Influencing mechanisms of microwave radiation duration on the efficiency of methane adsorption in coals
-
摘要:目的
微波辐射时间是微波辅助高效提升煤层气采收率的关键因素,其对煤层甲烷吸附效率的影响机制尚不明确,需深入研究微波辐射时长条件对煤层甲烷吸附效率的具体影响,揭示其内在约束机制。
方法以黄陵矿区2号煤层为研究对象,用700 W功率微波对煤样辐射0~18 min,开展等温吸附、低温液氮吸附和傅里叶红外光谱实验,分析不同微波辐射时长下煤的甲烷吸附能力、微观孔隙结构和分子结构的变化;利用多元统计学分析辐射后煤体结构参数与甲烷吸附参数的相关关系。
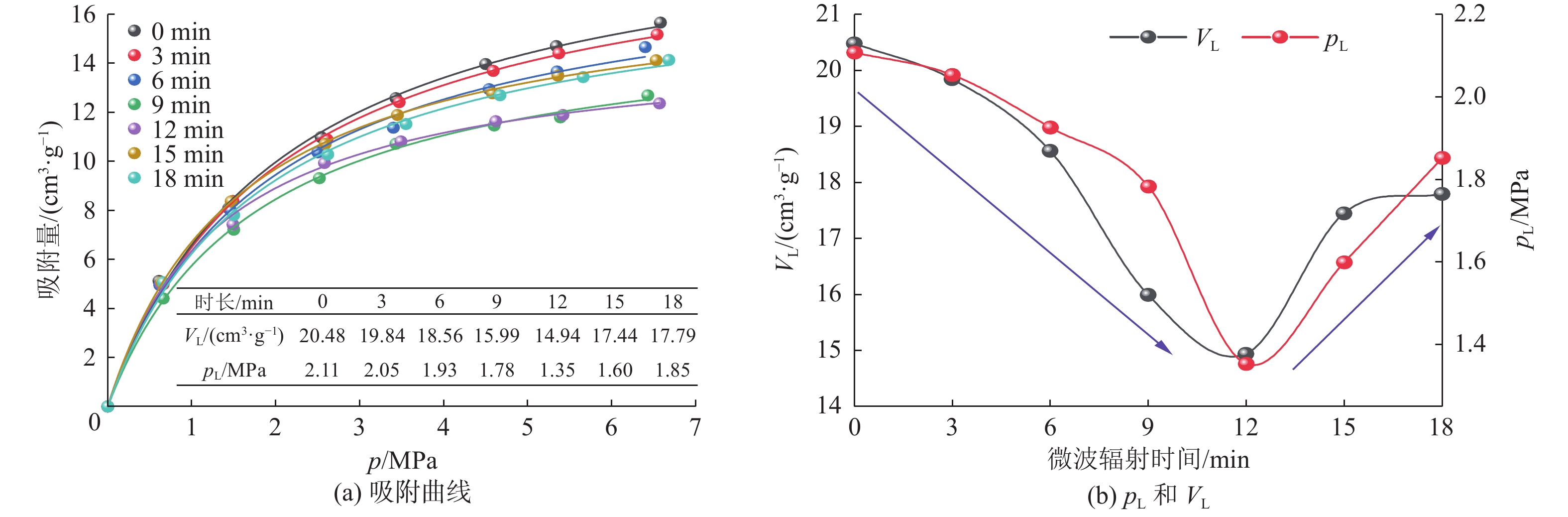
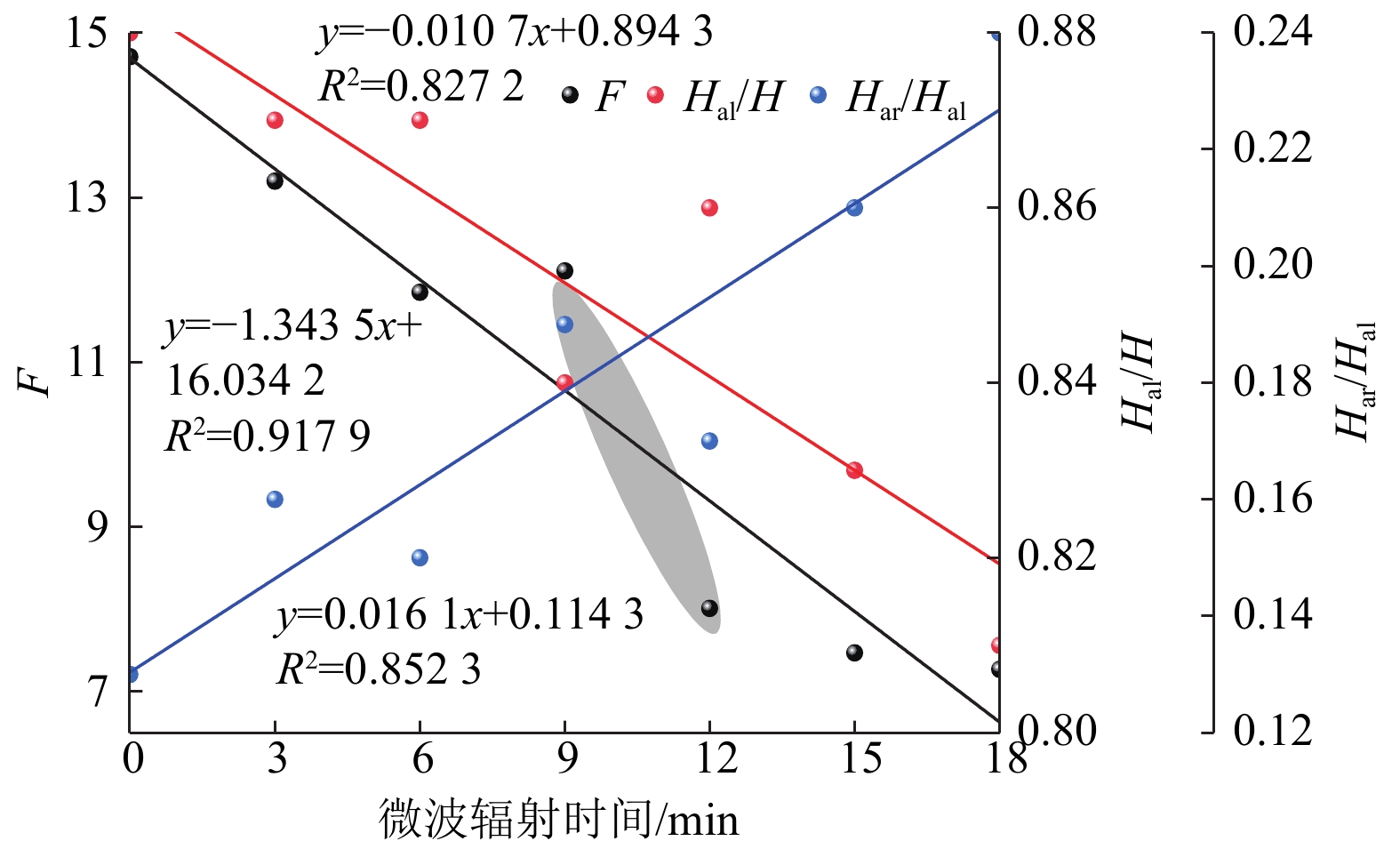
结果和结论实验结果显示,随着微波辐射时长的增加,煤的甲烷吸附量呈现出先减小后增加的变化趋势。当微波辐射时长达到12 min时,甲烷吸附量降至最低,仅为14.94 cm3/g。微波辐射对煤分子结构影响显著,随着辐射时长增加,煤样中脂肪族结构(CH2/CH3)、含氧官能团、芳香结构及羟基吸收带的响应强度整体减弱,而芳香度(Har/Hal)则呈现升高的趋势,总体分子稳定性增强,表明微波辐射通过降低支链化程度和增加芳香结构缩合,改变了煤的甲烷吸附能力。随着微波辐射时长的增加,煤微观孔隙呈现出先扩孔、后增孔的变化特征,具体表现为介孔的比表面积(SSA)先减小后增大,而孔体积(PV)则先增大后减小。基于Pearson相关性矩阵及主成分分析方法,发现2~10 nm介孔比表面积是制约煤层甲烷吸附效率的关键参数。研究成果可为微波辅助煤层气高效开发提供辐射时长等理论参数,并为后续多参数耦合机制的深入研究奠定了基础,有助于推动微波辐射技术在煤层气增产工程中的应用。
Abstract:ObjectiveMicrowave radiation duration represents a critical factor in enhancing coalbed methane (CBM) recovery using microwave-aided methods. However, the influencing mechanism of microwave radiation duration on the efficiency of methane adsorption in coal seams remains unclear. This necessitates delving into the specific effects of microwave radiation duration on the adsorption efficiency and unveiling their intrinsic constraints.
MethodsThis study investigated the No.2 coal seam in the Huangling mining area. The coal samples were irradiated for 0‒18 min using 700 W microwaves. Using experiments and analyses including isothermal adsorption, low-temperature liquid N2 adsorption, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), this study analyzed the changes in the methane adsorption capacity, microscopic pore structure, and molecular structure of coals under varying microwave radiation durations. Furthermore, it examined the correlation between the structural parameters and methane adsorption parameters of coals post-radiation using multivariate statistical analysis.
Results and ConclusionsThe experimental results demonstrate that the methane adsorption capacity of coals initially decreased and then increased as the microwave radiation duration increased. The minimum methane adsorption capacity (only 14.94 cm3/g) was observed in the case of a microwave radiation duration of 12 min. Microwave radiation significantly affected the molecular structure of coals. With an increase in the microwave radiation duration, the response intensities of aliphatic structures (CH2/CH3), oxygen-containing functional groups, aromatic structures, and hydroxyl absorption bands in the coal samples decreased generally. In contrast, the aromaticity (Har/Hal) of the coal samples showed an increasing trend, and their overall molecular stability also increased. These findings indicate that microwave radiation altered the methane adsorption capacity of coals by reducing the degree of branching and promoting aromatic condensation. As the microwave radiation duration increased, the micropores in coals underwent pore expansion initially and then pore formation. Specifically, the specific surface area (SSA) of mesopores decreased first and then increased, while their pore volume (PV) showed an opposite trend. The Pearson correlation matrix and principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the SSA of mesopores with sizes ranging from 2 nm to 10 nm is a key parameter that influences the efficiency of methane adsorption in coal seams. The results of this study can provide theoretical parameters such as optimal radiation duration for efficient CBM production using microwave-assisted methods while also laying a foundation for in-depth research on multi-parameter coupling mechanisms in the future. This study will promote the application of microwave radiation technology in CBM production growth projects.
-
-
图 8 微波辐射促进煤层气排采生产模式及机理
(a) 地面井微波加热工程(据文献[33],修改);(b) 微波增产机理
Fig. 8 Pattern and mechanism of microwave radiation enhanced CBM production
表 1 煤样工业分析和元素分析测试数据
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of coal samples
样品名称 工业分析w/% 元素分析w/% Rmax/% Mad Aad Vdaf FCad Cdaf Hdaf Odaf Ndaf St,ad 黄陵煤样 1.02 9.40 32.21 57.37 72.70 4.82 20.91 1.33 0.24 0.71 注:St,ad:空气干燥基的总硫;Mad和Aad:空气干燥基的水分和灰分;Vdaf:干无灰基的挥发分;FCad:空气干燥基的固定碳;w:质量百分数,%。 -
[1] 邹才能,杨智,何东博,等. 常规–非常规天然气理论、技术及前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(4):575−587. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2018.04.04 ZOU Caineng,YANG Zhi,HE Dongbo,et al. Theory,technology and prospects of conventional and unconventional natural gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(4):575−587. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2018.04.04
[2] 徐凤银,侯伟,熊先钺,等. 中国煤层气产业现状与发展战略[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(4):669−682. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20220856 XU Fengyin,HOU Wei,XIONG Xianyue,et al. The status and development strategy of coalbed methane industry in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2023,50(4):669−682. DOI: 10.11698/PED.20220856
[3] LU Y Y,ZHANG H D,ZHOU Z,et al. Current status and effective suggestions for efficient exploitation of coalbed methane in China:A review[J]. Energy & Fuels,2021,35(11):9102−9123.
[4] 王泽东,刘国磊,崔嵛,等. 低渗透煤层气液两相复合压裂卸压增透技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(11):76−82. WANG Zedong,LIU Guolei,CUI Yu,et al. Pressure relief and permeability enhancement technology of gas–liquid composite fracturing in low permeability coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2022,53(11):76−82.
[5] 蒋曙鸿,师素珍,赵康,等. 深部煤及煤层气勘探前景及发展方向[J]. 科技导报,2023,41(7):106−113. JIANG Shuhong,SHI Suzhen,ZHAO Kang,et al. Prospect and development direction of deep coal and coalbed methane exploration[J]. Science & Technology Review,2023,41(7):106−113.
[6] 王梓麟,时婧玥,徐栋,等. 煤储层无水压裂技术现状及展望[J]. 钻采工艺,2024,47(1):80−86. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2024.01.10 WANG Zilin,SHI Jingyue,XU Dong,et al. Research status and prospects of waterless fracturing technology in coal reservoir[J]. Drilling & Production Technology,2024,47(1):80−86. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2024.01.10
[7] 罗平亚,朱苏阳. 中国建立千亿立方米级煤层气大产业的理论与技术基础[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1755−1763. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311001 LUO Pingya,ZHU Suyang. Theoretical and technical fundamentals of a 100 billion–cubic–meter–scale large industry of coalbed methane in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1755−1763. DOI: 10.7623/syxb202311001
[8] 杨长鑫,杨兆中,李小刚,等. 中国煤层气地面井开采储层改造技术现状与展望[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(6):154−162. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.013 YANG Changxin,YANG Zhaozhong,LI Xiaogang,et al. Status and prospect of reservoir stimulation technologies for CBM surface well production in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2022,42(6):154−162. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.013
[9] CAI Yidong,LIU Dameng,YAO Yanbin,et al. Partial coal pyrolysis and its implication to enhance coalbed methane recovery,Part I:An experimental investigation[J]. Fuel,2014,132:12−19. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.04.084
[10] 李小刚,秦杨,刘紫微,等. 微波强化煤层气井压裂开采的物性规律[J]. 特种油气藏,2024,31(3):70−77. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2024.03.009 LI Xiaogang,QIN Yang,LIU Ziwei,et al. Physical property law of coalbed methane wells fracturing development enhanced by microwave[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2024,31(3):70−77. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2024.03.009
[11] MOGHADDAM R N,JAMIOLAHMADY M. Fluid transport in shale gas reservoirs:Simultaneous effects of stress and slippage on matrix permeability[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2016,163:87−99. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.06.018
[12] HAQUE K E. Microwave energy for mineral treatment processes:A brief review[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing,1999,57(1):1−24. DOI: 10.1016/S0301-7516(99)00009-5
[13] 张永利,刘婷,马玉林,等. 微波辐射煤体孔裂隙结构与渗流特性[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(6):481−489. ZHANG Yongli,LIU Ting,MA Yulin,et al. Coal pore and fissure structure and permeability under microwave radiation[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science),2022,41(6):481−489.
[14] 胡国忠,朱怡然,许家林,等. 可控源微波场强化煤体瓦斯解吸扩散的机理研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2017,46(3):480−484. HU Guozhong,ZHU Yiran,XU Jialin,et al. Mechanism of the controlled microwave field enhancing gas desorption and diffusion in coal[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2017,46(3):480−484.
[15] 鲍园,唐佳阳,琚宜文,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘黄陵矿区中生代煤系烃源层构造–热演化过程与生物气生成[J]. 地球科学进展,2021,36(10):993−1003. BAO Yuan,TANG Jiayang,JU Yiwen,et al. Tectonic–thermal evolution and biogas generation of source rocks from the mesozoic coal measures at the Huangling mining area,southeastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2021,36(10):993−1003.
[16] BAO Yuan,HU Yiliang,WANG Wenbo,et al. Accumulation model and geochemistry characteristics of oil occurring from Jurassic coal measures in the Huangling mining area of the Ordos Basin,China[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science,2023,17(1):158−169. DOI: 10.1007/s11707-022-1038-6
[17] 梁坤,周军,吴雷,等. 低变质煤微波热解数值模拟研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2020,43(4):20−28. LIANG Kun,ZHOU Jun,WU Lei,et al. Numerical simulation on microwave pyrolysis of low–rank coal[J]. Coal Conversion,2020,43(4):20−28.
[18] SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry,1985,57(4):603−619. DOI: 10.1351/pac198557040603
[19] 韩文成,李爱芬,方齐,等. 含水煤岩超临界等温吸附模型的对比分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(12):4095−4103. HAN Wencheng,LI Aifen,FANG Qi,et al. Comparative analysis of isothermal adsorption models for coals with water content under supercritical conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(12):4095−4103.
[20] 周三栋,刘大锰,蔡益栋,等. 低阶煤吸附孔特征及分形表征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2018,39(2):373−383. ZHOU Sandong,LIU Dameng,CAI Yidong,et al. Characterization and fractal nature of adsorption pores in low rank coal[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2018,39(2):373−383.
[21] JARONIEC M,KRUK M,OLIVIER J. Fractal analysis of composite adsorption isotherms obtained by using density functional theory data for argon in slitlike pores[J]. Langmuir,1997,13(5):1031−1035. DOI: 10.1021/la9505529
[22] 朱学栋,朱子彬,韩崇家,等. 煤中含氧官能团的红外光谱定量分析[J]. 燃料化学学报,1999,27(4):335−339. ZHU Xuedong,ZHU Zibin,HAN Chongjia,et al. Quantitative determination of oxygen–containing functional groups in coal by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,1999,27(4):335−339.
[23] IBARRA J,MOLINER R,BONET A J. FT–i. r. investigation on char formation during the early stages of coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,1994,73(6):918−924. DOI: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90287-9
[24] 郝长胜,袁迎春,贾廷贵,等. 不同变质程度煤的化学结构红外光谱研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(11):15−22. HAO Changsheng,YUAN Yingchun,JIA Tinggui,et al. Infrared spectral research on chemical structure of coal with different levels of metamorphism[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2022,53(11):15−22.
[25] 张新星. 神府次烟煤和肥煤的热溶及其热溶物配煤炼焦性能研究[D]. 马鞍山:安徽工业大学,2016. ZHANG Xinxing. Study on the properties of the thermal dissolution of Shenfu sub–bituminous and fat coals and the use their TDSFs in the coal blending for coke–making[D]. Maanshan:Anhui University of Technology,2016.
[26] YANG Wei,WANG Yihan,YAN Fazhi,et al. Evolution characteristics of coal microstructure and its influence on methane adsorption capacity under high temperature pyrolysis[J]. Energy,2022,254:124262. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.124262
[27] LI He,SHI Shiliang,LIN Baiquan,et al. Effects of microwave–assisted pyrolysis on the microstructure of bituminous coals[J]. Energy,2019,187:115986. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.115986
[28] 任棒. 不同煤阶煤的多微观结构特征对甲烷吸附能力的影响规律[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2022. REN Bang. Influence of multi–microstructure characteristics of different rank coals on methane adsorption capacity[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2022.
[29] 李帅魁. 高温高压条件下含瓦斯煤微观结构–解吸特性实验研究及应用[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2023. LI Shuaikui. Study on the microstructure–desorption characteristics of gas–bearing coal under high temperature–pressure and application[D]. Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2023.
[30] ZHOU Jun,WU Lei,ZHOU Jingjing,et al. Products optimization by FeS2 catalyst for low–rank coal microwave pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2019,255:115759. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115759
[31] 师庆民,米奕臣,王双明,等. 富油煤热解流体滞留特征及其机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(3):1329−1337. SHI Qingmin,MI Yichen,WANG Shuangming,et al. Trap characteristic and mechanism of volatiles during pyrolysis of tar–rich coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(3):1329−1337.
[32] 刘迈杰. 保德区块煤储层物性及气体吸附解吸特性研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2021. LIU Maijie. Study on the physical properties of coal reservoir and its adsorption and desorption characteristics in Baode Block[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2021.
[33] HUANG Jinxin,XU Guang,LIANG Yunpei,et al. Improving coal permeability using microwave heating technology:A review[J]. Fuel,2020,266:117022. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117022








 下载:
下载: