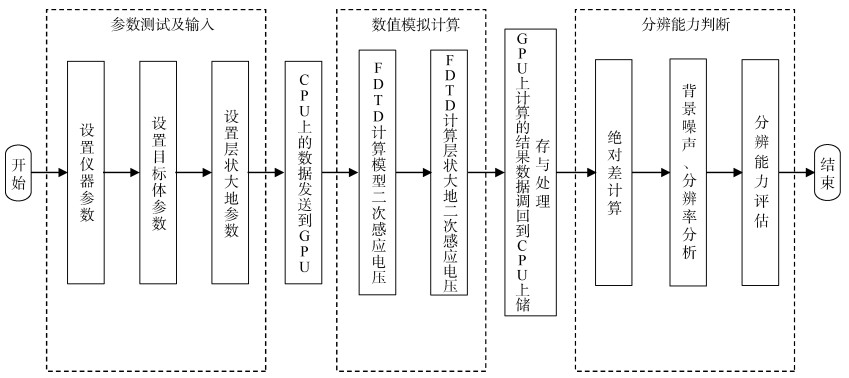
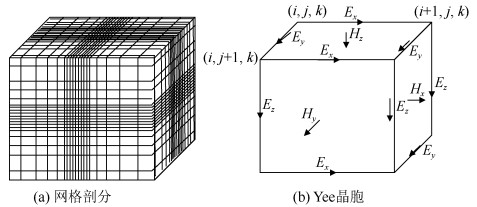
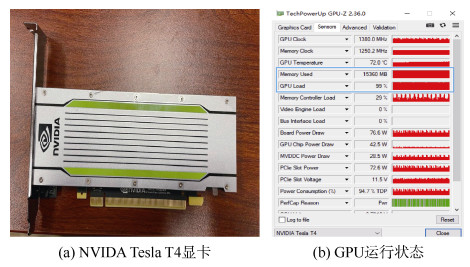
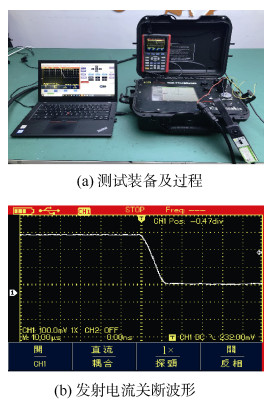
Evaluation on the resolution ability of underground transient electromagnetic instrument to disaster-causing water bodies
-
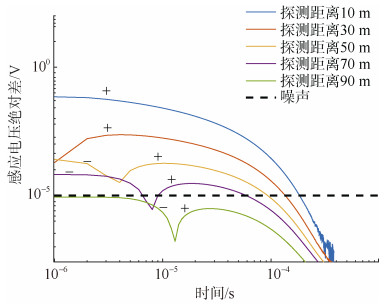
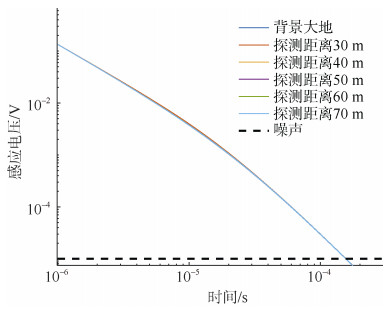
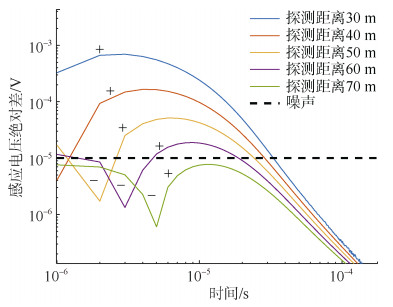
摘要: 井下瞬变电磁随掘探测技术是探测掘进面前方致灾水体的有效方法,从硬件方面评估仪器对致灾水体的分辨能力,是仪器能够在井下正确使用的重要手段。通过比较二次场绝对差和仪器分辨率、叠加后背景噪声之间的大小关系,分析含水致灾体识别的硬件条件和评估依据;提出从硬件方面评估井下瞬变电磁对致灾水体分辨能力的计算方法:根据致灾水体结构建立三维地质模型,推导梯形波关断与负阶跃波关断二次场感应电压的关系,在GPU上采用全空间三维有限差分并行算法计算了致灾水体二次场响应;测量某瞬变电磁仪的关断时间和综合噪声,根据致灾水体的硬件分辨依据,从硬件方面评估井下瞬变电磁仪对导水陷落柱、充水采空区的分辨能力。为井下瞬变电磁探测仪器的研制和现场准确探测提供技术参考,具有重大的研究意义。Abstract: The downhole transient electromagnetic detection technology is an effective method to detect the disaster-causing water body in front of the tunneling. It is an important means to evaluate the instrument's resolution ability to disaster-causing water from the aspect of hardware for the instrument to be used correctly in underground mines. By comparing the magnitude relationship between the absolute difference of the secondary field, the resolution of the instrument and the background noise after superposition, the hardware conditions and evaluation basis for distinguishing the water-bearing hazards are analyzed. A calculation method for evaluating the resolution ability of underground transient electromagnetic to disaster-causing water body from the aspect of hardware is put forward. A three-dimensional geological model is established based on the structure of the disaster-causing water body, and the relationship between the trapezoidal wave turn-off and the negative step wave turn-off secondary field induced voltage was deduced, and the full-space three-dimensional finite difference parallel was adopted on the GPU. The algorithm calculates the secondary field response of the disaster-causing water body. The turn-off time and background noise of a transient electromagnetic instrument are measured. According to the hardware discrimination basis of the disaster-causing water body, the ability of the underground transient electromagnetic instrument to distinguish water-conducting subsidence column and water-filled goaf was evaluated from the hardware aspect. The development of downhole transient electromagnetic detection instruments and accurate on-site detection provide technical reference, which is of great research significance.
-
-
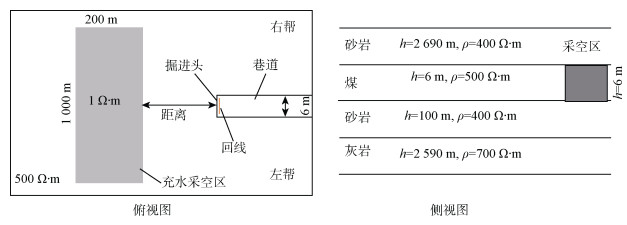
表 1 模型参数
Table 1 Model parameters
地层岩性 长×宽×高/(m×m×m) 电阻率/(Ω·m) 砂岩 5 385×5 385×2 690 400 煤 5 385×5 385×6 500 砂岩 5 385×5 385×100 400 灰岩 5 385×5 385×2 590 700 表 2 仪器参数
Table 2 Instrument parameters
计算参数类别 指标 装置形式 中心回线 发射电流/A 2.8 关断时间/μs 12 每匝发射回线面积/m2 4 发射回线匝数 10 磁探头有效面积/m2 4 800 综合噪声/μV 10 -
[1] 范立民, 孙魁, 李成, 等. 榆神矿区煤矿防治水的几点思考[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(1): 182-188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.019 FAN Limin, SUN Kui, LI Cheng, et al. Thoughts on mine water control and treatment in Yushen mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(1): 182-188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.019
[2] FANG Huiming. Hydrochemical characteristics and water hazard control of Tangjiahui Coal Mine, Ordos Basin, NW China[C]// Hubei Zhongke Institute of Geology and Environment Technology, China. Proceedings of the 8th Academic Conference of Geology Resource Management and Sustainable Development. 2020: 6.
[3] 虎维岳, 赵春虎. 基于充水要素的矿井水害类型三线图划分方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(5): 1-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.001 HU Weiyue, ZHAO Chunhu. Trilinear chart classification method of mine water hazard type based on factors of water recharge[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(5): 1-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.001
[4] 李超峰. 煤层顶板含水层涌水危险性评价方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(增刊1): 384-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2020S1042.htm LI Chaofeng. Method for evaluating the possibility of water inrush from coal seam roof aquifer[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(Sup. 1): 384-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2020S1042.htm
[5] XU Zhimin, SUN Yajun, GAO Shang, et al. Comprehensive exploration, safety evaluation and grouting of karst collapse columns in the Yangjian coalmine of the Shanxi Province, China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2021, 36(1): 16. DOI: 10.1007/s13146-021-00675-z
[6] 李洋, 王金平, 魏启明. 瞬变电磁法在井下工作面顶板导水裂缝探测中的应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(增刊1): 66-71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.S1.014 LI Yang, WANG Jinping, WEI Qiming. Application of transient electromagnetic method for detecting water-conducting crack in the roof of underground working face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(Sup. 1): 66-71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.S1.014
[7] 胡雄武, 徐虎, 彭苏萍, 等. 煤层采动覆岩富水性变化规律瞬变电磁法动态监测研究[J/OL]. 煤炭学报, [2021-04-11]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.ST21.8220 HU Xiongwu, XU Hu, PENG Suping, et al. Study on dynamic monitoring of water abundance of overlying strata in coal seam by transient electromagnetic method[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society, [2021-04-11]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.ST21.8220
[8] WANG Peng, LI Mingxing, YAO Weihua, et al. Detection of abandoned water-filled mine tunnels using the downhole transient electromagnetic method[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2020, 51(3): 1-16. DOI: 10.1080/08123985.2020.1746182
[9] 雷康信, 薛国强, 陈卫营, 等. 瞬变电磁法探测薄层的分辨能力与偏移距关系[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(6): 731-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202006004.htm LEI Kangxin, XUE Guoqiang, CHEN Weiying, et al. Relationship between the detection capability and offset of transient electromagnetic method for thin layers[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(6): 731-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202006004.htm
[10] 陈卫营, 薛国强. 电性源瞬变电磁对薄层的探测能力[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201504019.htm CHEN Weiying, XUE Guoqiang. Detection capability of grounded electric source TEM for thin layer[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201504019.htm
[11] 武军杰, 杨毅, 张杰, 等. TEM对于深部低阻层的分辨能力模拟分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(5): 547-554. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2014.05.06 WU Junjie, YANG Yi, ZHANG Jie, et al. Resolution capability preliminary analysis of deep conductive layer with TEM method[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(5): 547-554. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2014.05.06
[12] CHANG Jianghao, SU Benyu, MALEKIAN R, et al. Detection of water-filled mining goaf using mining transient electromagnetic method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 16(5): 1. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8654002
[13] CHANG Jianghao, XUE Guoqiang, MALEKIAN R. A comparison of surface-to-coal mine roadway TEM and surface TEM responses to water-enriched bodies[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 167320-167328. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2953844
[14] 嵇艳鞠, 栾卉, 李肃义, 等. 全波形时间域航空电磁探测分辨率[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(3): 885-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201103039.htm JI Yanju, LUAN Hui, LI Suyi, et al. Resolution of full waveform airborne TEM[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(3): 885-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201103039.htm
[15] 薛国强, 李海, 陈卫营, 等. 煤矿含水体瞬变电磁探测技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202101008.htm XUE Guoqiang, LI Hai, CHEN Weiying, et al. Progress of transient electromagnetic detection technology for water-bearing bodies in coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202101008.htm
[16] 王新苗, 韩保山, 宋焘, 等. 智能开采工作面三维地质模型构建及误差分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(2): 93-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.012 WANG Xinmiao, HAN Baoshan, SONG Tao, et al. 3D geological model construction and error analysis of intelligent mining working face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(2): 93-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.012
[17] 孙怀凤, 程铭, 吴启龙, 等. 瞬变电磁三维FDTD正演多分辨网格方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(12): 5096-5104. DOI: 10.6038/cjg2018L0659 SUN Huaifeng, CHENG Ming, WU Qilong, et al. A multi-scale grid scheme in three-dimensional transient electromagnetic modeling using FDTD[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(12): 5096-5104. DOI: 10.6038/cjg2018L0659
[18] CHENG Jiulong, XUE Junjie, ZHOU Jin, et al. 2.5-D inversion of advanced detection transient electromagnetic method in full space[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 8: 1. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8945357
[19] 杨海燕, 岳建华, 李锋平. 斜阶跃电流激励下多匝小回线瞬变电磁场延时特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(9): 3615-3628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201909031.htm YANG Haiyan, YUE Jianhua, LI Fengping. The decay characteristics of transient electromagnetic fields stimulated by ramp step current in multi-turn small coil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(9): 3615-3628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201909031.htm
[20] 米萨克·N·纳比吉安. 勘查地球物理电磁法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. NABIJIAN M N. Exploration geophysical electromagnetic method[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992.
[21] 葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002. GE Debiao, YAN Yubo. Finite difference time domain method for electromagnetic waves[M]. Xi'an: Xidian University Press, 2002.







 下载:
下载: