Prediction of fracture distribution and evaluation of shale gas preservation conditions in Longmaxi Formation in Dongxi area
-
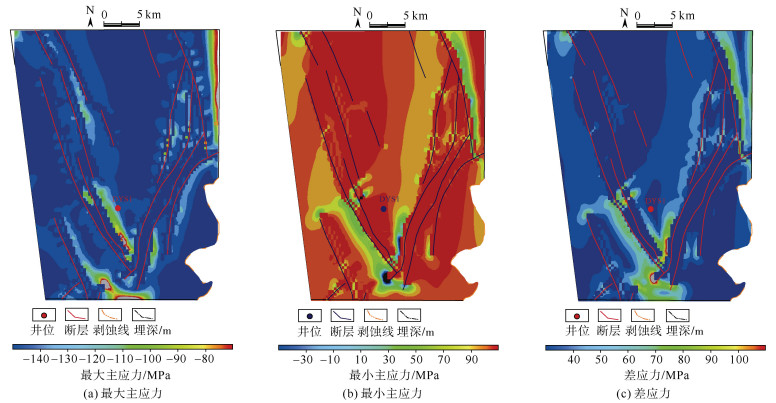
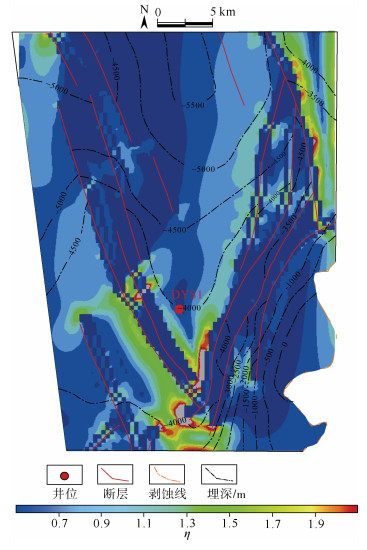
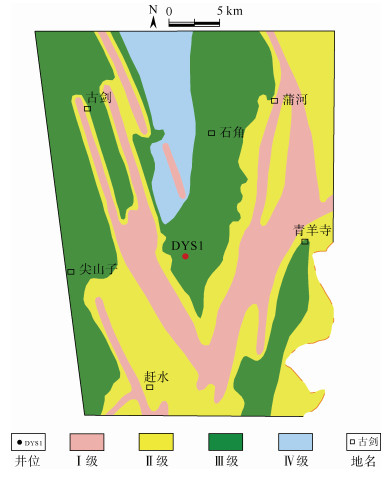
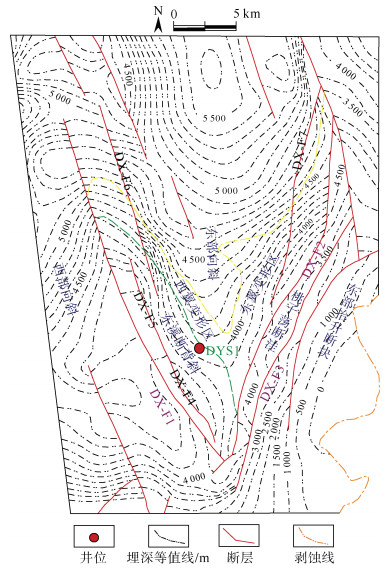
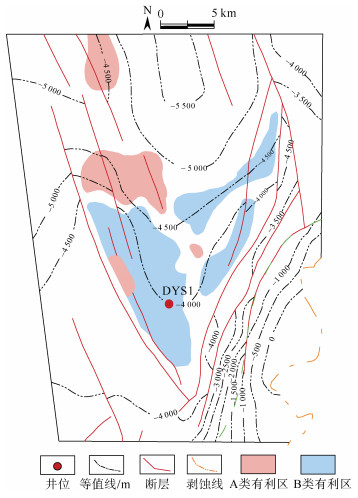
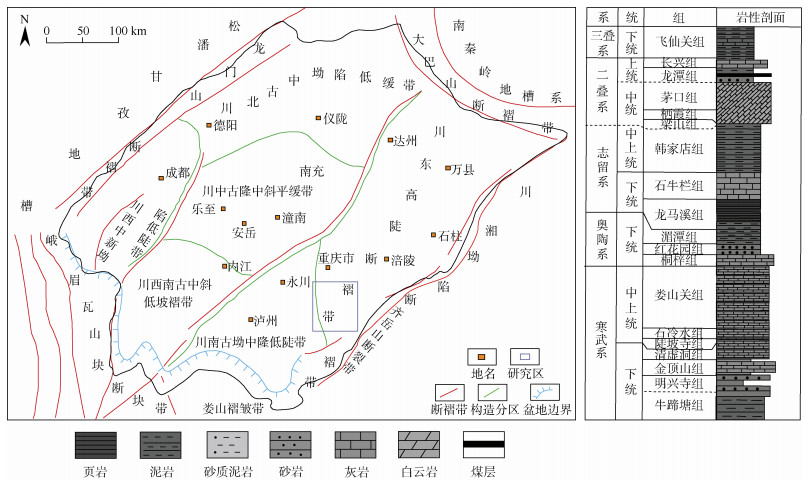
摘要: 页岩气的商业性开发证实成熟页岩具有较大的勘探潜力,川东南地区是我国南方页岩气勘探开发的战略先导区。裂缝发育情况是页岩气保存和开发部署的关键因素,对于构造环境复杂特殊的盆缘地区,在加大页岩裂缝研究难度的同时,也给页岩气勘探开发提供了新的方向。页岩气勘探作为我国油气勘探的新领域,尚未形成成熟的裂缝评价体系。以川东南东溪地区为例,基于三轴岩石力学实验结果,首先采用有限元数值模拟手段进行应力场模拟,而后利用岩石力学参数进行模型构建和模拟结果的反复试算,以获取东溪地区最大、最小主应力和应力差分布图,最后运用莫尔–库伦准则计算岩体破裂系数预测裂缝分布规律。结果表明:研究区裂缝发育情况主要分为4个级别,其中,Ⅰ级裂缝呈条带状分布在东西两侧断裂附近,Ⅱ级裂缝在Ⅰ级裂缝周围发育,而Ⅲ级裂缝分布在北部背斜核部和西部背斜翼部;优选页岩气埋深、距剥蚀区距离、距齐岳山断裂距离、断裂作用、应力差及压力系数等10个保存条件参数,采用组合权重法确定保存条件参数权重,其中一级参数权重分别为埋深(0.2)、距剥蚀区距离(0.1)、距齐岳山断裂距离(0.1)、断裂作用(0.25)、应力差(0.15)、压力系数(0.2),以此建立相对完善的页岩气评价体系与评价标准。优选出2类页岩气勘探目标有利区,其中A类、B类有利区分别分布在研究区南部背斜核部及翼部和中部宽缓褶皱两翼。研究成果为川东南地区的页岩气勘探提供重要的参考价值。Abstract: Commercial development of shale gas confirmed that mature shale has great potential for exploration, southeast Sichuan is the strategic pilot area of shale gas exploration and development in southern China, cracks are the key factor of shale gas preservation and development deployment, for the structural environment complex and special basin edge area, increasing the difficulty of shale crack research, but also provides a new direction for shale gas exploration and development. As a new field of oil and gas exploration in China, shale gas exploration has not yet developed a mature crack evaluation system. Taking Dongxi area of the southeast of Sichuan as an example, the stress field was simulated in the region by finite element numerical simulation. The model was constructed and calculated by rock mechanical parameters, the diagrams of maximum principal stress, minimum principal stress and differential stress distribution in Dongxi area were obtained through repeated debugging of the simulation results. Mohr-Coulomb criterion was used to calculate rock fracture coefficient and to predict the law of crack distribution in the study area, The prediction shows that the crack distribution of the study area is divided into four levels, GradeⅠcracks are distributed in bands near the east and west sides, grade cracks develop around gradeⅠcracks, the grade cracks are distributed in the northern dorsal nucleus and the western dorsal wing, respectively. At the same time, 10 preservation condition parameters, such as shale gas burial depth, distance from the ablative area, fracture distance from Qiyun Mountain, fracture action, differential stress and pressure coefficient, were clarified, and were used to determine the primary and secondary parameter weight by the combined weight method. Among them, the first stage parameters are buried depth(0.2), distance from the exfoliation area(0.1), fracture distance(0.1), fracture action(0.25), differential stress(0.15), and pressure coefficient(0.2). A relatively sound shale gas evaluation system and evaluation standards have been established. The two types of shale gas exploration targets are preferred, the favorable areas of the typeⅠand the typeⅡare located in the core and wings of the anticline core in the south of the study area and wings of the gentle folds in the middle of the study area, This study provides an important reference for shale gas exploration in southeast Sichuan.
-
-
表 1 DYS1井岩石力学参数
Table 1 Rock mechanical parameters of well DYS1
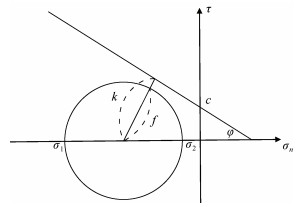
岩石类型 泊松比μ 弹性模量E/MPa 黏聚力c/MPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 密度ρ/(g·cm–3) 黑色含粉砂质泥岩 0.209 39 576.6 53.43 16.73 2.58 黑色炭质页岩 0.254 38 162.7 43.67 38.94 2.60 灰白色灰岩 0.237 35 497.1 2.82 36.78 2.65 表 2 不同单元类型岩石力学参数
Table 2 Rock mechanical parameters of different unit types
单元类型 弹性模量E/MPa 泊松比μ 黏聚力c/MPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 一级断裂 36 729 0.251 43 35 二级断裂 37 781 0.248 45 34 构造高区 39 576 0.207 44 36 构造低区 38 649 0.198 42 34 正常沉积区 38 000 0.213 40 35 表 3 东溪地区龙马溪组岩石裂缝预测的η值标准
Table 3 Predicted-η criteria for rock cracks in Longmaxi Formation in Dongxi area
η值 破裂程度 裂缝发育级别 < 0.737 不发育区 Ⅳ 0.737~1.053 发育临界区 Ⅲ > 1.053~1.368 较发育区 Ⅱ > 1.368~1.684 发育区 Ⅰ > 1.684 破坏区 断裂带 表 4 东溪地区断裂系统及断裂特征统计
Table 4 Statistical table of fracture system and fracture characteristics in Dongxi area
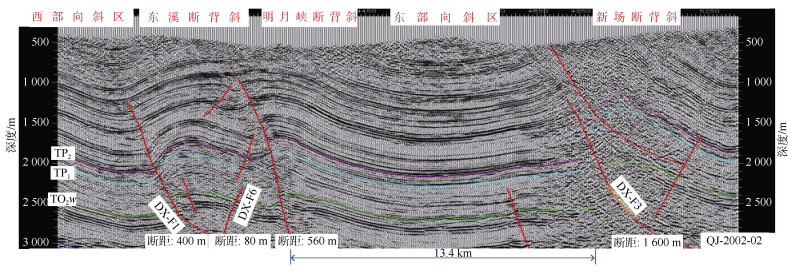
断层名称 断层性质 级别 走向 延伸距离/km 垂直断距/m 断开层位 形成时间 倾角/(°) 与现今最大主应力倾角/(°) DX-F2 逆断层 三级 NE 32.2 100 TS-TЄ 燕山晚期
Ⅰ幕55 75 DX-F3 逆断层 三级 NE 25.6 200 TP-TЄ 45 DX-F7 逆断层 四级 NE 20.1 50 TS-TЄ 65 DX-F1 逆断层 三级 NNW 32.0 700 TP-TЄ 燕山晚期Ⅱ幕 50 85 DX-F4 逆断层 四级 NNW 6.7 20 TS-TЄ 60 DX-F5 逆断层 四级 NNW 8.8 30 TS-TЄ 55 DX-F6 逆断层 四级 NNW 17.2 200 TS-TЄ 60 注释:TS表示时间域志留系;TP表示时间域二叠系;TЄ表示时间域寒武系。 表 5 东溪地区龙马溪组页岩气评价参数
Table 5 Shale gas evaluation parameters in Longmaxi Formation in Dongxi area
因素(一级权重) 评价参数(二级权重) 评分等级 好(1.0) 较好(0.75) 一般(0.5) 差(0.25) 埋深/m(0.2) 4 500~5 000 4 000~4 500 > 5 000 < 4 000 距剥蚀区距离/km(0.1) > 15 10~15 5~10 < 5 距齐岳山断裂距离/km(0.1) > 10 5~10 5~2 < 2 断裂作用(0.25) 次级断裂规模—断裂垂直断距/m (0.2) < 60 60~100 100~200 > 200 断裂分级分期(0.2) 早期Ⅲ、Ⅳ级 晚期Ⅰ、Ⅱ级 距离较大规模次级断裂(断距 > 150 m)水平距离/km (0.3) > 2 1~2 0.5~1 < 0.5 次级断裂倾角(0.2) < 45 45~55 55~65 > 65 裂缝发育程度(0.1) Ⅱ级发育区 Ⅲ级发育区 Ⅰ级发育区或欠发育区 应力差(0.15) 低 中 高 压力系数(0.2) > 1.4 1.2~1.4 0.9~1.2 < 0.9 -
[1] 邹才能, 杨智, 张国生, 等. 常规-非常规油气"有序聚集"理论认识及实践意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1): 14-27. ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Conventional and unconventional petroleum"orderly accumulation": Concept and practical significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1): 14-27.
[2] CURTIS J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1921-1938. http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=refg13/ref13&dbid=16&doi=10.1139%2Fcjes-2014-0188&key=10.1306%2F61EEDDBE-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
[3] FENG Weiping, WANG Feiyu, GUAN Jing, et al. Geologic structure controls on initial productions of Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale in south China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 91: 163-178. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.01.001
[4] 周文. 裂缝性油气储集层评价方法[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 1998. ZHOU Wen. Evaluation methods of fracture reservoir in oil and gas pool[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1998.
[5] 徐旭辉, 申宝剑, 李志明, 等. 页岩气实验地质评价技术研究现状及展望[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(1): 1-8. XU Xuhui, SHEN Baojian, LI Zhiming, et al. Status and prospect of experimental technologies of geological evaluation for shale gas[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(1): 1-8.
[6] 魏志红. 四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气的晚期逸散[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(4): 659-665. WEI Zhihong. Late fugitive emission of shale gas from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2015, 36(4): 659-665.
[7] 蔡周荣, 夏斌, 万志峰. 下扬子芜湖地区后期构造活动特征及其对古生界页岩气保存的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5): 890-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201305032.htm CAI Zhourong, XIA Bin, WAN Zhifeng. Characteristics of late tectonic activity in Wuhu and its influence on shale gas conservation in Paleozoic boundary[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(5): 890-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201305032.htm
[8] 任浩林, 刘成林, 刘文平, 等. 四川盆地富顺-永川地区五峰组-龙马溪组应力场模拟及裂缝发育区预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(1): 74-83. REN Haolin, LIU Chenglin, LIU Wenping, et al. Stress field simulation and fracture development prediction of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Fushun-Yongchuan Block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(1): 74-83.
[9] 张守仁, 万天丰, 陈建平. 川西坳陷孝泉-新场地区须家河组二-四段构造应力场模拟及裂缝发育区带预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004(1): 70-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200401012.htm ZHANG Shouren, WAN Tianfeng, CHEN Jianping. Tectonic stress field modeling and fracture prediction in T3x2-4 strata in Xiaoquan-Xinchang area, western Sichuan depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004(1): 70-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200401012.htm
[10] 聂海宽, 何治亮, 刘光祥, 等. 中国页岩气勘探开发现状与优选方向[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(1): 13-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202001002.htm NIE Haikuan, HE Zhiliang, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Status and direction of shale gas exploration and development in China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(1): 13-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202001002.htm
[11] 胡东风, 张汉荣, 倪楷, 等. 四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 17-23. HU Dongfeng, ZHANG Hanrong, NI Kai, et al. Main controlling factors for gas preservation conditions of marine shales in southeastern margins of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6): 17-23.
[12] 王濡岳, 胡宗全, 刘敬寿, 等. 中国南方海相与陆相页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素对比: 以黔北岑巩地区下寒武统为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(4): 631-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804002.htm WANG Ruyue, HU Zongquan, LIU Jingshou, et al. Comparative analysis of characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in marine and continental shales: A case study of the Lower Cambrian in Cengong area, northern Guizhou Province[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(4): 631-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804002.htm
[13] 魏祥峰, 李宇平, 魏志红, 等. 保存条件对四川盆地及周缘海相页岩气富集高产的影响机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2): 147-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201702002.htm WEI Xiangfeng, LI Yuping, WEI Zhihong, et al. Effects of preservation conditions on enrichment and high yield of shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 147-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201702002.htm
[14] SURPLESS B, WIGGINTON S S. The impact of inter-bed cohesion on fold-related fracture development, still well anticline, west Texas(USA)[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2020, 134: 103974. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191814119302998
[15] GAO Jian, ZHANG Jiankun, HE Sheng, et al. Overpressure generation and evolution in Lower Paleozoic gas shales of the Jiaoshiba region, China: Implications for shale gas accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 844-859. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000041591127699_86fc.html
[16] GUO Peng, REN Desheng, XUE Yanhui. Simulation of multi-period tectonic stress fields and distribution prediction of tectonic fractures in tight gas reservoirs: A case study of the Tianhuan depression in western Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 530-546. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817219302788
[17] JU Wei, WANG Jilin, FANG Huihuang, et al. Paleotectonic stress field modeling and prediction of natural fractures in the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale reservoirs, Nanchuan region, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 100: 20-30. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040909731010_52f6.html
[18] 耿一凯. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩储层质量控制因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017. GENG Yikai. Controlling factors on quality of shale reservoir of Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2017.
[19] 尤广芬. 储层裂缝预测的三维有限元数值模拟研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010. YOU Guangfen. Reservoir fracture prediction of three-dimensional finite element numerical simulation[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010.
[20] 丁文龙, 尹帅, 王兴华, 等. 致密砂岩气储层裂缝评价方法与表征[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(4): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201504022.htm DING Wenlong, YIN Shuai, WANG Xinghua, et al. Assessment method and characterization of tight sandstone gas reservoir fractures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(4): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201504022.htm
[21] 曾海容, 宋惠珍. 断裂端部特殊单元模型[J]. 地震地质, 1999, 21(3): 215-220. ZENG Hairong, SONG Huizhen. A special model for the tip of faults[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1999, 21(3): 215-220.
[22] 曾维特. 渝东南地区下古生界页岩储层裂缝发育特征与分布预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. ZENG Weite. The characteristics and distribution prediction of fractures in Lower Palaeozoic shale, southeast of Chongqing area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2014.
[23] LIU Jingshou, DING Wenlong, WANG Ruyue, et al. Simulation of paleo tectonic stress fields and quantitative prediction of multi-period fractures in shale reservoirs: A case study of the Niutitang Formation in the Lower Cambrian in the Cen'gong block, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 84: 289-310. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817217301356
[24] GUO Xusheng. Major factors controlling the shale gas accumulations in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation of the Pingqiao shale gas field in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 4(3): 129-138. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468256X19300355
[25] 谢佳彤, 秦启荣, 李斌, 等. 塔里木盆地中央隆起带良里塔格组预探阶段有利区带评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(6): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201806005.htm XIE Jiatong, QIN Qirong, LI Bin, et al. Favorable zone evaluation of Lianglitage Formation within pre-exploration stage in the central uplift of Tarim Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(6): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201806005.htm
[26] 漆艳茹. 确定指标权重的方法及应用研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2010. QI Yanru. The method of determining index weight and its application research[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2010.
[27] 翟常博. 川东南綦江-仁怀地区页岩气成蔵条件及有利目标区研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. ZHAI Changbo. Reservoir forming condition and exploration prospect of shale-gas in Qijiang-Renhuai area of southeast Sichuan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2013.
[28] 殷启春, 方朝刚, 郑红军, 等. 下扬子地区奥陶纪页岩气地质条件及远景区优选[J]. 华东地质, 2020, 41(1): 70-78. YIN Qichun, FANG Chaogang, ZHENG Hongjun, et al. Geological conditions of Ordovician shale gas and optimization for prospective areas in the Lower Yangtze region[J]. East China Geology, 2020, 41(1): 70-78.
[29] XIE Jiatong, QIN Qirong, FAN Cunhui. Quantitative prediction of fracture distribution of the Longmaxi Formation in the Dingshan area, China using FEM numerical simulation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 2019, 93(6): 1662-1672. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxbcn/uploadfile/dzxbcn/20190314/XIE%20Jiatong,%20QIN%20Qirong,%20Fan%20Cunhui.pdf







 下载:
下载: