Advances in research on technologies for large-scale coal gangue utilization for green mine construction
-
摘要:背景
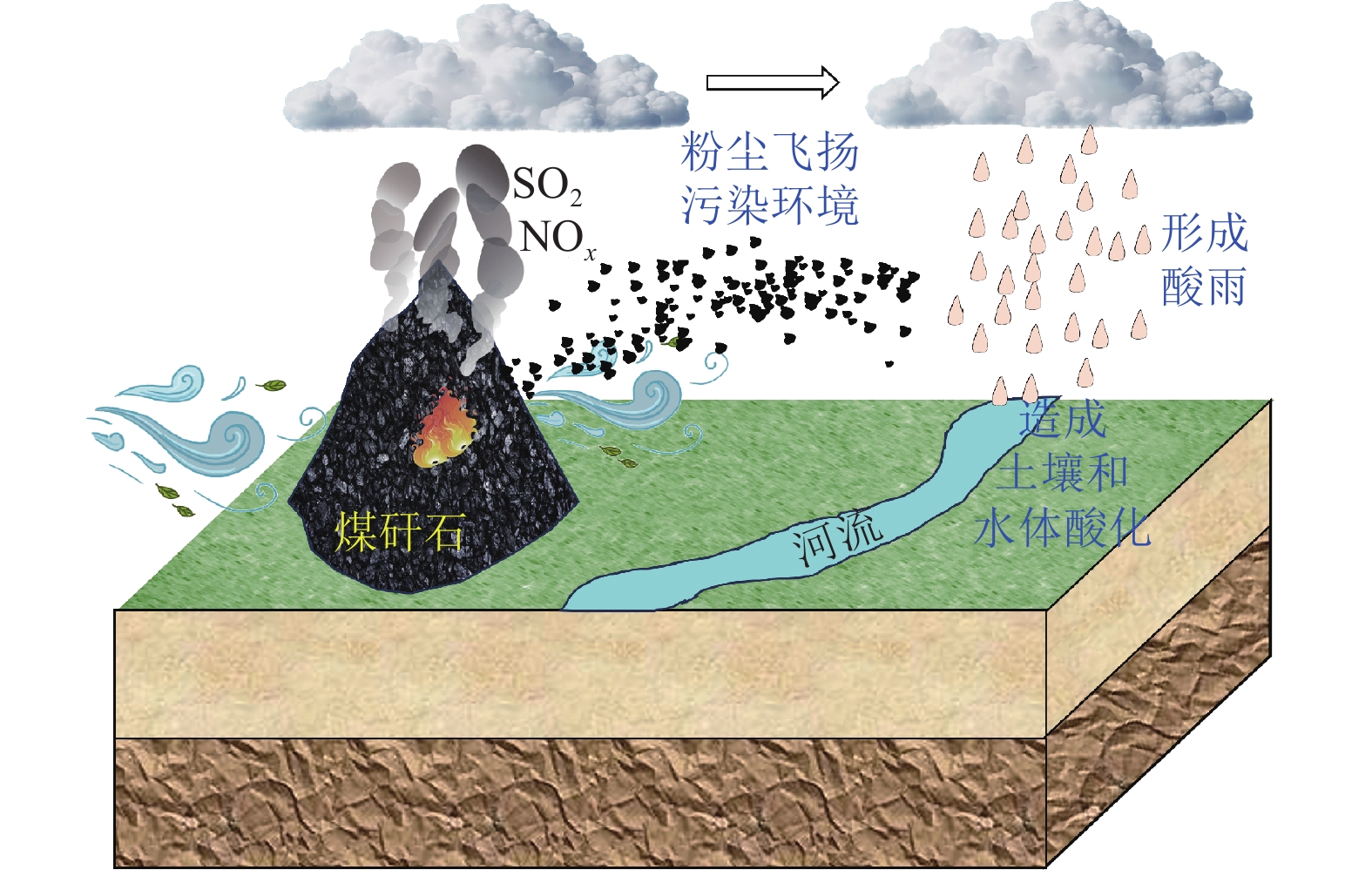
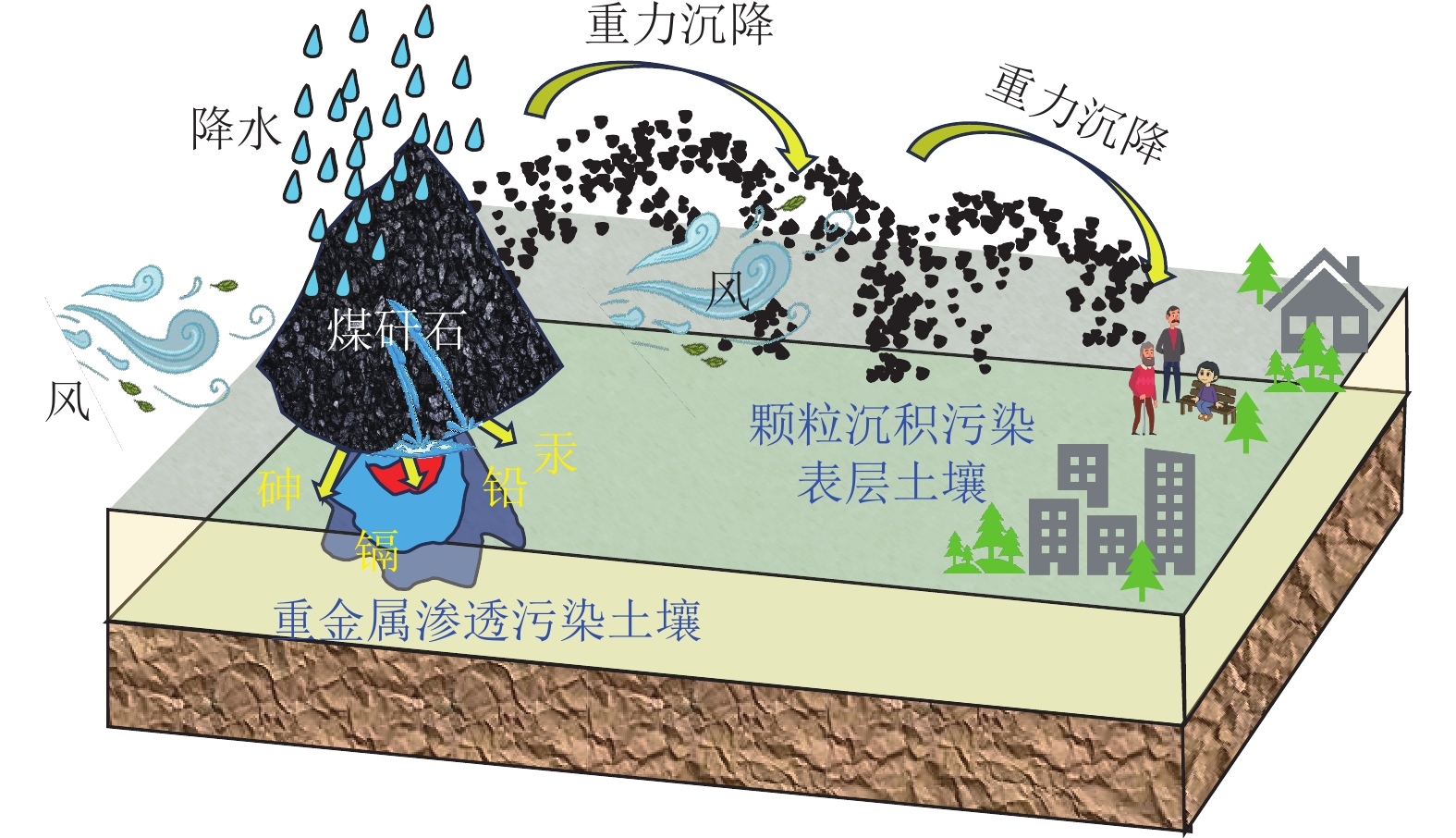
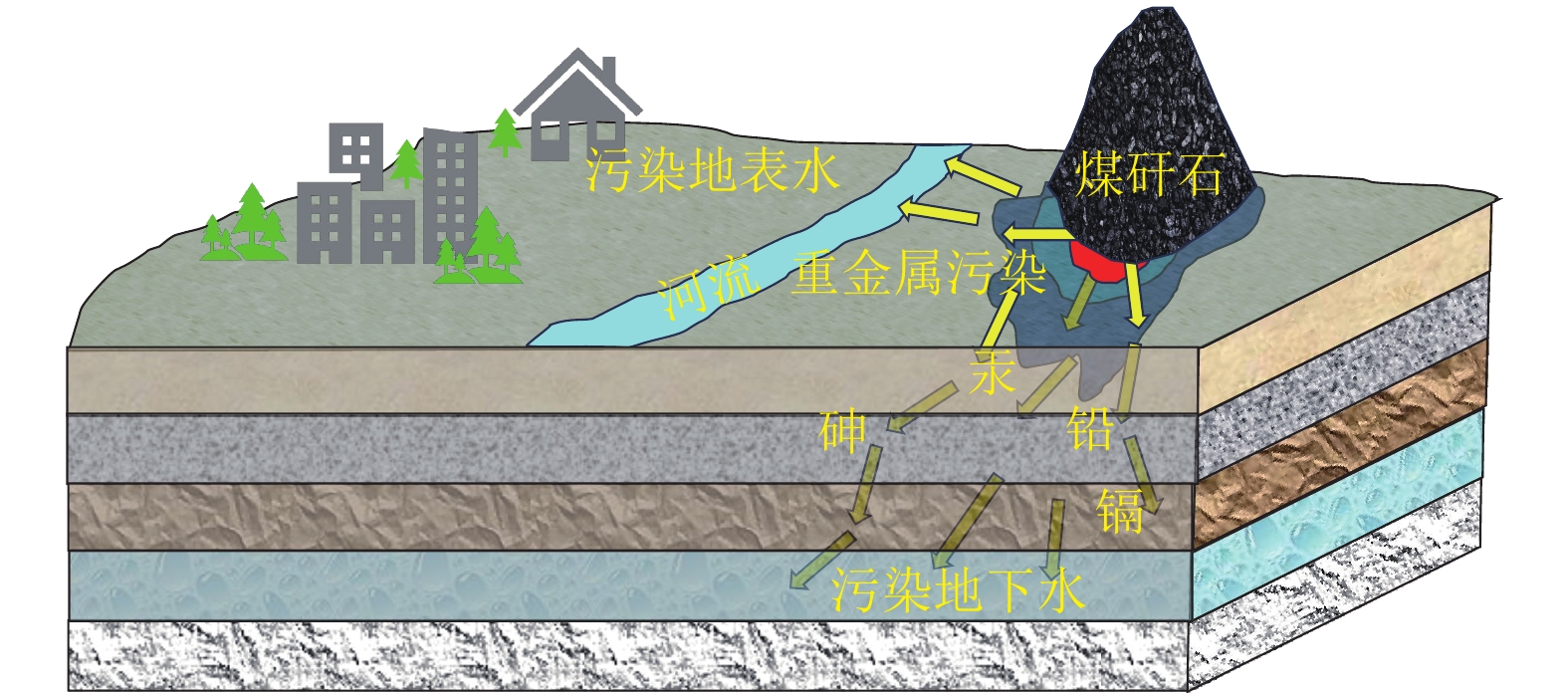
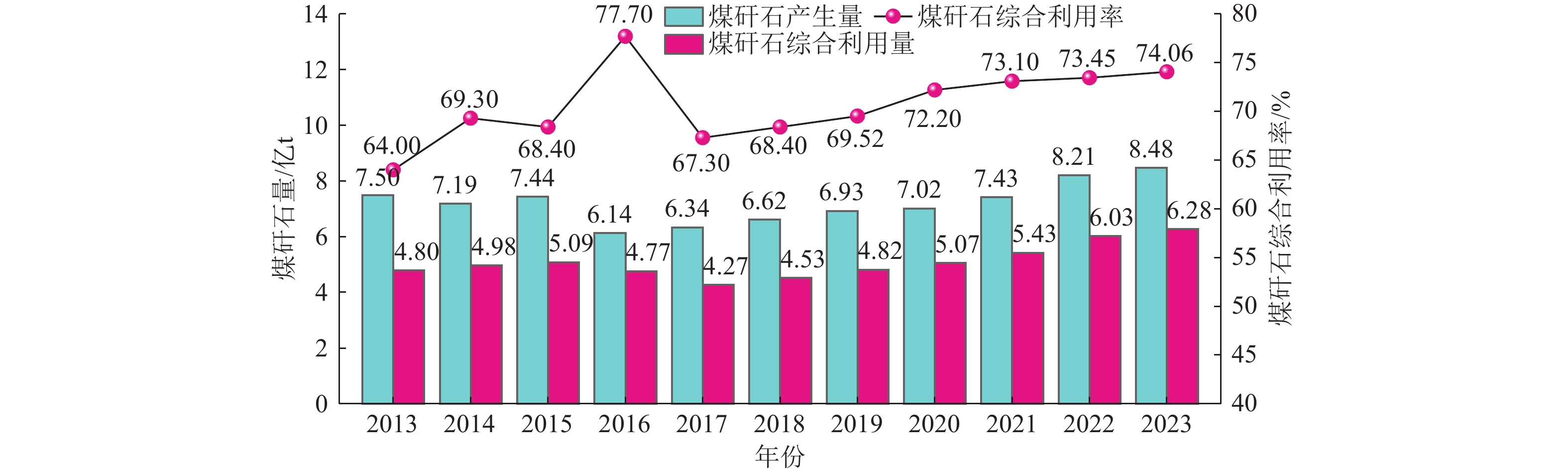
我国煤矸石固废产量大、堆存量持续增加,长期堆放会造成土地资源的浪费且污染矿区环境。利用煤矸石制备高附加值化工产品、提取有用元素等固废处理方式,存在消纳能力不足等问题,难以满足大宗固废规模化处置利用和绿色矿山建设要求。
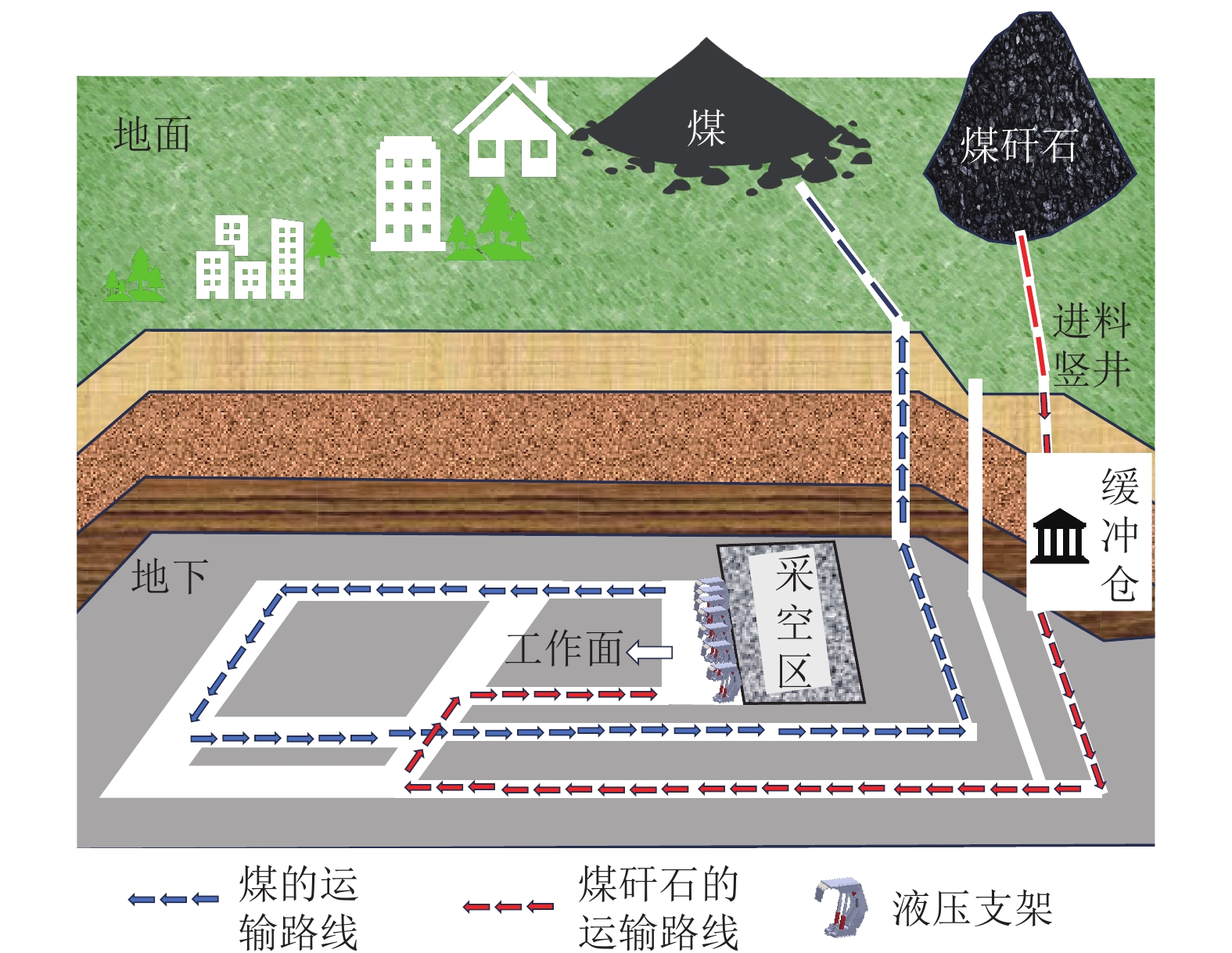
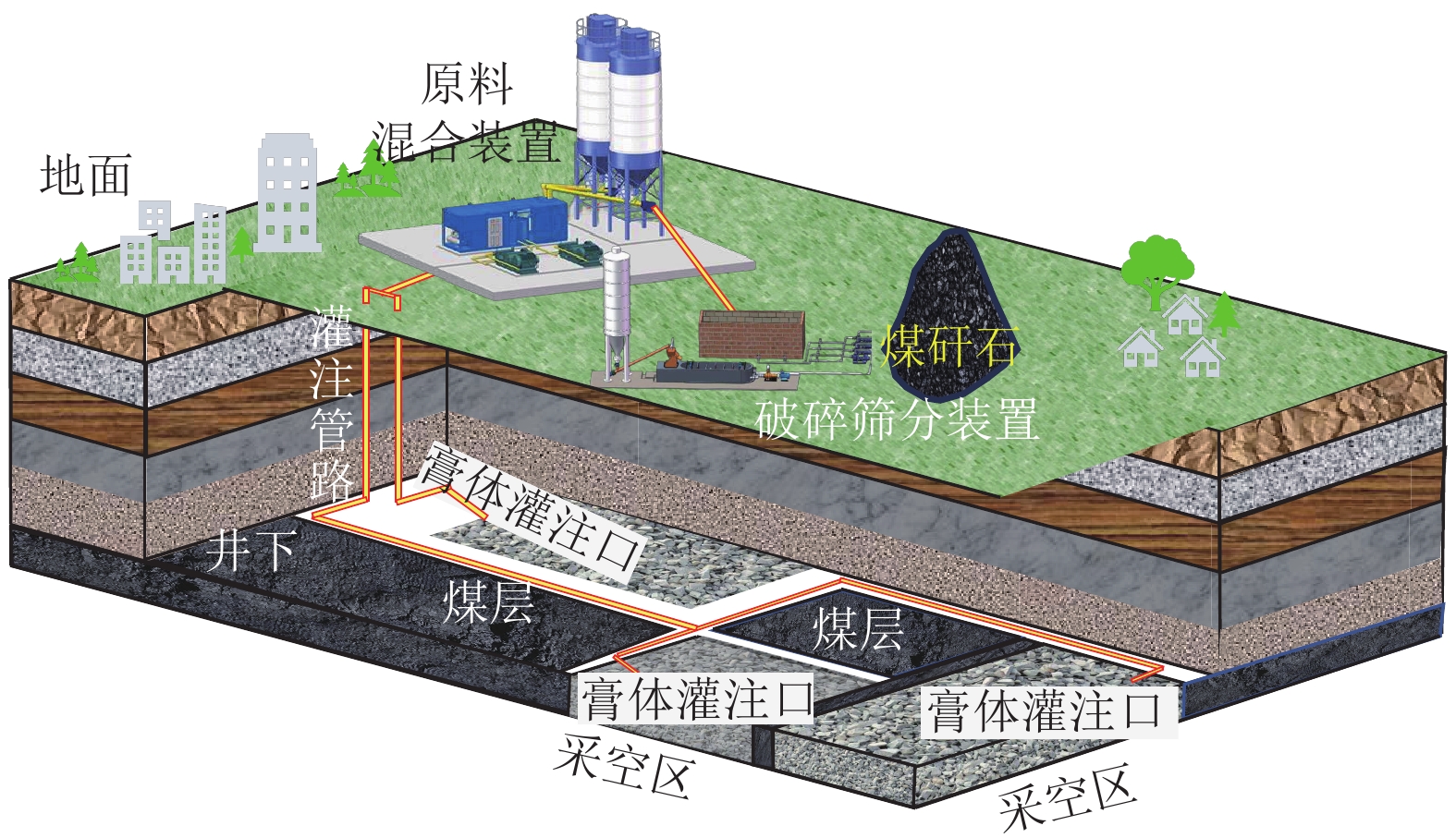
进展煤矸石在矿区复垦、井下充填等领域综合利用,是实现其规模化处置利用的重要发展方向。系统总结了煤矸石的物理化学特性及其资源属性,并分析了煤矸石长期堆放对矿区大气、土壤、水体等影响;以绿色矿山建设为出发点,重点介绍了煤矸石作为塌陷区复垦、地聚物注浆、固体充填、膏体充填及似膏体充填等材料的固废规模化处置与利用技术的原理、发展及应用效果。发现煤矸石复垦材料能够改善土壤性质、促进植物生长,但存在短期内重金属迁移污染环境等问题;煤矸石作为地聚物注浆材料实现了煤矸石重金属物质的有效固化,降低了重金属元素释放对环境的危害;煤矸石固体充填技术具有煤矸石处理工艺简便、辅助材料使用少的优势,但面临充填效果不均匀、污染地下水等挑战;归纳了煤矸石膏体充填材料、似膏体充填材料的原料配方及流动性优势,分析了材料的微观水化机理与流动特性,为矿井充填开采提供了关键技术支撑。最后提出目前煤矸石存在活性难以充分激发并利用、应用缺乏前期分类预处理、井下充填注浆利用成本高以及规模化利用缺乏激励性政策支持等问题。
展望为进一步推动煤矸石在矿区的安全高效、风险可控及规模化利用,未来将重点围绕煤矸石低成本复合活化方法、煤矸石固废利用过程环境友好性评估、煤矸石矿化封存CO2与负碳利用等开展研究,为煤矸石“绿色−高效−高值”综合利用路径发展提供思路,提高煤矸石的规模化利用和风险防范能力,促进固废利用与绿色矿山建设的协同发展。
Abstract:BackgroundThe coal gangue, a solid waste, features high production and a continuous increase in the amount piled in China. The long-term piling up of coal gangue will cause the waste of land resources and environmental pollution in mining areas. Various methods for utilizing coal gangue, such as preparing high-value-added chemical products and extracting useful elements, suffer a limited consumption capacity, failing to meet the requirements of large-scale disposal and utilization of solid wastes and green mine construction.
AdvancesThe comprehensive utilization of coal gangue for mining area reclamation and underground backfilling represents a critical direction for its large-scale disposal and utilization. This study systematically summarizes the physicochemical properties and resource attributes of coal gangue and analyzes the impacts of its long-term piling up on the atmosphere, soils, and water in mining areas. From the perspective of green mine construction, this study highlights the principles, advances, and application effects of technologies for large-scale disposal and utilization of coal gangue. These technologies include the utilization of coal gangue as materials for the reclamation of collapse areas, geopolymer grouting materials, solid filling materials, paste filling materials, and paste-like filling materials. The results reveal that when used as materials for reclamation, coal gangue can improve soil properties and promote plant growth, yet it poses challenges of short-term heavy metal migration and environmental contamination. When used as geopolymer grouting materials, coal gangue can effectively immobilize heavy metals within it, suppressing their release and reducing their damage to the environment. The solid backfilling technology tailored to coal gangue enjoys advantages including simple coal gangue processing technique and minimal consumption of auxiliary materials. However, this technology faces challenges like uneven filling and groundwater contamination. Furthermore, this study summarizes the composition and flowability advantages of coal gangue when used as paste and paste-like filling materials and analyzes its microscopic hydration mechanisms and flow properties, providing key technical support for backfill mining of mines. Finally, this study points out some issues concerning the utilization of coal gangue, including challenges in the full stimulation and utilization of the activity of coal gangue, the absence of classification and pretreatment in the early stage, high cost of utilization as underground backfilling and grouting materials, and a lack of incentive policies for large-scale utilization.
ProspectsTo promote the large-scale utilization of coal gangue in mining areas in a safe, efficient, and risk-controllable manner, future research will focus on the cost-effective composite activation methods, environmental friendliness assessment of utilization processes, CO2 mineralization and sequestration, and carbon-negative utilization of coal gangue. These efforts will provide insights for the comprehensive utilization of coal gangue following the "green-efficient-high value" roadmap, expand the large-scale utilization of coal gangue, and enhance the risk prevention abilities in this regard, thus promoting the synergetic development of solid waste utilization and green mine construction.
-
Keywords:
- green mine /
- coal gangue /
- solid waste utilization /
- reclamation /
- filling /
- activation /
- carbon-negative
-
-
表 1 煤矸石分类方法
Table 1 Classification methods of coal gangue
分类方法 分类指标 煤矸石分类 三级分类命名法 矸类(产出名称) 洗矸、煤巷矸、岩巷矸、手选矸、剥离矸 矸族(实用名称) 铝型、黏型、硅型、高热、中热、高硫 矸岩(岩石名称) 黏土岩、砂岩、钙质岩、铝质岩等 GB/T 29162—2012
《煤矸石分类》全硫质量分数St,d/% 低硫 (≤1.0) 中硫(>1.0~3.0) 中高硫(>3.0~6.0) 高硫(>6.0) 灰分产率Ad/% 低灰 (≤70.0) 中灰 (>70.0~85.0) 高灰(>85.0) 灰成分钙镁质量分数w(CaO+MgO)/% 钙镁型 (>10) 铝硅型 (≤10) 铝硅质量比m(Al2O3)/m(SiO2) 低级 (≤0.30) 中级 (>0.30~0.50) 高级 (>0.50) 表 2 煤矸石的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of coal gangue
化学成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO Fe2O3 K2O Na2O 烧失量 质量分数/% 40~65 15~50 1~7 1~4 2~9 1.0~2.5 <1 2~17 表 3 煤矸石作为塌陷区复垦材料研究进展
Table 3 Advances in research on the utilization of coal gangue for reclamation of collapse areas
文献 研究对象 研究内容 研究结果 [30] 煤矸石、玉米秸秆、
粉煤灰、保水剂优化煤矸石与添加剂对种植基质的影响 最佳配方:煤矸石与土壤1∶1、玉米秸秆50 g/kg、粉煤灰37 g/kg、保水剂1 g/kg,显著提高植物生长和土壤化学性质 [31] 煤矸石 分析煤矸石回填土壤中的6种重金属的分布、
迁移性及生态风险Cu、Pb、Zn浓度增加,Mn对生态威胁中等,其他重金属风险低 [32] 煤矸石 研究煤矸石作为回填材料在煤矿塌陷区的应用及其对环境污染风险的影响 模拟了煤矸石回填区域重金属在土壤中的迁移规律,重金属浓度均未超过限值,表明煤矸石回填塌陷区环境污染风险可控 [33] 煤矸石 研究煤矸石回填土地的土壤质量恢复,分析重建土壤的质量变量及相互关系 10 a后土壤变量恢复,但关联性增强,土壤更脆弱;复垦3~10 a后增加有机肥,或采用其他间接方法来提升土壤养分措施,有助于改善土壤质地 [34] 丛枝菌根真菌、白蜡、
煤矸石山土壤研究菌根真菌在煤矸石山土地复垦中的生态效果 菌根真菌促进植株生长、物种多样性、土壤改良,增强抗旱和抗病能力,显著改善生态环境 表 4 煤矸石作为地聚物注浆材料研究进展
Table 4 Advances in research on the utilization of coal gangue as geopolymer grouting materials
文献 研究对象 研究内容 研究结果 [41] 煤矸石、水泥、
粉煤灰、水玻璃等通过响应面法优化煤基固废地聚物注浆材料的配比,分析凝结时间、抗压强度、抗渗性能等指标 浆体凝结时间48 min,3 d抗压强度2.81 MPa,28 d抗压强度6.37 MPa,4次循环注浆后,注浆终压达到6.9 MPa [42] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
矿渣、聚丙烯纤维等加入氢氧化钠和聚丙烯纤维提升注浆材料的力学性能,改善抗裂和延展性 当氢氧化钠掺量为3%,纤维长度为9 mm、掺量为5‰时,28 d抗压强度达9.34 MPa,增强了界面结合力 [43] 煤矸石、高炉矿渣粉、
氢氧化钠、硅酸钠、
熟石灰等采用煅烧煤矸石与高炉矿渣、熟石灰混合,通过提高钙含量制备得到高强度地聚物 熟石灰掺量2.5%时,试件的3、28和60 d抗压强度较未加熟石灰试件分别提高了47.85%、43.93%和42.43% [44] 煤矸石、硅酸钠、
氢氧化钠、炉渣等研究不同碱性激发剂对煤矸石−矿渣−粉煤灰地聚物注浆材料的影响,分析其抗压强度、微观结构及反应产物 抗压强度随着硅酸钠含量的增加逐渐降低,90 d时抗压强度逐渐恢复 [45] 煤矸石、水玻璃、
氢氧化钠等研究机械和热激活方法对煤矸石反应性的影响,以及热激活煤矸石在改性硅酸钠碱溶液中的地质聚合性能 不同热活化条件下,试样的抗压强度存在差异,800 ℃下热活化的试样抗压强度为17.85 MPa,较700 ℃和900 ℃下分别提高66%和110% [46] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
氢氧化钙、氢氧化钠等研究钙含量对煤矸石和粉煤灰地聚物的影响,并优化煤矸石和粉煤灰地聚物的配比 当煤矸石掺量为30%时,28 d抗压强度为22 MPa;碱活化剂和氢氧化钙显著改善了注浆材料的微观结构,提升了强度 表 5 煤矸石作为固体充填材料研究进展
Table 5 Advances in research on the utilization of coal gangue as solid filling materials
文献 研究对象 研究内容及方法 研究结果 [49] 煤矸石、
粉煤灰、黄土研究煤矸石、粉煤灰、黄土比例对充填体强度与密实度的影响 优化材料配比后,1 d强度从0.144 MPa增至0.417~1.233 MPa,3 d为0.191~1.200 MPa,7 d为0.195~1.640 MPa,提升了抗压强度与稳定性 [50] 煤矸石、矿粉、石膏、硅酸盐熟料 研究低成本胶凝材料(矿粉、石膏、水泥熟料)在煤矿固体充填中的应用 最优配比下,充填体的7、28 d抗压强度分别为3.48和5.11 MPa,成本优势明显,且充填效率提高 [51] 圆柱体模型(煤矸石) 研究煤矸石下落过程中运动特性与抗风能力 进料能力增大,空气阻力逐步增大,煤矸石下落速度逐渐减缓 [52] 松散矸石 使用PFC3D数值模拟,研究试样尺寸对松散矸石力学性能的影响 煤矸石颗粒增大,松散矸石的压缩应力−应变曲线趋于双曲线型,侧压系数先增大后减小,并且较大尺寸试样的承载能力更强、变形更小 [53] 煤矸石 用PFC模拟4种不同粒径等级的煤矸石回填材料的压缩变形,分析粒径对压缩变形和颗粒破碎的
影响当粒径较小时,孔隙率较低,破碎颗粒填充孔隙;粒径较大时,孔隙率较高,破碎颗粒无法完全填充孔隙;合理的粒度比例增强了回填材料的变形能力,减少压缩
变形[54] 煤矸石 采用PFC3D颗粒流数值模拟研究煤矸石充填体在循环载荷下的力学特性 累积变形分为快速增长和逐步稳定2个阶段,每次加载应力上限为2 MPa;颗粒破碎对变形和力学特性有显著影响 表 6 煤矸石作为膏体充填材料研究进展
Table 6 Advances in research on the utilization of coal gangue as paste filling materials
文献 研究对象 研究内容 研究结果 [57] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥研究固体废弃物膏体充填料浆的工作特性和强度特性,分析粉煤灰、水泥、细矸率及质量分数对膏体的影响 最优配比为粉煤灰360 kg/m³,水泥170 kg/m³,细矸率40%,质量分数82%。3 d抗压强度2.9 MPa,7 d强度
6.32 MPa,28 d强度14.9 MPa[58] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥研究大粒径粗骨料(15~25 mm)对膏体性能的影响,分析坍落度、凝结时间、强度等随粗骨料比例的变化规律 粉煤灰掺量多时,电阻率相对较大,28 d抗压强度为
3.95 MPa,揭示了不同水泥掺量下凝结时间与强度变化规律[59] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
氯化钠研究氯化钠对膏体材料水化过程的影响作用 氯化钠掺入显著提高了膏体的抗压强度和弹性模量,
28 d强度为1008.25 kPa[60] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
气化渣研究充填材料的最优配比和材料损伤演化模型,分析水泥掺量对材料充填效果的影响 最优配比条件下充填材料的初终凝时间分别为5.65和11.73 h,抗压强度为2.32 MPa,抗拉强度为0.13 MPa,28 d损伤值为0.41,该膏体材料成本为25.76元/t [61] 煤矸石、水泥 研究了表面浆料处理方法对煤矸石浆料的优化,通过SEM和EDS分析微观结构变化,优化混合比设计 揭示了煤矸石与水泥混合后的微观结构变化,孔隙率降至2.62%,水泥水化产物形成复杂钙矾石骨架,分形维数显著增加 [62] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥研究煤矸石级配和粉煤灰比例对材料力学性能的影响 配比优化后,28 d抗压强度提升至3.30 MPa,弹性模量增至0.44 GPa,改善了膏体的力学性能 [63] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥研究膏体材料的力学性能,制备不同配比的煤矸石−粉煤灰充填混合物,并进行了抗压强度与流动性等试验 优化配比后,膏体的抗压强度和泌水率得到改善,早期强度0.13 MPa,后期强度2.47 MPa [64] 煤矸石 研究煤矿膏体充填对地下水环境的影响 煤矸石和粉煤灰配制的膏体充填对重金属元素有固化作用,重金属浸出毒性值低于原材料,符合地下水Ⅲ类水指标 表 7 煤矸石作为似膏体充填材料研究进展
Table 7 Advances in research on the utilization of coal gangue as paste-like filling materials
文献 研究对象 研究内容 研究结果 [66] 陶化煤矸石、新鲜煤矸石、粉煤灰、
复合减水剂研究煤矸石似膏体自流充填特性,分析抗压强度、坍落度等参数 陶化煤矸石提高了充填体的强度,7 d时强度提升30%,改善了材料的抗压强度、坍落度 [67] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥研究适用于孙村煤矿的似膏体料浆,以解决煤矸石排放与矿山安全问题 配比优化后抗压强度得到显著提升,流变性能(坍落度、稠度)也有所改善,粗粒新鲜煤矸石提高了流动性,材料强度明显增强 [68] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、PL膏体胶结料、速凝剂 开展煤矸石似膏体快速充填试验,分析了充填强度和凝结时间,确定最佳配比 浆体凝结时间小于6 h,28 d抗压强度达到1.05 MPa,适应不同施工需求 [69] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥、氯化物、河砂建立BP网络模型,探讨了似膏体充填材料各组分对性能的影响,并优化配比 BPNN算法优化后的配比显著改善了分层度和塌落度,长期抗压强度可达15.8 MPa [70] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥测试不同浓度和颗粒粒径下煤矸石似膏体料浆的流变参数,模拟管道输送过程 料浆浓度为78%时,浆体流动特性良好,沉降明显减少 [71] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥分析煤矸石似膏体充填料浆在管道自流输送过程中的运动和沉降规律,利用Fluent软件模拟料浆的输送过程 煤矸石浆体在管道输送过程中能够保持良好的悬浮状态,有效克服输送阻力 [72] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥通过Fluent模拟和流体力学理论计算方法,分析似膏体料浆管路输送特性 模拟结果表明,料浆具有良好的输送特性,符合工程应用标准 [73] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥、钢渣探讨材料的力学性能和胶结机理,设计了似膏体充填工艺流程及制备与输送系统 利用新型骨料、煤矸石和钢渣分别制备似膏体材料,其最大允许充填倍线分别为5.06、4.01和4.63,材料成本为34~57元/t [74] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
水泥、木钙研究减水剂对煤矸石似膏体充填料浆流变性能的影响,分析减水剂对料浆坍落度、坍落扩散度和稠度的作用 材料的流变性、强度等得到优化,坍落度为28.5 cm,坍落扩散度63.0 cm;减水剂对强度提升起到了关键作用 [75] 煤矸石、粉煤灰、
矿渣、熟料、石膏研究煤矸石凝石似膏体充填材料性能,分析煤矸石物相组成与热力学特性 3、7和28 d抗压强度分别为21.3、38.0和49.5 MPa [76] 煤矸石、水泥熟料、粉煤灰 通过对煤矸石煅烧激发其活性,采用复合热液蚀变方法确定最佳活化参数 优化配比显著提高了抗压强度,7和28 d抗压强度分别为35.5和49.6 MPa -
[1] 徐燕飞,陈永春,李静,等. 煤电基地CO2和CH4遥感监测及时空特征分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(6):79−90. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.09.0537 XU Yanfei,CHEN Yongchun,LI Jing,et al. Remote sensing monitoring and spatiotemporal characteristics of CO2 and CH4 concentrations in coal–electricity production bases[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(6):79−90. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.09.0537
[2] LIU Yin,WEN Hu,CHEN Changming,et al. Research status and development trend of coal spontaneous combustion fire and prevention technology in China:A review[J]. ACS Omega,2024,9(20):21727−21750. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00844
[3] 李华焜,郑刘根,陈永春,等. 基于CT扫描的重构土壤孔隙结构及其对水盐运移影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(4):120−127. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.09.0586 LI Huakun,ZHENG Liugen,CHEN Yongchun,et al. Exploring the pore structure of reconstructed soils and its effects on water and salt transport based on CT scanning[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(4):120−127. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.09.0586
[4] CAO Yachuan,ZHOU Chuncai,GAO Feiyue,et al. Lithium recovery from typical coal–based solid wastes:Critical technologies,challenges,and prospects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2024,498:155121. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.155121
[5] 朱琦,胡振琪,叶春,等. 基于化学–微生物法的煤矸石山酸化污染原位控制技术研究进展[J]. 中国矿业,2023,32(1):52−59. DOI: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2023.01.001 ZHU Qi,HU Zhenqi,YE Chun,et al. Research progress of in situ control technology for acidification pollution of coal gangue pile based on chemical–microbial method[J]. China Mining Magazine,2023,32(1):52−59. DOI: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2023.01.001
[6] WANG Haiyan,TAN Bo,ZHANG Xuedong. Research on the technology of detection and risk assessment of fire areas in gangue hills[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(31):38776−38787. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-09847-1
[7] PAN Rongkun,ZHENG Ligang,JIA H,et al. The environmental pollution and control of coal gangue spontaneous combustion in mining[J]. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,20(8):3555−3562.
[8] 李振,雪佳,朱张磊,等. 煤矸石综合利用研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用,2021,41(6):165−178. LI Zhen,XUE Jia,ZHU Zhanglei,et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of coal gangue[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources,2021,41(6):165−178.
[9] 王艳,左震,文波,等. 煤矸石粗集料理化性质和形状特征对混凝土强度的影响[J]. 矿业科学学报,2022,7(5):554−564. WANG Yan,ZUO Zhen,WEN Bo,et al. Influence of physicochemical properties and shape characteristics of coal gangue coarse aggregate on concrete strength[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2022,7(5):554−564.
[10] 姚苏琴,查文华,刘新权,等. 萍乡废弃煤矸石理化特性及热活化性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2021,40(7):2280−2287. YAO Suqin,ZHA Wenhua,LIU Xinquan,et al. Physicochemical and thermal activation properties of waste coal gangue in Pingxiang mining area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(7):2280−2287.
[11] 包宏亮. 山西西铭矿煤矸石基础性质及资源化利用研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2021,33(10):121−124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.10.24 BAO Hongliang. Study on coal gangue fundamental natures and reutilization in Ximing coalmine,Shanxi[J]. Coal Geology of China,2021,33(10):121−124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.10.24
[12] MA Hongqiang,WU Chao. Feasibility and performance evaluation of cementitious material mixed with coal gangue solid waste[M]//QI Chongchong,BENSON C H. Managing mining and minerals processing wastes. Amsterdam:Elsevier,2023:99–130.
[13] 庄红峰. 制砖物料中黏土矿物成分含量对烧结砖的影响[J]. 砖瓦,2020(2):46−49. ZHUANG Hongfeng. Effect of clay mineral content in brick making materials on fired brick[J]. Brick–Tile,2020(2):46−49.
[14] 贾建慧,马宁,董阳,等. 煤矸石综合利用研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2024,30(增刊1):36−45. JIA Jianhui,MA Ning,DONG Yang,et al. Review on the comprehensive utilization of coal gangue[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2024,30(Sup.1):36−45.
[15] 胡振琪,肖武. 关于煤炭工业绿色发展战略的若干思考:基于生态修复视角[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(4):35−42. HU Zhenqi,XIAO Wu. Some thoughts on green development strategy of coal industry:From aspects of ecological restoration[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(4):35−42.
[16] 王金满,杨曼,刘彪,等. 绿色矿山建设碳源/汇与减排增汇研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(3):1597−1610. WANG Jinman,YANG Man,LIU Biao,et al. Carbon sources/sinks and emission reduction and sink enhancement in green mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024,49(3):1597−1610.
[17] 刘萍,晏飞. 煤矸石对环境的危害及其综合治理[J]. 中国矿业,2008,17(8):49−51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2008.08.016 LIU Ping,YAN Fei. Coal rock harmful to the environment and comprehensive management[J]. China Mining Magazine,2008,17(8):49−51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2008.08.016
[18] 于水军,余明高,段玉龙,等. 自燃煤矸石山爆炸的热力学模拟[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(9):945−949. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2007.09.011 YU Shuijun,YU Minggao,DUAN Yulong,et al. Thermodynamic simulation of explosion of self–combustion gangue heap[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2007,32(9):945−949. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2007.09.011
[19] 刘迪. 煤矸石的环境危害及综合利用研究[J]. 气象与环境学报,2006,22(3):60−62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2006.03.017 LIU Di. Research on environmental effect and comprehensive utilization of coal–waste rocks[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment,2006,22(3):60−62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2006.03.017
[20] LI Yuanyuan,CAO Yingjia,RUAN Mengying,et al. Mechanism and in situ prevention of oxidation in coal gangue piles:A review aiming to reduce acid pollution[J]. Sustainability,2024,16(16):7208. DOI: 10.3390/su16167208
[21] DONG Yingbo,LU Huan,LIN Hai. Comprehensive study on the spatial distribution of heavy metals and their environmental risks in high–sulfur coal gangue dumps in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2024,136:486−497. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.12.023
[22] 秦建良. 煤矸石的危害及综合利用现状[J]. 广州化工,2015,43(4):25−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2015.04.011 QIN Jianliang. The harm of coal gangue and the present situation of comprehensive utilization[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2015,43(4):25−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2015.04.011
[23] 雷建红. 煤矸石的污染危害与综合利用分析[J]. 能源与节能,2017(4):90−91. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2017.04.044 LEI Jianhong. Analysis of pollution hazards and comprehensive utilization of coal gangue[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation,2017(4):90−91. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2017.04.044
[24] GAO Huadong,HUANG Yanli,LI Wei,et al. Explanation of heavy metal pollution in coal mines of China from the perspective of coal gangue geochemical characteristics[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(46):65363−65373. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14766-w
[25] 孔涛,张开,黄丽华,等. 菌剂混施对各粒径矸石性质及苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(增刊1):241−251 KONG Tao,ZHANG Kai,HUANG Lihua,et al. Effects of mixed application of microbial agents on growth and substrate properties of alfalfa in coal gangue matrix with different particle sizes[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(Sup.1):241−251.
[26] 周昊,郭娇娇,何绪文,等. 煤矿区固废改良土壤对植物生长的影响[J]. 煤炭技术,2018,37(3):23−25. ZHOU Hao,GUO Jiaojiao,HE Xuwen,et al. Research on impact of coal solid waste improved soil on plant growth[J]. Coal Technology,2018,37(3):23−25.
[27] ZHANG Kun,XU Liangji,HUANG Guodong,et al. Coupled variations of soil temperature and moisture in reclaimed fields filled with coal gangue of different grain size distributions[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2020,20(4):2248−2259. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-020-02579-2
[28] 郭友红,李树志,鲁叶江. 塌陷区矸石充填复垦耕地覆土厚度的研究[J]. 矿山测量,2008,36(2):59−61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2008.02.018 GUO Youhong,LI Shuzhi,LU Yejiang. Research on depth of the covering layer on reclaimed cultivated land backfilled with coal refuse in subsidence area[J]. Mine Surveying,2008,36(2):59−61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2008.02.018
[29] 胡振琪,康惊涛,魏秀菊,等. 煤基混合物对复垦土壤的改良及苜蓿增产效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(11):120−124. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.11.020 HU Zhenqi,KANG Jingtao,WEI Xiuju,et al. Experimental research on improvement of reclaimed soil properties and plant production based on different ratioes of coal–based mixed materials[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2007,23(11):120−124. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.11.020
[30] DU Tao,WANG Dongmei,BAI Yujie,et al. Optimizing the formulation of coal gangue planting substrate using wastes:The sustainability of coal mine ecological restoration[J]. Ecological Engineering,2020,143:105669. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105669
[31] TANG Quan,LI Liyuan,ZHANG Song,et al. Characterization of heavy metals in coal gangue–reclaimed soils from a coal mining area[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2018,186:1−11. DOI: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.018
[32] 冯印成,赵康,田向勤,等. 煤矸石回填塌陷区重金属淋溶迁移时空规律研究[J/OL]. 中国环境科学,2024:1–12 [2025-02-27]. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000–6923.20241104.002. FENG Yincheng,ZHAO Kang,TIAN Xiangqin,et al. Research on spatiotemporal patterns of heavy metal leaching and migration in coal gangue backfill subsidence area[J/OL]. China Environmental Science,2024:1–12 [2025-02-27]. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000–6923.20241104.002.
[33] LI Fang,LI Xinju,HOU Le,et al. A long–term study on the soil reconstruction process of reclaimed land by coal gangue filling[J]. CATENA,2020,195:104874. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104874
[34] 毕银丽,吴王燕,刘银平. 丛枝菌根在煤矸石山土地复垦中的应用[J]. 生态学报,2007,27(9):3738−3743. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.09.023 BI Yinli,WU Wangyan,LIU Yinping. Application of arbuscular mycorrhizas in land reclamation of coal spoil heaps[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2007,27(9):3738−3743. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.09.023
[35] 刘帆俞,宋慧平,吴海滨,等. 煤矸石土壤化利用与土壤改良剂研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用,2023,43(6):14−26. LIU Fanyu,SONG Huiping,WU Haibin,et al. Research progress on the utilization of coal gangue for soil remediation and as soil amendment agents[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources,2023,43(6):14−26.
[36] HAN Ruicong,GUO Xiaoning,GUAN Junfeng,et al. Activation mechanism of coal gangue and its impact on the properties of geopolymers:A review[J]. Polymers,2022,14(18):3861. DOI: 10.3390/polym14183861
[37] QIAN Lanping,XU Lingyu,ALREFAEI Y,et al. Artificial alkali–activated aggregates developed from wastes and by–products:A state–of–the–art review[J]. Resources,Conservation and Recycling,2022,177:105971.
[38] GUAN Xiao,CHEN Jixi,ZHU Mengyu,et al. Performance of microwave–activated coal gangue powder as auxiliary cementitious material[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2021,14:2799−2811. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.08.106
[39] LIU Yi,YAN Chunjie,ZHANG Zuhua,et al. A comparative study on fly ash,geopolymer and faujasite block for Pb removal from aqueous solution[J]. Fuel,2016,185:181−189. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.116
[40] ZHANG Benfeng,YANG Kang,ZHANG Kai,et al. Migration transformation,prevention,and control of typical heavy metal lead in coal gangue:A review[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology,2023,10(1):85.
[41] 郭凌志,周梅,王丽娟,等. 煤基固废地聚物注浆材料的制备及性能[J]. 建筑材料学报,2022,25(10):1092−1100. GUO Lingzhi,ZHOU Mei,WANG Lijuan,et al. Preparation and properties of coal–based solid waste geopolymer grouting materials[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2022,25(10):1092−1100.
[42] PANG Shuai,ZHANG Xiangdong,ZHU Kaixin,et al. Study on mechanical properties and micro characterization of fibre reinforced ecological cementitious coal gangue materials[J]. Polymers,2023,15(3):700. DOI: 10.3390/polym15030700
[43] HUANG Guodong,JI Yongsheng,LI Jun,et al. Improving strength of calcinated coal gangue geopolymer mortars via increasing calcium content[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,166:760−768. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.005
[44] GUO Lingzhi,LIU Juanhong,ZHOU Mei,et al. Effect of an alkali activators on the compressive strength and reaction mechanism of coal gangue–slag–fly ash geopolymer grouting materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2024,426:136012. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.136012
[45] ZHANG Weiqing,DONG Chaowei,HUANG Peng,et al. Experimental study on the characteristics of activated coal gangue and coal gangue–based geopolymer[J]. Energies,2020,13(10):2504. DOI: 10.3390/en13102504
[46] WANG Qingping,ZHU Longtao,LU Chunyang,et al. Investigation on the effect of calcium on the properties of geopolymer prepared from uncalcined coal gangue[J]. Polymers,2023,15(5):1241. DOI: 10.3390/polym15051241
[47] 徐法奎. 我国煤矿充填开采现状及发展前景[J]. 煤矿开采,2012,17(4):6−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2012.04.002 XU Fakui. Current status of stowing mining and its development prospect in China[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2012,17(4):6−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2012.04.002
[48] LI Junmeng,HUANG Yanli,CHEN Zhongwei,et al. Characterizations of macroscopic deformation and particle crushing of crushed gangue particle material under cyclic loading:In solid backfilling coal mining[J]. Powder Technology,2019,343:159−169. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.11.049
[49] 刘建功,王英. 固体充填材料比例特征及应力特性研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2017,43(5):38−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2017.05.008 LIU Jiangong,WANG Ying. Research on ratio characteristics and stress properties of solid filling materials[J]. China Coal,2017,43(5):38−42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2017.05.008
[50] 闫善飞,史艳楠,王翰秋,等. 固体充填胶凝材料试验研究与应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(3):143−147. YAN Shanfei,SHI Yannan,WANG Hanqiu,et al. Experimental research and application of solid filling cementitious materials[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(3):143−147.
[51] JU Feng,LI Baiyi,GUO Shuai,et al. Dynamic characteristics of gangues during vertical feeding in solid backfill mining:A case study of the Wugou Coal Mine in China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(20):1389. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-016-6194-0
[52] 孔国强,宋天奇,李俊孟. 松散矸石压缩特性的尺寸效应数值模拟[J]. 煤炭技术,2017,36(7):69−71. KONG Guoqiang,SONG Tianqi,LI Junmeng. Size effect of compression feature of loose gangue by numerical simulation[J]. Coal Technology,2017,36(7):69−71.
[53] LI Meng,LI Ailing,ZHANG Jixiong,et al. Effects of particle sizes on compressive deformation and particle breakage of gangue used for coal mine goaf backfill[J]. Powder Technology,2020,360:493−502. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.10.075
[54] 何泽全,巨峰,肖猛,等. 煤矸石充填材料在循环载荷作用下的细观变形特征分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(5):1002−1010. HE Zequan,JU Feng,XIAO Meng,et al. Characterization of meso–deformation of gangue backfilling materials under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2022,39(5):1002−1010.
[55] 李晓彤. 水–力耦合淋溶作用下煤矸石重金属析出释放规律研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2023. LI Xiaotong. Characterization of heavy metal releasing from coal gangue under water–force coupled leaching[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2023.
[56] 张云,刘永孜,来兴平,等. 基于导水裂隙扩展–重金属离子迁移的短壁块段式充填保水采煤机理研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(2):155−172. ZHANG Yun,LIU Yongzi,LAI Xingping,et al. Mechanism of short–wall block backfill water–preserved mining based on water–conducting fractures development–heavy metal ions migration[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(2):155−172.
[57] 刘文生,张燕凤,张贺然. 膏体充填材料的工作特性及强度特性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2015,34(4):1116−1120. LIU Wensheng,ZHANG Yanfeng,ZHANG Heran. Study on the working and strength characteristics of paste filling material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2015,34(4):1116−1120.
[58] 刘音,李金平,路瑶,等. 煤矸石大粒径粗骨料比例对充填膏体性能影响的试验研究[J]. 煤矿开采,2016,21(5):1−3. LIU Yin,LI Jinping,LU Yao,et al. Experimental studying of coal gangue large particle size coarse aggregate ratio to filling paste property[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2016,21(5):1−3.
[59] CHEN Shaojie,DU Zhaowen,ZHANG Zhen,et al. Effects of chloride on the early mechanical properties and microstructure of gangue–cemented paste backfill[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,235:117504. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117504
[60] 陈瑞毅. 煤基固废膏体充填材料力学特性实验研究[D]. 淮南:安徽理工大学,2022. CHEN Ruiyi. Experimental study on mechanical properties of coal based solid waste paste filling material[D]. Huainan:Anhui University of Science and Technology,2022.
[61] SUN Qi,WEI Xueda,WEN Zhijie. Preparation and strength formation mechanism of surface paste disposal materials in coal mine collapse pits[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,17:1221−1231. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.01.062
[62] ZHANG Leiming,LAI Xingping,PAN Jiliang,et al. Experimental investigation on the mixture optimization and failure mechanism of cemented backfill with coal gangue and fly ash[J]. Powder Technology,2024,440:119751. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2024.119751
[63] ZHANG Xinguo,LIN Jia,LIU Jinxiao,et al. Investigation of hydraulic–mechanical properties of paste backfill containing coal gangue–fly ash and its application in an underground coal mine[J]. Energies,2017,10(9):1309. DOI: 10.3390/en10091309
[64] 牛丽菊,郑帅亮. 煤矿膏体充填对地下水环境影响研究[J]. 煤,2024,33(3):100−104. [65] ZHANG Feng,LIU Jinxiao,NI Haiming,et al. Development of coal mine filling paste with certain early strength and its flow characteristics[J]. Geofluids,2021,2021(1):6699426.
[66] 王新民,龚正国,张传恕,等. 似膏体自流充填工艺在孙村煤矿的应用[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2008,28(2):10−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2763.2008.02.004 WANG Xinmin,GONG Zhengguo,ZHANG Chuanshu,et al. Application of gravity–flowed paste–like slurry filling technology in Suncun Coal Mine[J]. Mining Research and Development,2008,28(2):10−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2763.2008.02.004
[67] 王新民,曹刚,龚正国. 煤矸石作充填骨料的似膏体料浆流动性能试验研究[J]. 矿业快报,2008,24(1):20−23. WANG Xinmin,CAO Gang,GONG Zhengguo. Experimental research on flow performance of paste–like slurry with gangue as filling aggregate[J]. Express Information of Mining Industry,2008,24(1):20−23.
[68] 刘晓玲,王新民,吴鹏. 煤矸石似膏体快速充填试验研究[J]. 金属矿山,2011(6):6−8. LIU Xiaoling,WANG Xinmin,WU Peng. Experimental research of rapid filling with paste–like coal gangue[J]. Metal Mine,2011(6):6−8.
[69] 顾清恒. 似膏体充填材料配比的BP网络优化方法[J]. 金属矿山,2016(3):40−43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.03.008 GU Qingheng. Mixing proportion of paste–like filling material based on back–propagation neural network[J]. Metal Mine,2016(3):40−43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.03.008
[70] 郝宇鑫,黄玉诚,李育松,等. 矸石似膏体充填料浆临界流速影响因素研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(4):128−133. HAO Yuxin,HUANG Yucheng,LI Yusong,et al. Influencing factors of critical flow rate of gangue paste–like filler slurry[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(4):128−133.
[71] 张钦礼,谢盛青,郑晶晶,等. 充填料浆沉降规律研究及输送可行性分析[J]. 重庆大学学报,2011,34(1):105−109. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2011.01.018 ZHANG Qinli,XIE Shengqing,ZHENG Jingjing,et al. Sedimentation law research and transportation feasibility study of backfilling slurry[J]. Journal of Chongqing University,2011,34(1):105−109. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2011.01.018
[72] 赵卫强,吕艳奎,黄玉诚. 似膏体料浆管输中浆击分析与计算研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2015,47(8):96−98. ZHAO Weiqiang,LYU Yankui,HUANG Yucheng. Analysis and calculation of slurry water–hammer in paste–like slurry pipeline transport[J]. Coal Engineering,2015,47(8):96−98.
[73] 曹小刚. 新型骨料似膏体胶结充填技术研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2012. CAO Xiaogang. Study on new aggregate paste–like backfilling technology[D]. Changsha:Central South University,2012.
[74] 姚志全,张钦礼,王新民. 减水剂在似膏体胶结充填中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2009,40(1):43−45 [75] 崔增娣,孙恒虎. 煤矸石凝石似膏体充填材料的制备及其性能[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(6):896−899. CUI Zengdi,SUN Henghu. The preparation and properties of coal gangue based sialite paste–like backfill material[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(6):896−899.
[76] 王莹莹,谢光天,李泽荃. 煤矸石质似膏体充填胶结料的研制及水化机理研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2017,49(12):141−144. WANG Yingying,XIE Guangtian,LI Zequan. Research on coal gangue paste–like filling materials and its hydration mechanism[J]. Coal Engineering,2017,49(12):141−144.
[77] 张云,刘永孜,曹胜根,等. 短壁块段式充填采煤矸石充填材料重金属离子“下行”迁移规律及控制技术[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2023,40(2):284−294. ZHANG Yun,LIU Yongzi,CAO Shenggen,et al. Study on the migration law and control of heavy metal ions “downward” in gangue backfill materials in short–wall block backfill mining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2023,40(2):284−294.







 下载:
下载: