Dynamic gas supply mechanism and theoretical production modes of free gas-rich deep coal reservoirs
-
摘要:目的和方法
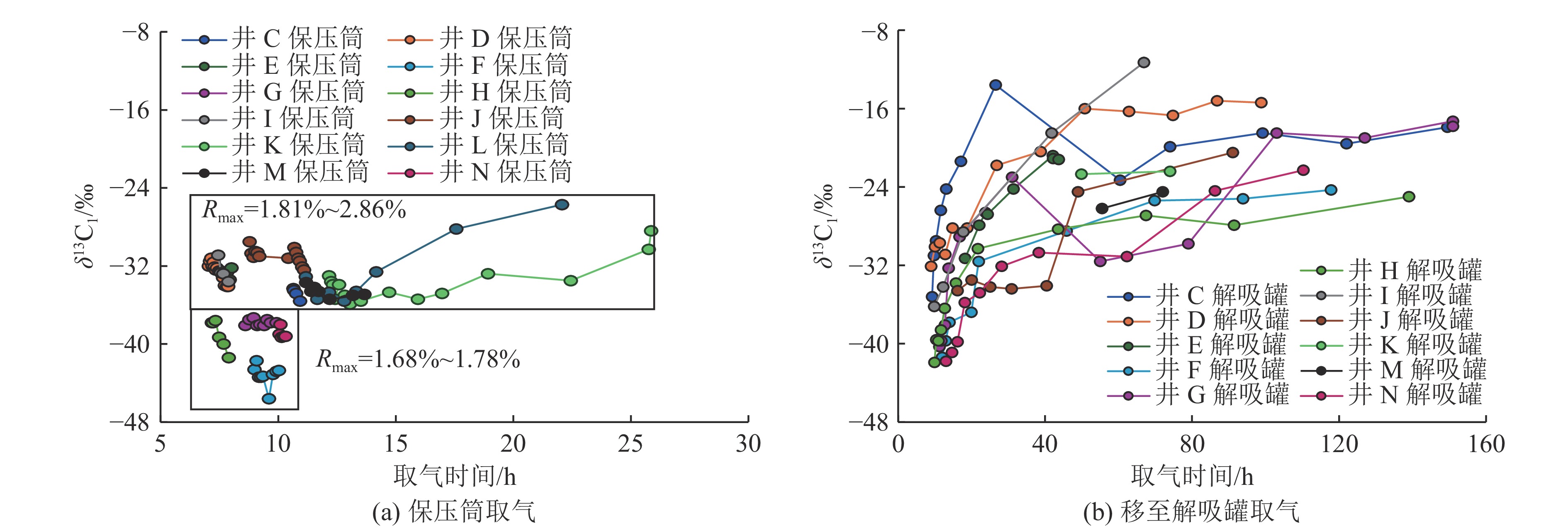
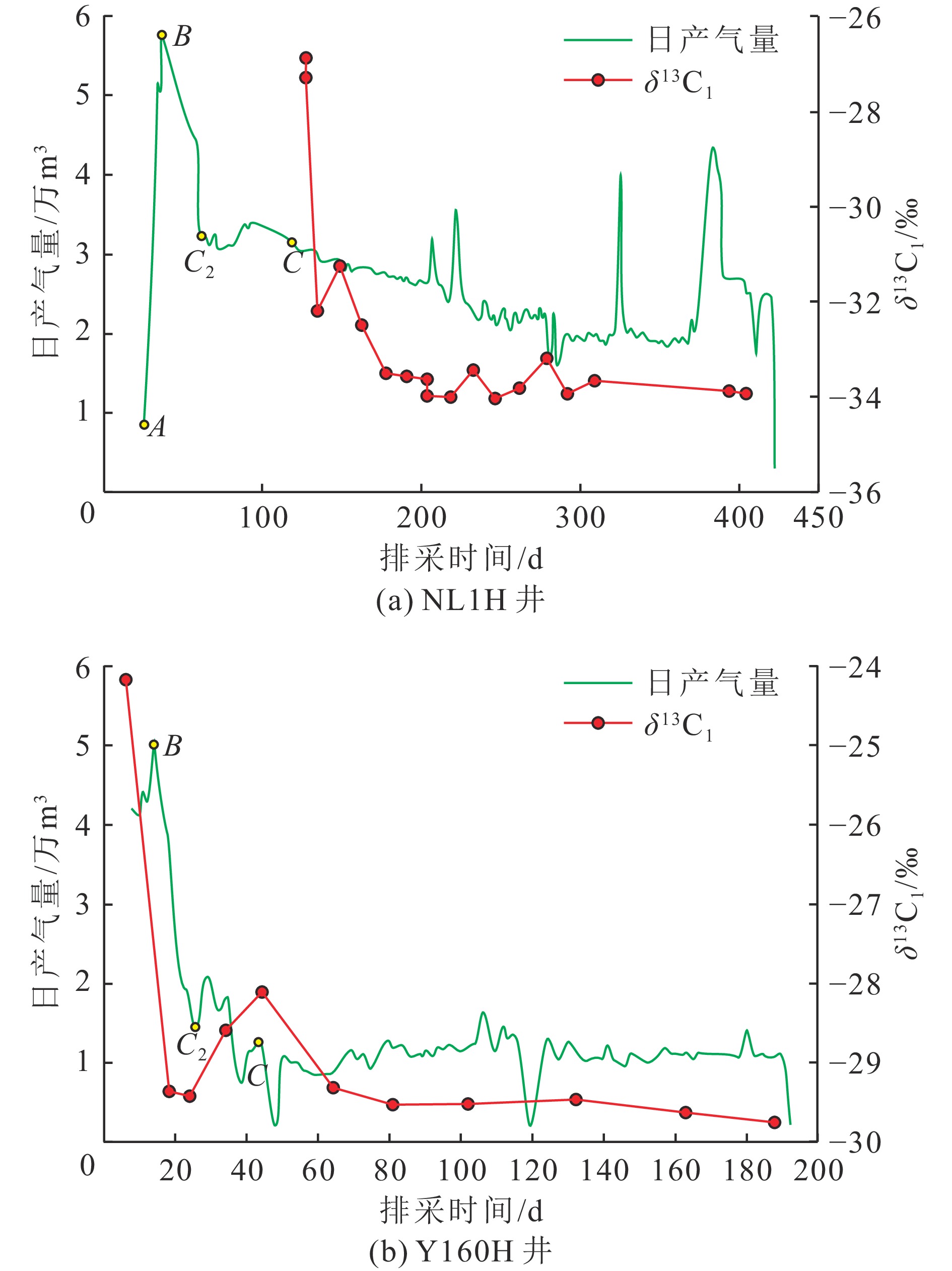
吸附气、游离气产出过程及其产出效率的动态配分机制是深部煤层气勘探开发亟待解决的关键科学问题。基于探井取心测试化验数据,系统分析了深部煤层气资源的理论可动性,结合数学/数值模型构建、甲烷碳同位素监测和排采曲线解剖,揭示了排采诱导的储层压降扩展、吸附气解吸扩散、游离气渗流的时空演化过程及其产出效应,提出了深部富游离气煤储层多态甲烷协同供气机制和理论生产模式。
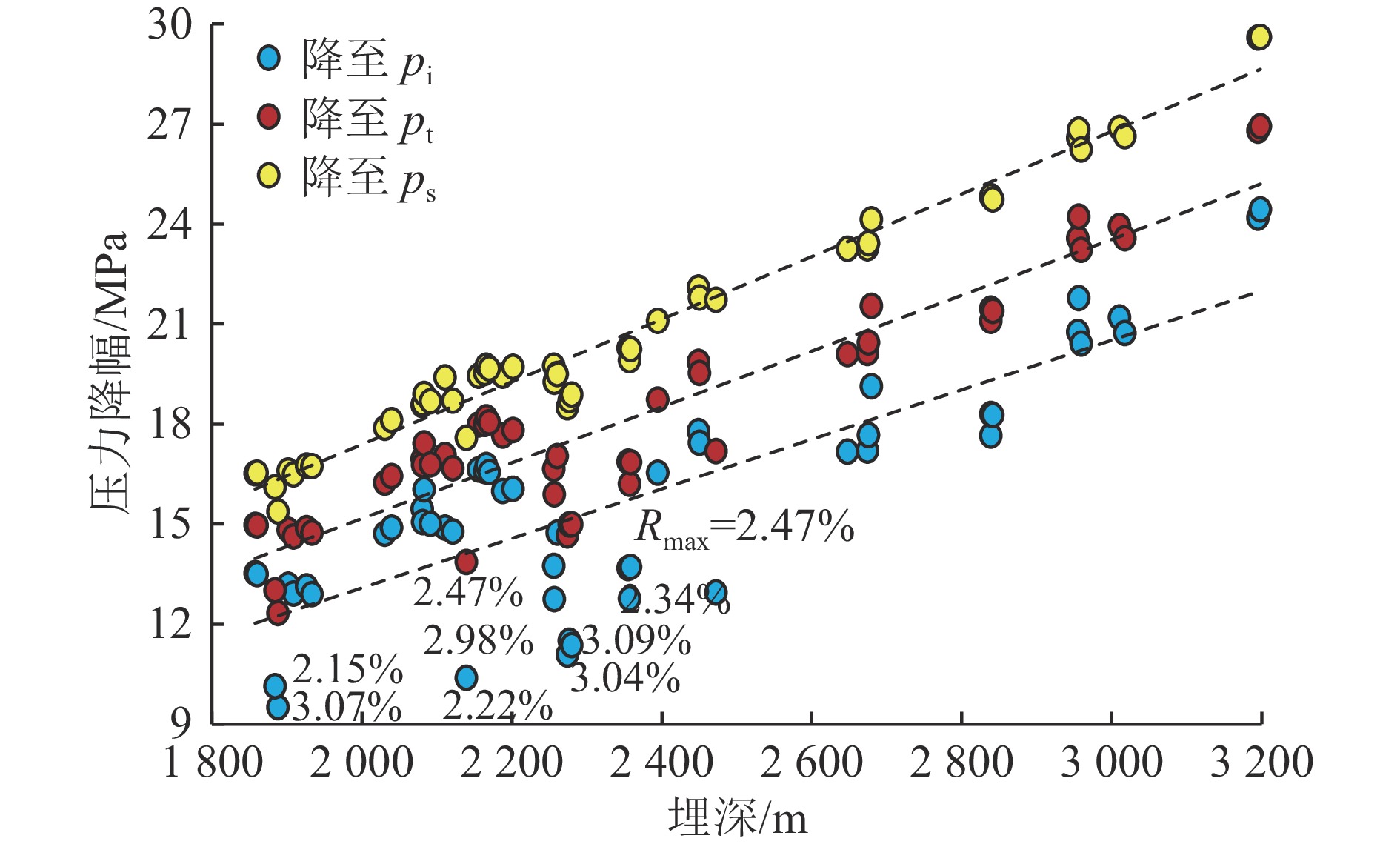
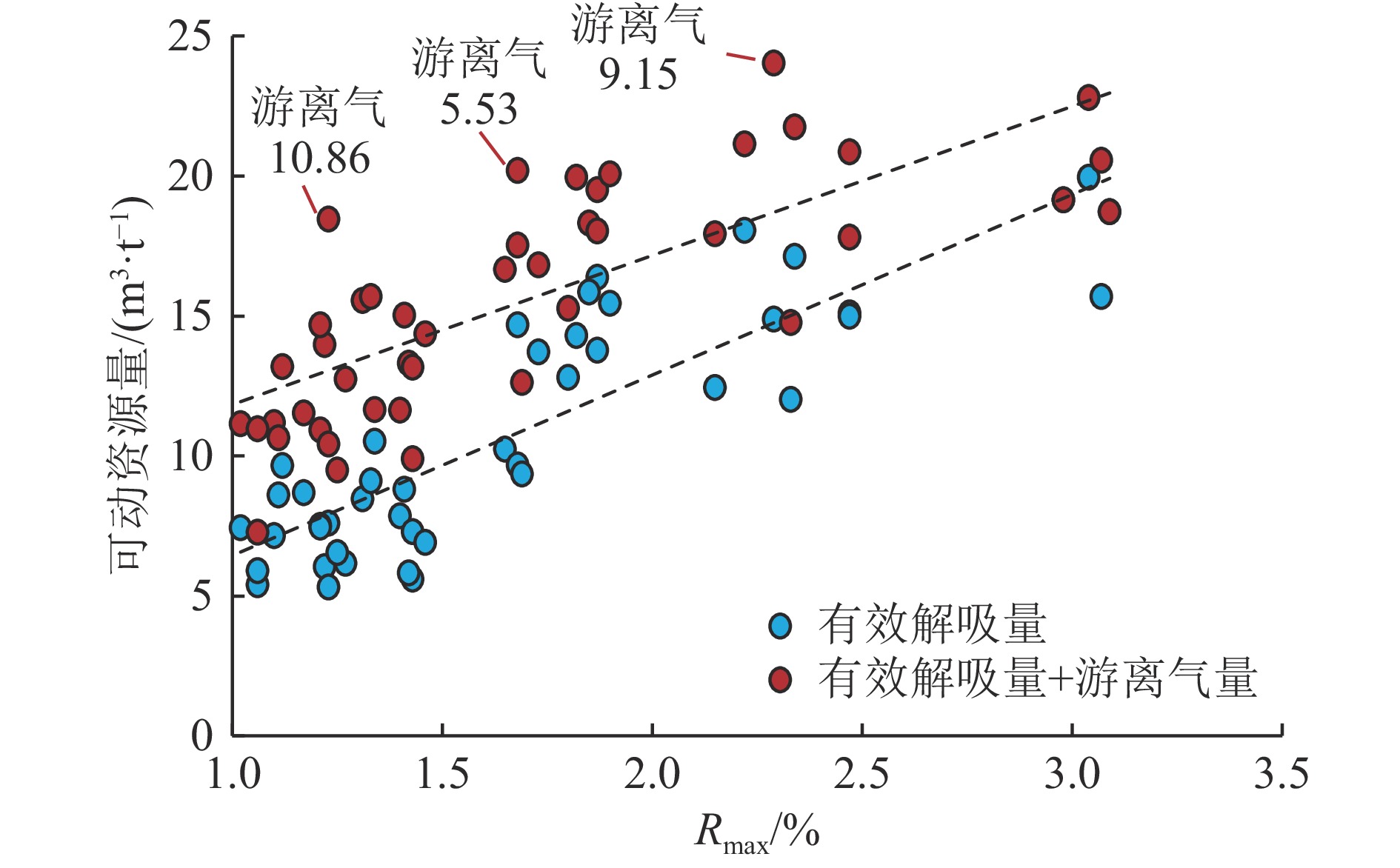
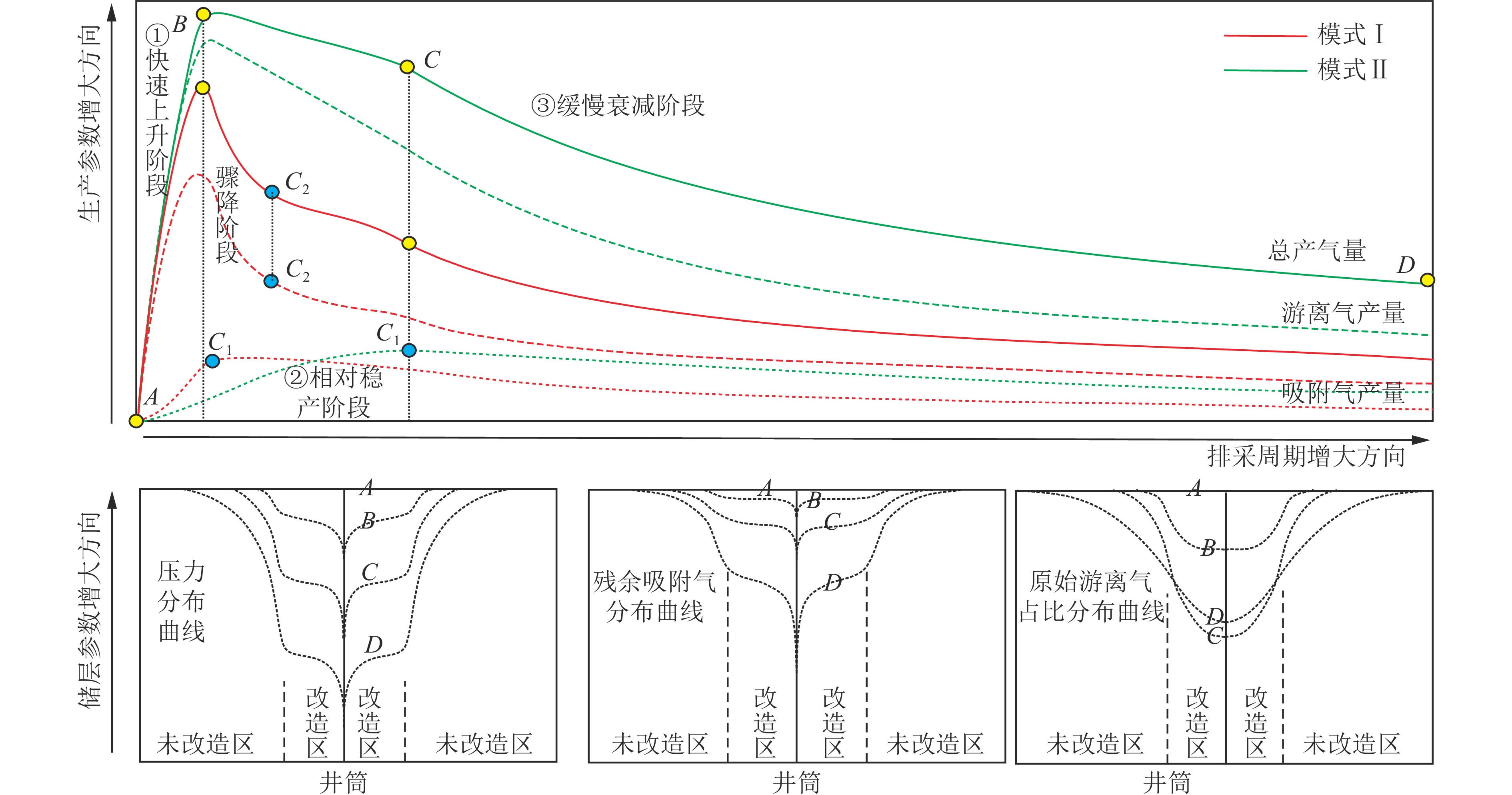
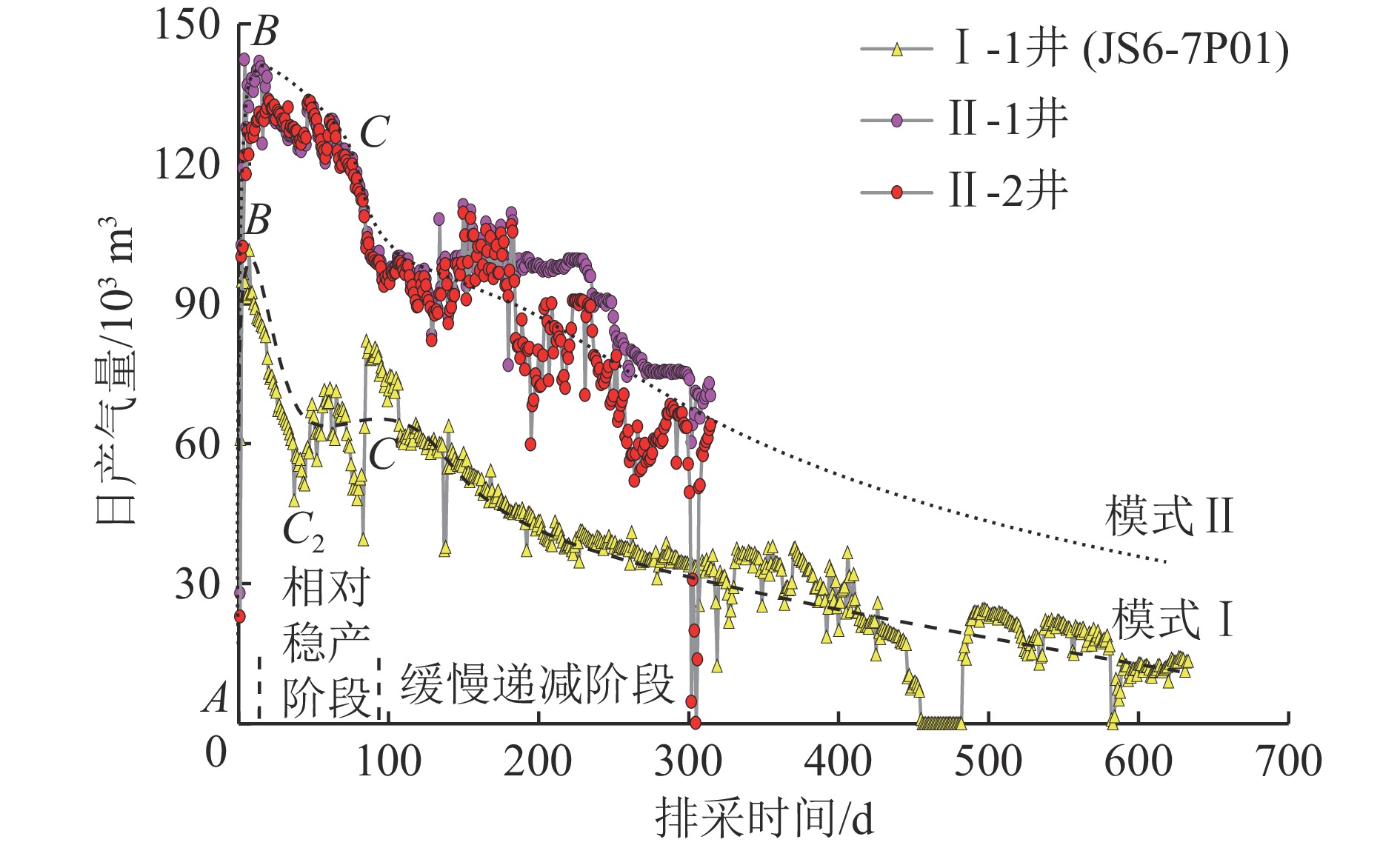
结果和结论(1) 深部煤层气井生产过程中,游离气和吸附气具备“连续−协同”的供气特点和“竞争产出”的配分关系,任意时刻产出气均为二者的混合气,不同赋存态甲烷的动态配分比例取决于不同生产阶段压力传播域内以“降压诱导解吸、压差驱动渗流”为核心的游离气传质效率和吸附气解吸补充效率的叠合。(2) 深部煤储层将经历解吸全过程,降至关键解吸节点所需压力降幅较大,初期高储层压力−低解吸效率与后期高解吸效率−低压降空间的矛盾难以调和,压降漏斗内吸附气平均解吸率偏低且供气单元主要集中在高渗改造区,游离气供气半径可持续拓展并始终占据较大产量比重,高密度井组联采或气−水分布的强非均质性会导致吸附气−游离气产出占比发生调整,调整过程取决于供气单元拓展与流体供给能力的动态匹配关系。(3) 游离气和吸附气分别具有“骤增−缓降或骤增−骤降−缓降”和“缓增−趋稳−缓降”的生产特征,总体产能存在快速上产、相对稳产和缓慢递减3个主要阶段,排采曲线形态受控于游离气量、原位渗透率、储层改造效果、排采降压制度等因素,部分井在相对稳产阶段存在先骤降后趋稳2个次级阶段。(4) 增大改造体积、提高水平段长、寻找富游离气−高孔渗区段是增产核心,探索提高吸附气解吸效率和压降下沉幅度的工艺技术是增加下探深度的关键,兼顾气井生命周期和流体产出效率构建“动态调控排采制度”是产能充分释放的重要前提。(5) 以地质−工程一体化原理为指导,合理确定深部不同地质单元煤层气产能目标及其所需井控面积,协同优化钻完井方式、井网密度、压裂参数、配产速率和生产周期,是深部煤层气效益建产的重要攻关方向。
Abstract:Objective and MethodsThe production processes of adsorbed and free gases and the dynamic partitioning mechanism behind the production efficiency of both gas types are critical scientific issues to be addressed urgently in the exploration and production of deep coalbed methane (CBM). Based on the test and assay data of cores from exploration wells, this study systematically analyzed the theoretical production of deep CBM resources. By integrating the building of mathematical and numerical models, carbon isotope monitoring of methane, and the analysis of production curves, this study revealed the spatiotemporal evolutionary processes of production-induced pressure drop expansion, adsorbed gas desorption, and free gas seepage, as well as their production effects. Finally, this study determined the synergistic gas supply mechanism and theoretical production modes of methane with multiple occurrence states in free gas-rich deep coal reservoirs.
Results and ConclusionsDuring the production of a deep CBM well, free and adsorbed gases exhibited a continuous, synergistic gas supply characteristic and a partitioning relationship characterized by competitive production, with the produced gas identified as a mixture of both gas types at any given time. The dynamic partitioning ratios of methane with varying occurrence states depended on the superposition of free gas mass transfer efficiency and adsorbed gas desorption efficiency within the pressure propagation domain in varying production stages, with the efficiencies centering on pressure drop-induced desorption and differential pressure-driven seepage. Deep coal reservoirs would experience an entire desorption process, with substantial pressure drop required to reach critical desorption nodes. It is challenging to resolve the inherent contradiction between the high reservoir pressure and low desorption efficiency in the early stage and the high desorption efficiency and limited pressure drop in the late stage. The pressure drop funnel, adsorbed gas exhibited a relatively low average desorption rate, with gas supply units concentrated primarily in high-permeability stimulated zones. Free gas showed a continuously expanding supply radius and a consistently high production proportion. High-density well group co-production or the heterogeneity of gas-water distribution can lead to adjustments in the adsorbed and free gas proportion, and the adjustment process depend on the dynamic matching relationship between gas supply unit expansion and fluid supply capacity. Free and adsorbed gases demonstrated the production characteristics of sharp increase - gentle decline (or sharp increase - sharp decline - gentle decline) and gentle increase - stability - gentle decline, respectively. Their overall production capacity can be divided into three stages primarily: rapid addition, relative stability, and slow decline. The morphologies of production curves were influenced by free gas volume, in-situ permeability, reservoir stimulation performance, and pressure drop system. For some wells, the relatively stable production stage can be further divided into two substages: sharp production decline followed by stable production. The core strategies for production growth include increasing the stimulated reservoir volume, extending the horizontal sections of wells, and pinpointing free gas-rich zones with high porosity and permeability. Meanwhile, the key to an increase in the exploration depths of deep CBM is to explore technologies for enhancing both the desorption efficiency of adsorbed gas and the overall influential depth of pressure drop. Constructing a “dynamic regulation system for drainage and production” that balances gas well lifecycle and fluid production efficiency forms the critical foundation for fully releasing production potential. Furthermore, the first priority for commercial production capacity construction of deep CBM is determining rational production capacity targets and required well-controlled areas for varying deep geological units and synergistically optimizing well completion methods, well pattern density, fracturing parameters, production allocation rates, and production cycles under the guidance of geological and engineering integration.
-
Keywords:
- deep coalbed methane (CBM) /
- adsorbed gas /
- free gas /
- production mechanism /
- production mode
-
-
表 1 基础物理场相关参数设置
Table 1 Settings of fundamental physical parameters
参数 取值(SI) 参数名 $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{B}} $ 0.8 比沃系数 $ {C}_{\text{φ}} $/MPa−1 0.13 孔隙率模量 $ {C}_{\mathrm{k}1} $/MPa−1 0.15 未改造区渗透率模量 $ {C}_{\mathrm{k}2} $/MPa−1 0.10 改造区渗透率模量 $ \varepsilon $ 0.0092 单位吸附量应变 $ K $/MPa 2250 体积模量 $ {k}_{10} $/10−3 µm2 0.1 未改造区初始渗透率 $ {k}_{20} $/10−3 µm2 10 改造区初始渗透率 $ {\varphi }_{0} $/% 2 初始孔隙率 $ {\rho }_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} $/(kg·m−3) 1500 煤的密度 $ {V}_{\mathrm{L}} $/(m3·t−1) 23.02 Langmuir体积 $ {p}_{\mathrm{L}} $/MPa 3.02 Langmuir压力 $ D $/10−6(m2·s−1) 4 扩散系数 $ {F}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}} $/104 m−2 240 形状因子 -
[1] 秦勇. 中国深部煤层气地质研究进展[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1791−1811. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311004 QIN Yong. Progress on geological research of deep coalbed methane in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1791−1811. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311004
[2] 康永尚,闫霞,皇甫玉慧,等. 深部超饱和煤层气藏概念及主要特点[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1781−1790. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311003 KANG Yongshang,YAN Xia,HUANGFU Yuhui,et al. Concept and main characteristics of deep oversaturated coalbed methane reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1781−1790. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311003
[3] 徐凤银,闫霞,李曙光,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部(层)煤层气勘探开发理论技术难点与对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):115−130. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.06.0503 XU Fengyin,YAN Xia,LI Shuguang,et al. Theoretical and technological difficulties and countermeasures of deep CBM exploration and development in the eastern edge of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):115−130. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.06.0503
[4] 陈世达,侯伟,汤达祯,等. 煤储层含气性深度效应与成藏过程耦合关系[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):52−59. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0670 CHEN Shida,HOU Wei,TANG Dazhen,et al. Effects of depth on gas–bearing properties of coal reservoirs and their coupling relationships with coalbed methane accumulation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):52−59. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0670
[5] 李国欣,张水昌,何海清,等. 煤岩气:概念、内涵与分类标准[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2024,51(4):783−795. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20240424 LI Guoxin,ZHANG Shuichang,HE Haiqing,et al. Coal–rock gas:Concept,connotation and classification criteria[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2024,51(4):783−795. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20240424
[6] 熊先钺,闫霞,徐凤银,等. 深部煤层气多要素耦合控制机理、解吸规律与开发效果剖析[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1812−1826. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311005 XIONG Xianyue,YAN Xia,XU Fengyin,et al. Analysis of multi–factor coupling control mechanism,desorption law and development effect of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1812−1826. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311005
[7] 聂志宏,徐凤银,时小松,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气开发先导试验效果与启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):1−12. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0645 NIE Zhihong,XU Fengyin,SHI Xiaosong,et al. Outcomes and implications of pilot tests for deep coalbed methane production on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):1−12. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0645
[8] 陈世达,汤达祯,侯伟,等. 深部煤层气地质条件特殊性与储层工程响应[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1993−2006. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311018 CHEN Shida,TANG Dazhen,HOU Wei,et al. Geological particularity and reservoir engineering response of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1993−2006. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311018
[9] 张政,秦勇,WANG Guoxiong,等. 基于等温吸附实验的煤层气解吸阶段数值描述[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2013,43(8):1352−1358. ZHANG Zheng,QIN Yong,WANG Guoxiong,et al. Numerical description of coalbed methane desorption stages based on isothermal adsorption experiment[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences,2013,43(8):1352−1358.
[10] 孟艳军,汤达祯,许浩,等. 煤层气解吸阶段划分方法及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(5):612−617. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.14 MENG Yanjun,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. Division of coalbed methane desorption stages and its significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014,41(5):612−617. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.14
[11] 石军太,徐凤银,曹运兴,等. 基于煤储层改造背景下深部煤层气藏物质平衡方程的建立与应用[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术,2025:1–19 [2025-03-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20250318.1319.002.html. SHI Juntai,XU Fengyin,CAO Yunxing,et al. Establishment and application of material balance equation for deep coalbed methane reservoirs based on coal formation stimulation background[J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology,2025:1–19 [2025-03-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.TD.20250318.1319.002.html.
[12] 陈明,王大猛,余莉珠,等. 大宁–吉县区块深部煤层气井排采制度研究与实践[J/OL]. 煤炭学报,2024:1–11 [2025-03-19]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2024.0318 CHEN Ming,WANG Dameng,YU Lizhu,et al. Drainage system research and application of deep coalbed methane gas reservoirs in the Daning–Jixian Block[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024:1–11 [2025-03-19]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2024.0318.
[13] 李曙光,王成旺,王红娜,等. 大宁–吉县区块深层煤层气成藏特征及有利区评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(9):59−67. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0842 LI Shuguang,WANG Chengwang,WANG Hongna,et al. Reservoir forming characteristics and favorable area evaluation of deep coalbed methane in Daning–Jixian Block[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022,50(9):59−67. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0842
[14] 江同文,熊先钺,金亦秋. 深部煤层气地质特征与开发对策[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1918−1930. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311013 JIANG Tongwen,XIONG Xianyue,JIN Yiqiu. Geological characteristics and development countermeasures of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1918−1930. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311013
[15] 王振至,傅雪海,潘结南,等. 深部储层煤层气产出影响因素[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2025,53(2):84−98. WANG Zhenzhi,FU Xuehai,PAN Jienan,et al. Factors influencing the production of coalbed methane from deep reservoirs[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2025,53(2):84−98.
[16] 康永尚,王金,姜杉钰,等. 量化指标在煤层气开发潜力定量评价中的应用[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(6):677−686. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201706007 KANG Yongshang,WANG Jin,JIANG Shanyu,et al. Application of quantitative indexes in quantitative evaluation of coalbed methane development potential[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2017,38(6):677−686. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201706007
[17] 秦勇,郑长东,王博洋,等. 基于等温吸附曲线的煤储层产气潜力定量评价:以黔北地区长岗矿区为例[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(9):40−47. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.005 QIN Yong,ZHENG Changdong,WANG Boyang,et al. Quantitative evaluation on the gas production potential of coal reservoirs based on isothermal adsorption curves:A case study of the Changgang Field,northern Guizhou,China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(9):40−47. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.005
[18] 陈世达,汤达祯,侯伟,等. 煤储层流体特征、聚气主控因素及富气模式:以鄂尔多斯盆地中东部上古生界为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2025,52(2):1−10. CHEN Shida,TANG Dazhen,HOU Wei,et al. Fluid characteristics,gas accumulation control factors and gas enrichment modes in coal reservoirs:A case study of the Upper Paleozoic in the central–eastern Ordos Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2025,52(2):1−10.
[19] 李站伟,陈世达,陶树,等. 黔西–滇东地区煤岩吸附–解吸特征及其对多层合采的指示意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2021,28(1):125−131. LI Zhanwei,CHEN Shida,TAO Shu,et al. CBM adsorption–desorption characteristics of coal in western Guizhou–eastern Yunnan region and its significance to commingled production[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2021,28(1):125−131.
[20] 李勇,徐立富,张守仁,等. 深煤层含气系统差异及开发对策[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(2):900−917. LI Yong,XU Lifu,ZHANG Shouren,et al. Gas bearing system difference in deep coal seams and corresponded development strategy[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(2):900−917.
[21] 康永尚,邓泽,皇甫玉慧,等. 中煤阶煤层气高饱和–超饱和带的成藏模式和勘探方向[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(12):1555−1566. KANG Yongshang,DENG Ze,HUANGFU Yuhui,et al. Accumulation model and exploration direction of high–to over–saturation zone of the medium–rank coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2020,41(12):1555−1566.
[22] 傅雪海,秦勇,韦重韬. 煤层气地质学[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2007. [23] 郭建春,张涛,武玺,等. 煤层气压裂水平井生产动态分析及其渗透率协同演化机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2025,50(1):516−531. GUO Jianchun,ZHANG Tao,WU Xi,et al. Production analysis and permeability evolution of fractured horizontal wells of coalbed methane reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2025,50(1):516−531.
[24] LANGMUIR I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute,1917,183(1):102−105.
[25] 石军太,李相方,徐兵祥,等. 煤层气解吸扩散渗流模型研究进展[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2013,43(12):1548–1557. SHI Juntai,LI Xiangfang,XU Bingxiang,et al. Review on desorption–diffusion–flow model of coal–bed methane[J]. Science China:Physics,Mechanics & Astronomy,2013,43(12):1548–1557.
[26] 董骏. 基于等效物理结构的煤体瓦斯扩散特性及应用[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2018. DONG Jun. Gas diffusion properties of coal mass based on equivalent physical structure and its application[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2018.
[27] ZHANG Taiyuan,CHEN Shida,TANG Dazhen. Anisotropic evolution of effective stress and pore pressure during coalbed methane drainage[J]. SPE Journal,2023,28(5):2534−2546.
[28] 张泰源. 倾角制约下储层流体传质机理及煤层气产出效应[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2024. ZHANG Taiyuan. Mechanism of reservoir fluid mass transfer and effect of coalbed methane production under dip angle constraint[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2024.
[29] 史锐,边利恒,张伟,等. 基于有效孔隙度的深部煤层游离气含量预测模型[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2025,54(1):161−171. SHI Rui,BIAN Liheng,ZHANG Wei,et al. Prediction model for free gas content in deep coal seams based on effective porosity[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2025,54(1):161−171.
[30] 孔祥言. 高等渗流力学(第3版)[M]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社,2020. [31] HENRY D. Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon[M]. Paris,1856.
[32] PAN Zhejun,CONNELL L D. Modelling permeability for coal reservoirs:A review of analytical models and testing data[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2012,92:1−44.
[33] ZHANG Taiyuan,TANG Shuling,TANG Dazhen,et al. Measurement of pore distribution and compression anisotropy by nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Natural Resources Research,2023,32(2):755−770.
[34] REISABADI M Z,HAGHIGHI M,SAYYAFZADEH M,et al. Stress distribution and permeability modelling in coalbed methane reservoirs by considering desorption radius expansion[J]. Fuel,2021,289:119951. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119951
[35] MEN Xinyang,TAO Shu,LIU Zhenxing,et al. Experimental study on gas mass transfer process in a heterogeneous coal reservoir[J]. Fuel Processing Technology,2021,216:106779. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106779
[36] 胡秋嘉,毛崇昊,石斌,等. 沁水盆地南部高煤阶煤层气井“变速排采–低恒套压”管控方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(6):1795−1803. HU Qiujia,MAO Chonghao,SHI Bin,et al. “Variable speed drainage–low casing pressure” control method of high rank CBM wells in south Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(6):1795−1803.
[37] 李文镖,卢双舫,李俊乾,等. 页岩气/煤层气运移过程中的同位素分馏研究进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2022,49(5):929−942. LI Wenbiao,LU Shuangfang,LI Junqian,et al. Research progress on isotopic fractionation in the process of shale gas/coalbed methane migration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2022,49(5):929−942.
[38] 李文镖,卢双舫,李俊乾,等. 页岩气运移过程中的碳同位素分馏:机理、表征及意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2020,50(4):553−569. LI Wenbiao,LU Shuangfang,LI Junqian,et al. Carbon isotope fractionation during shale gas transport:Mechanism,characterization and significance[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences,2020,50(4):553−569.
[39] 张道锋,孟康,黄有根,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地石炭系本溪组煤岩解析气甲烷碳同位素特征及其地质意义[J/OL]. 天然气地球科学,2025:1–24 [2025-03-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.te.20250225.1906.006.html. ZHANG Daofeng,MENG Kang,HUANG Yougen,et al. Characteristics and geological significance of methane carbon isotope of released gas from Carboniferous Benxi coal rock in Ordos Basin[J/OL]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2025:1–24 [2025-03-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.te.20250225.1906.006.html.
[40] 刘洪林,王红岩,赵国良,等. 稳定碳同位素δ13C1在煤层气田勘探中的应用[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2004,24(4):442−446. LIU Honglin,WANG Hongyan,ZHAO Guoliang,et al. Application of coal bed methane stable carbon isotope in exploration of coal bed methane field[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2004,24(4):442−446.
[41] 胡国艺,李谨,马成华,等. 沁水煤层气田高阶煤解吸气碳同位素分馏特征及其意义[J]. 地学前缘,2007,14(6):267−272. HU Guoyi,LI Jin,MA Chenghua,et al. Characteristics and implications of the carbon isotope fractionation of desorbed coalbed methane in Qinshui coalbed methane field[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2007,14(6):267−272.
[42] GAO Li,WU Sheng,DEEV A,et al. The gas isotope interpretation tool:A novel method to better predict production decline[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2017,101(8):1263−1275.
[43] ZHANG Mingjie,TANG Qingyan,CAO Chunhui,et al. Molecular and carbon isotopic variation in 3. 5 years shale gas production from Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2018,89:27–37.
[44] SHI Wenrui,WANG Xingzhi,ZHANG Chaomo,et al. Experimental study on gas content of adsorption and desorption in Fuling shale gas field[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2019,180:1069−1076.
[45] 黄道军,周国晓,杨兆彪,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地深部煤岩气井产出气–水地球化学特征及其地质响应[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2024,45(6):1617−1627. DOI: 10.11743/ogg20240609 HUANG Daojun,ZHOU Guoxiao,YANG Zhaobiao,et al. Geochemical characterization of gas–water output from deep coalrock methane wells in the Ordos Basin and its geological responses[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2024,45(6):1617−1627. DOI: 10.11743/ogg20240609
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张旭辉,解彦彬,杨文娟,张超,万继成,董征,王彦群,蒋杰,李龙. 煤矿井下采掘工作场景非均质图像去雾与增强技术. 煤田地质与勘探. 2025(01): 245-256 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张铁聪,陈华州,赵俊杰,王利景,贾冬冬. 基于数字孪生技术的煤矿掘进机自动截割方法研究. 中国煤炭. 2024(01): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾澎涛,靳路伟,王斌,郭风景,李娜. 采煤机截割部低照度图像的边缘检测技术. 煤田地质与勘探. 2024(04): 172-178 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 张旭辉,王悦,杨文娟,陈鑫,张超,黄梦瑶,刘彦徽,杨骏豪. 基于改进最佳缝合线的矿井图像拼接方法. 工矿自动化. 2024(04): 9-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 汪进超,韩增强,王益腾,王超,张国华. 基于像素空间信息的孔内低照度图像孔隙结构量化方法研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(S1): 3175-3186 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 丁序海,张侯,陈录平,党国杰. 基于多频无线电坑透技术的煤矿地质综合勘探研究. 能源与环保. 2024(06): 82-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 肖耀猛. 目标背景对比度优化下高煤尘低照度环境主动成像技术. 矿山机械. 2024(09): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陶荣颖,王守军,李南,朱伟. 煤矿副井口全景智能识别技术的研究与应用. 内蒙古煤炭经济. 2024(22): 154-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载: