Evolutionary pattern and a calculation method of in situ gas pressure based on pressure-retaining coal cores
-
摘要:目的和方法
煤层原位瓦斯压力是煤矿安全生产以及煤层气资源评估的重要参数。针对现阶段煤层原位瓦斯压力测定周期长、测算结果受多种参数影响等局限,利用自主搭建的保压煤心瓦斯压力演化实验系统,开展了不同含水率下保压煤心等温吸附和扩容解吸实验,在揭示保压煤样瓦斯压力演化规律的基础上,基于“深部煤层原位保压保瓦斯取心工艺”形成的“煤层原位瓦斯压力”理论计算原理,提出了考虑气体压缩因子与含水率的瓦斯压力计算修正模型,并验证了其可靠性。
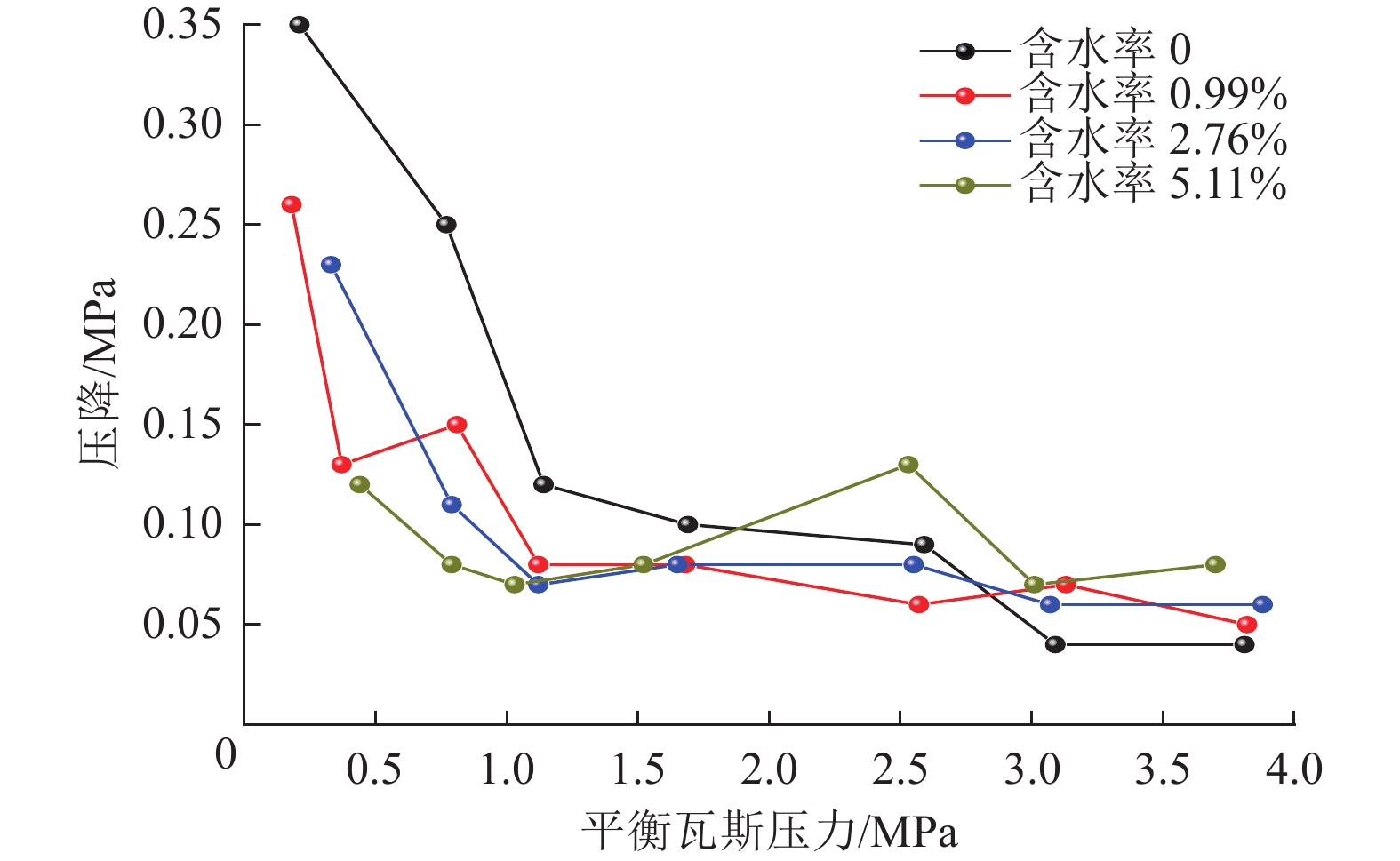
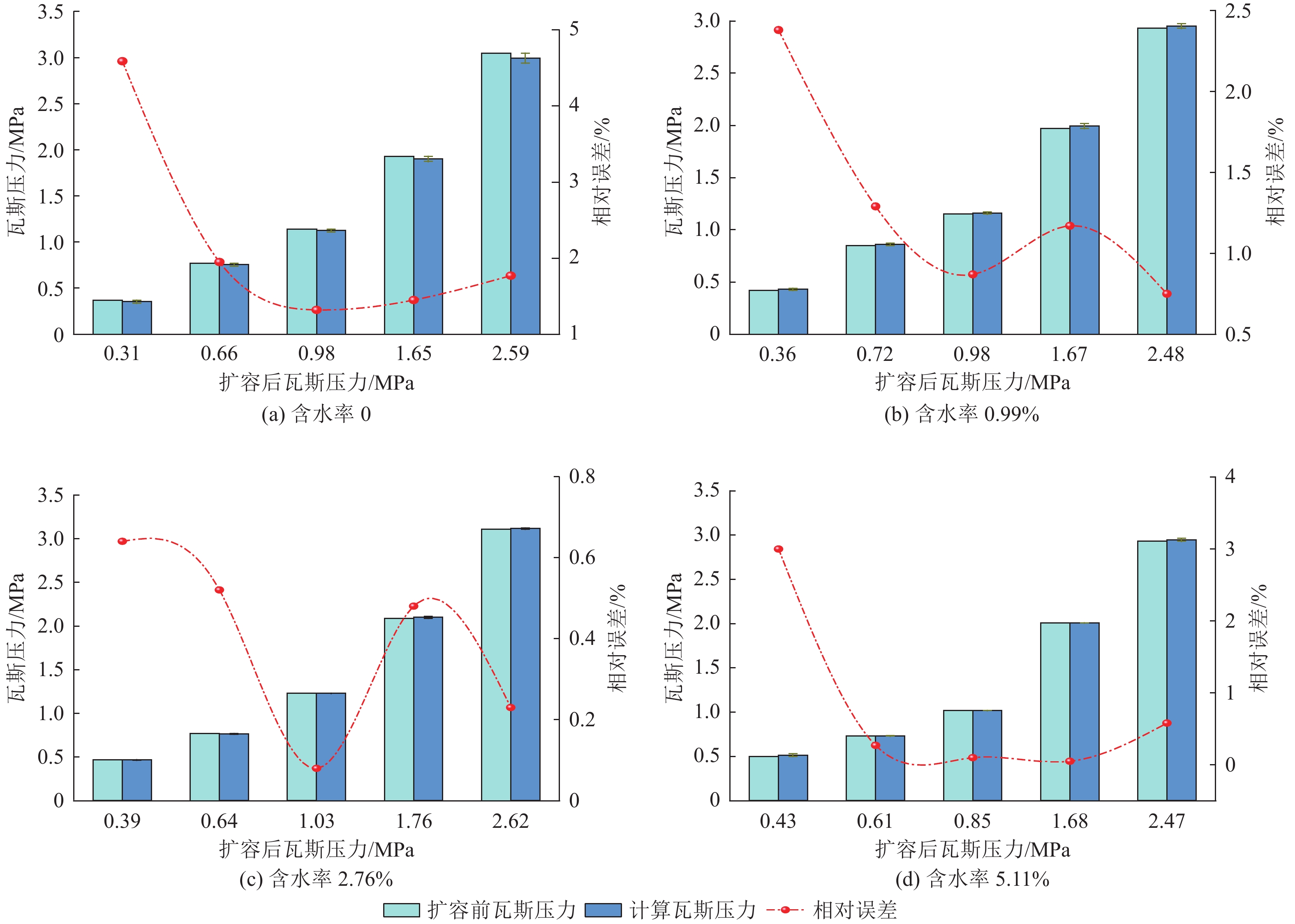
结果和结论结果表明:(1) 受高瓦斯压力影响,保压空间内瓦斯压力更容易达到新的平衡,在等温吸附过程中瓦斯压力呈阶段性演化特征,保压煤心瓦斯压力先快速下降至某一值,升压后再逐渐趋于平衡。(2) 受煤样介孔为主、微孔孔容较大孔隙特征影响,煤中水分含水率越高,煤对瓦斯的吸附阻力越大,从而导致平衡时间拉长,吸附压降值降低。(3) 基于不同含水率保压煤心扩容解吸实验计算了煤样瓦斯压力,各含水率下瓦斯压力计算结果平均相对误差分别为2.22%、1.29%、0.39%、0.80%,可见修正后的瓦斯压力计算方法有较高准确度。提出的瓦斯压力计算新方法有望为煤层原位瓦斯压力测定提供可靠、便捷、精准的计算方法。
Abstract:Objective and MethodsThe in situ gas pressure of coal seams represents a crucial parameter for the safe production of coal mines and the assessment of coalbed methane (CBM) resources. To overcome current limitations in determining the in situ gas pressure, such as prolonged measurement cycles and the influence of multiple parameters on the measurement results, this study conducted isothermal adsorption and volumetric expansion desorption experiments on pressure-retaining coal cores with varying moisture contents using a self-constructed experimental system for gas pressure evolution in pressure-retaining coal cores. As a result, the evolutionary pattern of gas pressure in pressure-retaining coal cores was determined. Accordingly, following the theoretical calculation principle of in situ gas pressure in coal seams, formed by the in situ pressure- and gas-retaining coring process for deep coal seams, this study proposed a correction model for gas pressure calculation that considered moisture content and verified its reliability.
Results and ConclusionsThe results indicate that: (1) Influenced by high gas pressure, the gas pressure within the pressure-preserved space more easily reaches a new equilibrium. During the isothermal adsorption process, the gas pressure exhibits a staged evolution characteristic, where the gas pressure in the pressure-preserved coal core first rapidly decreases to a certain value, then increases before gradually stabilizing. (2) Due to the pore characteristics of the coal sample being dominated by mesopores and having a large micropore volume, the higher the moisture content of coal leads to greater resistance to gas adsorption, resulting the longer the equilibrium time and the lower the adsorption pressure drop. (3) The gas pressure of the coal samples was calculated based on the expansion desorption experiments of pressure-preserved coal cores with different moisture contents. The average relative errors of the gas pressure calculation results under various moisture contents were 2.22%, 1.29%, 0.39%, and 0.80%, respectively. The corrected gas pressure calculation method demonstrated high accuracy. The proposed approach offers promising potential as a reliable, efficient, and accurate means for determining of in-situ coalbed gas pressure.
-
-
表 1 工业分析与全硫检测结果
Table 1 Proximate and total-sulfur analysis results
煤的工业分析w/% 全硫分析w/% Mad Aad Vad FCad St,ad St,d 0.85 30.41 8.81 59.93 0.22 0.24 表 2 煤样孔容、孔隙比表面积、孔径分布
Table 2 Pore volumes, specific surface areas, and pore size distributions in coal samples
模型 孔隙表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) BET 2.999 3 BJH 1.552 9 0.002 239 DFT 1.954 0 0.003 390 T-plot 1.443 5 0.000 601 平均孔径/nm 5.161 8 表 3 煤样基础物理参数取值与样品室参数值
Table 3 Values of fundamental physical parameters and sample chamber parameters of coal samples
基础参数 取值 吸附过程吸附常数a/(m3∙t−1) 20.85 吸附过程吸附常数b/MPa−1 3.25 吸附衰减系数 17.2 水分质量分数/% 0.85 灰分质量分数/% 30.41 挥发分产率/% 8.81 固定碳质量分数/% 59.93 镜质组体积分数/% 45.7 煤层基质孔隙率/% 6.5 甲烷分子摩尔质量/(g∙mol−1) 16 煤层温度/K 30.15 标准状况下甲烷摩尔体积/(L∙mol−1) 22.4 理想气体常数/(J∙mol−1∙K−1) 8.314 含水率1/% 0 含水率2/% 0.99 含水率3/% 2.76 含水率4/% 5.11 -
[1] 谢和平,周宏伟,薛东杰,等. 我国煤与瓦斯共采:理论、技术与工程[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(8):1391−1397. XIE Heping,ZHOU Hongwei,XUE Dongjie,et al. Theory,technology and engineering of simultaneous exploitation of coal and gas in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(8):1391−1397.
[2] 崔鹏飞,高明忠,尚德磊,等. 基于保压取心的深部煤层原位压力计算原理及方法初探[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,20,51(8):59–67. CUI Pengfei,GAO Mingzhong,SHANG Delei,et al. A preliminary study of pressure–preserved coring calculation principle and method for in–situ pressure in deep coal seams[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,20,51(8):59–67.
[3] 张超林,王恩元,许江,等. 煤层瓦斯压力对瓦斯抽采效果的影响[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,20,39(3):634–64. ZHANG Chaolin,WANG Enyuan,XU Jiang,et al. The influence of gas pressure on drainage effect in coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,20,39(3):634–64.
[4] 李回贵,王军,李晓龙,等. 瓦斯压力对突出煤层煤样力学特征影响规律的研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2022,49(4):129−134. LI Huigui,WANG Jun,LI Xiaolong,et al. Study on influence law of gas pressure on mechanical characteristic of coal samples in outburst coal seam[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2022,49(4):129−134.
[5] 孙东玲,曹偈,杨慧明,等. 陕西侏罗纪煤层瓦斯灾害特点及突出发生条件的探讨[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2024,51(3):1−7. SUN Dongling,CAO Ji,YANG Huiming,et al. Discussion on characteristics and outburst conditions of Jurassic coal seam gas disaster in Shaanxi Province[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2024,51(3):1−7.
[6] 邵帆. 基于Spark的煤与瓦斯突出预警研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2019. SHAO Fan. Research on early warning of coal and gas outburst based on Spark[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2019.
[7] 胡社荣,彭纪超,黄灿,等. 千米以上深矿井开采研究现状与进展[J]. 中国矿业,2011,20(7):105−110. HU Sherong,PENG Jichao,HUANG Can,et al. An overview of current status and progress in coal mining of the deep over a kilometer[J]. China Mining Magazine,2011,20(7):105−110.
[8] 谢和平. 深部岩体力学与开采理论研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(5):1283−1305. XIE Heping. Research review of the state key research development program of China:Deep rock mechanics and mining theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(5):1283−1305.
[9] 赵嵘,齐黎明. 井下直接法测定煤层瓦斯压力研究现状及分析[J]. 煤炭技术,2017,36(3):202−20. ZHAO Rong,QI Liming. Research status of direct method of gas pressure measurement in coal seam under mine and its analysis[J]. Coal Technology,2017,36(3):202−20.
[10] 蒋云,朱天成,汪腾翔. 胶囊–聚氨酯联合封孔测压技术的研究与应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2015,11(7):80−84. JIANG Yun,ZHU Tiancheng,WANG Tengxiang. Research and application of pressure measurement technology by combination sealing of capsule and polyurethane[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2015,11(7):80−84.
[11] 王振锋,周英,孙玉宁,等. 新型瓦斯抽采钻孔注浆封孔方法及封堵机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(3):588−595. WANG Zhenfeng,ZHOU Ying,SUN Yuning,et al. Novel gas extraction borehole grouting sealing method and sealing mechanism[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(3):588−595.
[12] GAO Yingjun,YAO Banghua,ZHANG Hongtu,et al. Study on the test of coal mass fracture grouting sealing with coal–based materials and its application[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,20,10:1089248.
[13] 杨宏民,杨峰峰,安丰华,等. 煤层瓦斯压力测定的合理封孔注浆压力研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2015,11(5):13−17. YANG Hongmin,YANG Fengfeng,AN Fenghua,et al. Study on reasonable grouting sealing pressure for hole sealing in the determination of coal seam gas pressure[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2015,11(5):13−17.
[14] 齐黎明,赵玉岐,王轶波,等. 基于封孔前瓦斯损失量的测压结果修正分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(1):60−6. QI Liming,ZHAO Yuqi,WANG Yibo,et al. Analysis on the gas pressure measurement result revision on the basis of gas loss quantity before bore being sealed[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2007,32(1):60−6.
[15] 王法凯,蒋承林,公衍伟,等. 基于M–Ⅱ型瓦斯压力测定仪+套管法的穿多煤层测定瓦斯压力技术[J]. 工矿自动化,2011,37(3):1−4. WANG Fakai,JIANG Chenglin,GONG Yanwei,et al. Technology of detecting gas pressure by puncturing multi–seam based on M–Ⅱ gas pressure detector and casing method[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2011,37(3):1−4.
[16] 刘垒,杨胜强,陈凯. 复杂地质条件下的煤层瓦斯压力测定[J]. 煤矿安全,201,44(1):130–1. LIU Lei,YANG Shengqiang,CHEN Kai. Gas pressure measurement of coal seam under complex geological conditions[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,201,44(1):130–1.
[17] 谢和平,崔鹏飞,尚德磊,等. 深部煤层原位保压取心技术原理与瓦斯参数测定研究进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,20,51(8):1–1. XIE Heping,CUI Pengfei,SHANG Delei,et al. Research advances on the in–situ pressure–preserved coring and gas parameter determination for deep coal seams[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,20,51(8):1–1.
[18] 高明忠,陈领,凡东,等. 深部煤矿原位保压保瓦斯取芯原理与技术探索[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):885−897. GAO Mingzhong,CHEN Ling,FAN Dong,et al. Principle and technology of coring with in–situ pressure and gas maintaining in deep coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(3):885−897.
[19] LEVY J H,DAY S J,KILLINGLEY J S. Methane capacities of Bowen Basin coals related to coal properties[J]. Fuel,1997,76(9):813−819. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00078-1
[20] PAN Zhejun,CONNELL L D,CAMILLERI M,et al. Effects of matrix moisture on gas diffusion and flow in coal[J]. Fuel,2010,89(11):3207−3217. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.05.038
[21] WANG Shugang,ELSWORTH D,LIU Jishan. Permeability evolution in fractured coal:The roles of fracture geometry and water–content[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2011,87(1):13−25. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.04.009
[22] 武洋,姚强岭,吴宝杨,等. 不同含水状态下煤样蠕变实验研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2024,51(3):72−77. WU Yang,YAO Qiangling,WU Baoyang,et al. Experimental study on coal samples creep in different water content states[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2024,51(3):72−77.
[23] CHEN Dong,PAN Zhejun,LIU Jishan,et al. Modeling and simulation of moisture effect on gas storage and transport in coal seams[J]. Energy & Fuels,201,26(3):1695–1706.
[24] 褚鹏,尚德磊,李建华,等. 原位保压取心气体组分对煤层瓦斯压力测算的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,20,51(8):79–87. CHU Peng,SHANG Delei,LI Jianhua,et al. Influence of gas components on the determination of gas pressure in coal seams under in–situ pressure–preserved coring[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,20,51(8):79–87.
[25] 赵金,张遂安. 煤层气排采储层压降传播规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,201,40(10):65–68. ZHAO Jin,ZHANG Sui’an. Study on pressure drop transmission law of coal bed methane drainage reservoir stratum[J]. Coal Science and Technology,201,40(10):65–68.
[26] 李来成,傅雪海,罗斌. 大块煤样逐次降压解吸实验研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2015,27(9):18−21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2015.09.05 LI Laicheng,FU Xuehai,LUO Bin. Experimental study on large coal sample desorption under successive depressurization[J]. Coal Geology of China,2015,27(9):18−21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2015.09.05
[27] 石迎爽,梁冰,孙维吉,等. 压降及储层压力与煤变形的相关性研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(6):140−146. SHI Yingshuang,LIANG Bing,SUN Weiji,et al. A study on the correlation between the pressure drawdown gradient and reservoir pressure and the coal deformation[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2017,39(6):140−146.
[28] 赵泓超,赵鹏翔,许永刚,等. 倾斜厚煤层覆岩瓦斯高渗区应力场−渗流场联动演化采高效应[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2024,44(5):866−879. ZHAO Hongchao,ZHAO Pengxiang,XU Yonggang,et al. Mining height effect of stress field-seepage field linkage evolution in gas high permeability zone of overlying strata in inclined thick coal seam[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2024,44(5):866−879.
[29] 曾泉树,高清春,汪志明. 煤岩吸附高压甲烷的实验与模型研究[J]. 石油科学通报,2020,5(1):78−9. ZENG Quanshu,GAO Qingchun,WANG Zhiming. Experimental and modeling studies on high pressure methane adsorbed on coals[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin,2020,5(1):78−9.
[30] 韩恩光,刘志伟,冉永进,等. 不同粒度煤的瓦斯解吸扩散规律实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2019,15(12):83−87. HAN Enguang,LIU Zhiwei,RAN Yongjin,et al. Experimental study on gas desorption and diffusion laws of coal with different particle sizes[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2019,15(12):83−87.
[31] 何满潮,谢和平,彭苏萍,等. 深部开采岩体力学研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(16):2803−281. HE Manchao,XIE Heping,PENG Suping,et al. Study on rock mechanics in deep mining engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(16):2803−281.
[32] 晋城煤业集团成庄矿. 成庄矿(2011—2013)瓦斯治理规划[R]. 晋城:成庄煤矿,2011:6. -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张旭辉,解彦彬,杨文娟,张超,万继成,董征,王彦群,蒋杰,李龙. 煤矿井下采掘工作场景非均质图像去雾与增强技术. 煤田地质与勘探. 2025(01): 245-256 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张铁聪,陈华州,赵俊杰,王利景,贾冬冬. 基于数字孪生技术的煤矿掘进机自动截割方法研究. 中国煤炭. 2024(01): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾澎涛,靳路伟,王斌,郭风景,李娜. 采煤机截割部低照度图像的边缘检测技术. 煤田地质与勘探. 2024(04): 172-178 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 张旭辉,王悦,杨文娟,陈鑫,张超,黄梦瑶,刘彦徽,杨骏豪. 基于改进最佳缝合线的矿井图像拼接方法. 工矿自动化. 2024(04): 9-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 汪进超,韩增强,王益腾,王超,张国华. 基于像素空间信息的孔内低照度图像孔隙结构量化方法研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(S1): 3175-3186 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 丁序海,张侯,陈录平,党国杰. 基于多频无线电坑透技术的煤矿地质综合勘探研究. 能源与环保. 2024(06): 82-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 肖耀猛. 目标背景对比度优化下高煤尘低照度环境主动成像技术. 矿山机械. 2024(09): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陶荣颖,王守军,李南,朱伟. 煤矿副井口全景智能识别技术的研究与应用. 内蒙古煤炭经济. 2024(22): 154-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载: