and controlling the trenching time. If the length of a single trench section does not exceed 21 m, the trench can be kept upright and stable, and the long trench technique is feasible.
-
-
表 1 岩土(石)层物理力学性质
Table 1 Physico-mechanical properties of soil (rock) layers
岩土层 密度/ (kg·m−3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 黏聚力c/MPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa 砂砾石 2 460 17.31 0.36 0 34.0 0 泥砾石 2 480 13.73 0.37 0.80 28.0 0 粗砂岩 2 790 21.11 0.27 4.00 37.8 1.00 细砂岩 2 870 29.32 0.19 5.20 34.0 1.50 炭质泥岩 2 510 8.79 0.21 3.53 32.0 0.75 煤层 1 435 2.44 0.31 0.50 24.0 0.35 表 2 二维和三维水平条分法验算方案及结果
Table 2 The schemes and results of checking for 2D and 3D horizontal slice method
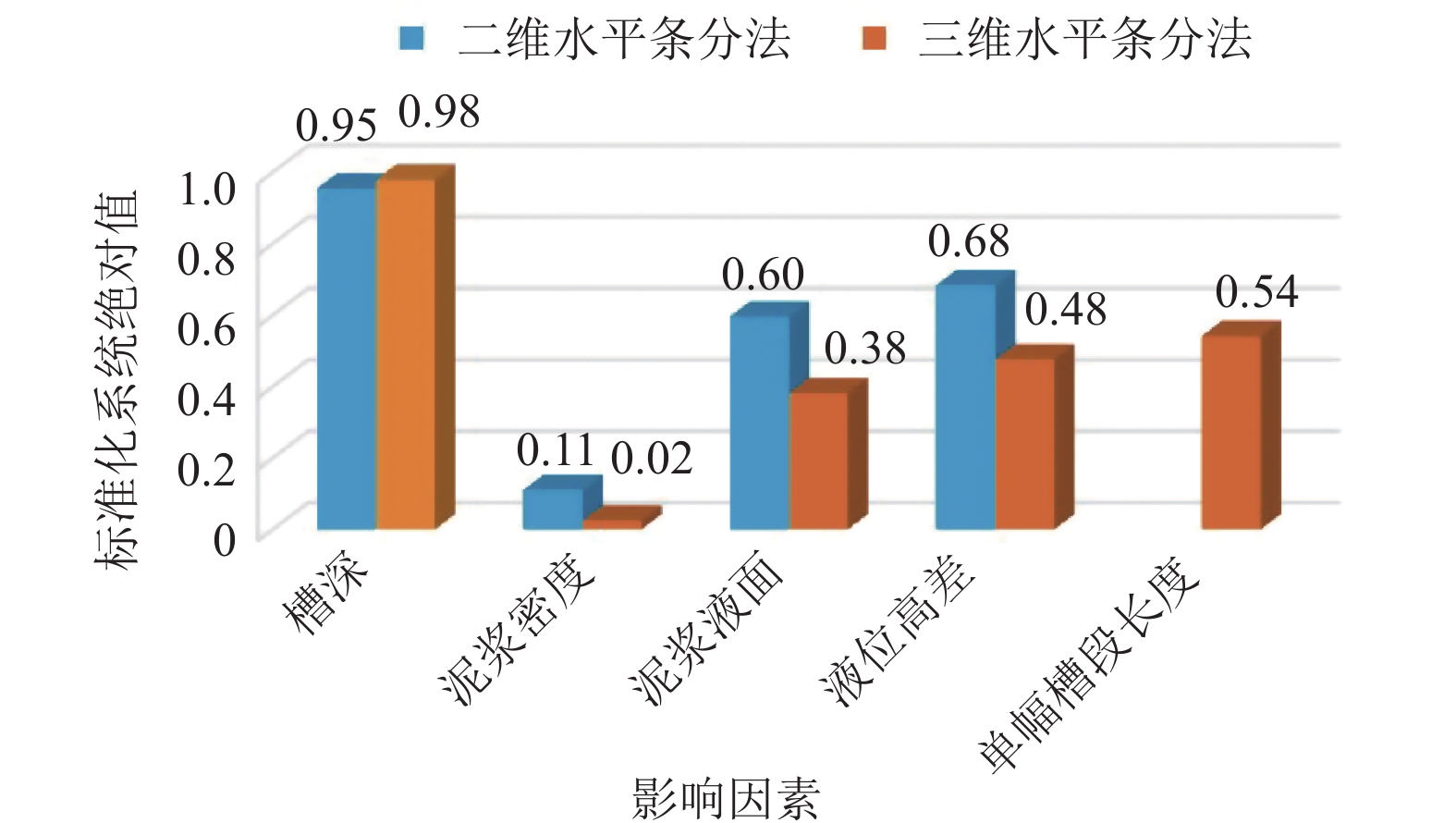
影响因素 安全系数${\eta _{\rm{s}}}$ 槽深/m 泥浆液面/m 泥浆密度/(kg·m−3) 液位高差/m 单幅槽段长度/m 二维水平条分法 三维水平条分法 21 0 1.15 21 21 0.517 0.839 21 21 1.15 21 21 0.830 1.211 5 0 1.15 21 21 1.309 2.168 10 0 1.15 21 21 1.022 1.588 15 0 1.15 21 21 0.876 1.352 21 5 1.15 21 21 0.586 0.897 21 10 1.15 21 21 0.686 1.015 21 15 1.15 21 21 0.799 1.150 21 21 1.20 21 21 0.872 1.237 21 21 1.25 21 21 0.918 1.290 21 21 1.30 21 21 0.966 1.348 21 21 1.15 0 21 0.274 0.498 21 21 1.15 7 21 0.509 1.018 21 21 1.15 14 21 0.721 1.178 21 21 1.15 21 7 1.891 21 21 1.15 21 14 1.364 21 21 1.15 21 22.5 1.098 表 3 泥浆的性能指标
Table 3 Performance indicators of mud
泥浆/方法 性能指标 密度/(g·cm−3) 黏度/(Pa·s) 含砂率/% 失水率/(mL·30 min–1) 泥皮厚/(mm·30 min–1) 胶体率/% pH值 新制泥浆 1.04~1.10 20~30 <4 <10 <1.0 ≥98 8~9 循环泥浆 1.15~1.25 18~30 ≤10 <15 <1.5 ≥96 8~11 检查方法 泥浆比重计 500 mL漏斗法 含砂量杯 失水量仪 失水量仪 量筒法 pH试纸 -
[1] 曹海东, 苗贺朝, 迟赞, 等. 基于低强度抗渗混凝土的露天煤矿帷幕截水技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(4): 61–67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.009 CAO Haidong, MIAO Hechao, CHI Zan, et al. Water cutoff curtain technology of open–pit coal mine based on low strength impermeable concrete[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(4): 61–67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.009
[2] 张雁. 露天煤矿防渗墙截渗减排机制及工程应用研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2018. ZHANG Yan. Study on the mechanism and engineering application of seepage cutoff and drainage reduction of diaphragm wall in open–pit coal mine[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2018.
[3] 董书宁, 王海, 黄选明, 等. 基于保障生态地下水位的露天煤矿主动保水技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(4): 49–57. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.04.006 DONG Shuning, WANG Hai, HUANG Xuanming, et al. Research on active water conservation technology in open–pit coal mine based on ecological protection groundwater level[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(4): 49–57. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.04.006
[4] 张雁, 田增林, 曹海东, 等. MJS工法在砾石层中的应用及成桩差异性[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(2): 147–151. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.023 ZHANG Yan, TIAN Zenglin, CAO Haidong, et al. Application of MJS construction method in gravel layer and pile forming difference[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(2): 147–151. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.023
[5] 彭巍, 王海, 王仲全, 等. 深厚砂卵石层低温动水条件下咬合桩帷幕材料研发[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(4): 80–86. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.012 PENG Wei, WANG Hai, WANG Zhongquan, et al. Properties of the occluded pile curtain material under low temperature and dynamic water condition in deep and thick gravel layer[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(4): 80–86. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.012
[6] 王海, 彭巍, 曹海东, 等. 露天煤矿截水帷幕效果检验方法及截水效果分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(4): 87–93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.013 WANG Hai, PENG Wei, CAO Haidong, et al. Inspection method and analysis of the effect of water cutoff curtain in open–pit coal mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(4): 87–93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.013
[7] 丁勇春, 李光辉, 程泽坤, 等. 地下连续墙成槽施工槽壁稳定机制分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(增刊1): 2704–2709. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.z1.017 DING Yongchun, LI Guanghui, CHENG Zekun, et al. Analysis of trench face stability of diaphragm wall panel during slurry trenching[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(Sup. 1): 2704–2709. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.z1.017
[8] 黄选明, 张雁, 李文嵩, 等. 我国露天煤矿水害特征与防治水技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(4): 53–60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.008 HUANG Xuanming, ZHANG Yan, LI Wensong, et al. Summary of water disaster characteristics and water prevention and control technology in open–pit coal mines in China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(4): 53–60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.008
[9] 张厚美, 夏明耀. 地下连续墙泥浆槽壁稳定的三维分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2000, 33(1): 73–76. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2000.01.014 ZHANG Houmei, XIA Mingyao. 3–D stability analysis of slurry trenches[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2000, 33(1): 73–76. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2000.01.014
[10] 缪圆冰, 江松, 黄明, 等. 基于强度折减的泥浆护壁槽局部稳定性计算及影响因素[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(4): 874–881. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-334 MIAO Yuanbing, JIANG Song, HUANG Ming, et al. Local stability calculation and factors of slurry trench with strength reduction method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(4): 874–881. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-334
[11] 路乾, 胡长明, 王晓华, 等. 地下连续墙成槽施工槽壁整体稳定性分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(3): 864–871. LU Qian, HU Changming, WANG Xiaohua, et al. Analysis on the overall stability of trenching construction of diaphragm wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(3): 864–871.
[12] 丁勇春, 程泽坤, 王建华, 等. 地下连续墙施工力学性状数值分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(增刊1): 87–92. DING Yongchun, CHENG Zekun, WANG Jianhua, et al. Numerical simulation of mechanical behavior of diaphragm wall during construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(Sup. 1): 87–92.
[13] 夏元友, 裴尧尧, 王震, 等. 地下连续墙施工影响应力重分布的数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(11): 3433–3438. XIA Yuanyou, PEI Yaoyao, WANG Zhen, et al. Numerical simulation of stress redistribution during diaphragm wall construction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(11): 3433–3438.
[14] ZHUO Hongchun,YANG Yuyou,ZHANG Zixin,et al. Stability of long trench in soft soils by bentonite–water slurry[J]. Journal of Central South University,2014,21(9):3674−3681. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-014-2350-4
[15] 邱明明, 杨果林, 申权, 等. 深厚砂层地下连续墙槽壁稳定性特征及影响因素研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(5): 1129–1139. QIU Mingming, YANG Guolin, SHEN Quan, et al. Study on characteristics and influence factors of slurry trench stability of diaphragm wall in deep sandy stratum[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(5): 1129–1139.
[16] 夏元友, 裴尧尧, 王智德, 等. 地下连续墙泥浆槽壁稳定性评价的水平条分法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(6): 1128–1133. XIA Yuanyou, PEI Yaoyao, WANG Zhide, et al. Horizontal slice method for stability of slurry trench[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(6): 1128–1133.
[17] FOX P. Analytical solutions for stability of slurry trench[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2004,130(7):749−758. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:7(749)
[18] LI Yuchao,PAN Qian,CLEALL P J,et al. Stability analysis of slurry trenches in similar layered soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2013,139(12):2104−2109. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000958
[19] 黄茂松, 王鸿宇, 谭廷震, 等. 地下连续墙成槽整体稳定性的工程评价方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(5): 795–803. HUANG Maosong, WANG Hongyu, TAN Tingzhen, et al. Engineering evaluation method for overall stability of slurry trenches[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(5): 795–803.
[20] 董书宁, 李日润, 虎维岳. 元宝山露天矿疏干优化设计[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2000, 28(5): 38–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2000.05.012 DONG Shuning, LI Rirun, HU Weiyue. Optimal design of drainage borehole layout in Yuanbaoshan open pit[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2000, 28(5): 38–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2000.05.012
[21] 姚道坤. 中国膨润土矿床及其开发应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994. [22] 上海市住房和城乡建设管理委员会. 基坑工程技术标准: DG/TJ 08–61–2018 J 11577—2018[S]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2018. [23] MONTGOMERY D C, PECK E A, VINING G G. Introduction to linear regression analysis[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2012.








 下载:
下载: