Stratigraphic characteristics and shale gas enrichment interval distribution of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation, Upper Yangtze region, China
-
摘要:目的
上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩不仅保留重要的原始沉积海洋信息,更是重要的烃源岩和储集层,已展示出巨大的页岩气勘探潜力。
方法基于地震、钻井和露头资料,通过系统地层划分和对比,开展页岩地层和分布,明确页岩气甜点段。
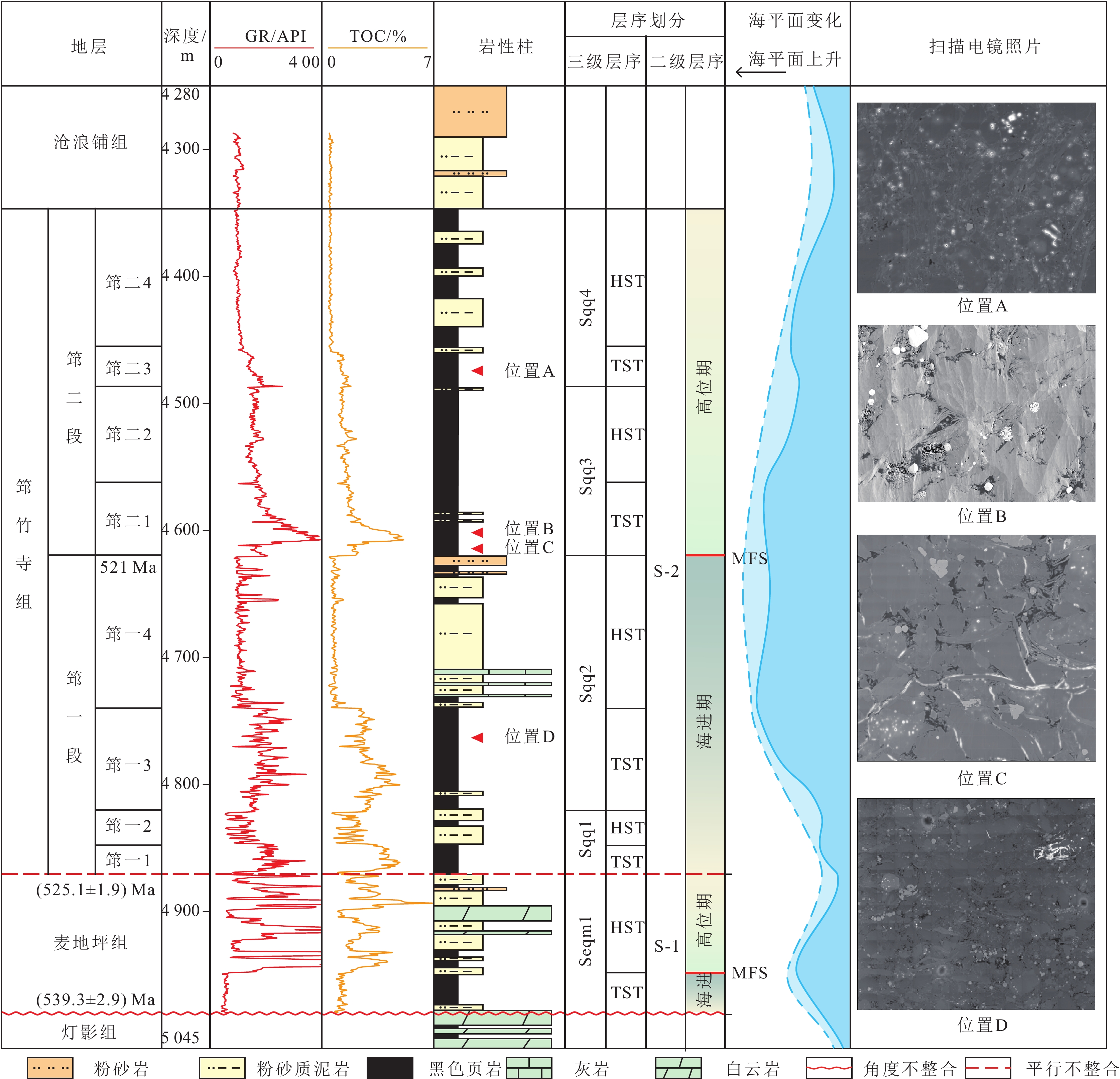
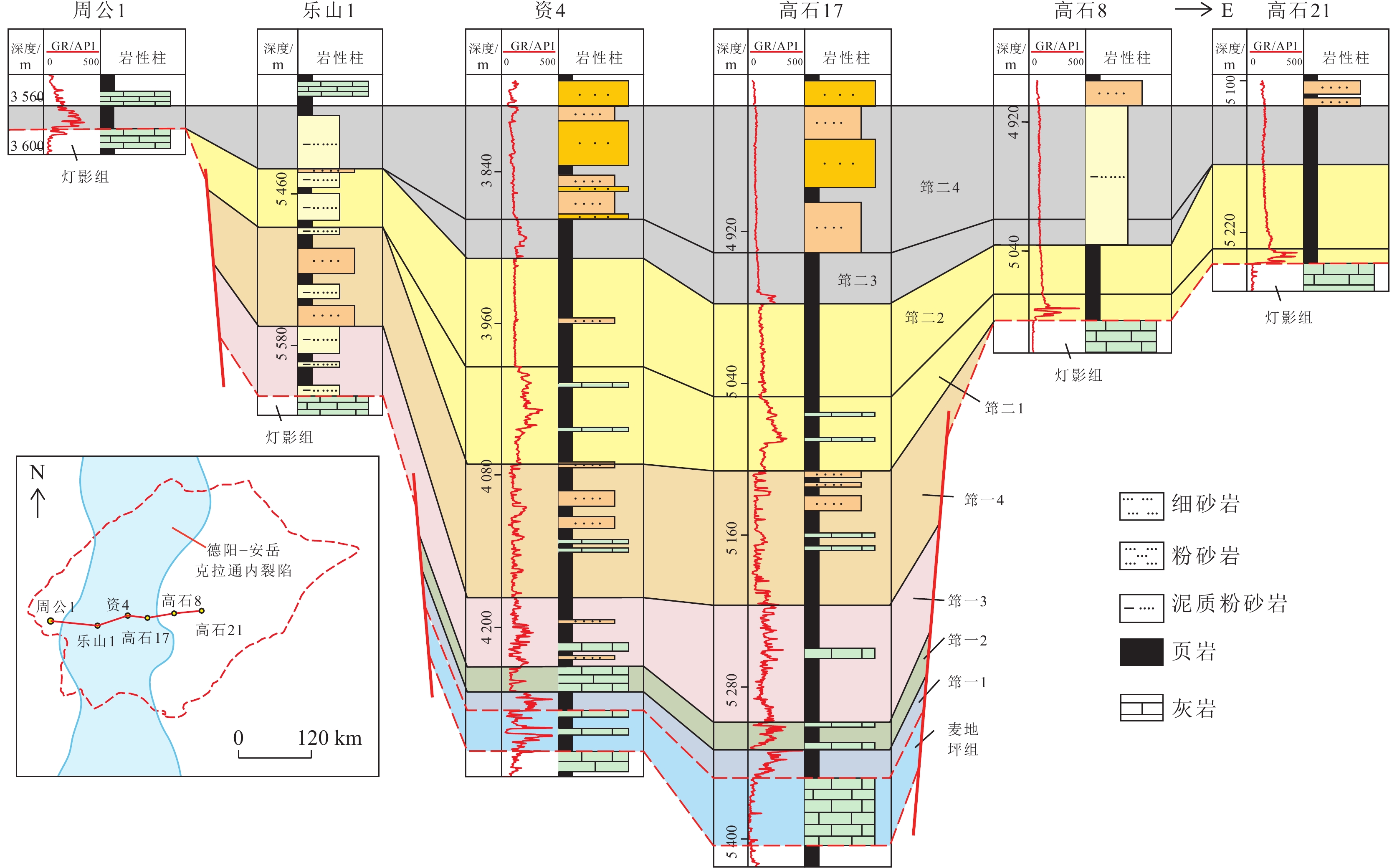
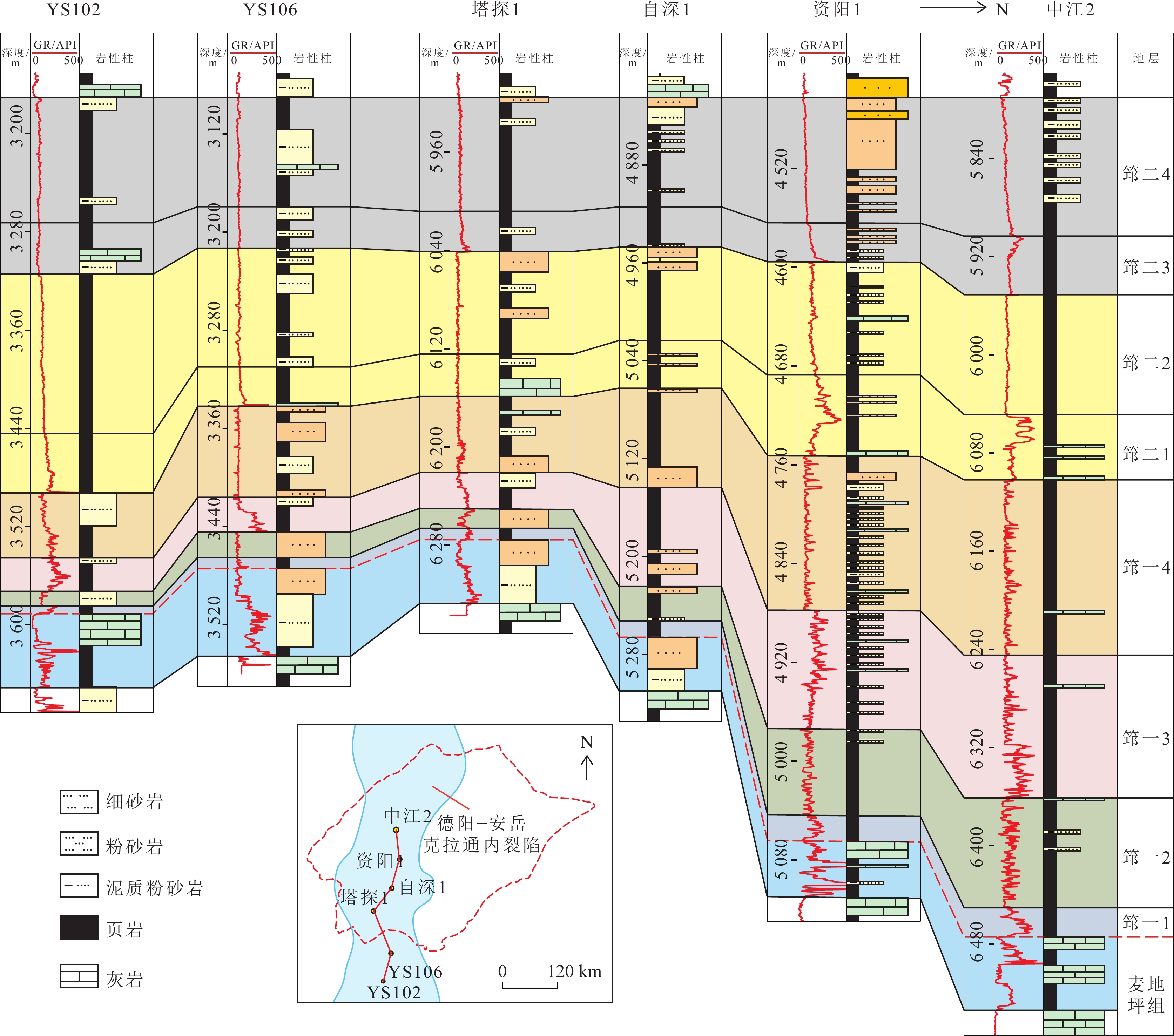
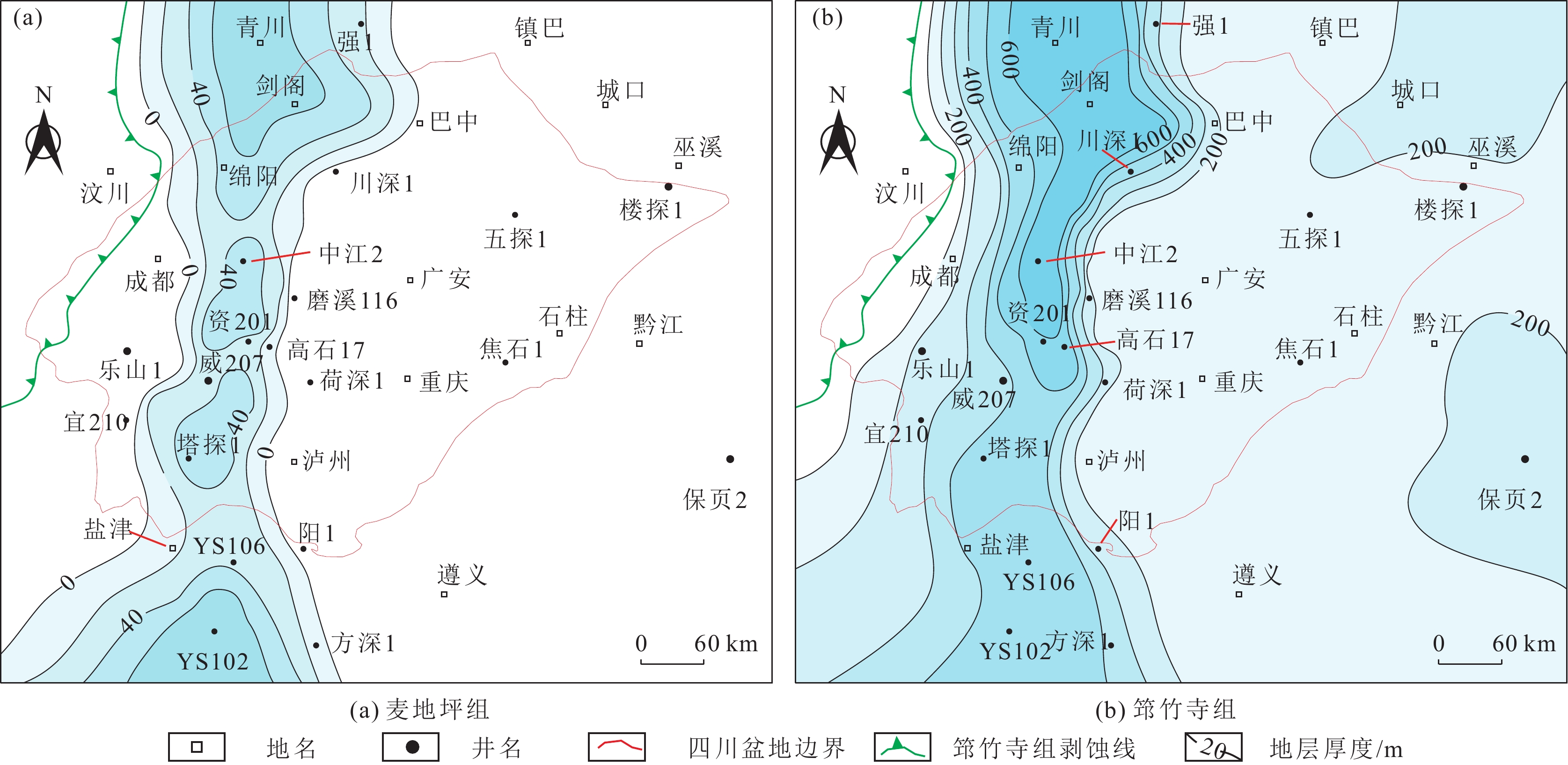
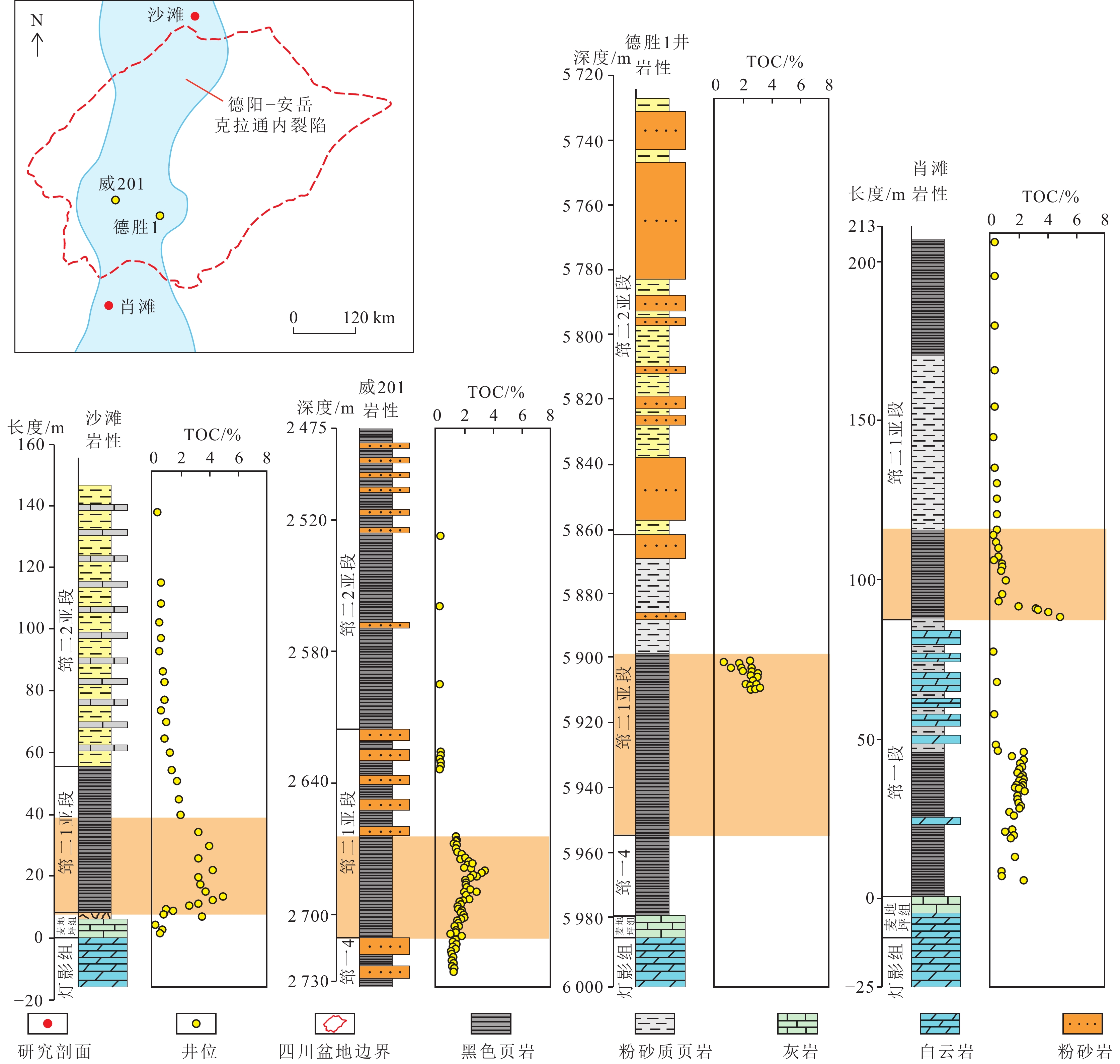
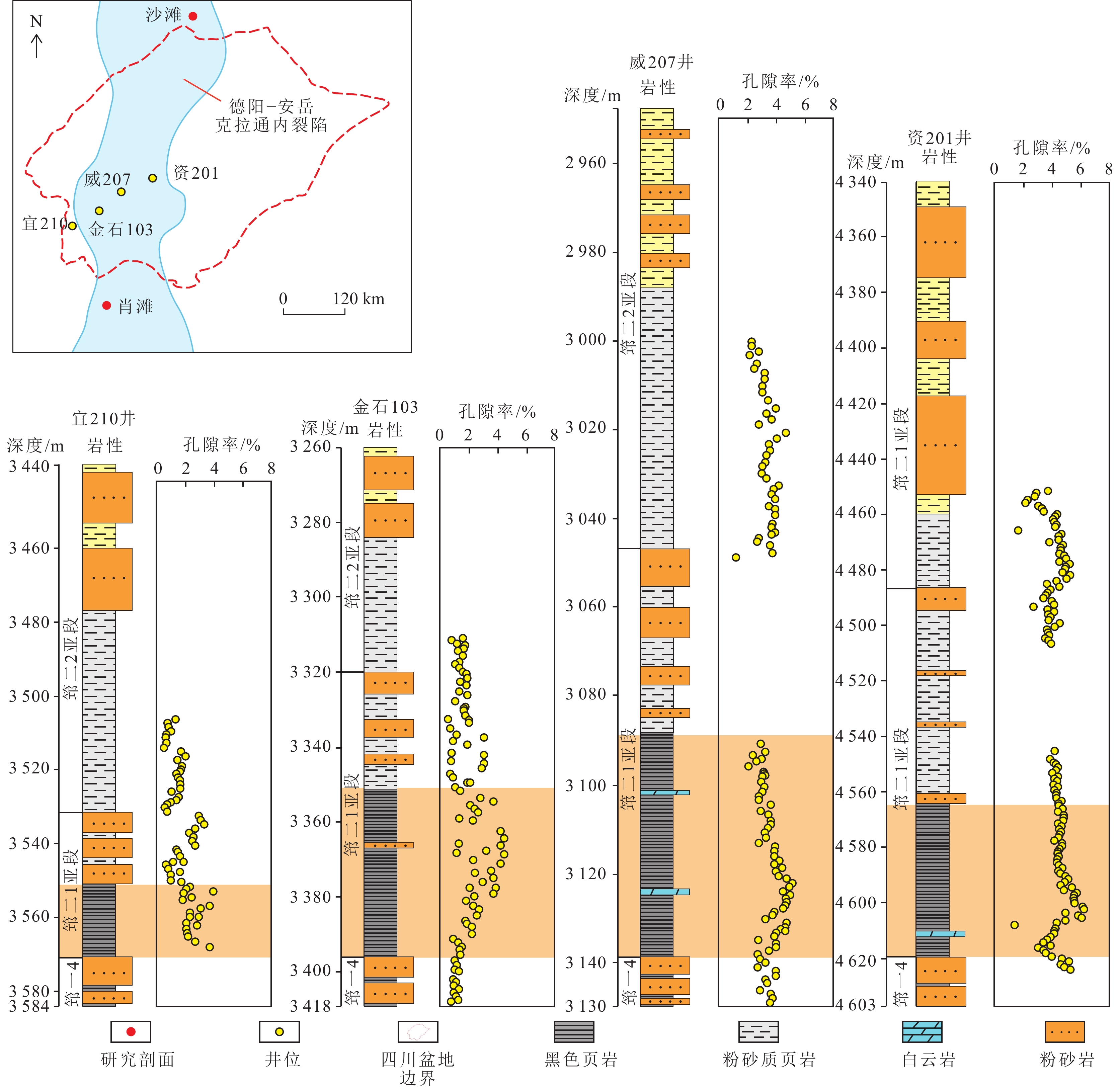
结果和结论结果表明:上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组划分为,筇一段(筇一1至筇一4亚段)和筇二段(筇二1至筇二4亚段)。(2) 麦地坪组和筇一段主要发育于德阳—安岳克拉通内裂陷内,而筇二段在裂陷外亦有广泛分布。裂陷内部地层结构表现为麦地坪组至筇一段东西两侧终止于灯影组灰岩,西侧厚度变化较缓,东侧地层快速尖灭;南北方向上,筇一段由北向南减薄,筇二段中部薄而南北厚。裂陷外部则以筇二段全区发育为特征,其中筇二1亚段直接超覆于筇一段或灯影组灰岩之上。(3) 筇二1亚段页岩具有优越的生烃、储集以及垂向和侧向封堵条件,为页岩气的富集段。内裂陷北段天星1井筇二1亚段页岩微孔隙和微裂缝发育,测井孔隙率为4.93%~6.57%,平均5.08%;德阳—安岳克拉通内裂陷槽中部的威页1井筇竹寺组筇二1亚段页岩有机质孔发育,测井孔隙率为4.20%~4.70%,平均4.51%;内裂陷南部的云南曲靖地区钻井井位有曲页1井、曲地1井等,筇竹寺组黑色页岩孔隙发育,高压压汞孔隙率为1.59%~11.33%,平均5.0%。(4)相比之下,尽管筇一段页岩在生烃和储集条件上表现良好,但其生成的页岩气易侧向沿岩溶带或断层逸散,不利于原地聚集成藏。如,内裂陷北段的川深1井,筇一3亚段厚约40 m,测井TOC含量平均3.5%,测井孔隙率平均6.4%,均为优质烃源岩和储集层,不利于原位聚集成藏。综上,筇二1亚段页岩因其高孔隙率和良好的封堵条件,为页岩气勘探的“甜点段”,为下一步油气勘探提供依据和指导。
Abstract:ObjectiveShales in the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation within the Upper Yangtze region preserve critical information about primitive oceans. Furthermore, these shales serve as vital source rocks and reservoirs, having demonstrated considerable potential for shale gas exploration.
MethodsUsing seismic, borehole, and outcrop data, this study investigated the shale strata and their distribution in the Qiongzhusi Formation through comparative analysis. Accordingly, the sweet-spot interval was determined.
Results and conclusionsThe results indicate that the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Upper Yangtze region can be divided into the first and second members (also referred to as the Qiong 1 and 2 members, respectively), with the former consisting of Q1-1 to Q1-4 sub-members and the latter comprising Q2-1 to Q2-4 sub-members. The Maidiping Formation and the Qiong 1 Member predominantly occur within the Deyang-Anyue intracratonic rift, while the Qiong 2 Member is extensively distributed both inside and outside the rift. Within the rift, the west and east sides of the Maidiping Formation - Qiong 1 Member terminates at the limestone of the Dengying Formation, with the west side gradually thinning while the east side pinching out rapidly. In the north-south direction, the Qiong 1 Member thins southward, while the Qiong 2 Member is thin in the central part but thick in the northern and southern parts. Outside the rift, the Qiong 2 Member is distributed throughout the region, with the Q2-1 sub-member directly overlapping either the Qiong 1 Member or the limestone of the Dengying Formation. Shales in the Q2-1 sub-member enjoy superior hydrocarbon generation and reservoir conditions, as well as vertical/lateral sealing performance, emerging as a shale gas enrichment interval. For instance, in the northern part of the intracratonic rift, shales in the Q2-1 sub-member in well Tianxing-1 contain well-developed micropores and microfractures, with logging-derived porosity ranging from 4.93% to 6.57% (average: 5.08%). In the central part of the Deyang-Anyue intracratonic rift trough, shales in the Q2-1 sub-member in well Weiye-1 well exhibit organic matter-hosted pores, with logging-derived porosity ranging from 4.20% to 4.70% (average: 4.51%). In the Qujing area, Yunnan Province, within the southern part of the rift, black shales in the Qiongzhusi Formation in wells Qudi-1 and Quye-1 reveal well-developed black shales with high-pressure mercury injection-derived porosity spanning 1.59% to 11.33% (average: 5.0%). Although shales in the Qiong 1 Member exhibit favorable source-reservoir properties, the shale gas generated is prone to escape along karst zones or faults, unconducive to in-situ accumulation. For instance, in the northern part of the intracratonic rift, the Q1-3 submember in well Chuanshen-1 exhibits a thickness of about 40 m, logging-derived average TOC of 3.5%, and logging-derived porosity of 6.4%, suggesting high-quality source rocks and reservoirs but unfavorable conditions for in-situ accumulation. Overall, shales in the Q2-1 sub-member are identified as a sweet-spot interval for shale gas exploration due to their high porosity and great sealing performance. This study can serve as a critical basis and guide for future shale gas exploration in the Upper Yangtze region.
-
-
图 1 上扬子地区地质及沉积概况
(a) 早寒武世华南板块位置[40];(b) 上扬子地区早寒武世古地貌及研究点分布;(c) 上扬子地区前寒武纪—寒武纪地层综合柱状图
Fig. 1 Geological and sedimentary overview of the Upper Yangtze region
图 4 大薄片照片展示上扬子地区威207井下寒武统麦地坪组—筇竹寺组不同层段页岩沉积构造特征
(a) 小型交错层理,3 018.84 m,筇二2亚段;(b) 波状交错层理,3 056.54 m,筇二1亚段;(c) 书页状水平层理,3 146.60 m,筇一4亚段;(d) 书页状水平层理,3 236.23 m,筇一1亚段
Fig. 4 Photomicrographs of large thin sections showing the sedimentary texture characteristics of shales in the Lower Cambrian Maidiping and Qiongzhusi formations in well Wei 207 in the Upper Yangtze region
表 1 上扬子地区下寒武统相关的地层划分方案[5]
Table 1 Stratigraphic subdivision scheme for the Lower Cambrian in the Upper Yangtze region[5]

表 2 上扬子地区下寒武统麦地坪组—筇竹寺组地层划分及特征
Table 2 Stratigraphic subdivision and characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Maidiping and Qiongzhusi formations, Upper Yangtze region
地层 岩性特征 电性特征 沉积相 生物组合 沧浪铺组 深灰色薄层页岩及粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩互层 自然伽马和声波均呈低值锯
齿状,电阻率振荡增大潮坪相 筇竹寺组 筇二段 筇二4 浅灰色粉砂质泥岩、
泥质粉砂岩互层箱状低自然伽马和声波,
电阻率较大、平直状浅水陆棚 Parabadiella-MianxiandiscusEoredlichia-Wutingaspis 筇二3 灰色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩 漏斗状低自然伽马和声波,
电阻率较大、平直状浅水陆棚 筇二2 浅灰色页岩,
夹有少量粉砂岩漏斗状中自然伽马,中声波,平直状中高电阻率 深水陆棚 Lapworthella-Tannuolina-Sinoscachites 筇二1 黑色、深灰色页岩、
炭质页岩,夹有少量粉砂岩指状中高自然伽马,高声波,平直状中高电阻率 深水陆棚 筇一段 筇一4 深灰色泥质砂岩、粉砂岩,夹少量灰岩及泥岩 箱形低自然伽马和声波,
电阻率较大、平直状浅水陆棚 筇一3 黑色炭质页岩 中高自然伽马、高声波,
中低电阻率深水陆棚 筇一2 灰黑色粉砂质页岩与
泥岩互层箱形低自然伽马和声波,
齿状低电阻浅水陆棚 筇一1 黑色炭质页岩、粉砂质页岩 中高自然伽马和声波,
中高指状电阻率深水陆棚 麦地坪组 硅质页岩、白云岩、
磷块岩等自然伽马值高低相间、
中高电阻深水坳拉槽 Anabarites trisulcatus-Protohertzina anabarica带、Siphogonuchites pusilliformis-Paragloborilus subglobosus带、Heraultipegma yunnanensis带 灯影组 白云岩 低伽马、高电阻 碳酸盐岩台地相 表 3 上扬子地区下寒武统麦地坪组—筇竹寺组不同层段页岩矿物组成
Table 3 Mineral compositions of shales in different intervals of the Lower Cambrian Maidiping and Qiongzhusi formations, Upper Yangtze region
% 层位 黏土总量 石英 正长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 菱铁矿 沧浪铺组 37.2 39.3 0 7.8 15.8 1.5 1.5 0 筇二4 35.4 38.1 0.9 9.1 14.0 2.4 2.5 0 筇二3 35.8 31.8 1.4 11.4 8.7 7.2 3.7 0 筇二2 21.3 45.6 2.4 21.1 3.5 4.3 1.8 0 筇二1 23.6 38.4 3.7 23.3 3.1 3.8 4.2 0 筇一4 15.6 39.6 4.5 25.5 9.8 3.4 1.8 0 筇一3 25.9 34.3 4.7 12.3 3.7 9.7 9.4 0 筇一2 33.0 33.5 3.5 18.0 9.5 0.0 2.5 0 筇一1 5.5 68.1 0.9 3.2 6.4 2.3 6.6 7 麦地坪组 11.4 56.2 0 5.7 1.2 5.4 11.1 9.15 -
[1] HOFFMAN P F,KAUFMAN A J,HALVERSON G P,et al. A Neoproterozoic snowball Earth[J]. Science,1998,281(5381):1342−1346. DOI: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1342
[2] DONNADIEU Y,GODDÉRIS Y,RAMSTEIN G,et al. A “snowball Earth” climate triggered by continental break–up through changes in runoff[J]. Nature,2004,428:303−306. DOI: 10.1038/nature02408
[3] MARSHALL C R. Explaining the Cambrian “explosion” of animals[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2006,34:355−384. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.33.031504.103001
[4] PENG S C,BABCOCK L E,AHLBERG P. The Cambrian period[M]//GRADSTEIN F M,OGG J G,SCHMITZ M D,et al. Geologic time scale 2020. Amsterdam:Elsevier,2020:565–629.
[5] 朱光有,赵坤,李婷婷,等. 中国华南地区下寒武统烃源岩沉积环境、发育模式与分布预测[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(12):1567−1586. ZHU Guangyou,ZHAO Kun,LI Tingting,et al. Sedimentary environment,development model and distribution prediction of Lower Cambrian source rocks in South China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2020,41(12):1567−1586.
[6] 梁霄,李香华,徐剑良,等. 从优质烃源岩到储层:构造–沉积分异格局下的四川盆地中西部下寒武统页岩气勘探前景[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(5):30−41. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.05.004 LIANG Xiao,LI Xianghua,XU Jianliang,et al. Exploration prospects of Lower Cambrian shale gas in the central–western Sichuan Basin under the pattern of tectonic–depositional differentiation:From high–quality source rocks to reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(5):30−41. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.05.004
[7] 张科,苏劲,陈永权,等. 塔里木盆地寒武系–奥陶系烃源岩油源特征与超深层油气来源[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(6):2026−2041. ZHANG Ke,SU Jin,CHEN Yongquan,et al. The biogeochemical features of the Cambrian–Ordovician source rocks and origin of ultra–deep hydrocarbons in the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(6):2026−2041.
[8] 汪建国,陈代钊,王清晨,等. 中扬子地区晚震旦世–早寒武世转折期台–盆演化及烃源岩形成机理[J]. 地质学报,2007,81(8):1102−1109. WANG Jianguo,CHEN Daizhao,WANG Qingchen,et al. Platform evolution and marine source rock deposition during the terminal Sinian to Early Cambrian in the middle Yangtze Region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(8):1102−1109.
[9] 欧阳征健,冯娟萍,姚韦卓,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地及周缘寒武系烃源岩地质特征及有利区带优选[J]. 地质科学,2023,58(4):1291−1308. OUYANG Zhengjian,FENG Juanping,YAO Weizhuo,et al. Characteristics and favorable areas of Cambrian natural gas reservoirs in Ordos Basin and its periphery areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2023,58(4):1291−1308.
[10] GORIN G E,RACZ L G,WALTER M R. Late Precambrian–Cambrian sediments of Huqf group,sultanate of Oman[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1982,66(12):2609−2627.
[11] ZHURAVLEV A Y,WOOD R A. The two phases of the Cambrian explosion[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):16656. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34962-y
[12] WILLE M,NÄGLER T F,LEHMANN B,et al. Hydrogen sulphide release to surface waters at the Precambrian/Cambrian boundary[J]. Nature,2008,453(7196):767−769. DOI: 10.1038/nature07072
[13] ZHU Maoyan,LI Xianhua. Introduction:From snowball Earth to the Cambrian explosion–evidence from China[J]. Geological Magazine,2017,154(6):1187−1192. DOI: 10.1017/S0016756817000644
[14] OKADA Y,SAWAKI Y,KOMIYA T,et al. New chronological constraints for Cryogenian to Cambrian rocks in the Three Gorges,Weng’an and Chengjiang areas,South China[J]. Gondwana Research,2014,25(3):1027−1044. DOI: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.001
[15] JIANG Shaoyong,PI Daohui,HEUBECK C,et al. Early Cambrian ocean anoxia in South China[J]. Nature,2009,459(7248):E5−E6. DOI: 10.1038/nature08048
[16] XU Lingang,MAO Jingwen. Trace element and C–S–Fe geochemistry of Early Cambrian black shales and associated polymetallic Ni–Mo sulfide and vanadium mineralization,South China:Implications for paleoceanic redox variation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,135:104210. DOI: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104210
[17] FANG Xinyan,WU Liangliang,GENG Ansong,et al. Formation and evolution of the Ediacaran to Lower Cambrian black shales in the Yangtze Platform,South China[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2019,527:87−102.
[18] XIANG Lei,SCHOEPFER S D,ZHANG Hua,et al. Evolution of primary producers and productivity across the Ediacaran–Cambrian transition[J]. Precambrian Research,2018,313:68−77. DOI: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.05.023
[19] EL–GHALI M A K,SHELUKHINA O,ABBASI I A,et al. Depositional and sequence stratigraphic controls on diagenesis in the Upper Cambrian–Lower Ordovician Barik Formation,central Oman:Implications for prediction of reservoir porosity in a hybrid–energy delta system[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2024,160:106611. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106611
[20] 张天怡,黄士鹏,李贤庆,等. 四川盆地下寒武统筇竹寺组沉积地球化学特征与有机质富集机制[J]. 天然气地球科学,2024,35(4):688−703. ZHANG Tianyi,HUANG Shipeng,LI Xianqing,et al. Sedimentary geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2024,35(4):688−703.
[21] 魏国齐,杨威,谢武仁,等. 克拉通内裂陷及周缘大型岩性气藏形成机制、潜力与勘探实践:以四川盆地震旦系–寒武系为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2022,49(3):465−477. WEI Guoqi,YANG Wei,XIE Wuren,et al. Formation mechanisms,potentials and exploration practices of large lithologic gas reservoirs in and around an intracratonic rift:Taking the Sinian–Cambrian of Sichuan Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2022,49(3):465−477.
[22] 魏国齐,王志宏,李剑,等. 四川盆地震旦系、寒武系烃源岩特征、资源潜力与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(1):1−13. WEI Guoqi,WANG Zhihong,LI Jian,et al. Characteristics of source rocks,resource potential and exploration direction of Sinian and Cambrian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(1):1−13.
[23] 谢增业,李剑,杨春龙,等. 川中古隆起震旦系–寒武系天然气地球化学特征与太和气区的勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(7):1−14. XIE Zengye,LI Jian,YANG Chunlong,et al. Geochemical characteristics of Sinian–Cambrian natural gas in central Sichuan paleo–uplift and exploration potential of Taihe gas area[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(7):1−14.
[24] 杜金虎,汪泽成,邹才能,等. 古老碳酸盐岩大气田地质理论与勘探实践[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2015. [25] 杨威,魏国齐,谢武仁,等. 古隆起在四川盆地台内碳酸盐岩丘滩体规模成储中的作用[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(4):1−12. YANG Wei,WEI Guoqi,XIE Wuren,et al. Role of paleouplift in the scale formation of intra–platform carbonate mound–bank body reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(4):1−12.
[26] POTTER C J. Paleozoic shale gas resources in the Sichuan Basin,China[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2018,102(6):987−1009. DOI: 10.1306/0828171607817072
[27] WANG Wenyang,PANG Xiongqi,CHEN Zhangxin,et al. Quantitative prediction of oil and gas prospects of the Sinian–Lower Paleozoic in the Sichuan Basin in Central China[J]. Energy,2019,174:861−872. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.018
[28] 魏国齐,杨威,杜金虎,等. 四川盆地震旦纪–早寒武世克拉通内裂陷地质特征[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(1):24−35. WEI Guoqi,YANG Wei,DU Jinhu,et al. Geological characteristics of the Sinian–Early Cambrian intracratonic rift,Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2015,35(1):24−35.
[29] 钟勇,李亚林,张晓斌,等. 川中古隆起构造演化特征及其与早寒武世绵阳–长宁拉张槽的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,41(6):703−712. ZHONG Yong,LI Yalin,ZHANG Xiaobin,et al. Evolution characteristics of central Sichuan palaeouplift and its relationship with Early Cambrian Mianyang–Changning intracratonic sag[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition),2014,41(6):703−712.
[30] 李忠权,刘记,李应,等. 四川盆地震旦系威远–安岳拉张侵蚀槽特征及形成演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(1):26−33. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2015.01.03 LI Zhongquan,LIU Ji,LI Ying,et al. Formation and evolution of Weiyuan–Anyue extension–erosion groove in Sinian system,Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2015,42(1):26−33. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2015.01.03
[31] PI Daohui,LIU Congqiang,SHIELDS–ZHOU G A,et al. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of black shale and kerogen in the Early Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Guizhou Province,South China:Constraints for redox environments and origin of metal enrichments[J]. Precambrian Research,2013,225:218−229. DOI: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.07.004
[32] ZHOU Lei,KANG Zhihong,WANG Zongxiu,et al. Sedimentary geochemical investigation for paleoenvironment of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation shales in the Yangtze Platform[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2017,159:376−386. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.09.047
[33] MA Yiquan,LU Yongchao,LIU Xiaofeng,et al. Depositional environment and organic matter enrichment of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in western Hubei Province,South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,109:381−393. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.039
[34] 马子杰,唐玄,张金川,等. 上扬子地区寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩有机质孔隙发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(3):124−137. MA Zijie,TANG Xuan,ZHANG Jinchuan,et al. Organic matter–hosted pores in the Cambrian Niutitang shales of the Upper Yangtze region:Pore development characteristics and main controlling factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2023,30(3):124−137.
[35] 王濡岳,丁文龙,龚大建,等. 渝东南–黔北地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝发育特征与主控因素[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(7):832−845. WANG Ruyue,DING Wenlong,GONG Dajian,et al. Development characteristics and major controlling factors of shale fractures in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation,southeastern Chongqing–northern Guizhou area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(7):832−845.
[36] 梁峰,吴伟,张琴,等. 四川盆地南部下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩孔隙结构特征与页岩气赋存模式[J]. 天然气工业,2024,44(3):131−142. LIANG Feng,WU Wei,ZHANG Qin,et al. Shale pore structure characteristics and shale gas occurrence pattern of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2024,44(3):131−142.
[37] WANG Ruyue,DING Wenlong,ZHANG Yeqian,et al. Analysis of developmental characteristics and dominant factors of fractures in Lower Cambrian marine shale reservoirs:A case study of Niutitang Formation in Cen’gong Block,Southern China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2016,138:31−49. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.12.004
[38] 周慧,李伟,张宝民,等. 四川盆地震旦纪末期–寒武纪早期台盆的形成与演化[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(3):310−323. ZHOU Hui,LI Wei,ZHANG Baomin,et al. Formation and evolution of Upper Sinian to Lower Cambrian intraplatformal basin in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2015,36(3):310−323.
[39] WANG Jian,LI Zhengxiang. History of Neoproterozoic rift basins in South China:Implications for Rodinia break–up[J]. Precambrian Research,2003,122(1/2/3/4):141−158.
[40] LI Z X,BOGDANOVA S V,COLLINS A S,et al. Assembly,configuration,and break–up history of Rodinia:A synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research,2008,160(1/2):179−210.
[41] 黎荣,王永骁,汪泽成,等. 四川盆地晚震旦世–早寒武世德阳–安岳裂陷槽南段地质特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(2):285−296. LI Rong,WANG Yongxiao,WANG Zecheng,et al. Geological characteristics of the southern segment of the Late Sinian–Early Cambrian Deyang–Anyue rift trough in Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2023,50(2):285−296.
[42] 谢武仁,姜华,马石玉,等. 四川盆地德阳–安岳裂陷晚震旦世–早寒武世沉积演化特征与有利勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学,2022,33(8):1240−1250. XIE Wuren,JIANG Hua,MA Shiyu,et al. Sedimentary evolution characteristics and favorable exploration directions of Deyang–Anyue rift within the Sichuan Basin in Late Sinian–Early Cambrian[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2022,33(8):1240−1250.
[43] 杜金虎,汪泽成,邹才能,等. 上扬子克拉通内裂陷的发现及对安岳特大型气田形成的控制作用[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(1):1−16. DOI: 10.1038/aps.2015.144 DU Jinhu,WANG Zecheng,ZOU Caineng,et al. Discovery of intra–cratonic rift in the Upper Yangtze and its control effect on the formation of Anyue giant gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(1):1−16. DOI: 10.1038/aps.2015.144
[44] 杨威,魏国齐,谢武仁,等. 克拉通内裂陷边缘台缘丘滩体规模储层发育主控因素与成因模式:以四川盆地德阳–安岳克拉通内裂陷东侧灯影组四段为例[J]. 天然气地球科学,2022,33(10):1541−1553. YANG Wei,WEI Guoqi,XIE Wuren,et al. Main controlling factors and genetic mechanism for the development of high–quality reservoirs in the mound–shoal complexes on the platform margin mound–beach body at platform margin of the inner cratonic rift:Case study of the fourth member of Dengying Formation in the east side of the Deyang–Anyue cratonic rifts,Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2022,33(10):1541−1553.
[45] COMPSTON W,ZHANG Zichao,COOPER J A,et al. Further SHRIMP geochronology on the Early Cambrian of South China[J]. American Journal of Science,2008,308(4):399−420. DOI: 10.2475/04.2008.01
[46] WANG Xinqiang,SHI Xiaoying,JIANG Ganqing,et al. New U–Pb age from the basal Niutitang Formation in South China:Implications for diachronous development and condensation of stratigraphic units across the Yangtze Platform at the Ediacaran–Cambrian transition[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,48:1−8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.023
[47] 刘瑞崟,周文,徐浩,等. 层序格架下构造–沉积分异对页岩气储层特征的控制:以四川盆地西南部筇竹寺组为例[J]. 沉积学报,2023,41(5):1478−1494. LIU Ruiyin,ZHOU Wen,XU Hao,et al. Control of the pattern of tectonic–depositional differentiation on shale gas reservoir characteristics within a sequence stratigraphic framework:A case study from the Qiongzhusi Formation in the southwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2023,41(5):1478−1494.
[48] YAWAR Z,SCHIEBER J. On the origin of silt laminae in laminated shales[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2017,360:22−34. DOI: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.09.001
[49] SCHIEBER J,SOUTHARD J,THAISEN K. Accretion of mudstone beds from migrating floccule ripples[J]. Science,2007,318(5857):1760−1763. DOI: 10.1126/science.1147001
[50] 施振生,赵圣贤,周天琪,等. 海相含气页岩水平层理类型、成因及其页岩气意义:以川南地区古生界五峰组–龙马溪组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2023,44(6):1499−1514. SHI Zhensheng,ZHAO Shengxian,ZHOU Tianqi,et al. Types and genesis of horizontal bedding of marine gas–bearing shale and its significance for shale gas:A case study of the Wufeng–Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2023,44(6):1499−1514.
[51] 施振生,邱振. 海相细粒沉积层理类型及其油气勘探开发意义[J]. 沉积学报,2021,39(1):181−196. SHI Zhensheng,QIU Zhen. Main bedding types of marine fine–grained sediments and their significance for oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2021,39(1):181−196.
[52] SHI Zhensheng,ZHOU Tianqi,WANG Hongyan,et al. Depositional structures and their reservoir characteristics in the Wufeng–Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Energies,2022,15(5):1618. DOI: 10.3390/en15051618
[53] GOLDBERG T,STRAUSS H,GUO Qingjun,et al. Reconstructing marine redox conditions for the Early Cambrian Yangtze Platform:Evidence from biogenic sulphur and organic carbon isotopes[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2007,254(1/2):175−193.
[54] OCH L M,SHIELDS–ZHOU G A,POULTON S W,et al. Redox changes in Early Cambrian black shales at Xiaotan section,Yunnan Province,South China[J]. Precambrian Research,2013,225:166−189. DOI: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.10.005
[55] 胡琳,薛晓辉,杜伟,等. 云南曲靖地区筇竹寺组泥页岩储层发育特征与影响因素[J]. 高校地质学报,2022,28(4):617−622. HU Lin,XUE Xiaohui,DU Wei,et al. Reservoir characteristics of the Qiongzhusi shales and their influencing factors in the Qujing area,Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2022,28(4):617−622.
[56] 王玉满,董大忠,程相志,等. 海相页岩有机质碳化的电性证据及其地质意义:以四川盆地南部地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩为例[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(8):1−7. WANG Yuman,DONG Dazhong,CHENG Xiangzhi,et al. Electric property evidences of the carbonification of organic matters in marine shales and its geologic significance:A case of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi shale in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2014,34(8):1−7.
[57] 王玉满,李新景,陈波,等. 海相页岩有机质炭化的热成熟度下限及勘探风险[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(3):385−395. WANG Yuman,LI Xinjing,CHEN Bo,et al. Lower limit of thermal maturity for the carbonization of organic matter in marine shale and its exploration risk[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(3):385−395.
[58] 杨威,魏国齐,谢武仁,等. 四川盆地绵竹–长宁克拉通内裂陷东侧震旦系灯影组四段台缘丘滩体成藏特征与勘探前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(6):1174−1184. YANG Wei,WEI Guoqi,XIE Wuren,et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration prospect of mound–shoal complexes on the platform margin of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the east of Mianzhu–Changning intracratonic rift,Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2020,47(6):1174−1184.
[59] 魏国齐,杜金虎,徐春春,等. 四川盆地高石梯–磨溪地区震旦系–寒武系大型气藏特征与聚集模式[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(1):1−12. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201501001 WEI Guoqi,DU Jinhu,XU Chunchun,et al. Characteristics and accumulation modes of large gas reservoirs in Sinian–Cambrian of Gaoshiti–Moxi region,Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2015,36(1):1−12. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201501001








 下载:
下载: