Advances in research on the mechanical responses of hot dry granites under varying cooling conditions in China
-
摘要:意义
增强型地热系统(EGS)是目前开发干热岩的关键技术手段,在EGS的建设与运行过程中,储层岩石会遇到高温冷却、循环冷却、遇水冷却等多种冷却条件。因此,研究不同冷却条件下花岗岩(典型干热岩)的力学响应特征意义重大。
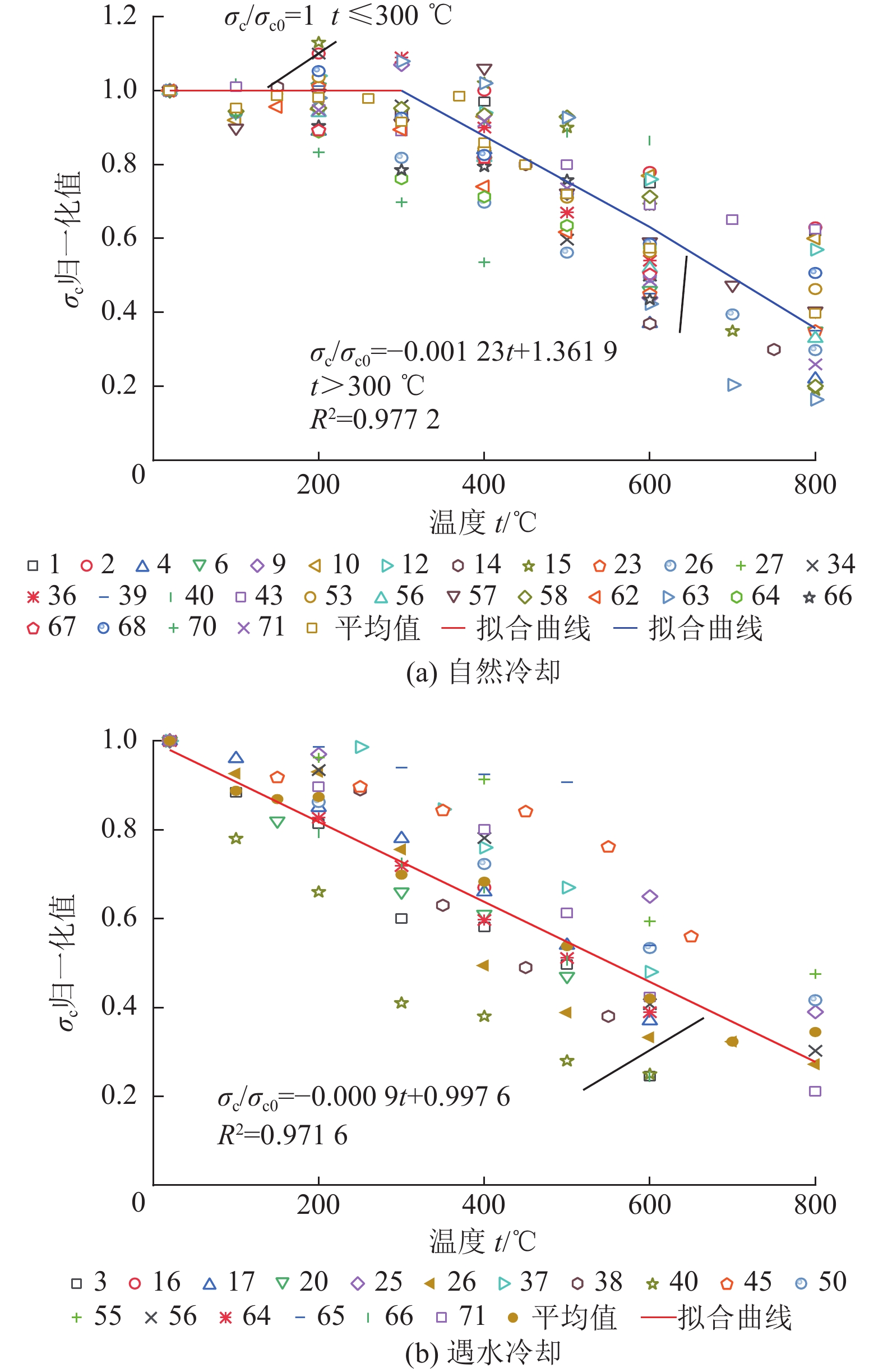
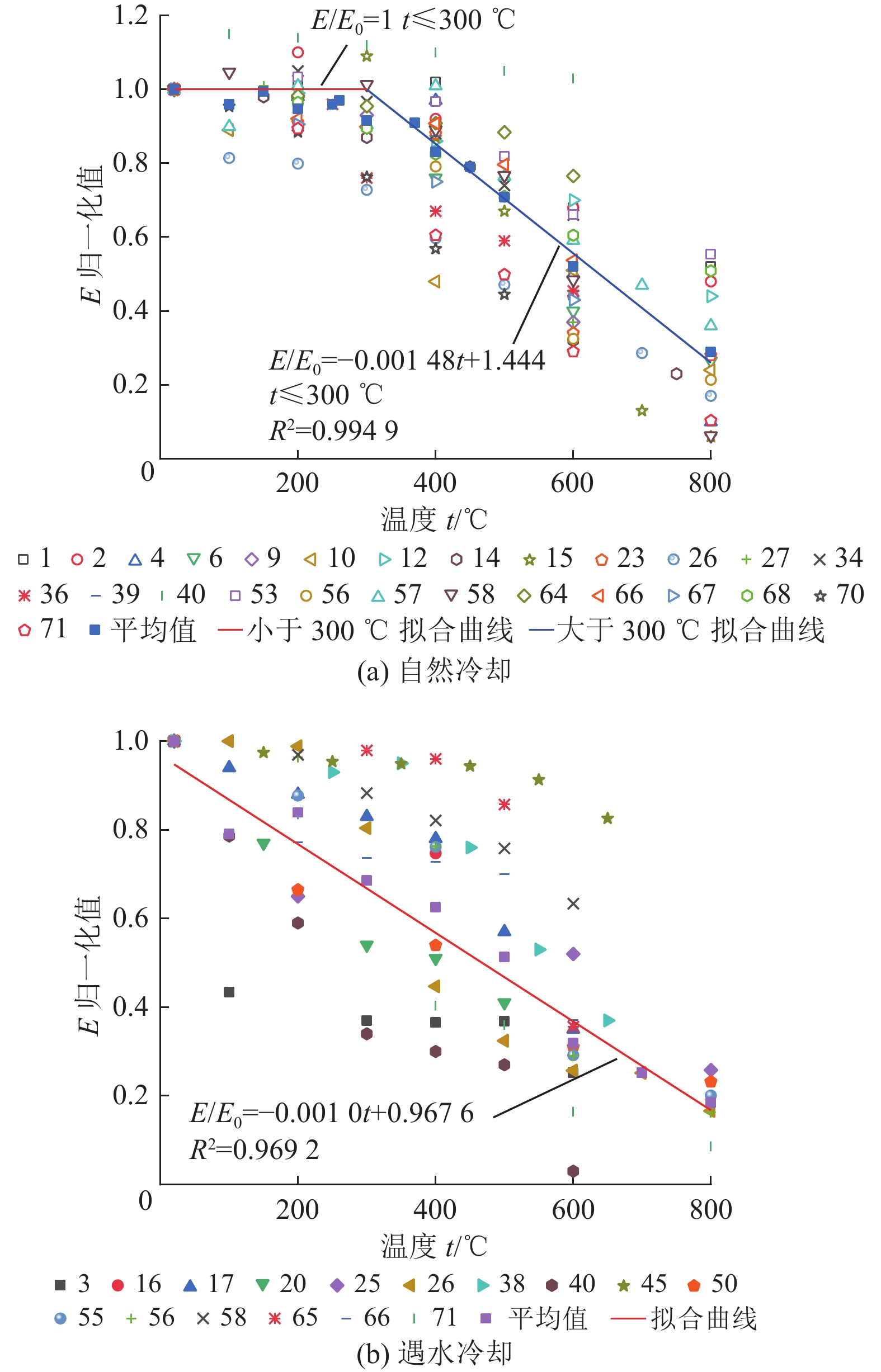
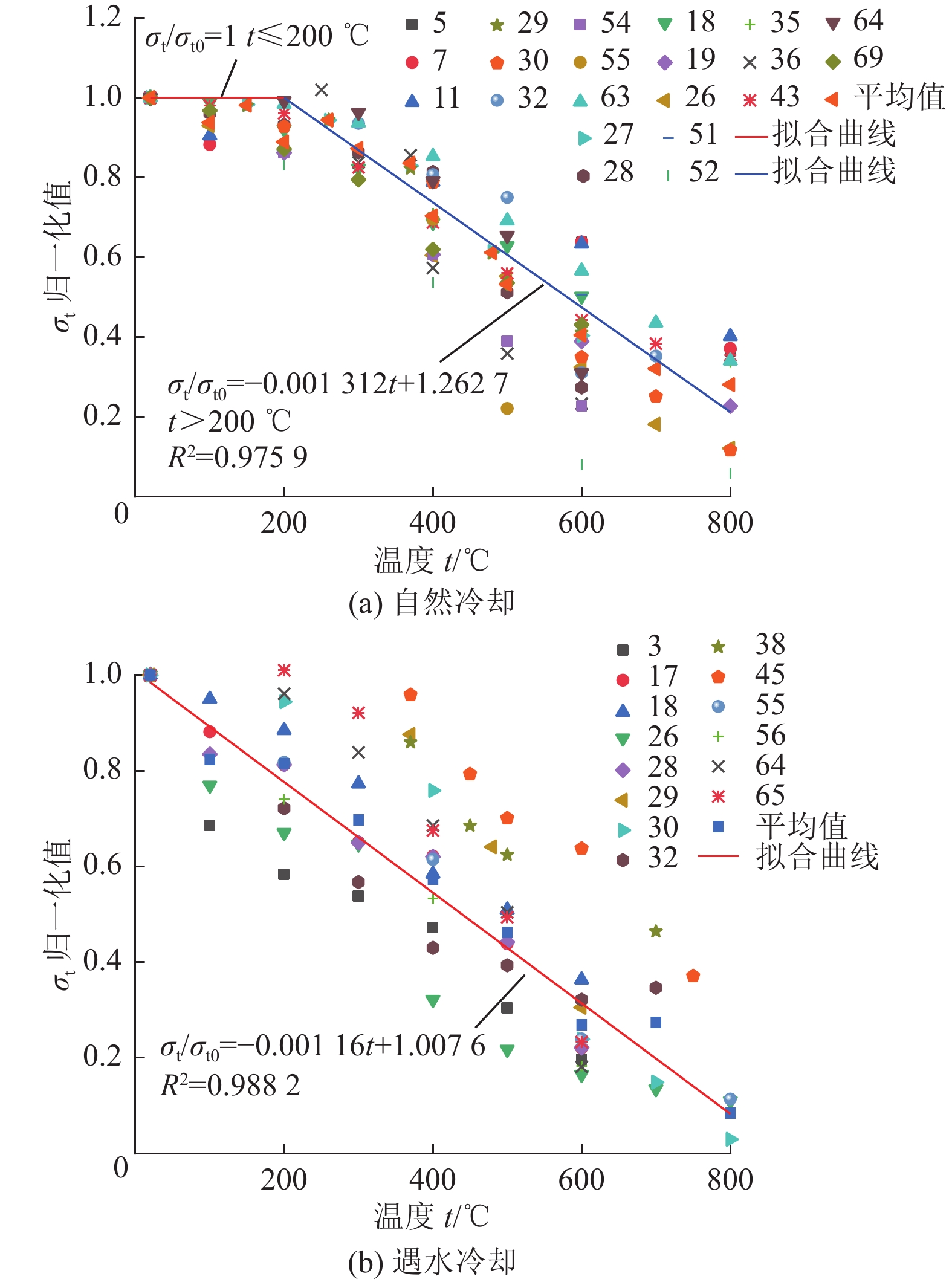
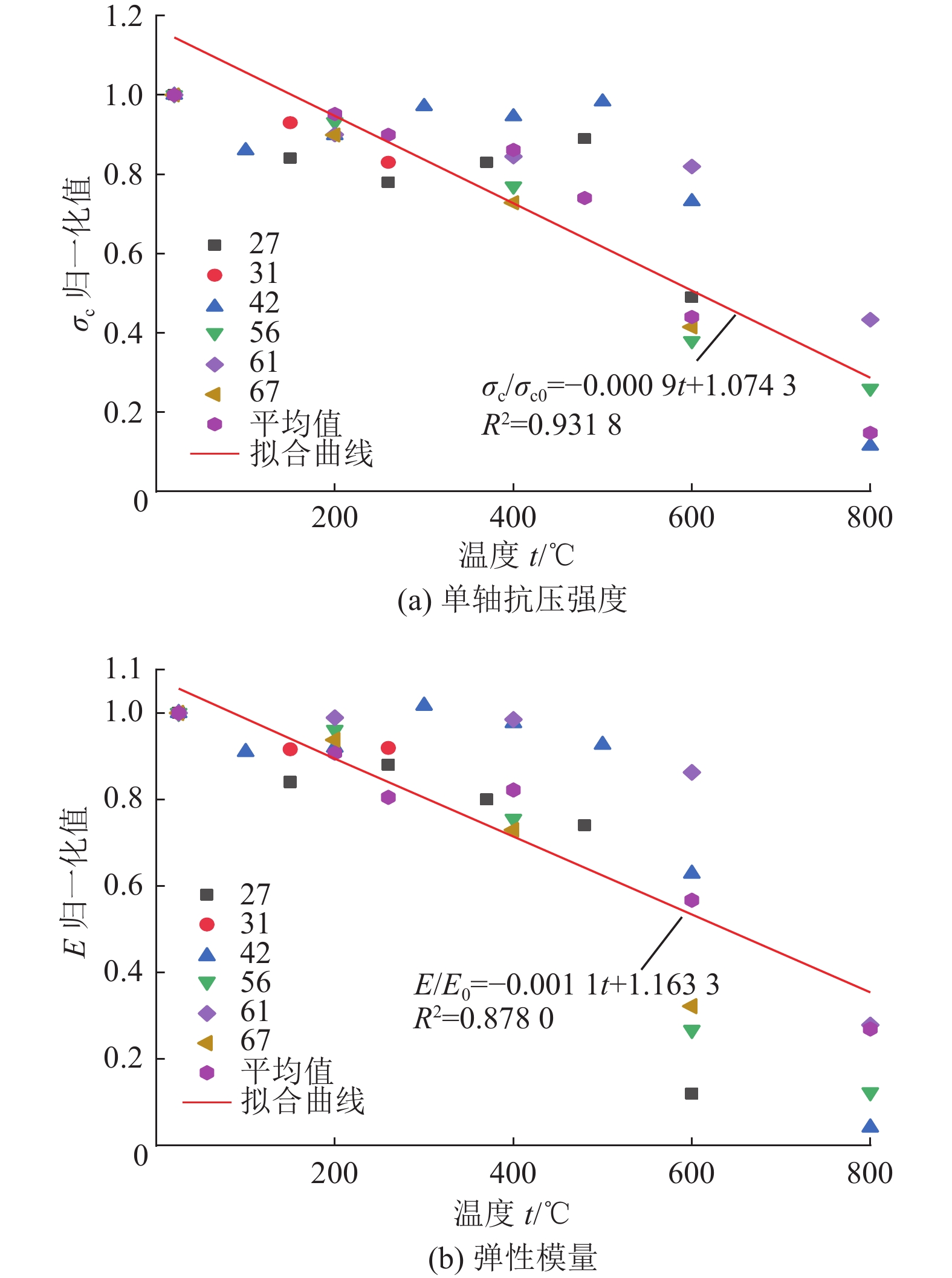
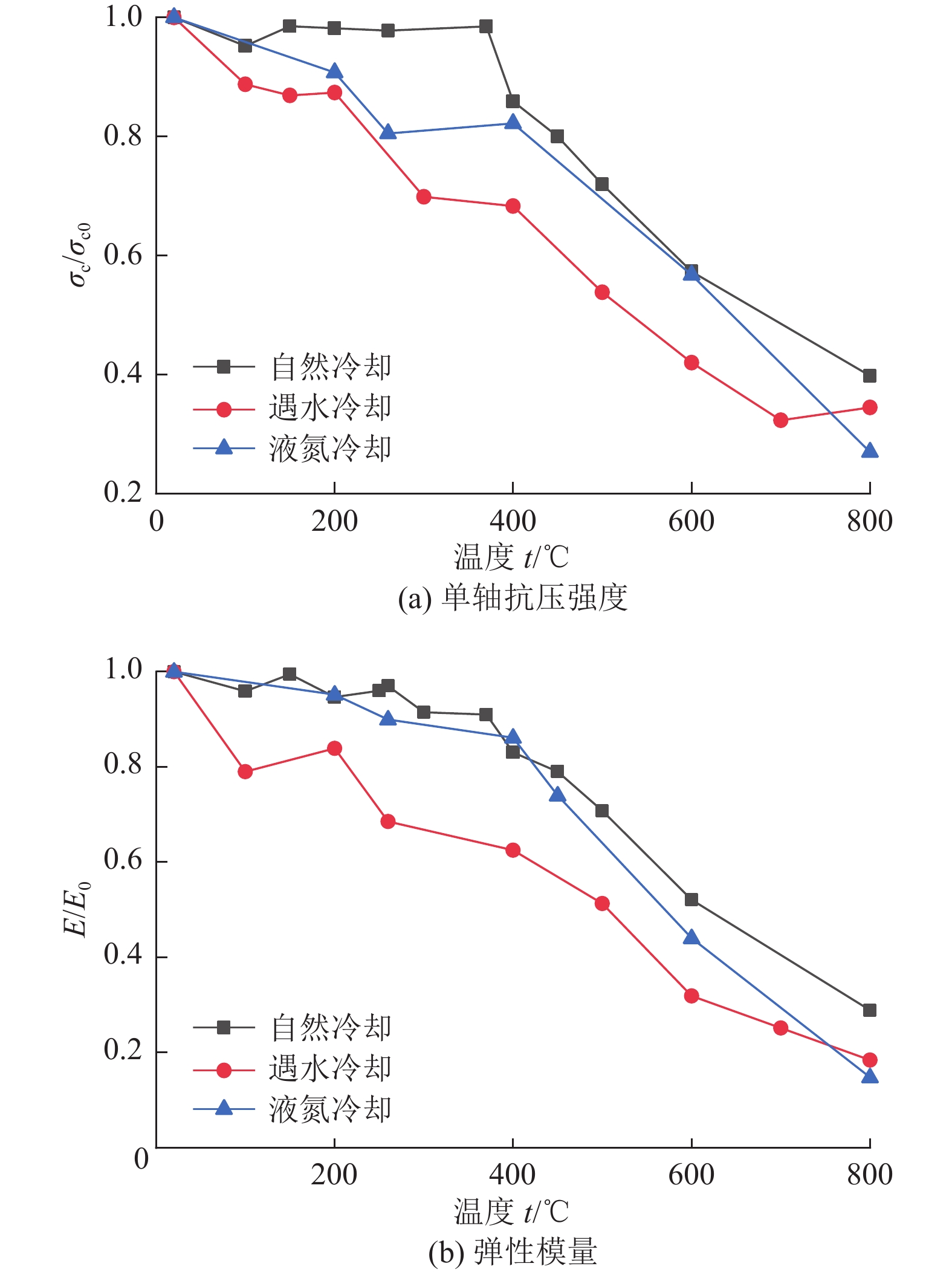
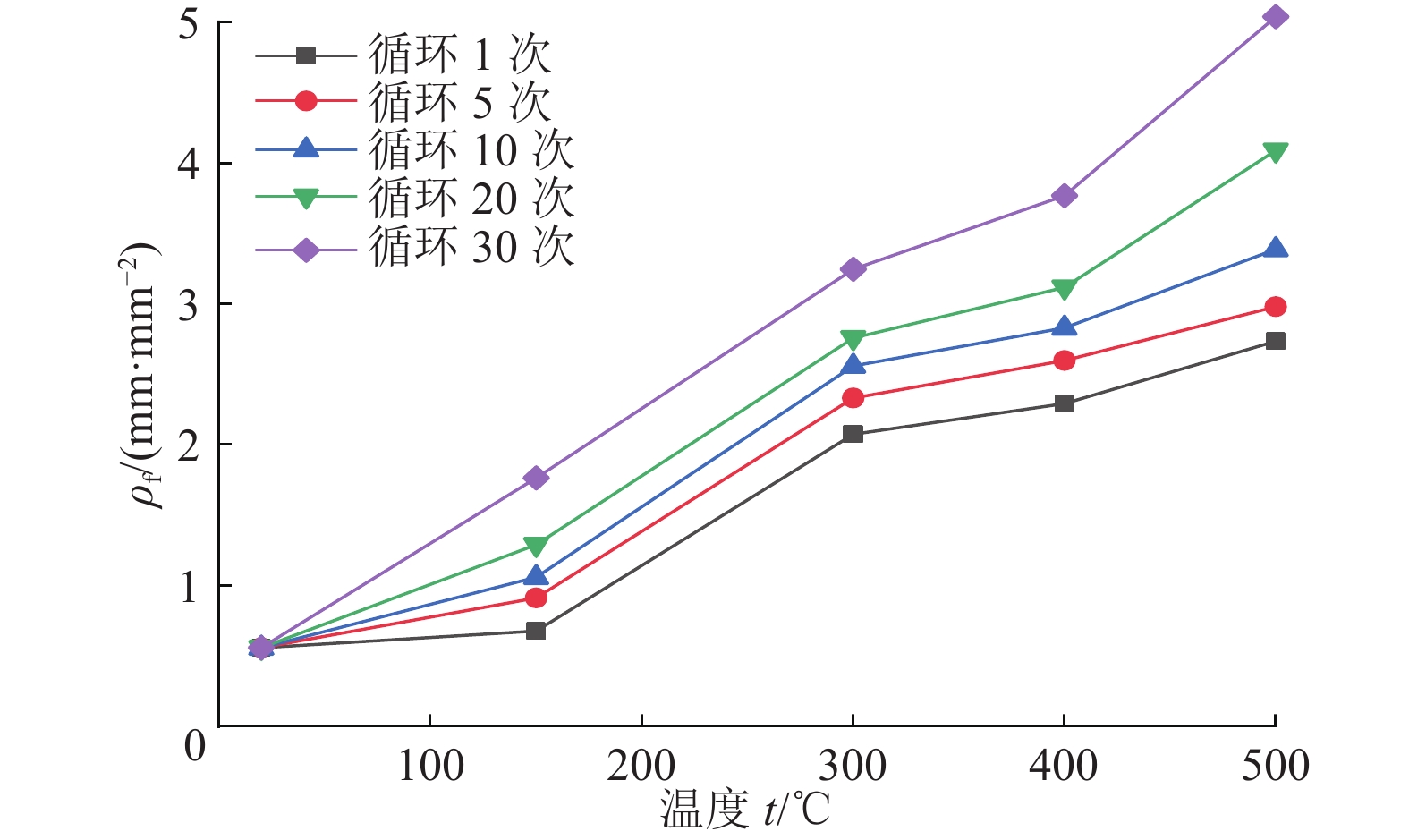
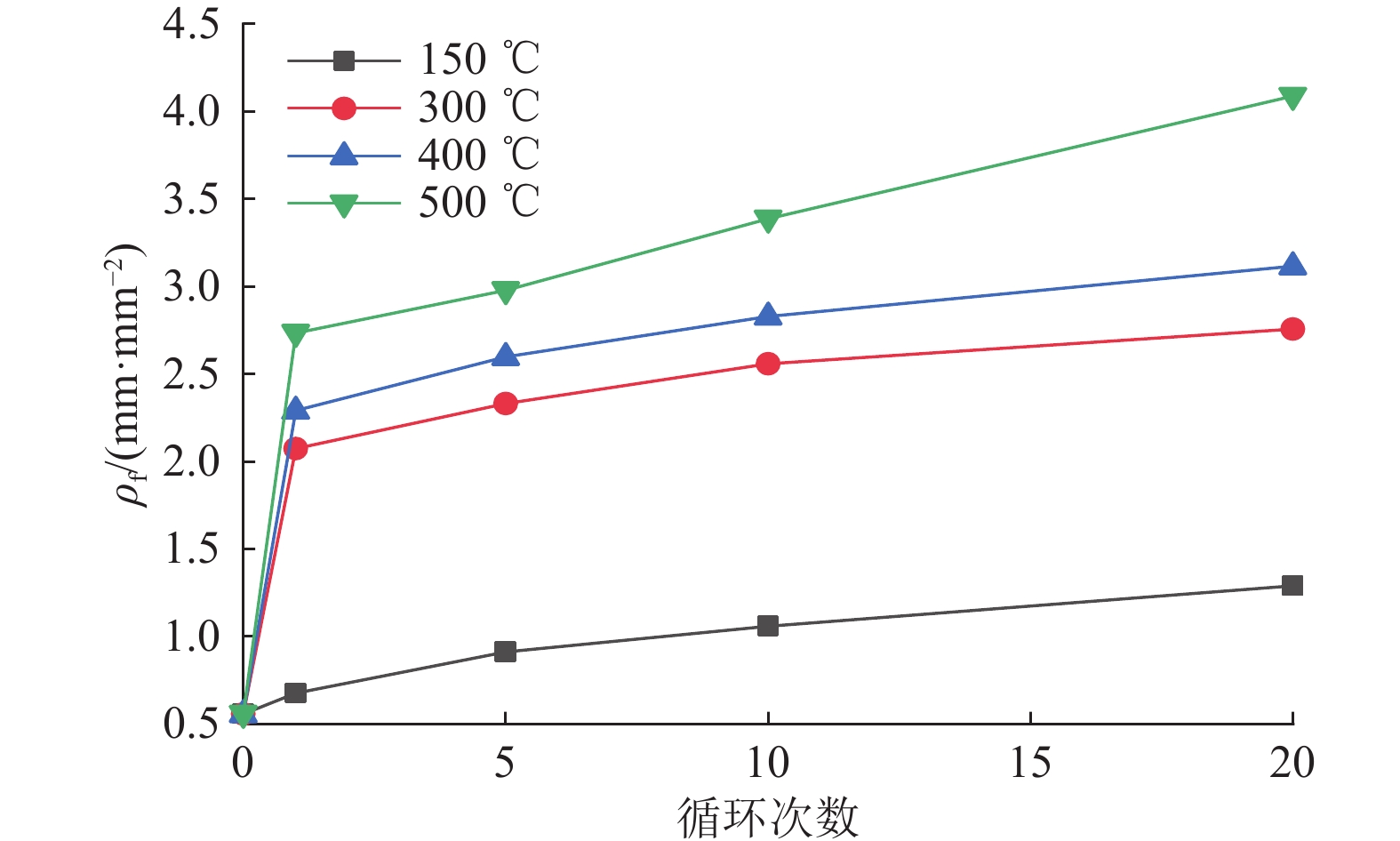
进展(1) 总结并分析了不同冷却条件(高温自然冷却、遇水冷却、循环冷却)下我国典型花岗岩在力学响应(单轴抗压强度σc、弹性模量E、抗拉强度σt和泊松比ν)方面的实验数据,指出温度低于200或300 ℃时,高温自然冷却后花岗岩的σc、E和σt略有降低;温度高于200或300 ℃时,σc、E和σt随温度升高近线性减小。(2) 在任意温度下,遇水冷却后花岗岩σc、E和σt随温度的升高近线性减小。循环冷却下,在经历第1次循环后花岗岩σc、E和σt迅速降低,而当循环次数大于5时,σc、E和σt逐渐趋于定值。高温自然冷却下,ν随温度升高而降低,其降幅大于高温遇水冷却条件下的ν。(3) 高温花岗岩在不同冷却条件下力学性能劣化的主因是内部微裂纹的起裂和扩展。统计了不同冷却条件下干热花岗岩力学响应数据并分析其内在机理,对力学参数归一化值与温度的关系进行拟合,并提出了经验公式。
展望提出高温花岗岩岩石力学研究的未来发展趋势,包括干热岩开采与CO2地质封存结合过程中的力学响应、多场−多相−多过程耦合作用下干热岩力学响应、基于干热岩开发过程中的实际条件开展实验研究等,以期为干热岩开发的相关设计、计算和数值模拟提供理论支撑。
Abstract:SignificanceEnhanced geothermal systems (EGSs) serve as a key technique for exploiting hot dry rocks (HDRs) presently. During the construction and operation of EGSs, rocks of the HDR reservoirs will experience various cooling conditions, such as natural cooling, cyclic cooling, and water cooling, rendering it greatly significant to investigate the mechanical response characteristics of granites—typical HDRs—under varying cooling conditions.
AdvancesThis study offers a summary and analysis of experimental data about the mechanical responses, i.e., uniaxial compressive strength (σc), elastic modulus (E), tensile strength (σt), and Poisson's ratio (ν), of typical granites in China under varying cooling conditions including natural, water, and cyclic cooling. The results reveal that after natural cooling, the σc, E, and σt values of the granites decrease slightly at temperatures below 200 ℃ or 300 ℃ but decrease nearly linearly with an increase in temperature at temperatures greater than 200 ℃ or 300 ℃. After water cooling, these values decrease nearly linearly with an increase in the temperature at any temperature. Under cyclic cooling, these values decrease rapidly after cooling for the first time and then gradually tend to remain constant after more than five times of cooling. Under natural cooling, the value of ν decreases with a rise in temperature, with the decreasing amplitude greater than that under water cooling. The deterioration of the mechanical properties of high-temperature granites under varying cooling conditions is primarily due to the generation and propagation of microcracks in them. Based on the statistics and the internal mechanism analysis of the mechanical response data on hot dry granites under varying cooling conditions, this study conducts the fitting of normalized mechanical parameters with temperature and proposes relevant empirical formulas.
ProspectsThis study proposes that future research on the mechanical properties of high-temperature granites will focus on the mechanical responses of HDR during their exploitation combined with CO2 sequestration, the mechanical responses of HDRs under the coupling effects of multiple fields, phases, and processes, and experimental studies based on the actual conditions of HDR exploitation. All these are expected to provide some theoretical support for the design, calculation, and numerical simulation of HDR exploitation.
-
-
表 1 不同冷却条件下高温花岗岩力学参数
Table 1 Mechanical parameters of high-temperature granites under different cooling conditions
序号 试样产地 σc0/MPa E0/GPa σt0/MPa 加热速率/
(℃·min−1)恒温
时长/h试样
个数冷却
方式尺寸/
(mm×mm)试样形状 参考文献 1 河南焦作 162.0 27.7 10/3 3 2 自然 50×100 圆柱 杜守继等[17] 2 河南焦作 152.3 34.7 10/3 3 5 自然 50×100 圆柱 邱一平等[18] 3 山东平邑 130.5 16.7 17.90 4 3 遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 郤保平等[19] 4 浙江宁波 85.5 14.8 10 6 3 自然 40×80 圆柱 陈有亮等[20] 5 陕西秦岭 8.89 10 2 3 自然 50×25 圆柱 支乐鹏等[21] 6 山东潍坊 120.4 14.2 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 徐小丽等[22] 7 陕西秦岭 90.4 8.94 10 3 3 自然 50×25 圆柱 Liu Shi等[23] 8 华北燕山 63.7 23.4 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Wang Yu等[24] 9 福建晋江 123.0 29.1 10 4 1 自然 25×50 圆柱 蔡燕燕等[25] 10 陕西秦岭 90.4 39.3 10 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Liu Shi等[26] 11 陕西秦岭 8.96 10 3 3 自然 50×25 圆柱 方新宇等[27] 12 甘肃北山 155.7 39.5 5 4 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 胡少华等[28] 13 北京房山 83.3 26.6 5 4 3 自然 25×50 圆柱 田红等[29] 14 福建泉州 165.2 51.6 5 4 1 自然 30×80×160 立方柱 Huang Yanhua等[30] 15 山东日照 80.1 37.4 5 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Yang Shengqi等[31] 16 湖北大别山 150.0 33.9 5 4 3 遇水 50×100 圆柱 操旺进[32] 17 山东日照 130.1 12.8 7.93 2 2 3 遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 靳佩桦等[33] 18 福建晋江 5.20 5 2 1 自然&遇水 50×25 圆柱 梁铭等[34] 19 未明采样地 196.6 10.59 5 2 4 自然 50×25 圆柱 吴顺川等[35] 20 湖北随州 189.1 21.2 5 2 3 遇水 50×100 圆柱 朱振南等[36] 21 山东日照 125.0 10 1 1 遇水&循环 50×100 圆柱 Ge Zhenlong等[37] 22 福建晋江 168.7 39.8 10 4 3 自然&循环 50×100 圆柱 Rong Guan等[38] 23 山东兖州 120.4 31.3 10 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Xu Xiaoliang等[39] 24 湖北大别山 168.0 11.3 5 1 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Zhang Fan等[40] 25 北京房山 79.9 16.0 3 2 3 遇水 25×50 圆柱 陈宇等[41] 26 辽宁松辽盆地 164.7 44.6 14.30 30 4 3 自然&遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 崔翰博等[42] 27 北京房山 153.6 33.7 9.89 5 12 3 自然&液氮 25×50 &
50×25圆柱 黄中伟等 [43] 28 山东某地 130.1 12.8 7.93 2 2 3 自然&遇水 50×25 圆柱 Jin Peihua等[44] 29 山东某地 154.2 33.2 9.91 5 10 3 自然&遇水 50×25 圆柱 Wu Xiaoguang等[45] 30 湖北汝城 107.3 30.3 8.78 6 3 自然&遇水 50×25 圆柱 Wu Qiuhong等[46] 31 山东某地 147.8 33.8 5 10 2 液氮 25×50 圆柱 Wu Xiaoguang等[47] 32 未明采样地 14.00 8 2 1 自然&遇水 50×25 圆柱 邓龙传等[48] 33 青海共和 115.2 37.6 5 2 1 自然 25×50 圆柱 卢运虎等[49] 34 青海共和 152.7 8.2 2 2 3 自然 50×100 圆柱 罗生银等[50] 35 甘肃北山 9.59 5 2 1 自然 50×25 圆柱 闵明等[51] 36 青海共和 132.2 14.8 3 3 3 自然 50×100 圆柱 吴阳春等[52] 37 青海共和 173.4 5 3 1 自然&遇水 50×100 圆柱 郤保平等[53] 38 福建漳州 123.1 69.3 4.76 10 2 2 遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 朱栋等[54] 39 山东潍坊 120.7 36.4 2 3 自然 50×100 圆柱 Guo Hongjun等 [55] 40 未指明采样地 144.0 7.2 4 8 4 自然&遇水 50×100 圆柱 Li Chun等 [56] 41 北京房山 84.8 14.0 3 2 1 自然 25×50 圆柱 Qin Yan等[57] 42 湖南汪罗 174.0 23.0 5 4 3 液氮 25×50 圆柱 Shao Zuliang等[58] 43 甘肃北山 158.6 5 2 5 自然 80×80×80 立方体 Tang Zhicheng等[59] 44 山东日照 97.0 22.3 5 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Yang Shengqi等[60] 45 湖南某地 195.0 37.7 9.43 5 2 3 遇水 50×100 圆柱 Yang Fujian等[61] 46 甘肃北山 134.2 34.0 3 2 3 自然&循环 50×100 圆柱 Yu Peiyang等[62] 47 湖北大别山 151.4 33.0 5 3 3 自然&遇水 37×74 圆柱 Zhang Fan等[63] 48 湖北麻城 161.4 40.9 3 4 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Zhang Zhenyu等[64] 49 湖北随州 118.6 18.4 5 2 3 遇水&循环 50×100 圆柱 Zhu Zhennan等 [65] 50 辽宁锦州 238.9 20.2 2 4 3 遇水 50×100 圆柱 贾蓬等[66] 51 河南泌阳 7.27 5 2 2 自然 50×25 圆柱 杨圣奇等[67] 52 山东汶上 5.86 5 2 2 自然 50×25 圆柱 杨圣奇等[67] 53 广东珠江 116.1 12.1 5 2 3 自然 50×100 圆柱 Ding Qile等 [68] 54 江西铅山 10.59 5 2 3 自然 50×25 圆柱 Guo Pei等[69] 55 山东某地 242.3 42.7 9.31 5 2 1 遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 Kang Fangchao等[70] 56 山东某地 115.4 32.6 9.24 5 2 3 自然&遇水&液氮 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 Kang Fangchao等[71] 57 湖北罗田 148.0 20.8 20 4 2 自然 50×100 圆柱 Ma Tianshou等[72] 58 甘肃北山 115.7 34.4 5 4 2 自然 100×50×30 长方体 Miao Shuting等[73] 59 山东济宁 157.6 16.6 5 2 3 遇水 50×100 圆柱 Ning Pei等[74] 60 湖北麻城 160.4 70.1 5.42 5 4 1 自然&液氮 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 Rong Guan等 [75] 61 湖南某地 185.3 20.4 2 2 1 液氮 50×100 圆柱 Wang Tianzuo等[76] 62 甘肃玉门 114.0 8 4 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Wu Yun等[77] 63 甘肃北山 151.0 6.20 8 2 1 自然 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 Wu Yun等[78] 64 江苏徐州 101.7 8.1 6.13 5 2 3 自然&遇水 50×100 圆柱 Xiao Pei等[79] 65 湖南船山坪 138.0 25.9 10.20 5 2 3 遇水 50×100 &
50×25圆柱 Zhang Fan等[80] 66 福建南安 163.7 24.0 5 2 3 自然&遇水 50×100 圆柱 Zhu Zhennan等[81] 67 湖北麻城 178.5 68.8 5.42 5 4 1 自然&液氮 50×100 圆柱 Chen Zhiheng等[82] 68 广东东莞 110.1 11.4 1.00 5 2 3 自然 50×100 圆柱 Ding Qile等[83] 69 河南驻马店 180.6 16.7 6.52 2 2 1 自然 50×25 圆柱 Hu Yuefei等[84] 70 湖北某地 178.7 20.1 2 2 1 自然 50×100 圆柱 Zhang Xiaowu等[85] 71 山东临沂 190.8 48.9 10 1 1 自然&遇水 30×80×160 立方体 Zhao Fei等[86] 注:σc0、E0和σt0分别表示岩石初始单轴抗压强度、初始弹性模量和初始抗拉强度。 表 2 高温自然和遇水冷却后花岗岩力学参数归一化值与温度的拟合曲线方程
Table 2 Fitted equations of temperature-varying normalized mechanical parameters of granites after natural cooling and water cooling
力学参数 自然冷却 遇水冷却 液氮冷却 单轴抗压强度 ${ {\sigma } }_{ {\mathrm{c} } }/{ {\sigma } }_{ {\mathrm{c} }0}=\left\{\begin{aligned}& 1,\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad t\leqslant 300 \;{\text{℃} }\\& -0.001\;23t+1.361\;9\quad t > 300 \;{\text{℃} }\text{,}{ {R} }^{2}=0.977\;2\end{aligned}\right.$ ${ {\sigma } }_{{\rm{c}}}/{ {\sigma } }_{{\rm{c}}0}=-0.000\;9t+0.997\;6$
${{R} }^{2}=0.971\;6$${ {\sigma } }_{{\rm{c}}}/{ {\sigma } }_{{\rm{c}}0}=-0.000\;9t+1.074\;3$
${{R} }^{2}=0.931\;8$弹性模量 $E/{E}_{0}=\left\{\begin{aligned}& 1,\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\; t\leqslant 300 \;{\text{℃} }\\&-0.001\;48t+1.444\quad t > 300 \;{\text{℃} }\text{,}{ {R} }^{2}=0.994\;9\end{aligned}\right.$ $E/{E}_{0}=-0.001t+0.967\;6$
${{R} }^{2}=0.969\;2$$E/{E}_{0}=-0.001\;1t+1.163\;3$
${ {R} }^{2}=0.878\;0$抗拉强度 ${ {\sigma } }_{ {\rm{t} } }/{ {\sigma } }_{ {\rm{t} }0}=\left\{\begin{aligned}& 1,\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\; t\leqslant 200 \;{\text{℃} }\\& -0.001\;31t+1.262\;7\quad t > 200 \;{\text{℃} }\text{,}{{R} }^{2}=0.975\;9\end{aligned}\right.$ ${ {\sigma } }_{ {\rm{t} } }/{ {\sigma } }_{ {\rm{t} }0}=-0.001\;16t+1.007\;6$
${ {R} }^{2}=0.988\;2$ -
[1] 汪集暘,孔彦龙,段忠丰,等. “双碳”目标下煤田区地热资源开发利用与储能技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(2):1−11. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.02.0104 WANG Jiyang,KONG Yanlong,DUAN Zhongfeng,et al. Geothermal energy exploitation and storage in coal field under the dual carbon goal[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(2):1−11. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.02.0104
[2] 侯正猛,吴旭宁,罗佳顺,等. 深部地热能系统主要挑战与耦合储能的增强型创新开发模式[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(1):1−13. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.12.0848 HOU Zhengmeng,WU Xuning,LUO Jiashun,et al. Major challenges of deep geothermal systems and an innovative development mode of REGS integrated with energy storage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(1):1−13. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.12.0848
[3] 王贵玲,刘彦广,朱喜,等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):1−9. WANG Guiling,LIU Yanguang,ZHU Xi,et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):1−9.
[4] 许天福,胡子旭,李胜涛,等. 增强型地热系统:国际研究进展与我国研究现状[J]. 地质学报,2018,92(9):1936−1947. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.09.012 XU Tianfu,HU Zixu,LI Shengtao,et al. Enhanced geothermal system:International progresses and research status of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2018,92(9):1936−1947. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.09.012
[5] 庞忠和,段忠丰. 华北赋煤区地热资源富集模式及开发利用方向[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(9):14−22. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.24.03.0159 PANG Zhonghe,DUAN Zhongfeng. Accumulation patterns and exploitation and utilization targets of geothermal resources in the coal–bearing area in North China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(9):14−22. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.24.03.0159
[6] 解经宇,王丹,李宁,等. 干热岩压裂建造人工热储发展现状及建议[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(3):321−329. XIE Jingyu,WANG Dan,LI Ning,et al. Development status and suggestions of hot dry rock hydraulic fracturing for building geothermal reservoirs[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(3):321−329.
[7] 汪集旸,胡圣标,庞忠和,等. 中国大陆干热岩地热资源潜力评估[J]. 科技导报,2012,30(32):25−31. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.32.002 WANG Jiyang,HU Shengbiao,PANG Zhonghe,et al. Estimate of geothermal resources potential for hot dry rock in the continental area of China[J]. Science & Technology Review,2012,30(32):25−31. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.32.002
[8] 蔺文静,王贵玲,邵景力,等. 我国干热岩资源分布及勘探:进展与启示[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(5):1366−1381. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.004 LIN Wenjing,WANG Guiling,SHAO Jingli,et al. Distribution and exploration of hot dry rock resources in China:Progress and inspiration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(5):1366−1381. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.004
[9] 庞忠和,罗霁,程远志,等. 中国深层地热能开采的地质条件评价[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):134−151. PANG Zhonghe,LUO Ji,CHENG Yuanzhi,et al. Evaluation of geological conditions for the development of deep geothermal energy in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):134−151.
[10] OLASOLO P,JUÁREZ M C,MORALES M P,et al. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS):A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2016,56:133−144. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.031
[11] 王志刚,胡志兴,李宽,等. 干热岩钻完井的挑战及技术展望[J]. 科技导报,2019,37(19):58−65. WANG Zhigang,HU Zhixing,LI Kuan,et al. Challenges and technical prospects of dry–hot rock drilling and completion[J]. Science & Technology Review,2019,37(19):58−65.
[12] XIE Jingyu,CHENG Wan,WANG Rongjing,et al. Experiments and analysis on the influence of perforation mode on hydraulic fracture geometry in shale formation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,168:133−147. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.05.017
[13] 赵阳升,孟巧荣,康天合,等. 显微CT试验技术与花岗岩热破裂特征的细观研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(1):28−34. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.01.005 ZHAO Yangsheng,MENG Qiaorong,KANG Tianhe,et al. Micro–CT experimental technology and meso–investigation on thermal fracturing characteristics of granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(1):28−34. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.01.005
[14] HEUZE F E. High–temperature mechanical,physical and thermal properties of granitic rocks:A review[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1983,20(1):3−10.
[15] HOMAND–ETIENNE F,HOUPERT R. Thermally induced microcracking in granites:Characterization and analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1989,26(2):125−134.
[16] DWIVEDI R D,GOEL R K,PRASAD V V R,et al. Thermo–mechanical properties of Indian and other granites[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2008,45(3):303−315. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.05.008
[17] 杜守继,刘华,职洪涛,等. 高温后花岗岩力学性能的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(14):2359−2364. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.14.010 DU Shouji,LIU Hua,ZHI Hongtao,et al. Testing study on mechanical properties of post–high–temperature granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(14):2359−2364. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.14.010
[18] 邱一平,林卓英. 花岗岩样品高温后损伤的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(6):1005−1010. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.06.032 QIU Yiping,LIN Zhuoying. Testing study on damage of granite samples after high temperature[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2006,27(6):1005−1010. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.06.032
[19] 郤保平,赵阳升. 600 ℃内高温状态花岗岩遇水冷却后力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(5):892−898. XI Baoping,ZHAO Yangsheng. Experimental research on mechanical properties of water–cooled granite under high temperatures within 600 ℃[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(5):892−898.
[20] 陈有亮,邵伟,周有成. 高温作用后花岗岩力学性能试验研究[J]. 力学季刊,2011,32(3):397−402. CHEN Youliang,SHAO Wei,ZHOU Youcheng. Experimental study on mechanical properties of granite after high temperature[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2011,32(3):397−402.
[21] 支乐鹏,许金余,刘志群,等. 高温后花岗岩巴西劈裂抗拉实验及超声特性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(增刊1):61−66. ZHI Lepeng,XU Jinyu,LIU Zhiqun,et al. Research on ultrasonic characteristics and Brazilian splitting–tensile test of granite under post–high temperature[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(Sup.1):61−66.
[22] 徐小丽,高峰,张志镇. 高温后围压对花岗岩变形和强度特性的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(12):2246−2252. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE201412012 XU Xiaoli,GAO Feng,ZHANG Zhizhen. Influence of confining pressure on deformation and strength properties of granite after high temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(12):2246−2252. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE201412012
[23] LIU Shi,XU Jinyu. Mechanical properties of Qinling biotite granite after high temperature treatment[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2014,71:188−193. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.07.008
[24] WANG Yu,LIU Baolin,ZHU Haiyan,et al. Thermophysical and mechanical properties of granite and its effects on borehole stability in high temperature and three–dimensional stress[J]. The Scientific World Journal,2014,2014(1):650683.
[25] 蔡燕燕,罗承浩,俞缙,等. 热损伤花岗岩三轴卸围压力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(7):1173−1180. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE201507002 CAI Yanyan,LUO Chenghao,YU Jin,et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of thermal–damage granite rock under triaxial unloading confining pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(7):1173−1180. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE201507002
[26] LIU Shi,XU Jinyu. An experimental study on the physico–mechanical properties of two post–high–temperature rocks[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,185:63−70. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.013
[27] 方新宇,许金余,刘石,等. 高温后花岗岩的劈裂试验及热损伤特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊1):2687−2694. FANG Xinyu,XU Jinyu,LIU Shi,et al. Research on splitting–tensile tests and thermal damage of granite under post–high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(Sup.1):2687−2694.
[28] 胡少华,章光,张淼,等. 热处理北山花岗岩变形特性试验与损伤力学分析[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(12):3427−3436. HU Shaohua,ZHANG Guang,ZHANG Miao,et al. Deformation characteristics tests and damage mechanics analysis of Beishan granite after thermal treatment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(12):3427−3436.
[29] 田红,梅钢,郑明燕. 高温作用后岩石物理力学特性[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,2016. [30] HUANG Yanhua,YANG Shengqi,TIAN Wenling,et al. Physical and mechanical behavior of granite containing pre–existing holes after high temperature treatment[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,2017,17(4):912−925. DOI: 10.1016/j.acme.2017.03.007
[31] YANG Shengqi,RANJITH P G,JING Hongwen,et al. An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments[J]. Geothermics,2017,65:180−197. DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
[32] 操旺进. 循环加卸载条件下花岗岩气体渗透性试验研究[D]. 武汉:湖北工业大学,2018. CAO Wangjin. Experimental study on the gas permeability of granite under cyclic loading and unloading[D]. Wuhan:Hubei University of Technology,2018.
[33] 靳佩桦,胡耀青,邵继喜,等. 急剧冷却后花岗岩物理力学及渗透性质试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(11):2556−2564. JIN Peihua,HU Yaoqing,SHAO Jixi,et al. Experimental study on physico–mechanical and transport properties of granite subjected to rapid cooling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(11):2556−2564.
[34] 梁铭,张绍和,舒彪. 不同冷却方式对高温花岗岩巴西劈裂特性的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2018,29(2):186−193. DOI: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.02.31 LIANG Ming,ZHANG Shaohe,SHU Biao. Effect of different cooling ways on Brazilian tension characteristics of heat–treated granite[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering,2018,29(2):186−193. DOI: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.02.31
[35] 吴顺川,郭沛,张诗淮,等. 基于巴西劈裂试验的花岗岩热损伤研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(增刊2):3805−3816. WU Shunchuan,GUO Pei,ZHANG Shihuai,et al. Study on thermal damage of granite based on Brazilian splitting test[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(Sup.2):3805−3816.
[36] 朱振南,田红,董楠楠,等. 高温花岗岩遇水冷却后物理力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(增刊2):169−176. ZHU Zhennan,TIAN Hong,DONG Nannan,et al. Experimental study of physico–mechanical properties of heat–treated granite by water cooling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(Sup.2):169−176.
[37] GE Zhenlong,SUN Qiang. Acoustic emission (AE) characteristics of granite after heating and cooling cycles[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2018,200:418−429. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.08.011
[38] RONG Guan,PENG Jun,CAI Ming,et al. Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,141:174−185. DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.126
[39] XU X L,KARAKUS M. A coupled thermo–mechanical damage model for granite[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2018,103:195−204. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.030
[40] ZHANG Fan,ZHAO Jianjian,HU Dawei,et al. Laboratory investigation on physical and mechanical properties of granite after heating and water–cooling treatment[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2018,51(3):677−694. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-017-1350-8
[41] 陈宇,徐能雄,秦严,等. 高温花岗岩遇水快速冷却后力学性质实验研究[J]. 力学与实践,2019,41(2):171−177. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0879-18-297 CHEN Yu,XU Nengxiong,QIN Yan,et al. Experimental study of mechanical properties of water–cooled granite under high temperature[J]. Mechanics in Engineering,2019,41(2):171−177. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0879-18-297
[42] 崔翰博,唐巨鹏,姜昕彤. 自然冷却和遇水冷却后高温花岗岩力–声特性试验研究[J]. 固体力学学报,2019,40(6):571−582. CUI Hanbo,TANG Jupeng,JIANG Xintong. Experimental study on mechanical and acoustic characteristics of high–temperature granite after natural cooling and water cooling[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics,2019,40(6):571−582.
[43] 黄中伟,温海涛,武晓光,等. 液氮冷却作用下高温花岗岩损伤实验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2019,43(2):68−76. HUANG Zhongwei,WEN Haitao,WU Xiaoguang,et al. Experimental study on cracking of high temperature granite using liquid nitrogen[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2019,43(2):68−76.
[44] JIN Peihua,HU Yaoqing,SHAO Jixi,et al. Influence of different thermal cycling treatments on the physical,mechanical and transport properties of granite[J]. Geothermics,2019,78:118−128. DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.12.008
[45] WU Xiaoguang,HUANG Zhongwei,SONG Hengyu,et al. Variations of physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after rapid cooling with liquid nitrogen[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2019,52(7):2123−2139. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-018-1727-3
[46] WU Qiuhong,WENG Lei,ZHAO Yanlin,et al. On the tensile mechanical characteristics of fine–grained granite after heating/cooling treatments with different cooling rates[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,253:94−110. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.03.014
[47] WU Xiaoguang,HUANG Zhongwei,ZHANG Shikun,et al. Damage analysis of high–temperature rocks subjected to LN2 thermal shock[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2019,52(8):2585−2603. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-018-1711-y
[48] 邓龙传,李晓昭,吴云,等. 不同冷却方式对花岗岩力学损伤特征影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(增刊1):187−199. DENG Longchuan,LI Xiaozhao,WU Yun,et al. Mechanical damage characteristics of granite with different cooling methods[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(Sup.1):187−199.
[49] 卢运虎,王世永,陈勉,等. 高温热处理共和盆地干热岩力学特性实验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2020,16(1):114−121. LU Yunhu,WANG Shiyong,CHEN Mian,et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of hot dry rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2020,16(1):114−121.
[50] 罗生银,窦斌,田红,等. 自然冷却后与实时高温下花岗岩物理力学性质对比试验研究[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):178−184. LUO Shengyin,DOU Bin,TIAN Hong,et al. Comparative experimental study on physical and mechanical properties of granite after natural cooling and under real–time high temperature[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):178−184.
[51] 闵明,张强,蒋斌松,等. 实时高温下北山花岗岩劈裂试验及声发射特性[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(3):108−113. DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20181195 MIN Ming,ZHANG Qiang,JIANG Binsong,et al. Splitting tests and acoustic emission characteristics of Beishan granite under real–time high temperature[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(3):108−113. DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20181195
[52] 吴阳春,郤保平,王磊,等. 高温后花岗岩的物理力学特性试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2020,51(1):193−203. WU Yangchun,XI Baoping,WANG Lei,et al. Experimental study on physico–mechanical properties of granite after high temperature[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2020,51(1):193−203.
[53] 郤保平,吴阳春,赵阳升,等. 不同冷却模式下花岗岩强度对比与热破坏能力表征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(2):286−300. XI Baoping,WU Yangchun,ZHAO Yangsheng,et al. Experimental investigations of compressive strength and thermal damage capacity characterization of granite under different cooling modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(2):286−300.
[54] 朱栋,宗义江,张修峰. 花岗岩循环加热水冷却后力学特征试验研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2020,40(5):113−118. ZHU Dong,ZONG Yijiang,ZHANG Xiufeng. Experimental study on mechanical properties of granite under cyclic heating and water cooling[J]. Mining Research and Development,2020,40(5):113−118.
[55] GUO Hongjun,JI Ming,LIU Dapeng. Transition threshold of granite mechanical characteristics at high temperature[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2020,2020(1):8846376. DOI: 10.1155/2020/8846376
[56] LI Chun,HU Yaoqing,MENG Tao,et al. Experimental study of the influence of temperature and cooling method on mechanical properties of granite:Implication for geothermal mining[J]. Energy Science & Engineering,2020,8(5):1716−1728.
[57] QIN Yan,TIAN Hong,XU Nengxiong,et al. Physical and mechanical properties of granite after high–temperature treatment[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2020,53(1):305−322. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-019-01919-0
[58] SHAO Zuliang,WANG Yong,TANG Xuhai. The influences of heating and uniaxial loading on granite subjected to liquid nitrogen cooling[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,271:105614. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105614
[59] TANG Zhicheng,ZHANG Yingbin. Temperature–dependent peak shear–strength criterion for granite fractures[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,269:105552. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105552
[60] YANG Shengqi,TIAN Wenling,ELSWORTH D,et al. An experimental study of effect of high temperature on the permeability evolution and failure response of granite under triaxial compression[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2020,53(10):4403−4427. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-019-01982-7
[61] YANG Fujian,WANG Guiling,HU Dawei,et al. Calibrations of thermo–hydro–mechanical coupling parameters for heating and water–cooling treated granite[J]. Renewable Energy,2021,168:544−558. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.12.042
[62] YU Peiyang,PAN Pengzhi,FENG Guangliang,et al. Physico–mechanical properties of granite after cyclic thermal shock[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2020,12(4):693−706. DOI: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.03.001
[63] ZHANG Fan,ZHANG Yuhao,YU Yudong,et al. Influence of cooling rate on thermal degradation of physical and mechanical properties of granite[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2020,129:104285. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104285
[64] ZHANG Zhenyu,MA Bing,RANJITH P G,et al. Indications of risks in geothermal systems caused by changes in pore structure and mechanical properties of granite:An experimental study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(10):5399−5414. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-020-01901-z
[65] ZHU Zhennan,TIAN Hong,CHEN Jie,et al. Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after water cooling[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(5):2457−2465. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-019-01705-w
[66] 贾蓬,杨其要,刘冬桥,等. 高温花岗岩水冷却后物理力学特性及微观破裂特征[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(6):1568−1578. JIA Peng,YANG Qiyao,LIU Dongqiao,et al. Physical and mechanical properties and related microscopic characteristics of high–temperature granite after water–cooling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(6):1568−1578.
[67] 杨圣奇,田文岭,董晋鹏. 高温后两种晶粒花岗岩破坏力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(2):281−289. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE202102008 YANG Shengqi,TIAN Wenling,DONG Jinpeng. Experimental study on failure mechanical properties of granite with two grain sizes after thermal treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(2):281−289. DOI: 10.11779/CJGE202102008
[68] DING Qile,WANG Peng,CHENG Zheng. Influence of temperature and confining pressure on the mechanical properties of granite[J]. Powder Technology,2021,394:10−19. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.08.036
[69] GUO Pei,WU Shunchuan,ZHANG Guang,et al. Effects of thermally–induced cracks on acoustic emission characteristics of granite under tensile conditions[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2021,144:104820. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104820
[70] KANG Fangchao,LI Yingchun,TANG Chun’an. Grain size heterogeneity controls strengthening to weakening of granite over high–temperature treatment[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2021,145:104848. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104848
[71] KANG Fangchao,JIA Tianrang,LI Yingchun,et al. Experimental study on the physical and mechanical variations of hot granite under different cooling treatments[J]. Renewable Energy,2021,179:1316−1328. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.07.132
[72] MA Tianshou,ZHU Gongsheng,PENG Nian,et al. Physical–mechanical properties and thermal–induced damage of granite after high–temperature pretreatment[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(15):1449. DOI: 10.1007/s12517-021-07870-1
[73] MIAO Shuting,PAN Pengzhi,ZHAO Xingguang,et al. Experimental study on damage and fracture characteristics of Beishan granite subjected to high–temperature treatment with DIC and AE techniques[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2021,54(2):721−743. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-020-02271-4
[74] NING Pai,JU Feng,SU Haijian,et al. An investigation on the deterioration of physical and mechanical properties of granite after cyclic thermal shock[J]. Geothermics,2021,97:102252. DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102252
[75] RONG Guan,SHA Song,LI Bowen,et al. Experimental investigation on physical and mechanical properties of granite subjected to cyclic heating and liquid nitrogen cooling[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2021,54(5):2383−2403. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-021-02390-6
[76] WANG Tianzuo,WANG Linxiang,XUE Fei,et al. Investigation of the mechanical and permeability evolution effects of high–temperature granite exposed to a rapid cooling shock with liquid nitrogen[J]. Geofluids,2021,2021(1):3243243.
[77] WU Yun,LI Xiaozhao,HUANG Zhen,et al. Effect of temperature on physical,mechanical and acoustic emission properties of Beishan granite,Gansu Province,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,107(2):1577−1592. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-021-04647-3
[78] WU Yun,LI Xiaozhao,HUANG Zhen,et al. Effect of thermal damage on tensile strength and microstructure of granite:A case study of Beishan,China[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo–Energy and Geo–Resources,2021,7(3):82.
[79] XIAO Peng,ZHENG Jun,DOU Bin,et al. Mechanical behaviors of granite after thermal shock with different cooling rates[J]. Energies,2021,14(13):3721. DOI: 10.3390/en14133721
[80] ZHANG Fan,DAI Cong,ZHANG Yuhao,et al. Experimental investigations on the tensile behaviour of granite after heating and water–cooling treatment[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(7):5909−5920. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-021-02284-5
[81] ZHU Zhennan,KEMPKA T,RANJITH P G,et al. Changes in thermomechanical properties due to air and water cooling of hot dry granite rocks under unconfined compression[J]. Renewable Energy,2021,170:562−573. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.019
[82] CHEN Zhiheng,SHA Song,XU Lida,et al. Damage evaluation and statistic constitutive model of high–temperature granites subjected to liquid nitrogen cold shock[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2022,55(4):2299−2321. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-022-02779-x
[83] DING Qile,WANG Peng,CHENG Zheng. Permeability evolution of fractured granite after exposure to different high–temperature treatments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2022,208:109632. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109632
[84] HU Yuefei,HU Yaoqing,ZHAO Guokai,et al. Experimental investigation of the relationships among P–wave velocity,tensile strength,and mode–I fracture toughness of granite after high–temperature treatment[J]. Natural Resources Research,2022,31(2):801−816. DOI: 10.1007/s11053-022-10020-3
[85] ZHANG Xiaowu,XU Jinhai,CAO Yue,et al. On the microcrack propagation and mechanical behavior of granite induced by thermal cycling treatments[J]. Processes,2022,10(8):1551. DOI: 10.3390/pr10081551
[86] ZHAO Fei,SUN Qiang,GE Zhenlong,et al. Laboratory investigation on engineering mechanics properties of granite after various heating/cooling treatments[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023,30(5):12532−12544.
[87] ZHU Zhennan,RANJITH P G,TIAN Hong,et al. Relationships between P–wave velocity and mechanical properties of granite after exposure to different cyclic heating and water cooling treatments[J]. Renewable Energy,2021,168:375−392. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.12.048
[88] ISAKA B L A,GAMAGE R P,RATHNAWEERA T D,et al. An influence of thermally–induced micro–cracking under cooling treatments:Mechanical characteristics of Australian granite[J]. Energies,2018,11(6):1338. DOI: 10.3390/en11061338
[89] 尤明庆,华安增. 岩石试样的三轴卸围压试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1998,17(1):24−29. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1998.01.004 YOU Mingqing,HUA Anzeng. Triaxial confining depressure test of rock sample[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1998,17(1):24−29. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1998.01.004
[90] 解经宇,陆洪智,陈磊,等. 龙马溪组层状页岩微观非均质性及力学各向异性特征[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):67−77. XIE Jingyu,LU Hongzhi,CHEN Lei,et al. Micro scopic heterogeneity and mechanical anisotropy of the laminated shale in Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):67−77.
[91] 黄润秋,黄达. 高地应力条件下卸荷速率对锦屏大理岩力学特性影响规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(1):21−33. HUANG Runqiu,HUANG Da. Experimental research on affection laws of unloading rates on mechanical properties of Jinping marble under high geostress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(1):21−33.
[92] ZHU Zhennan,TIAN Hong,JIANG Guosheng,et al. Effects of high temperature on the mechanical properties of Chinese marble[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2018,51(6):1937−1942. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-018-1426-0
[93] XIE Jingyu,CAO Han,WANG Dan,et al. A comparative study on the hydraulic fracture propagation behaviors in hot dry rock and shale formation with different structural discontinuities[J]. Journal of Energy Engineering,2022,148(6):04022040. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)EY.1943-7897.0000869
[94] XIE Jingyu,WANG Ren,ZHAO Meng,et al. AE responses characteristics of intersections between hydraulic fractures and embedded–discontinuous rock in granitic HDR[J]. Journal of Energy Engineering,2025,151(3):04025014.
[95] 朱振南,王殿永,杨圣奇,等. 不同冷却速率下干热花岗岩渗透率演化特征对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2024,43(2):385−398. ZHU Zhennan,WANG Dianyong,YANG Shengqi,et al. A comparative study on permeability evolution of hot dry granite under different cooling rates[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2024,43(2):385−398.
[96] FAN Lifeng,GAO Jingwei,DU Xiuli. Thermal cycling effects on micro–property variation of granite by a spatial micro–observation[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2020,53(6):2921−2928. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-020-02065-8
[97] 古启雄,黄震,钟文,等. 高温循环后花岗岩孔隙结构与物理力学特性演化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(6):1450−1465. GU Qixiong,HUANG Zhen,ZHONG Wen,et al. Study on the variations of pore structure and physico–mechanical properties of granite after high temperature cycling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(6):1450−1465.
[98] CHEN Shiwan,YANG Chunhe,WANG Guibin. Evolution of thermal damage and permeability of Beishan granite[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,110:1533−1542. DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.075
[99] XI Yan,XING Junhao,JIANG Hailong,et al. Pore characteristic evolution and damage deterioration of granite subjected to the thermal and cooling treatments combined with the NMR method[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(5):182. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-023-03215-2








 下载:
下载: