Fracture activation in the overburden and aquiclude stability under the mining of close-distance coal seams
-
摘要:背景
陕北侏罗纪煤田近距离煤层重复采动覆岩裂隙活化发育加剧,易导致隔水层失稳,引起地下水流失。
方法为揭示近距离煤层开采覆岩裂隙发育特征及隔水层稳定性,采用实测统计、物理相似模拟及理论分析相结合的方法,提出基于陕北侏罗纪煤田近距离煤层保水开采的主要煤岩组合类型划分,分析重复采动裂隙活化发育规律,建立重复采动隔水层稳定性判据。
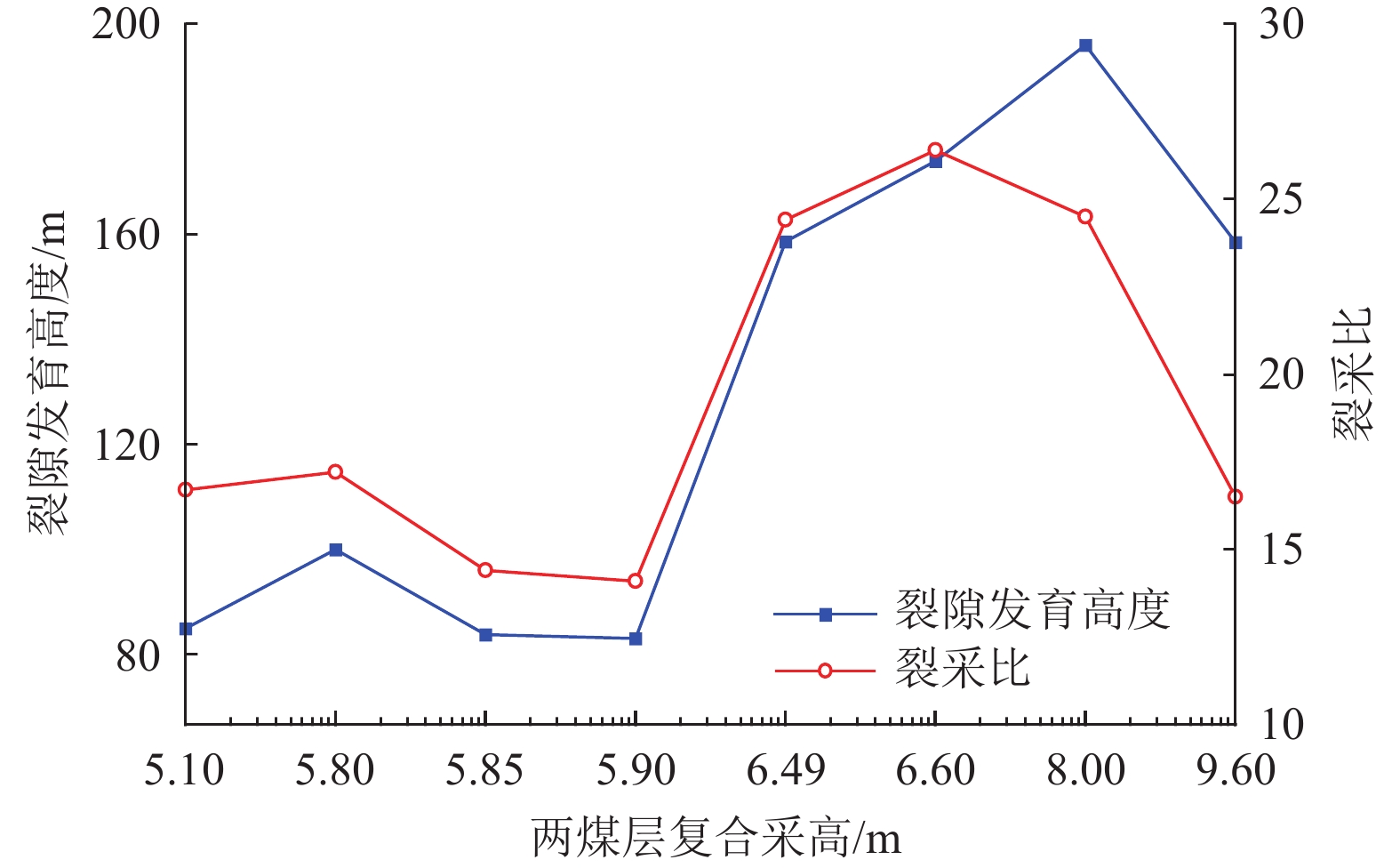
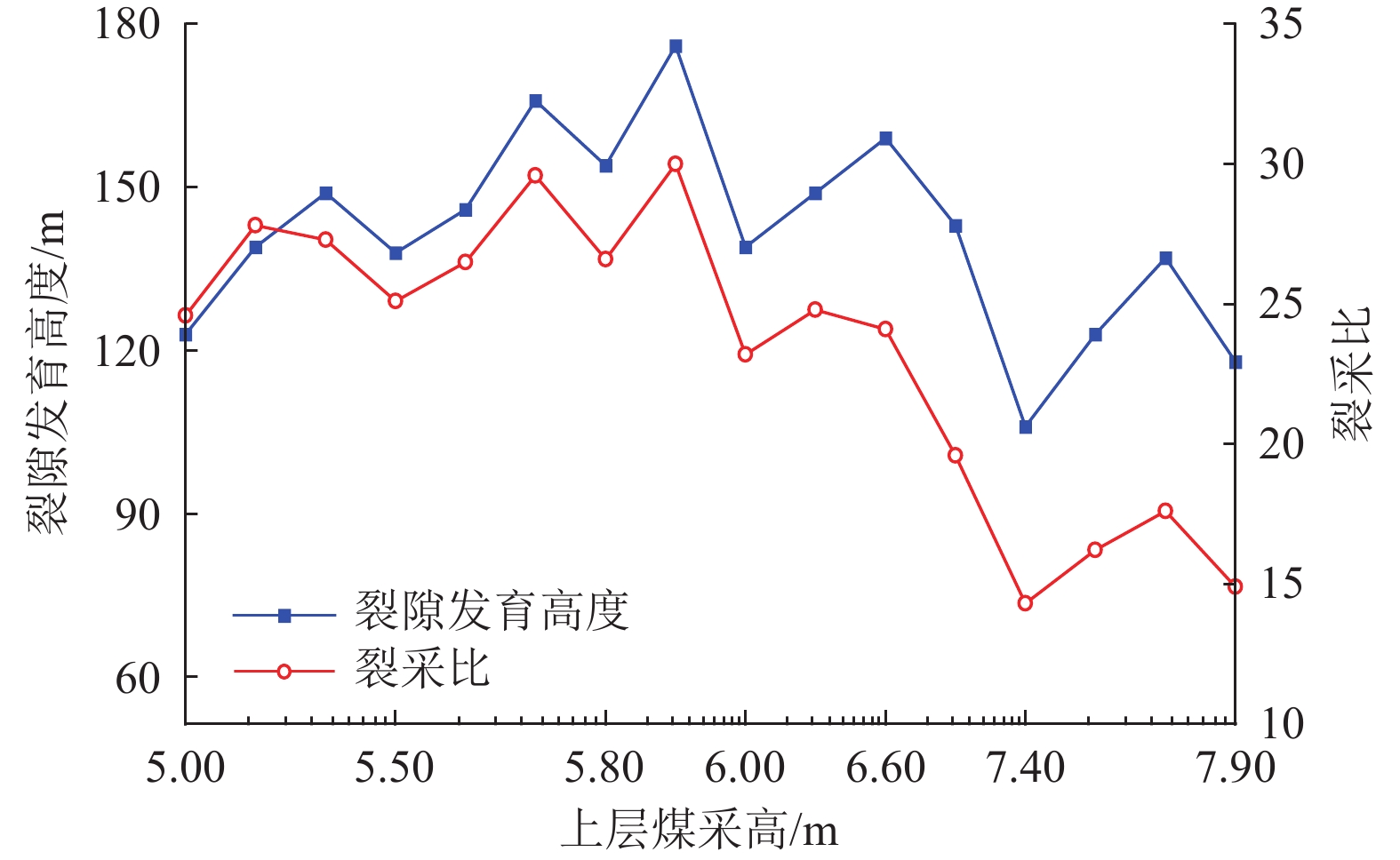
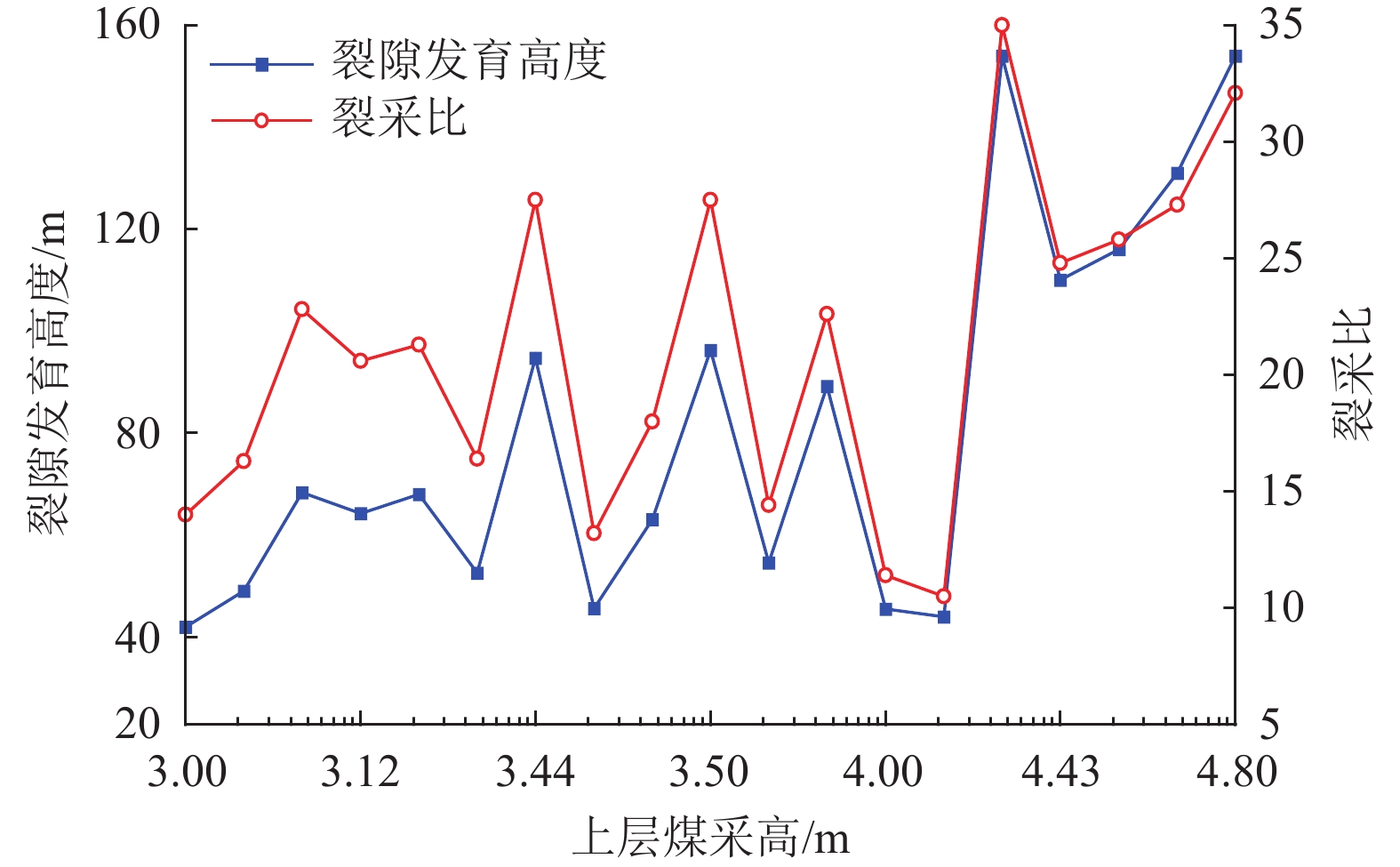
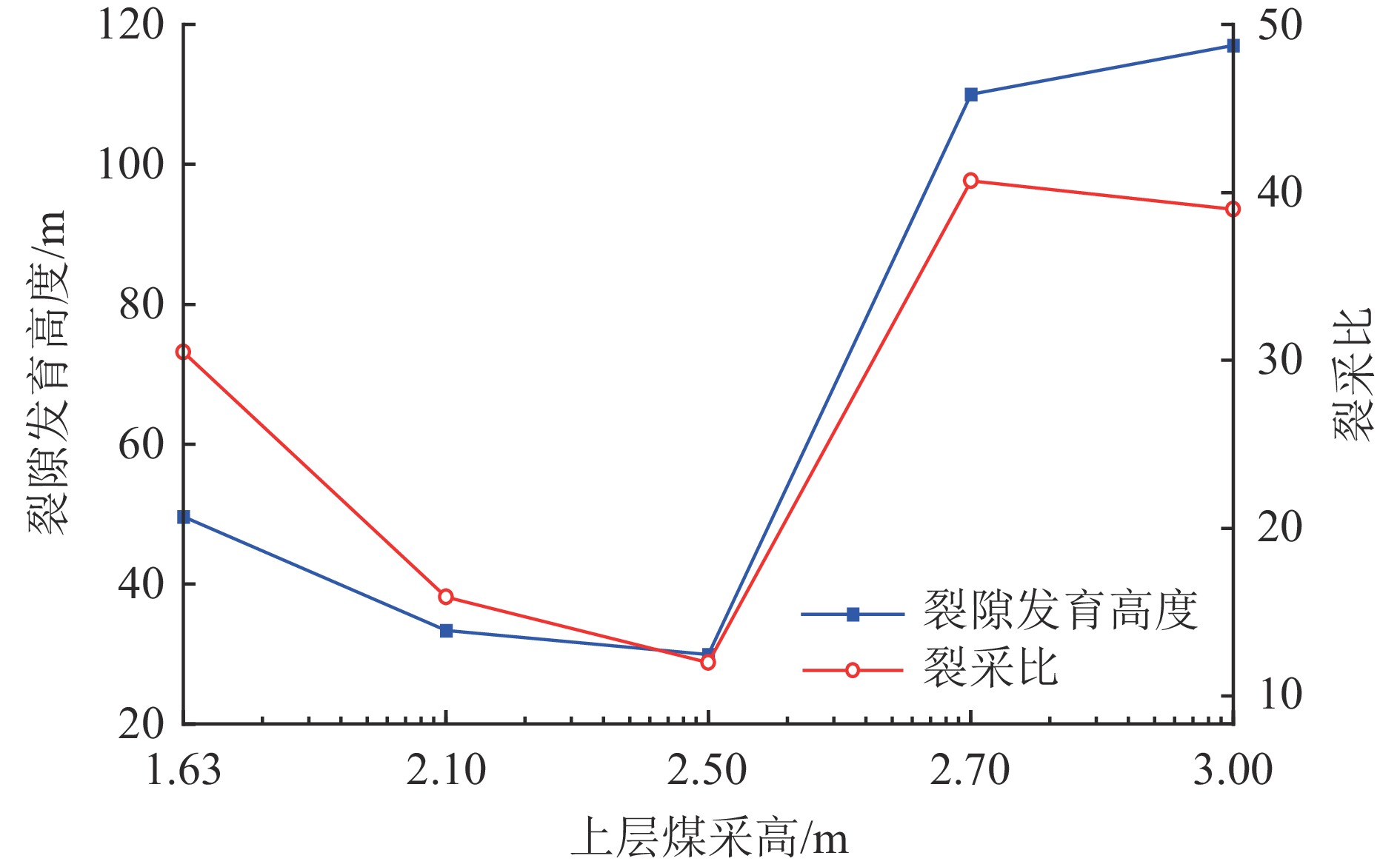
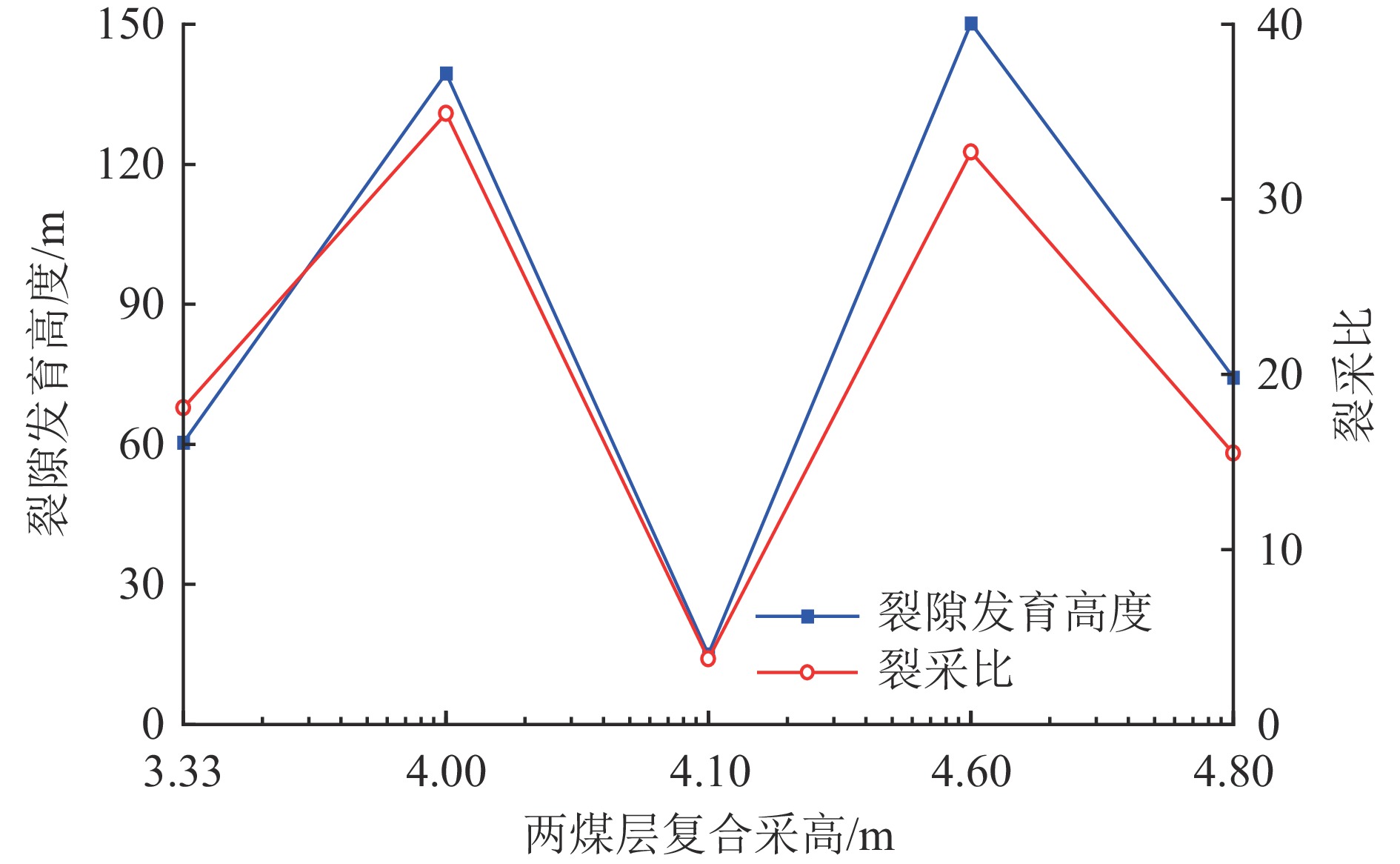
结果和结论研究表明,依据该煤田上部近距离两层可采煤层煤−水赋存条件及地质特征,可分为薄及中厚−厚型(Ⅰ型)、厚−薄及中厚型(Ⅱ型)、厚−厚型(Ⅲ型)、薄及中厚−薄及中厚型(Ⅳ型)4种类型。得出基于上述4类条件采动覆岩上行与下行裂隙发育的隔水层破坏特征,重复采动裂采比(上行裂隙发育高度/复合采高)一般为14~30,相比上部单一煤层开采显著减小,下行裂隙发育深度为复合采高的1.6~3.0倍。建立基于重复采动裂隙发育高度(深度)的隔水层稳定性判据,当隔水层厚度大于等于重复采动裂隙发育高度、深度、安全厚度之和时,隔水层稳定,反之失稳;给出陕北侏罗纪煤田重复采动隔水层稳定性评价,包括稳定−稳定、稳定−失稳、失稳−失稳3种情况。研究成果可为陕北侏罗纪煤田近距离煤层保水开采的隔水层稳定性判据确定与控制提供理论基础。
Abstract:BackgroundIn the Jurassic coalfield of northern Shaanxi Province, the repeated mining of close-distance coal seams exacerbates the activation of fractures in the overburden. This is prone to cause aquiclude instability, leading to groundwater loss.
MethodsThis study aims to reveal the characteristics of fractures in the overburden and the aquiclude stability in the mining of close-distance coal seams. Using a method combining measurement statistics, physical simulations using similar materials, and theoretical analysis, this study proposed categorizing primary coal-rock combinations based on the water-preserved mining of close-distance coal seams in the Jurassic coalfield of northern Shaanxi. Additionally, this study analyzed the patterns of fracture activation induced by repeat mining and established the stability criterion for aquicludes under repeated mining.
Results and ConclusionsThe results indicate that, based on the coal-water occurrence conditions and geological characteristics of two minable, close-distance coal seams in the upper part of the coalfield, the coal-rock combinations can be categorized into four types: thin and medium thick-thick (Type Ⅰ), thick-thin and medium thick (Type Ⅱ), thick-thick (Type Ⅲ), and thin and medium thick-thin and medium thick (Type Ⅳ) types. The characteristics of aquiclude failure caused by the development of upward and downward fractures in the overburden under the mining of the four coal-rock combinations were determined. Specifically, the upward fracture/composite mining height ratios under repeated mining generally vary from 14 to 30, significantly less than those under the mining of the single upper coal seam. Furthermore, the depths of downward fractures are 1.6 to 3.0 times the composite mining heights. The stability criterion for aquicludes was determined based on the repeat mining-induced fracture height (depth). Specifically, an aquiclude remains stable when its thickness is greater than or equal to the sum of repeat mining-induced fracture height (depth) and fracture-free thickness. Otherwise, they were unstable. The stability assessment of aquicludes in the Jurassic coalfield under repeated mining reveals that the aquicludes are in three conditions: stable-stable, stable-unstable, and unstable-unstable. These findings provide a theoretical basis for determining and controlling aquiclude stability in water-preserved mining of close-instance coal seams in the Jurassic coalfield of northern Shaanxi.
-
-
表 1 1−2、2−2和3−1煤煤层特征
Table 1 Characteristics of coal seams 1−2, 2−2, and 3−1
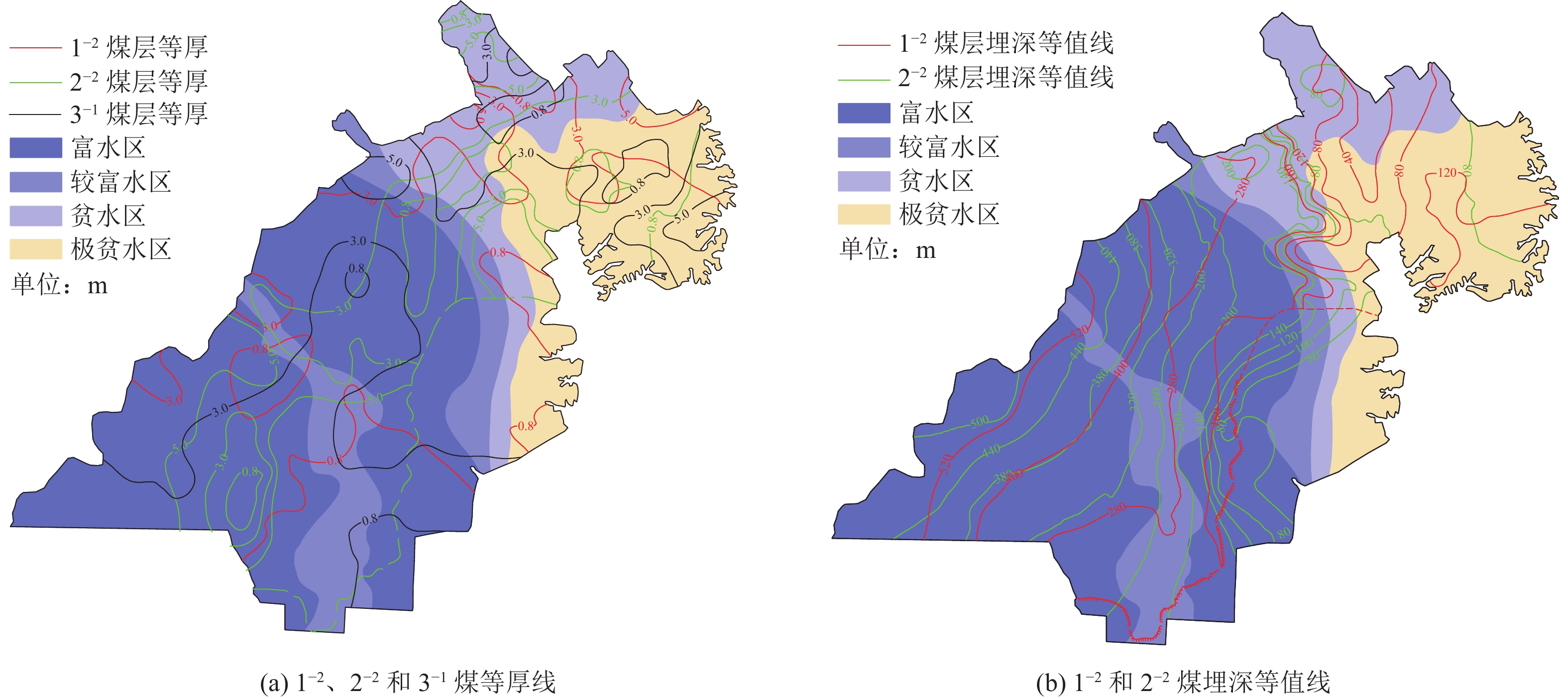
煤层编号 煤厚/m 煤层间距/m 煤层结构与稳定性 1−2煤 l~3(大部分);3~5(少数) 13.11~40.00/25.00 (在1−2煤与2−2煤之间) 厚度变化缓慢,结构简单,稳定煤层 2−2煤 0.26~12.16/6.50 一般无夹矸,稳定的中至巨厚煤层 3−1煤 0.18~4.01/2.48 20.52~41.08/30.00 厚度变化小,结构简单,稳定的中厚煤层 注:0.26~12.16/6.50表示最小~最大值/平均值,其他同。 表 2 研究区主要地质组合分类
Table 2 Classification of main geological combinations in the study area
地质组合类型 煤层
厚度/m煤层
间距/m埋深/m 顶煤覆岩组成及厚度/m 主要井田与赋水条件 区域
占比/%土层 基岩 风化层 薄及中厚–厚型
(Ⅰ型)1−2:0.8~3.0
2−2:3.0~5.010~40 40~520
40~48020~80 20~420 20~60 贫水区:大柳塔、石圪台、柠条塔
富水区:大保当、尔林兔、小壕兔24.82 1−2:0.8~3.0
2−2:>5.010~40 40~520
80~50020~120 40~360 20~60 贫水区:柠条塔、哈拉沟、红柳林(4−2、5−2煤)
富水区:孟家湾西
较富水区:小保当22.26 1−2:0.8~3.0
3−1:3.0~5.020~40 80~280
80~24020~80 20~160 20~60 贫水区:凉水井
富水区:尔林兔、锦界、大保当
较富水区:红柳林12.37 厚–薄及中厚型
(Ⅱ型)2−2:>5.0
3−1:0.8~3.020~40 80~460
140~52020~140 80~260 20~60 贫水区:哈拉沟、大柳塔
富水区:大保当、金鸡滩、西湾、小壕兔
较富水区:曹家滩、榆树湾、杭来湾12.61 厚–厚型(Ⅲ型) 1−2:3.0~5.0
2−2:3.0~5.010~40 40~400
40~32020~60 20~420 10~40 贫水区:石圪台、哈拉沟、袁家梁、
郭家湾、活鸡兔、大柳塔(1−2上、1−2煤)
较富水区:尔林兔、中鸡10.90 薄及中厚–薄及
中厚型(Ⅳ型)1−2:0.8~3.0
2−2:0.8~3.010~40 40~460
60~46020~80 80~400 20~60 贫水区:大海则、郭家湾、哈拉沟(1−2上、1−2煤)
富水区:尔林兔、小壕兔、孟家湾、大保当
较富水区:小保当、柠条塔17.04 表 3 Ⅰ型开采的上行裂隙发育高度统计
Table 3 Statistics of upward fracture heights under the mining of the Type Ⅰ
矿井 煤层 上煤层 下煤层 来源 采高/m 基岩厚度/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 采高/m 煤层间距/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 红柳林煤矿 4−2煤 2.87 57.4 98.2 15.5 实测 隆德煤矿 1−2煤与2−2煤 1.80 110.0 35.0 15.1 4.00 50.0 100.0 32.0 实测 榆树泉煤矿 下8与下10煤 1.69 46.0 3.41 8.6 85.0 实测 布尔台煤矿 2−2煤与4−2煤 3.00 埋深335.0 79.4 21.0 6.60 71.2 158.5 34.7 实测 柠条塔煤矿 1−2煤与2−2煤 1.89 81.7 63.0 12.0 4.60 33.3 158.6 23.6 实验 榆北某矿 1−2煤与2−2煤 2.00 253.6 56.0 7.0 6.00 39.9 196.0 16.0 实验 石圪台煤矿 1−2煤与2−2煤 2.30 40.8 40.8 17.4 3.50 40.7 83.8 15.6 实验 阳煤一矿 12煤与15煤 1.90 埋深438.0 60.0 12.0 4.70 24.4 174.0 25.5 实验 贵州某矿 16煤与18煤 2.60 78.5 53.0 11.0 3.30 22.5 83.0 13.0 实验 表 4 Ⅱ型开采的上行裂隙发育高度统计
Table 4 Statistics of upward fracture heights under the mining of the Type Ⅱ
矿井 煤层 上煤层 煤层间距/m 来源 采高/m 基岩厚度/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 金鸡滩矿 2−2煤 5.50 202.0 146 20.6 实测 曹家滩矿 2−2煤 6.00 214.0 139 实测 2−2煤 5.00 173.3 123 实测 榆树湾矿 2−2煤 5.50 170.0 138 25.4 实测 2−2煤 6.00 144.0 149 27.1 实测 2−2煤 5.00 151.1 139 实测 张家峁矿 2−2煤 5.60 117.0 166 37.0 实测 柠条塔矿 2−2煤 5.80 埋深171.0 154 35.3 实测 1−2煤 5.46 埋深186.1 149 14.2 实测 大柳塔矿 5−2煤 7.79 137 19.8 实测 补连塔矿 1−2煤 7.60 261.0 123 37.4 实测 1−2煤 7.40 207.0 106 35.1 实测 柳巷矿 2煤 7.90 118 54.7 实测 布尔台矿 4−2煤 6.60 159 实测 大柳塔矿 5−2煤 7.30 170.0 143 18.0 实验 小保当矿 2−2煤 5.86 254.1 176 40.1 33.20 实验 3−1煤 2.00 234 9.0 哈拉沟矿 2−2煤 6.00 埋深82.0 贯通地表 46.14 实验 3−1煤 1.80 贯通地表 表 5 Ⅲ型开采的上行裂隙发育高度统计
Table 5 Statistics of upward fracture heights under the mining of the Type Ⅲ
矿井 煤层 上煤层 下煤层 来源 采高/m 基岩厚度/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 采高/m 煤层间距/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 榆阳矿 2−2煤 3.50 埋深208.0 96.3 17.20 实测 锦界矿 3−1煤 3.00 60.8 68.3 9.10 实测 杭来湾矿 4−2煤 4.50 150.0 116.0 22.20 实测 大柳塔矿 1−2煤 3.79 埋深54.6 54.6 8.10 实测 大柳塔矿 1−2煤 3.95 埋深89.2 89.2 13.50 实测 补连塔矿 1−2煤 4.40 242.0 154.0 17.10 实测 凉水井矿 4−2煤 3.12 37.2 64.2 30.20 实测 凉水井矿 4−2煤 3.45 28.9 45.6 10.85 实测 韩家湾矿 2−2煤 4.43 埋深160.0 110.0 实测 柠条塔矿 2−2煤 4.80 埋深151.0 131.0 33.50 实测 补连塔矿 2−2煤 4.80 174.0 154.0 实测 黄陵矿 2煤 3.20 550.0 68.0 18.00 实验 红柳林矿 2−2、3−1煤 3.44 30.1 94.7 15.00 3.05 28.5 126.0 16.5 实验 锦界矿 3−1、4−2煤 3.20 63.0 52.6 13.00 3.5 20.0 73.0 14.0 实验 大柳塔矿 2−2、2−3煤 4.20 46.5 43.9 18.60 4.2 6.0 69.3 23.5 实验 成家庄矿 4、5煤 4.00 450.0 45.5 17.40 3.0 26.0 68.5 26.0 实验 神东某矿 1−2、2−2煤 3.50 95.0 63.0 14.00 4.5 30.0 143.5 实验 张集矿 11−2、8煤 3.00 38.5 42.0 16.00 3.0 72.5 55.0 13.0 实验 淮南某矿 13−1、11−2煤 3.00 225.0 49.0 14.00 3.0 14.5 95.0 10.0 实验 表 6 Ⅳ型开采的上行裂隙发育高度统计
Table 6 Statistics of upward fracture heights under the mining of the Type Ⅳ
矿井 煤层 上煤层 下煤层 来源 采高/m 基岩厚度/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 采高/m 煤层间距/m 导水裂隙带高度/m 垮落带高度/m 韩家湾矿 3−1、4−2煤 2.70 50.0 110.0 17.6 1.9 37 150.2 13.8 实测 凉水井矿 4−2、4−3煤 3.00 40.4 117.0 1.0 19.80 139.5 实测 哈拉沟矿 1-2上、1−2煤 1.63 38.3 49.7 9.0 1.7 9.04 60.4 13.0 实验 松河煤矿 3、9煤 2.50 49.3 30.0 8.0 1.5 60.00 15.0 实验 石圪台矿 11、22煤 2.10 66.5 33.4 2.7 20.00 74.3 实验 表 7 煤层开采后下行裂隙发育实测统计
Table 7 Statistics of measured downward fractures after coal seam mining
矿井 煤层/工作面 采高/m 隔水层构成 下行裂隙实测深度/m 下行裂隙深度/采高 五沟矿 10煤 3.5 基岩厚度约43 m,松散层和土层厚度230 m 5.50 1.6 祁东矿 7114工作面 3.0 主要岩性为黏土、粉砂岩及细砂岩,厚度78 m 5.76 1.9 7122工作面 2.4 主要岩性为黏土、粉砂岩及细砂岩,厚度118.4 m 5.64 2.4 张家峁矿 5−2煤 5.5 基岩厚度平均117 m,黄土层60 m 18.00 3.2 表 8 研究区主要矿井上部两层可采煤层采动隔水层稳定性
Table 8 Stability assessment of aquicludes under the mining of two minable coal seams in the upper parts of primary mines in the study area
地质组合类型 矿井 开采方式 隔水层稳定性 薄及中厚–厚型(Ⅰ型) 大柳塔、石圪台、哈拉沟(1−2煤、2−2煤) 单一煤层 均失稳 重复采动 柠条塔(1−2煤、2−2煤)、锦界、凉水井、红柳林(1−2煤、3−1煤) 单一煤层 稳定 重复采动 失稳 尔林兔、孟家湾西、小壕兔、小保当(1−2煤、2−2煤)、大保当(1−2煤、3−1煤) 单一煤层 均稳定 重复采动 厚–薄及中厚型(Ⅱ型) 大柳塔、哈拉沟(2−2煤、3−1煤) 单一煤层 均失稳 重复采动 金鸡滩、曹家滩、榆树湾、杭来湾、大保当、小壕兔、西湾(2−2煤、3−1煤) 单一煤层 均稳定 重复采动 厚–厚型(Ⅲ型) 活鸡兔、哈拉沟、石圪台、袁家梁、郭家湾、大柳塔、朱盖塔、孙家岔 单一煤层 均失稳 重复采动 尔林兔、活鸡兔(1−2煤、2−2煤) 单一煤层 均失稳 重复采动 薄及中厚–薄及中厚型(Ⅳ型) 大海则、郭家湾、哈拉沟(1−2煤、2−2煤) 单一煤层 均失稳 重复采动 孟家湾、小壕兔、中鸡、尔林兔(1−2煤、2−2煤) 单一煤层 稳定 -
[1] 徐祝贺,李全生,张国军,等. 神东矿区多煤层开采覆岩破坏及导水裂隙带高度特征研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2023,5(6):063042. XU Zhuhe,LI Quansheng,ZHANG Guojun,et al. Study on the feature of overlying rock failure and the height of water–conducting fracture zone after multi–seam coal mining in Shendong Mining Area[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2023,5(6):063042.
[2] 吴群英,郭重威,翟鸿良,等. 重复采动覆岩裂隙率空间分布相似模拟研究:以陕北矿区为例[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(1):105−111. WU Qunying,GUO Zhongwei,ZHAI Hongliang,et al. Physical simulation on spatial distribution of void fraction in overburden due to repeated mining in north Shaanxi Mining Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(1):105−111.
[3] 曹健,黄庆享. 浅埋近距煤层开采覆岩与地表裂缝发育规律及控制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(4):213−220. CAO Jian,HUANG Qingxiang. Regularity and control of overburden and surface fractures in shallow–contiguous seams[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(4):213−220.
[4] 姚邦华,周海峰,陈龙. 重复采动下覆岩裂隙发育规律模拟研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2010,27(3):443−446. YAO Banghua,ZHOU Haifeng,CHEN Long. Numerical simulation about fracture development in overlying rocks under repeated mining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2010,27(3):443−446.
[5] 范立民,孙强,马立强,等. 论保水采煤技术体系[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):196−204. FAN Limin,SUN Qiang,MA Liqiang,et al. Technological system of water–conserving coal mining[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):196−204.
[6] PU Hai,MIAO Xiexing. Numerical analysis of the capability of water–resisting key strata to prevent water seepage in mined rock mass[M]//CAI Meifeng,WANG Jin’an. Boundaries of rock mechanics. Boca Raton:CRC Press,2008:373–378.
[7] 蒋泽泉,王建文,王宏科. 浅埋煤层关键隔水层隔水性能及采动影响变化[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2011,23(4):26−31. JIANG Zequan,WANG Jianwen,WANG Hongke. Impermeability and mining impacts of key aquifuges for shallowly buried coal seams[J]. Coal Geology of China,2011,23(4):26−31.
[8] 高召宁,应治中,王辉. 厚风积沙薄基岩浅埋煤层保水开采研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(4):108−113. GAO Zhaoning,YING Zhizhong,WANG Hui. Research on water–preserved–mining of shallow seam covered with thin bedrock and thick windblown sands[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(4):108−113.
[9] 刘世奇. 厚煤层开采覆岩破坏规律及粘土隔水层采动失稳机理研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2016. LIU Shiqi. The law of the overburden failure in thick coal seam mining and instability criterion of the clay aquiclude under the influence of mining[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining & Technology (Beijing),2016.
[10] 黄庆享,张文忠,侯志成. 固液耦合试验隔水层相似材料的研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(增刊1):2813−2818. HUANG Qingxiang,ZHANG Wenzhong,HOU Zhicheng. Study of simulation materials of aquifuge for solid–liquid coupling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(Sup.1):2813−2818.
[11] 桑盛. 煤层隔水覆岩裂隙自愈演化和渗流容限机制[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. SANG Sheng. Evolution of fracture self–healing in water–proof overburden rock and limitation mechanism of seepage after coal mining[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[12] 李涛,高颖,张嘉睿,等. 陕北保水采煤背景下MICP再造隔水土层的试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(9):2984−2994. LI Tao,GAO Ying,ZHANG Jiarui,et al. Experimental study on reconstruction of aquiclude by MICP under the background of water preserved coal mining in northern Shaanxi[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(9):2984−2994.
[13] 侯立晓. 固废疏水性材料注浆再造杭来湾煤矿30201工作面覆岩隔水层[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2024. HOU Lixiao. Grouting FSHS material to reconstruction the overlying aquiclude in 30201 working face of Hanglaiwan Coal Mine[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2024.
[14] 郑磊,白海波,李海龙. 薄基岩近距煤层煤矿防治水规律研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2017,36(6):161−163. ZHENG Lei,BAI Haibo,LI Hailong. Research on rule of thin bedrock and close distance coal seam mine’s water prevention and control[J]. Coal Technology,2017,36(6):161−163.
[15] 潘卫东,姜鹏,许延春,等. 薄基岩近距离煤层开采“水–岩”致灾演变模型及规律研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(3):543−552. PAN Weidong,JIANG Peng,XU Yanchun,et al. The model and law of “water–rock” disaster in near–distance coal seam mining in thin bedrock[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(3):543−552.
[16] 王双明,黄庆享,范立民,等. 生态脆弱区煤炭开发与生态水位保护[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2010. [17] 黄庆享. 浅埋煤层覆岩隔水性与保水开采分类[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(增刊2):3622−3627. HUANG Qingxiang. Impermeability of overburden rock in shallow buried coal seam and classification of water conservation mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(Sup.2):3622−3627.
[18] 李海军. 红柳林煤矿浅埋煤层群开采覆岩导水裂隙带发育规律研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2019. LI Haijun. Study on the development characteristics of overburden water flowing fracture zone in shallow coal seam group of Hongliulin Coal Mine[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2019.
[19] 李青海. 石圪台煤矿浅埋较薄煤层开采覆岩运动规律研究[D]. 青岛:山东科技大学,2009. LI Qinghai. Study on the movement of surrounding rocks during shallow thinner seam mining in Shigetai Coal Mine[D]. Qingdao:Shandong University of Science and Technology,2009.
[20] 梁勇,薛彦平,胡胜勇. 近距离煤层群重复采动覆岩破坏规律分析研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2021,41(4):72−75. LIANG Yong,XUE Yanping,HU Shengyong. Study on overburden failure law of close distance coal seam group under repeated mining[J]. Mining Research and Development,2021,41(4):72−75.
[21] 李磊. 浅埋厚砂层近距离煤层开采覆岩结构演化规律研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2021. LI Lei. Research on evolution rule of overlying strata structure in repeat mining of shallow close distance seams[D]. Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2021.
[22] 李磊明. 煤层群重复采动卸压瓦斯储运区演化规律及应用[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2021. LI Leiming. Evolution law and application of pressure relief gas storage and transportation area in coal seam group with repeated mining[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2021.
[23] 范立民,马雄德,蒋泽泉,等. 保水采煤研究30年回顾与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(7):1−30. FAN Limin,MA Xiongde,JIANG Zequan,et al. Review and thirty years prospect of research on water–preserved coal mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(7):1−30.
[24] 姜钰泉. 小保当一号井主采煤层采动覆岩变形规律研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2021. JIANG Yuquan. Study on deformation law of overlying strata induced by mining in main coal seam of Xiaobaodang No.1 Well[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2021.
[25] 于水,黄克军,杨建辉. 曹家滩煤矿首采面导水裂隙带高度研究[J]. 陕西煤炭,2020(2):42−46. YU Shui,HUANG Kejun,YANG Jianhui. Study on the height of water flowing fractured zone in the first mining face of Caojiatan Coal Mine[J]. Shaanxi Coal,2020(2):42−46.
[26] 霍晓斌. 浅埋大采高工作面覆岩破坏规律及导水裂隙带发育高度研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2018. HUO Xiaobin. Study on overlying rock failure above large mining height longwall face with shallow cover and development height of water flowing fractured zone[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2018.
[27] 侯恩科,张萌,孙学阳,等. 浅埋近距离煤层群开采覆岩与地表移动破坏规律研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2022,34(5):31−36. HOU Enke,ZHANG Meng,SUN Xueyang,et al. Study on shallow small interval coal seam group mining overburden and surface movement failure regularity[J]. Coal Geology of China,2022,34(5):31−36.
[28] 王跃. 浅埋近距双煤层开采覆岩破坏动态规律研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021. WANG Yue. Research on the dynamic law of overlying strata failure in shallow burying and short distance double coal seam mining[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2021.
[29] 杨家坤. 多煤层开采覆岩分布式光纤监测及破坏特征研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2018. YANG Jiakun. Research on distributed fiber monitoring and damage characteristics of overlying strata in multi–coal mining[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2018.
[30] 黄远. 双煤层重复采动下覆岩变形破坏特征及导高发育研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2014. HUANG Yuan. Study on the height development of cracking zone and the deformation and failure characteristics of the overburden during repeated mining of double seam[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2014.
[31] 文虎,于志金,翟小伟,等. 叠加开采下浅埋煤层裂隙演化与连通特征[J]. 煤矿安全,2015,46(12):46−49. WEN Hu,YU Zhijin,ZHAI Xiaowei,et al. Crack development and interconnected characteristics of closely spaced shallow coal seams under overlapping mining[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2015,46(12):46−49.
[32] 马荣振. 厚松散层及承压水失水条件下重复采动地表移动变形规律研究[D]. 淮南:安徽理工大学,2014. MA Rongzhen. Research the law of surface movement and deformation of multiple mining under confined water loss and thick unconsolidated layers[D]. Huainan:Anhui University of Science & Technology,2014.
[33] 吴鸿涛. 厚松散层重复采动下地表沉陷移动规律研究[D]. 淮南:安徽理工大学,2016. WU Hongtao. Study on the law of surface movement and deformation caused by repeat mining under thick loose layer[D]. Huainan:Anhui University of Science & Technology,2016.
[34] 卢少帅,高超,霍军鹏,等. 韩家湾煤矿浅埋近距离煤层群覆岩破坏规律研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(1):107−111. LU Shaoshuai,GAO Chao,HUO Junpeng,et al. Failure law of overburden under shallow contiguous coal seams in Hanjiawan Coal Mine[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(1):107−111.
[35] 孙峰. 凉水井矿采空区下薄煤层开采覆岩运动与矿压显现规律研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. SUN Feng. Study on the movement of overlying rock and the law of mine pressure appearance in the mining of thin coal seam under the goaf of Liangshuijing Mine[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[36] 胡永忠. 山体赋存煤层群混合开采覆岩破断规律及顶板控制研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2014. HU Yongzhong. Study on characteristics of overlying strata breaking and roof control technology of coal seam group mixed mining under mountain[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2014.
[37] 郭文兵,杨达明,谭毅,等. 薄基岩厚松散层下充填保水开采安全性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(1):106−111. GUO Wenbing,YANG Daming,TAN Yi,et al. Study on safety of overlying strata by backfilling in water–preserved mining under thick alluvium and thin bedrock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(1):106−111.
[38] 刘启蒙,刘瑜,谢志钢,等. 基于“双行裂隙”模型的两淮矿区高承压厚松散层突水机理[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(3):140−149. LIU Qimeng,LIU Yu,XIE Zhigang,et al. Water inrush mechanism of thick alluvium aquifer with high pressure based on the “bidirectional fractures” model in Huainan and Huaibei Mining Area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(3):140−149.
[39] 潘瑞凯,曹树刚,李勇,等. 浅埋近距离双厚煤层开采覆岩裂隙发育规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(8):2261−2268. PAN Ruikai,CAO Shugang,LI Yong,et al. Development of overburden fractures for shallow double thick seams mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(8):2261−2268.
[40] CAO Jian,SU Haitao,WANG Chao,et al. Research on the evolution and height prediction of WCFZ in shallow close coal seams mining[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo–Energy and Geo–Resources,2023,9(1):128.
[41] CAO Jian,WEI Xumin. Research on mining–induced surface soil cracking mechanism and development depth of downward fracture[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2024,160:108180.







 下载:
下载: