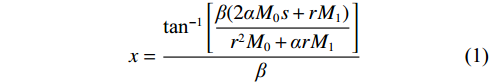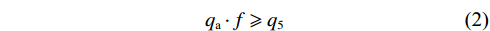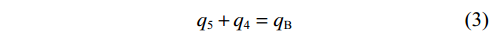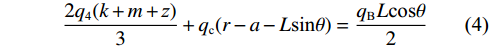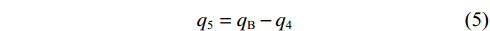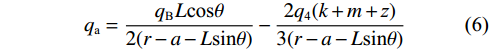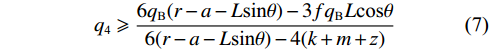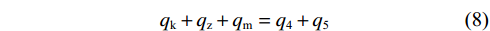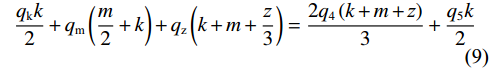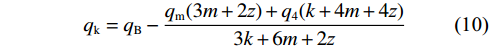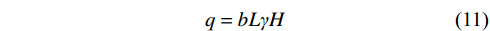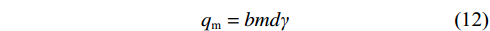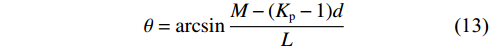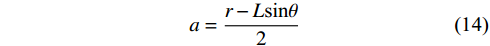Evolutionary pattern and control technology of mine pressure when mining face for coal pillars in main roadways passing through abandoned roadways
-
摘要:目的
由于矿井工作面布置方式的调整,煤柱工作面经常会面临通过废弃巷道时覆岩顶板难以控制的情况。
方法为解决这一问题,以河南赵固二矿二盘区外侧煤柱工作面过空巷为工程背景,采用理论分析、数值模拟和现场试验等方法,研究工作面与空巷覆岩破断组合结构,模拟不同支护强度下顶板应力−位移全周期演化规律,分析工作面矿压显现特征,提出相应的控制技术。
结果和结论结果表明,基本顶不同破断形式对矿压显现特征影响显著,关键块断裂位置可分为煤柱上方、空巷上方和实体煤上方3种类型。通过建立工作面过空巷力学模型,研究基本顶超前破断力学机理,基本顶受到空巷−煤柱−工作面支护系统支撑作用,形成“砌体梁”稳定承载结构,判定基本顶滑落失稳时空巷支护强度的临界值为4.6 MPa。数值模拟显示,工作面超前支承压力与空巷应力集中产生的叠加效应对煤柱影响显著,当工作面推进至距空巷5 m时,煤柱失稳破坏,基本顶易发生超前破断。在工作面过空巷过程中,煤柱超前支承压力分布特征由“双峰型”转变为“孤峰型”。不同支护强度下的顶板应力分布特征存在明显差异,确定空巷支护强度为4.5 MPa能够防止基本顶超前破断。最后,在研究区二盘区外侧煤柱工作面采用“锚网索”支护方式对空巷顶板进行补强支护,过空巷期间液压支架工作阻力在研究区域处于安全范围内,未发生顶板垮落和压架等事故,解决了二盘区外侧煤柱工作面过空巷技术难题,可为类似工作面提供参考依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveWith the adjustment of the mining face layout in mines, the overburden roof of the mining face for coal pillar recovery is frequently difficult to control when the mining face passes through abandoned roadways.
MethodsTo address this challenge, this study investigated the coal pillar mining face outside the No.2 panel in the Zhaogu No.2 Coal Mine in Henan Province, which passes through abandoned roadways. Using methods like theoretical analysis, numerical simulation, and in-situ tests, this study examined the composite structure of the mining face and the broken overburden of abandoned roadways, followed by simulation of the full-cycle evolutionary patterns of the stress and displacement of the mining face roof under different support strengths. Finally, it analyzed the mine pressure behavior on the mining face and proposed corresponding control technology.
Results and ConclusionsThe results indicate that the breaking forms of the main roof significantly influenced the mine pressure behavior. The breaking of its key blocks might occur above the coal pillar, abandoned roadway, or solid coal. The mechanical mechanisms underlying the advance breaking of the main roof were explored using the established mechanical models of the mining face passing through an abandoned roadway. The main roof was found to be supported by the support system consisting of the abandoned roadway, coal pillar, and mining face, which formed a stable bearing structure in the form of a masonry beam. The critical support strength of the abandoned roadway in the case of the sliding instability of the main roof was determined at 4.6 MPa. The numerical simulation results indicate that the superimposed effects of the advance support pressure of the mining face and the stress concentration in the abandoned roadway significantly affected the coal pillar. As the mining face advanced to 5 m away from the abandoned roadway, the coal pillar experienced instability failure, and the main roof was prone to undergo advance breaking. When the mining face passed through the abandoned roadway, the advance support pressure of the coal pillar shifted from the bimodal to unimodal distribution. The roof stress exhibited varying distribution characteristics under different support strengths, and it was discovered that the support strength of 4.5 MPa of the abandoned roadway could prevent the advance breaking of the main roof. For the coal pillar mining face outside the No.2 panel in the study area, cable anchors were employed as the reinforced support of the abandoned roadway roofs. Consequently, when the mining face passed through the abandoned roadways, the working resistance of hydraulic supports fell within the safe range in the study area, avoiding accidents such as roof collapse and support crushing. This study addressed the technical challenges faced when the coal pillar mining face outside the No.2 panel passed through abandoned roadways, providing a reference for similar mining face.
-
Keywords:
- abandoned roadway /
- coal pillar /
- mechanical model /
- rock burst /
- numerical simulation /
- in-situ test
-
随着采煤技术的不断提高,我国煤炭相对储量逐渐减少,提高煤炭资源回采效率迫在眉睫。回收煤柱是提高资源回采效率的重要措施之一,但煤柱中复杂的煤层赋存条件和周边采空区遗留的废弃空巷会对煤柱回收工作造成很大困难。在工作面推进过程中,空巷上方的基本顶发生超前断裂,形成超长关键块,导致工作面发生压架和大面积顶板垮落等事故,严重影响工作面安全回采,因此,研究煤柱回收工作面安全过空巷[1-3]技术有着重要的实际意义。
诸多学者针对工作面过空巷的问题从采场覆岩运移规律和空巷稳定性等方面进行了大量研究,并取得了一些成果[4-6]。许家林等[7]采用相似模拟结合现场实测的方法研究了特大采高工作面关键层结构形态及工作面矿压显现特征,发现关键层之间相互作用会造成周期来压呈现大小周期性变化,并提出了不同关键层结构下的支架阻力确定方法。徐青云等[8]研究了综放工作面过空巷顶板稳定机理,并采用理论计算和数值模拟确定了空巷顶板最小支护强度,在现场试验中对比了不同支护方式的支护效果,证明了充填效果最佳。刘畅等[9-11]通过建立工作面过空巷力学模型研究了基本顶破断力学机理,并采用相似模拟的方法发现了工作面过不同宽度空巷的围岩破坏特征和支架载荷变化,提出了一系列针对性控制措施并解决了工作面过空巷支架阻力选型的问题。赵文光等[12]采用3DEC软件对浅埋综采工作面过空巷顶板运移特征进行了模拟研究,并通过现场实践验证了“锚索补强+泵送支柱”空巷控顶技术的可行性。谢生荣等[13]结合数值模拟方法和力学分析对近水平工作面过空巷围岩破坏特征进行研究,提出了停采等压、强力锚杆索支护和注浆固结修复等控制技术,并取得良好实践效果。周海丰等[14]采用FLAC3D模拟软件研究了大采高综采工作面过空巷群基本顶破断特征,采用“泵送支柱+锚索+W钢带”联合支护方式支护空巷,并在现场取得了良好效果。
目前,工作面空巷多采用充填、木垛、单体支柱以及锚杆索加强支护等方式控制空巷顶板沉降[15-17]。但由于木垛和单体支柱装卸较为繁琐且支护效果不佳,对工作面回采进度造成极大影响,而充填方式经济条件要求较高,因此,国内大部分矿井结合自身经济条件采用锚杆和锚索对空巷进行加强支护,保证人员施工安全以及工作面安全高效回采。采用锚杆和锚索支护空巷最主要的因素是支护强度,确定支护强度是保障工作面安全回采的首要目标。
笔者在前人研究的基础上,对河南赵固二矿二盘区外侧大巷煤柱工作面过空巷情况进行分析。工作面采用放顶煤开采方式,工作面内部存在周边采空区遗留下来的巷道和大巷之间的联络巷,针对平行工作面方向的空巷进行理论分析和数值模拟,提出锚网索加强支护空巷顶板的支护方式,研究支护强度对综放工作面过空巷的影响,并进行现场试验,分析工作面矿压显现特征,为类似条件下大巷煤柱回收工作面开采提供一定参考依据。
1 工作面概况
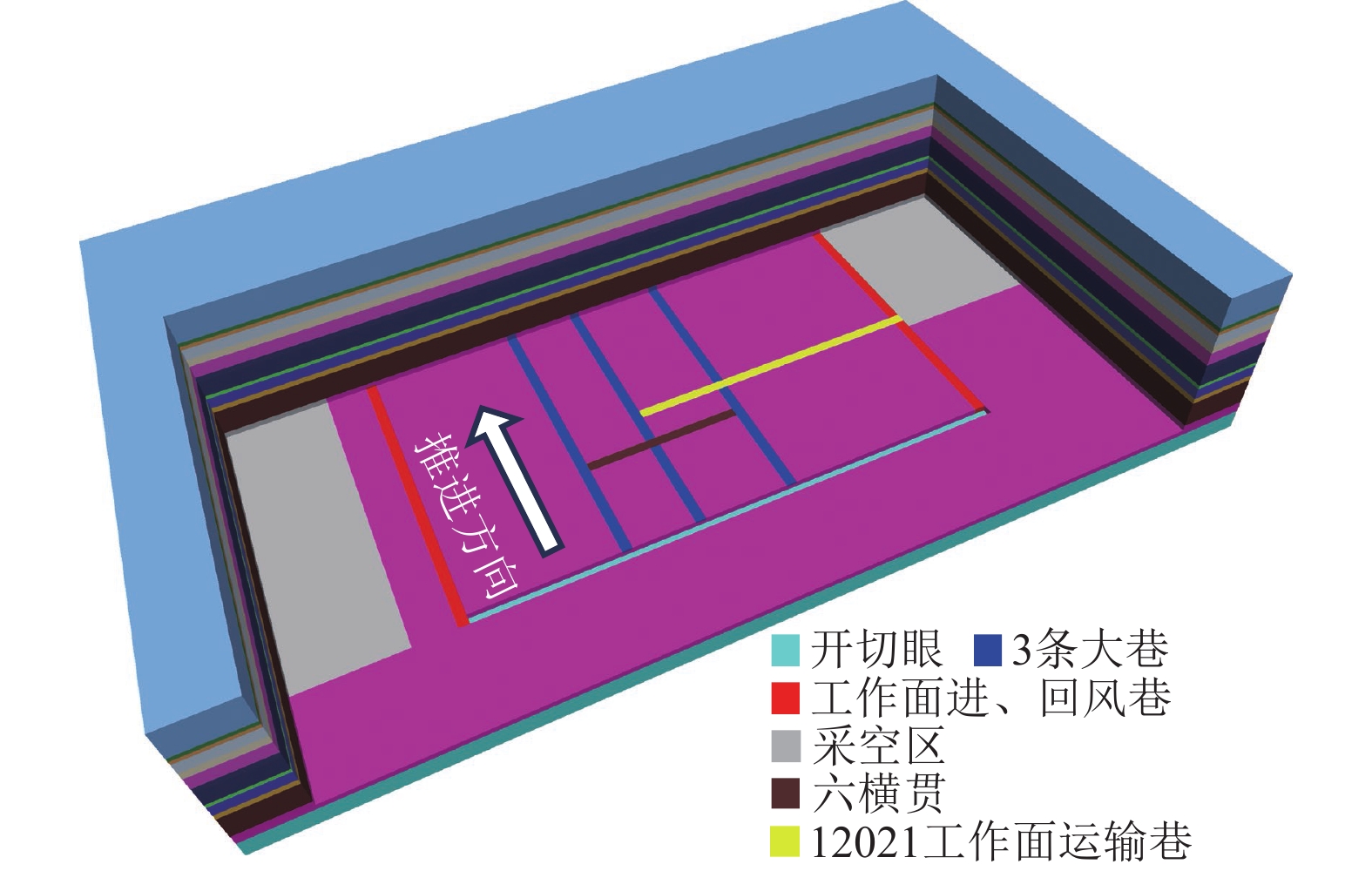
为了提高煤炭资源开采效率,赵固二矿决定对二盘区外侧煤柱工作面进行资源回收。二盘区外侧煤柱工作面东侧紧邻12011、12012、12021和12022工作面采空区,南侧靠近F30-1断层,西侧与11071和11072工作面的采空区相接,北侧与F30断层相连。工作面沿回采方向持续揭露二盘区外侧煤柱工作面轨道巷、胶带巷和辅助巷,3条大巷沿顶掘进,并在工作面推进过程中面临多条空巷以及大巷之间的联络巷,其中六横贯与开切眼距离较近,为39.7~59.0 m,平均距离为50.0 m,空巷宽度为4.6~5.3 m,高度在3.7~4.0 m。二盘区外侧煤柱工作面煤层倾向236°~307°,倾角2°~6°,煤层埋深为650.1~696.9 m,煤层平均厚度为6.0 m,设计回采长度776.8 m,倾向长257.6 m,工作面直接顶为砂质泥岩,厚度为4.5~15.0 m,基本顶为粉砂岩和砂质泥岩,厚度为5.5~10.5 m,抗压强度为47.4~108.0 MPa。根据关键层判别软件确定基本顶上方厚度为3.29 m的中粒砂岩为关键层,控制上覆岩层运动,工作面放顶煤开采的采放比为1∶1,工作面位置以及钻孔柱状图如图1所示。
2 综放工作面过空巷基本顶破断机理研究
2.1 基本顶破断特征
研究表明[18-19],空巷与工作面之间煤柱失稳是基本顶破断的主要因素,基本顶在空巷上方发生断裂进而导致空巷和工作面顶板来压。但是在实际生产过程中,随着工作面推进,空巷与工作面之间的距离、周期来压步距以及煤柱承受载荷不断发生变化,充满不确定性,当工作面靠近空巷,煤柱失稳后,基本顶是否发生断裂是众多因素共同作用的结果,而空巷和工作面顶板来压则是根据基本顶断裂位置确定的。基本顶断裂后,形成不同的关键块体,位于煤壁前方的关键块称为关键块A,由煤壁和工作面支架支撑的关键块称为关键块B,位于矸石上方的关键块称为关键块C。
当工作面前方存在空巷时,随着工作面推进,空巷与工作面之间的煤柱宽度逐渐减小,煤柱承载能力不断降低,当煤柱宽度减小到临界值时,煤柱则会发生失稳破坏,煤柱强度大幅度下降。在此过程中,基本顶断裂线超前移动,关键块B长度增加,岩块回转力增大,基本顶所受弯矩逐渐增大导致弯曲下沉,当弯矩超过了基本顶的抗弯能力,基本顶发生破断,支架及围岩应力增大,容易引发压架事故。
针对工作面过空巷基本顶破断位置建立力学模型,将基本顶视为弹性介质,采用Winkler地基梁理论进行分析[20-23]。基本顶断裂位置的受力结构如图2所示。
对基本顶破断力学模型进行分析,得到基本顶断裂位置[24]预测公式:
$$ x = \frac{{{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left[ {\dfrac{{\beta (2\alpha {M_0}s + r{M_1})}}{{{r^2}{M_0} + \alpha r{M_1}}}} \right]}}{\beta } $$ (1) 2.2 基本顶破断结构
基本顶断裂位置存在3种情况:处于煤柱上方、处于空巷上方、处于空巷后方实体煤上方,结构如图3所示。
在工作面靠近空巷的过程中,若基本顶在煤柱发生失稳破坏之前便已经断裂,如图3a所示,此时,断裂线位于煤柱上方,空巷未受到关键块B影响,下沉量无明显变化,工作面正常周期来压。随着工作面继续推进,在基本顶关键块A下一次断裂时,工作面已正常通过空巷,且工作面通过空巷时基本顶形成“悬臂梁”结构,工作面和空巷无明显来压现象,工作面的周期性来压步距保持正常。若工作面推进至图3b位置时,此时煤柱达到极限宽度即将发生失稳,承载能力还未下降,位于空巷正上方基本顶发生断裂,关键块B跨过工作面和煤柱并覆盖部分空巷区域,此时关键块B的下部支撑力主要由工作面支架、煤柱、空巷支护结构以及采空区矸石组成,空巷下沉量增加,工作面来压强度增加,在这种情况下,工作面和空巷将面临潜在的危险。当工作面推进至图3c位置时,此时煤柱在超前支承压力作用下发生失稳,承载能力骤降,基本顶弯矩激增,顶板下沉量增大,关键块B提前发生回转并产生超前破断,断裂线位于空巷后方实体煤上方,形成“跨巷超长关键块”。此时关键块B的支撑点在空巷后方实体煤上,由于空巷两侧应力集中,此部分实体煤是否失稳与支撑点和空巷之间的距离相关。“跨巷超长关键块”导致工作面的来压强度急剧增加,引发压架问题和空巷顶板垮塌,最终可能导致严重事故的发生。
综上所述,根据基本顶不同破断位置对工作面造成来压程度的不同,将工作面顶板来压特征对应基本顶破断结构分为3个级别:
(1) 当基本顶在工作面与空巷之间煤柱上方发生破断时,矿压无明显异常,对工作面安全开采无影响。
(2)当基本顶在空巷上方发生破断时,工作面来压强度增加,对工作面安全开采造成一定影响。
(3)当基本顶在空巷后方实体煤上方发生破断时,支架压力急剧增加,可能导致严重事故发生。
2.3 空巷支护强度的确定
经上述分析可得,决定工作面是否能顺利通过空巷的岩块是关键块B,为了防止关键块B形成“跨巷超长关键块”,避免工作面顶板突然出现大面积来压,造成压架和大面积顶板垮落等安全事故,空巷顶板支护措施必须形成有效支护。基本顶在空巷上方发生超前断裂时,此时关键块B长度为临界值;当关键块B悬顶长度再次增加,极易造成工作面压架等事故,应针对此时工作面—空巷支护系统力学特性进行研究。假设关键块B所受载荷为关键层下方覆岩自重,并且破断线位置在空巷k/2上方,如图4所示。关键块之间互相铰接,为了简化计算过程并参考相关文献[13],定义空巷支护阻力作用在k/2处,煤柱支护阻力作用在m/2处,工作面支护阻力作用在靠近煤壁z/3处,建立关键块B破断后力学模型(图4)。
根据砌体梁“S-R”稳定理论,防止关键块B发生滑落失稳需要满足以下平衡条件:
$$ {q_{\text{a}}} \cdot f \geqslant {q_5} $$ (2) 根据图4对关键块B进行力学分析,建立垂直方向受力及关键块A与关键块B接触面力矩平衡方程:
$$ {q_{\text{5}}} + {q_{\text{4}}} = {q_{\text{B}}} $$ (3) $$ \frac{{2{q_{\text{4}}}(k + m + {\textit{z}})}}{3} + {q_{\text{c}}}(r - a - L\sin \theta ) = \frac{{{q_{\text{B}}}L\cos \theta }}{2} $$ (4) 由于静力平衡作用,水平方向qa=qc,联立式(3)和式(4)得:
$$ {q_{\text{5}}} = {q_{\text{B}}} - {q_{\text{4}}} $$ (5) $$ {q_{\text{a}}} = \frac{{{q_{\text{B}}}L\cos \theta }}{{2(r - a - L\sin \theta )}} - \frac{{2{q_{\text{4}}}(k + m + {\textit{z}})}}{{3(r - a - L\sin \theta )}} $$ (6) 将式(5)和(6)代入式(2)得:
$$ {q_{\text{4}}} \geqslant \frac{{6{q_{\text{B}}}(r - a - L\sin \theta ) - 3f{q_{\text{B}}}L\cos \theta }}{{6(r - a - L\sin \theta ) - 4(k + m + {\textit{z}})}} $$ (7) 列出直接顶与煤层组合结构竖直方向受力平衡方程以及O点弯矩平衡公式:
$$ {q_{\text{k}}} + {q_{\text{z}}} + {q_{\text{m}}} = {q_{\text{4}}} + {q_{\text{5}}} $$ (8) $$ \frac{{{q_{\text{k}}}k}}{2} + {q_{\text{m}}}\left(\frac{m}{2} + k\right) + {q_{\text{z}}}\left(k + m + \frac{{\textit{z}}}{3}\right) = \frac{{2{q_4}\left(k + m + {\textit{z}}\right)}}{3} + \frac{{{q_5}k}}{2} $$ (9) 联立式(5)、式(8)和式(9)得:
$$ {q_{\mathrm{k}}} = q_{\mathrm{B}} - \frac{{{q_{\mathrm{m}}}(3m + 2{\textit{z}}) + {q_4}(k + 4m + 4{\textit{z}})}}{{3k + 6m + 2{\textit{z}}}} $$ (10) 其中:
$$ q = bL\gamma H $$ (11) $$ {q_{\text{m}}} = bmd\gamma $$ (12) $$ \theta = \arcsin \frac{{M - ({K_{\mathrm{p}}} - 1)d}}{L} $$ (13) $$ a = \frac{{r - L\sin \theta }}{2} $$ (14) 联立式(7)和式(10),代入赵固二矿相关参数进行计算得到,当空巷支护强度超过4.6 MPa时,可以防止关键块B发生滑落失稳,避免工作面发生大面积顶板垮落。
3 工作面过空巷顶板破断应力场时空演化规律
3.1 数值模型建立
结合赵固二矿二盘区外侧煤柱工作面实际情况,建立三维数值模型(图5),二盘区外侧煤柱工作面两侧建立采空区,由于其余空巷和工作面相互位置关系基本相同,因此为了简化计算,模型只建立12021工作面运输巷和二盘区六横贯进行分析。为了模型计算更加快捷,对模型各岩层厚度进行折减(对岩层厚度小数部分进行四舍五入),模型长×宽×高=290 m×380 m×78 m,工作面宽度260 m,空巷宽×高=5 m×4 m,建立六横贯时取平均距离,距开切眼50 m,12021工作面运输巷距开切眼70 m。由于工作面平均埋深为660 m,根据覆岩高度与模型高度的关系,在模型顶部施加16.5 MPa的应力边界模拟覆岩自重,模型两边固定水平位移,底边固定垂直位移,岩层物理力学参数见表1。模型共划分499 380个单元和521 385节点,模型采用Mohr-Coulomb模型屈服准则进行计算分析。
表 1 模型岩层及物理力学参数Table 1. Physico-mechanical parameters and rock layers in the model层号 岩层名称 厚度/m 密度/(kg·m−3) 体积模量/GPa 剪切模量/GPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa 1 砂质泥岩 11 2510 14.1 8.5 4.30 33 3.5 2 泥岩 2 2420 9.8 7.1 2.70 31 1.8 3 中粒砂岩 1 2580 12.3 6.1 8.50 35 1.7 4 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.4 9.0 4.20 35 3.5 5 中粒砂岩 3 2580 12.5 6.1 8.30 36 1.6 6 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.6 9.1 4.12 34 3.2 7 细粒砂岩 3 2800 18.3 9.3 6.50 30 2.3 8 砂质泥岩 9 2510 13.2 8.6 4.40 35 3.3 9 细粒砂岩 2 2800 18.3 9.3 6.50 30 2.3 10 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.2 8.6 4.40 35 3.3 11 粉砂岩 2 2640 18.0 10.2 6.00 30 2.1 12 砂质泥岩 14 2510 13.5 9.3 4.15 34 3.1 13 二1煤 6 1500 7.5 3.8 1.60 27 1.3 14 砂质泥岩 7 2510 13.2 9.0 4.12 35 3.0 结合矿井实际情况对空巷采取“锚网索”加强支护,将围岩与稳定的岩体相结合在一起,从而产生悬吊效果、组合梁效果以及补强效果。在工作面过空巷过程中,防止空巷产生顶板下沉量过大而导致工作面无法正常推进等问题。
在FLAC3D数值模拟云图中,拉为正、压为负是传统材料力学中的应力状态定义,正应力表示拉伸状态,负应力表示压缩状态,可以直观地判断材料在不同受力状态下的力学行为。为了研究空巷支护强度对工作面过空巷时覆岩运动的影响,通过数值模拟对不同支护方案下空巷围岩应力场时空演化规律进行分析,结合理论计算结果,为工业性试验提供理论依据。
3.2 无支护条件下覆岩应力演化规律
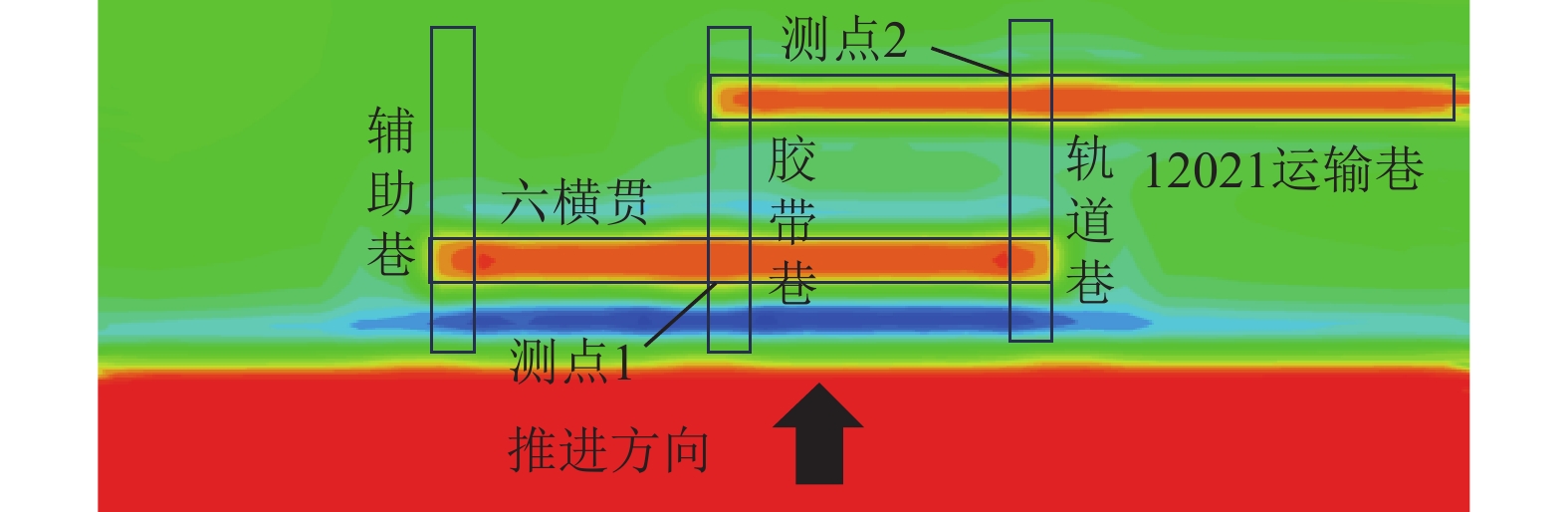
在六横贯和12021运输巷无支护的条件下,工作面推进过程中空巷围岩应力分布如图6所示。
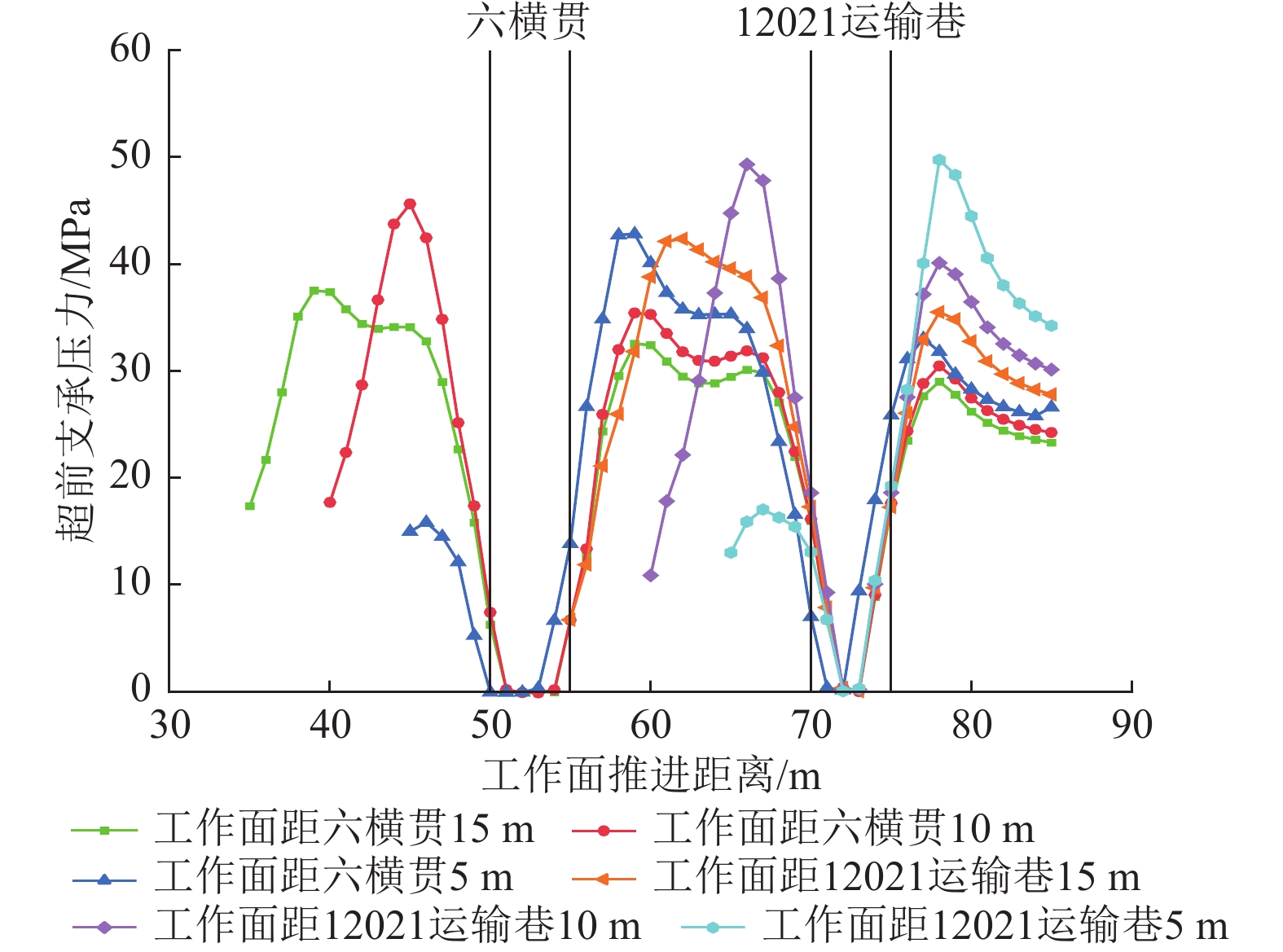
从图6可以看出,当工作面推进至距六横贯15 m时,工作面采动产生的超前支承压力与六横贯开挖产生的应力集中开始逐渐汇聚,应力重新分布并相互叠加,煤柱承受载荷增大,在煤柱上方形成“双峰型”应力分布。当工作面距六横贯10 m时,煤柱上方应力特征呈现“孤峰型”分布,这是由于工作面超前支承压力和空巷围岩应力汇聚叠加而产生的结果,此时,煤柱内应力接近煤柱极限强度。随着工作面继续推进,超前支承压力向前方移动,在工作面距六横贯5 m时(图6c),工作面与六横贯之间煤柱应力集中消失,并且工作面与空巷上方应力分布互相连接,表明煤柱内应力超过煤柱极限强度,应力集中转移至六横贯后方,煤柱发生失稳破坏,承载能力急剧下降,从而导致工作面上方基本顶发生超前破断。当工作面继续向前方推进,靠近12021运输巷围岩应力与工作面靠近六横贯时分布特征相似,在工作面距12021运输巷5 m时,煤柱发生失稳,应力集中向空巷后方转移,此时,工作面和空巷顶板发生来压,需采取相应措施防止工作面产生片帮和顶板垮落。
工作面推进过程中,煤层顶板超前支承压力监测结果如图7所示。由图7可知,最大采动超前支承压力分布在工作面前方5 m左右。随着工作面与空巷距离的减小,超前支承压力与空巷开挖的应力集中相互叠加接连呈现“平台型”与“孤峰型”分布特征,应力集中逐渐由工作面与空巷之间煤柱转移至空巷后方。当工作面推进至距六横贯15 m时,此时煤柱超前支承压力峰值为37.53 MPa,应力集中系数达到1.97。工作面距六横贯10 m时,超前支承压力峰值达到45.63 MPa,应力集中系数为2.40。工作面距六横贯5 m时,煤柱超前支承压力峰值为16.7 MPa,应力集中系数为0.87。当工作面通过12021运输巷时,覆岩应力演化规律与工作面过六横贯时相似。从图7可以看出,工作面与空巷距离15 m时,煤柱上方垂直应力呈现不对称 “双峰型”分布,这是由于工作面采动空间与空巷开挖宽度存在巨大差距,煤柱承载载荷不均匀,从而导致采动超前支承压力高于空巷开挖产生的应力集中。工作面与空巷距离在15~10 m时,煤柱两侧应力集中逐渐汇聚,应力特征表现为“孤峰型”分布,此时,煤柱承载载荷接近极限。工作面与空巷距离在10 m与5 m时,由于煤柱宽度减小,承载载荷增大,煤柱逐渐产生变形失稳,煤柱强度急剧降低,此时图中曲线在煤柱上方应力集中程度存在显著差别,但此时煤柱尚且存在一部分承载能力。在工作面推进过程中,煤柱与实体煤上方垂直应力始终在距空巷5 m范围发生急剧下降,表明空巷塑性破坏影响范围为5 m。
3.3 不同支护强度下覆岩应力演化规律
随着工作面推进,由于工作面开采引起的超前支承压力与空巷开挖产生的应力集中相互叠加,空巷围岩承受载荷逐渐加剧,煤柱中积聚能量越来越高,煤柱逐渐达到极限强度发生失稳破坏从而导致基本顶超前破断,容易对工作面人员和设备造成不利影响。
通过数值模拟对空巷顶板增设不同支护强度的锚杆与锚索,对比分析工作面过空巷过程中覆岩应力演化规律如图8所示。当支护强度为0、1以及3 MPa时,超前支承压力无明显变化,支护效果不明显。当支护强度为5 MPa时,空巷顶板垂直应力发生显著变化,煤柱上方超前支承压力相较支护强度为3 MPa,最高下降1.3 MPa,对空巷支撑能力明显提高。继续提高支护强度,由于锚索对顶板产生的悬吊作用显著,空巷顶板处产生压力积聚现象,超前支承压力下降幅度不明显。从应力分布特征方面看,空巷顶板支护强度接近5 MPa最为合适。
由上述分析可知,采动超前支承压力峰值在工作面前方5 m左右,当工作面推进至距空巷10 m时,采动超前支承压力与空巷开挖应力集中相互叠加,煤柱承受载荷增大。当工作面推进至距空巷10 m时,在不同支护强度下,提取工作面方向空巷前方5 m处煤柱垂直应力,研究工作面方向煤柱承受载荷分布特征,如图9所示。
由图9可知,随着支护强度的提高,煤柱超前支承压力减小,但是由于此矿区煤层松软,当上覆岩层产生的压力达到一定程度后,煤体产生塑性破坏,减小自身承载载荷,在不同支护强度下,超前支承压力总体上相差较小。在工作面前方存在空巷区域和不存在空巷区域两种条件下,煤柱超前支承压力差异显著。如图9a所示,工作面前方存在空巷时,煤柱最大超前支承压力达到50.16 MPa,应力集中系数为2.62。工作面前方不存在空巷时,最大超前支承压力达到37.32 MPa,应力集中系数为1.95。两者之间差异主要是由于空巷开挖产生的应力重新分布,在煤柱上方形成应力集中,与采动超前支承压力相互叠加而造成煤柱承受载荷明显增大。如图9b所示,同样呈现超前支承压力自轨道巷和辅助巷向两侧逐渐递减,也是由于大巷开挖产生的应力集中分布在大巷两侧,向深处逐渐减小,与采动超前支承压力叠加造成的结果。由于开挖宽度远远小于工作面采动空间,因此,巷道开挖产生的围岩应力集中对煤柱承受载荷整体变化趋势影响较小。
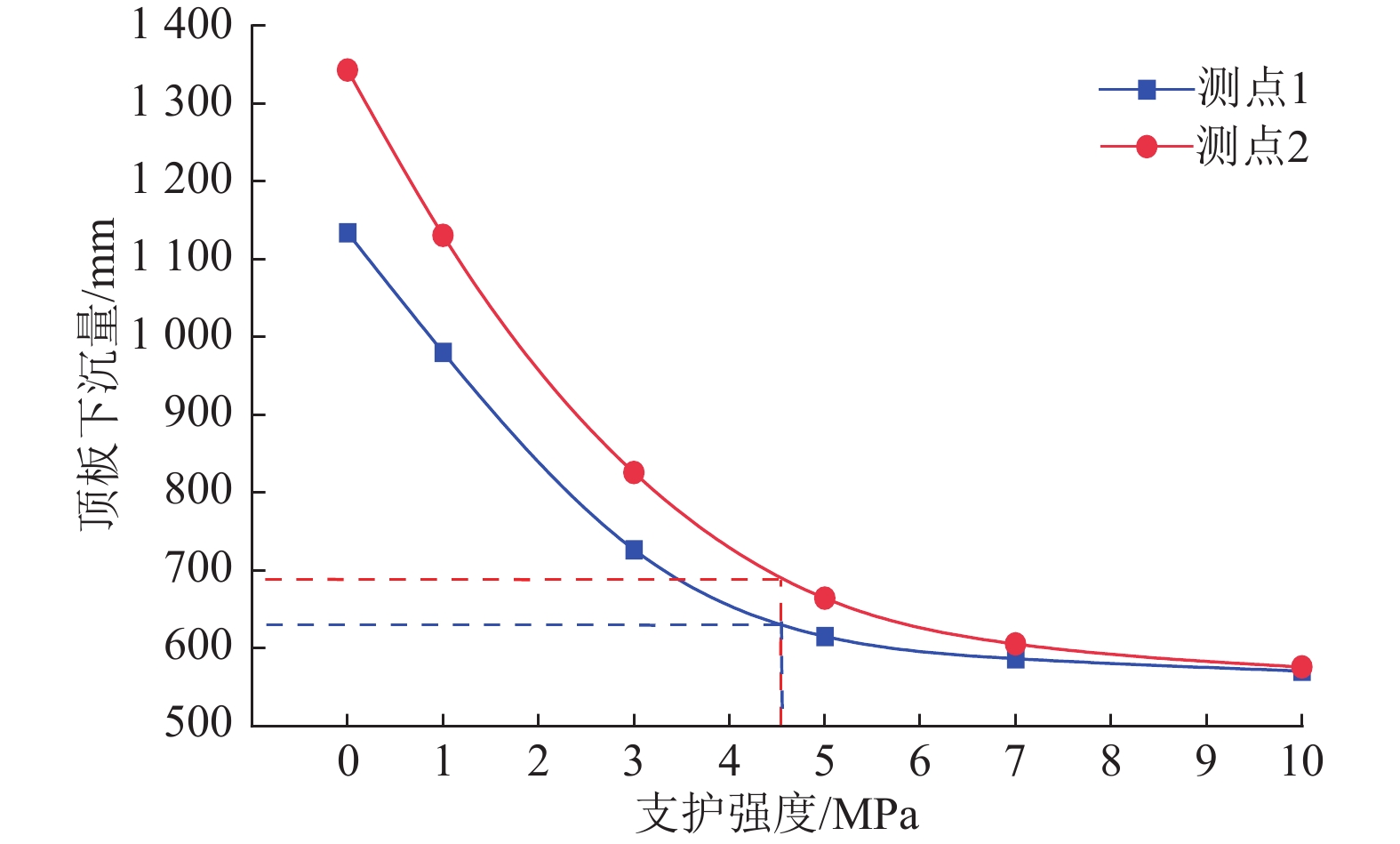
在大巷与六横贯交叉处布置两处测点监测巷道顶板下沉量(图10)。提取巷道垂直位移模拟结果并通过拟合得到顶板下沉量和支护强度的关系,如图11所示。
依据图11的拟合曲线分析,在支护强度为0~3 MPa时,巷道顶板下沉幅度较大且变化速率显著,表明在此强度下,锚索难以有效控制顶板沉降,覆岩运动较为剧烈。当支护强度达到3.0~4.5 MPa时,下沉变化速率显著降低,位移趋于平缓,表明此时覆岩平衡结构逐渐稳定,岩层运动得到有效控制。当支护强度进一步增加至4.5~10.0 MPa时,顶板下沉基本稳定,说明顶板下沉得到控制,但由于较大支护强度对顶板产生过度悬吊作用,导致顶板易发生破碎。因此,当巷道支护强度达到4.5 MPa时,锚索对巷道顶板的支护效果最为显著。
综合应力分布特征以及顶板位移变化规律可得,当空巷顶板支护强度达到4.5 MPa时,锚索对顶板支撑效果最佳,可防止顶板突然发生垮落。
4 工业性试验
二盘区外侧煤柱工作面推进过程中经过的空巷原有支护方式为锚网索梁+36U钢棚+喷浆+注浆联合支护,顶板支护参数如图12所示,支护强度达到3.16 MPa。
为保证工作面生产安全,现场施工预留一定支护强度,结合理论分析和数值模拟研究结果,针对空巷顶板进行“锚网索”补强支护后,经计算空巷顶板支护强度达到4.68 MPa,空巷加强支护要求如下。
针对空巷进行超前回收钢棚棚腿、底拱施工,为确保施工过程中人员安全,考虑到经济因素和技术条件限制,对空巷进行“锚网索”补强支护,防止回收钢棚棚腿造成顶板突然垮落,巷道支护方案情况如图13所示。针对顶板打设3排槽钢梁锚索进行加强支护,锚索规格为ø21.6 mm×8 250 mm;排间距为1 000 mm×(1 300~1 800) mm,托盘为
2400 mm长的16号槽钢梁与尺寸为12 mm×120 mm×120 mm(12 mm×80 mm×80 mm)钢板配合使用,锚索锚固长度不小于2 000 mm,锚索破断力取504 kN,锚索预紧力张拉泵压力表读数不小于49.5 MPa。工作面推进过程中,空巷交叉点巷道围岩难以控制,为加强工作面回采期间顶板管理,在工作面回采前对二盘区3条大巷及横贯交叉口进行注浆加固,巷道顶板中部打设长
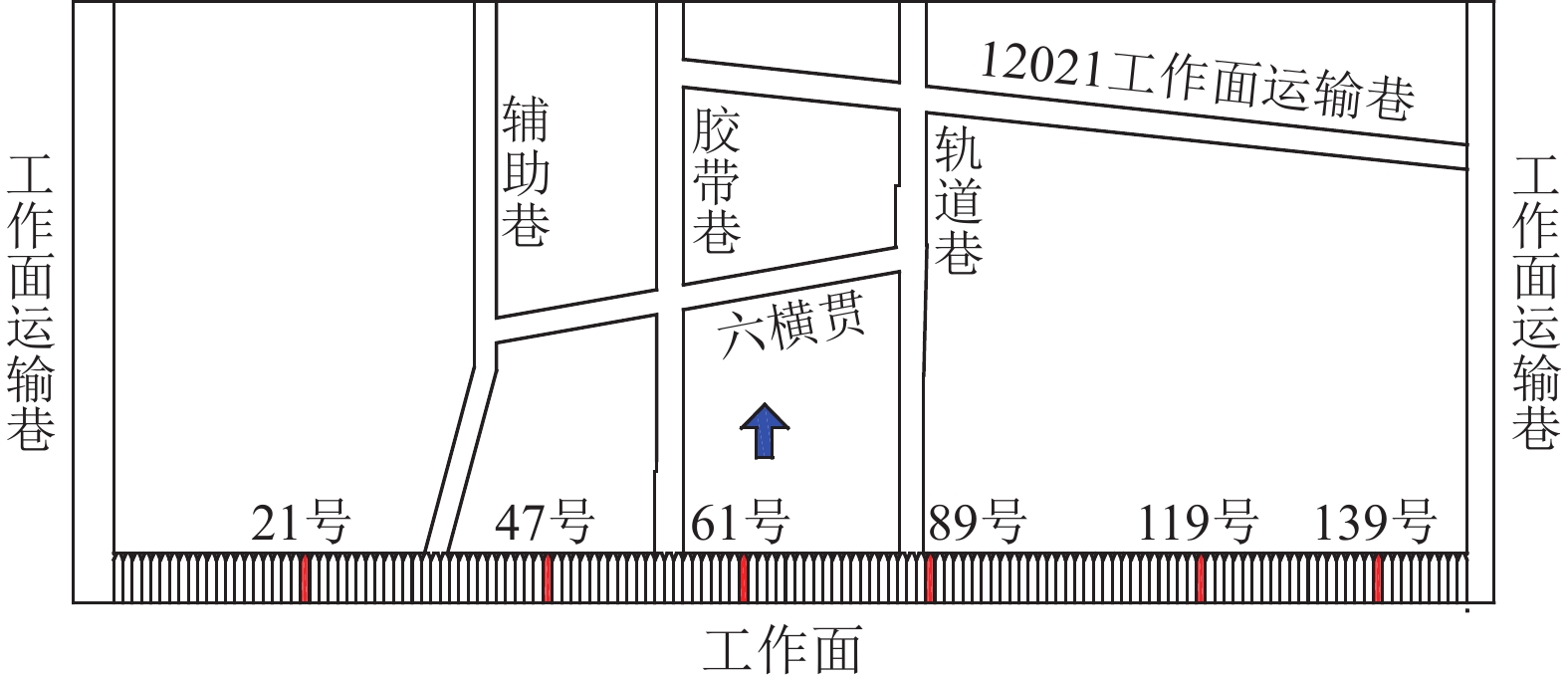
2400 mm的16号槽钢梁,中间孔打设ø22 mm×8 300 mm注浆锚索。大巷与横贯交叉口5 m范围内两侧肩部施工注浆孔。巷道顶板变形量较大区域可适当减小注浆孔间距,同时可根据注浆效果复注,保证工作面安全通过空巷。选取工作面21、47、61、89、119、139号液压支架,分析工作面矿压显现特征,支架位置如图14所示。液压支架工作阻力如图15所示,反映了工作面矿压显现规律。
在工作面频繁经过空巷时,支架高阻力持续运行阶段出现时间较短,一方面主要由于空巷之间煤柱宽度较大,超过极限承载宽度,煤柱对基本顶形成较大的支撑能力,有效缓解了工作面支架承载压力。另一方面当工作面部分区域支架出现高阻力运行时,工作面立即采取相关措施降低支架压力,主要通过加快采煤速度快速通过高压区域,降低支架高度,释放覆岩中积聚的能量,保证工作面安全生产。
由于现场试验区域空巷与工作面之间存在一定倾斜角度,现场实际推进过程中针对工作面会进行调斜。由图15分析可知,当工作面推进至40~53 m时,工作面中部首先通过六横贯,工作面整体发生来压现象,表明基本顶此时达到极限弯矩,导致关键块发生超前破断。当工作面推进至72~87 m时,工作面通过12021运输巷,顶板悬露长度增大,煤柱承载载荷转移至工作面,支架发生来压。整体来看,工作面靠近空巷以及通过空巷过程中,支架工作阻力有一定程度的提升,但整体表现平和,工作面没有发生顶板垮落和压架事故,支架压力处于安全范围,表明锚网索支护在工作面通过空巷期间有效控制了上覆岩层运动。
5 结 论
(1) 基于砌体梁理论,建立了工作面过空巷基本顶破断力学模型,发现关键块B是导致空巷和工作面来压的主要因素。根据基本顶破断位置对工作面来压影响程度,将断裂线位置分为3种类型,即位于煤柱上方、空巷上方以及实体煤上方。研究表明,当空巷顶板支护强度超过4.6 MPa时,可以防止基本顶发生滑落失稳,为现场工程提供了理论支撑。
(2) 在数值模拟实验中,随着煤柱宽度的逐渐减小,煤柱垂直应力由“双峰型”逐渐过渡为“孤峰形”,煤柱宽度减小至5 m时发生失稳,导致工作面来压。在空巷区域和无空巷区域,工作面前方煤柱应力分布特征差异显著,当空巷支护强度达到4.5 MPa时,锚杆索对顶板支撑效果最佳,为基本顶破断结构演化及力学响应反演提供有力支撑。
(3) 现场工作面液压支架工作阻力处于安全范围内,工作面未发生顶板垮落和压架事故,在空巷顶板锚网索支护下,覆岩运动得到了有效控制。
(4) 本次研究仅分析了基本顶破断对支护系统的影响。由于实际工程存在破断角、悬顶距等多种因素的影响,造成不同程度的应力水平差异。因此,后续应对工作面过空巷影响因素以及权重做进一步深入研究。
符号注释:
a为关键块之间的接触高度,m;b为支架宽度,m;d为直接顶厚度,m;f为岩块间的摩擦因数,一般取0.2;H为基本顶与上方关键层之间的覆岩厚度(图1中5.97 m厚的砂质泥岩与3.29 m厚的中粒砂岩之间的覆岩厚度),m;Kp为碎胀系数;k为空巷宽度,m;L为周期来压步距,m;m为煤柱宽度,m;M为煤层厚度,m;M0、M1为与工作面煤壁位置所对应的弹性地基梁的弯矩,kN·m;q1为梁的上部载荷,kN;q2为已经断裂的岩块对梁的挤压力,kN;q3为已经断裂的岩块对梁的支撑力,kN;q4为直接顶单位载荷,MPa;q5为关键块A对关键块B的垂直作用力,MPa;qa为关键块A对关键块B的水平作用力,MPa;qB为关键块B自重及所受载荷,MPa;qc为关键块C对关键块B的水平作用力,MPa;qk为空巷支护阻力,MPa;qm为煤柱支护强度,MPa;qz为工作面支护阻力,MPa;r为基本顶厚度,m;s为断裂面面积,m2;x为基本顶断裂位置距煤壁水平距离,m;z为控顶距,m;α、β为不同垫层系数,m−2、m−1;θ为关键块B的旋转角,(°);γ为岩层容重,kN/m3。
-
表 1 模型岩层及物理力学参数
Table 1 Physico-mechanical parameters and rock layers in the model
层号 岩层名称 厚度/m 密度/(kg·m−3) 体积模量/GPa 剪切模量/GPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa 1 砂质泥岩 11 2510 14.1 8.5 4.30 33 3.5 2 泥岩 2 2420 9.8 7.1 2.70 31 1.8 3 中粒砂岩 1 2580 12.3 6.1 8.50 35 1.7 4 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.4 9.0 4.20 35 3.5 5 中粒砂岩 3 2580 12.5 6.1 8.30 36 1.6 6 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.6 9.1 4.12 34 3.2 7 细粒砂岩 3 2800 18.3 9.3 6.50 30 2.3 8 砂质泥岩 9 2510 13.2 8.6 4.40 35 3.3 9 细粒砂岩 2 2800 18.3 9.3 6.50 30 2.3 10 砂质泥岩 6 2510 13.2 8.6 4.40 35 3.3 11 粉砂岩 2 2640 18.0 10.2 6.00 30 2.1 12 砂质泥岩 14 2510 13.5 9.3 4.15 34 3.1 13 二1煤 6 1500 7.5 3.8 1.60 27 1.3 14 砂质泥岩 7 2510 13.2 9.0 4.12 35 3.0 -
[1] 张文杰,何满潮,王炯,等. 逆断层影响下无煤柱自成巷矿压规律及围岩控制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(5):1−10. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.11.0850 ZHANG Wenjie,HE Manchao,WANG Jiong,et al. Application of pillar-free self-formed roadway technology under the influence of reserse faults:Strata behavior law and surrounding rock control[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(5):1−10. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.11.0850
[2] 孟巧荣,王慧娴,王朋飞,等. 深埋倾斜特厚煤层窄煤柱护巷机理与围岩控制[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(3):38−52. MENG Qiaorong,WANG Huixian,WANG Pengfei,et al. Gateroad protection mechanism and surrounding rock control for gob-side entry with slender pillar in deep and inclined extra-thick coal seams[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(3):38−52.
[3] 彭林军,吴家遥,何满潮,等. 深部特厚煤层综放沿空掘巷煤柱优化及巷道支护[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2024,44(3):563−574. PENG Linjun,WU Jiayao,HE Manchao,et al. Optimization of coal pillar and tunnel support for fully mechanized caving along gob in deep and extra thick coal seams[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2024,44(3):563−574.
[4] 刘江斌,刘晓刚,刘茂福,等. 榆神矿区多层厚硬顶板强矿压显现及覆岩破断运动规律研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2024,50(4):46−56. LIU Jiangbin,LIU Xiaogang,LIU Maofu,et al. Study on strong mine pressure behavior and overburden fracture movement law of multi-layer thick and hard roof in Yushen mining area[J]. China Coal,2024,50(4):46−56.
[5] 尹超宇,冯光明,高鹏,等. 工作面过空巷围岩失稳机理研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(3):457−464. YIN Chaoyu,FENG Guangming,GAO Peng,et al. Research on instability mechanism of surrounding rock in stage of working face passing abandoned roadway[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2018,35(3):457−464.
[6] 陈志维,张彦董. 窄煤柱沿空掘巷围岩稳定协同控制技术研究与应用[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2023,50(1):65−70. CHEN Zhiwei,ZHANG Yandong. Research and application of coordinated control technology for surrounding rock stability of gob-side entry driving with narrow coal pillar[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2023,50(1):65−70.
[7] 许家林,鞠金峰. 特大采高综采面关键层结构形态及其对矿压显现的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(8):1547−1556. XU Jialin,JU Jinfeng. Structural morphology of key stratum and its influence on strata behaviors in fully-mechanized face with super-large mining height[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(8):1547−1556.
[8] 徐青云,宁掌玄,朱润生,等. 综放工作面充填过空巷顶板失稳机理及控顶研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(3):505−512. XU Qingyun,NING Zhangxuan,ZHU Runsheng,et al. Study on instability mechanism and top control of overfilled roof in fully mechanized caving face[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2019,36(3):505−512.
[9] 刘畅,张俊文,杨增强,等. 工作面过空巷基本顶超前破断机制及控制技术[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(4):1411−1421. LIU Chang,ZHANG Junwen,YANG Zengqiang,et al. Mechanism of advance fracture of main roof and its control technology when workface crossing abandoned roadway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(4):1411−1421.
[10] 刘畅,杨增强,弓培林,等. 工作面过空巷基本顶超前破断压架机理及控制技术研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(8):1932−1940. LIU Chang,YANG Zengqiang,GONG Peilin,et al. Mechanism and control technology of supports crushing induced by main roof’s breaking ahead of workface when crossing abandoned roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(8):1932−1940.
[11] 刘畅,弓培林,王开,等. 复采工作面过空巷顶板稳定性[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(2):314−322. LIU Chang,GONG Peilin,WANG Kai,et al. Roof stability for repeated mining workface passing through abandoned parallel gateway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(2):314−322.
[12] 赵文光,解振华. 基于3DEC的过空巷群采动来压突显特征模拟研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(增刊1):54−58. ZHAO Wenguang,XIE Zhenhua. Simulation study on the salient characteristics of mining-induced pressure in goaf group based on 3DEC[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(Sup.1):54−58.
[13] 谢生荣,李世俊,魏臻,等. 综放工作面过空巷时支架−围岩稳定性控制[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(3):502−508. XIE Shengrong,LI Shijun,WEI Zhen,et al. Stability control of support-surrounding rock system during fully mechanized caving face crossing abandoned roadway period[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(3):502−508.
[14] 周海丰,黄庆享. 大采高工作面过空巷群顶板破断及矿压规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(2):70−79. ZHOU Haifeng,HUANG Qingxiang. Study on the law of roof breakage and mine pressure passing large cross-section gob group in the fully-mechanized face with high mining height[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(2):70−79.
[15] 高海滨,侯可可,王兆其,等. 极近距离煤层采空区下沿空留巷技术研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2024,50(4):68−78. GAO Haibin,HOU Keke,WANG Zhaoqi,et al. Research on technology of gob-side entry retaining under goaf in extremely close distance coal seam[J]. China Coal,2024,50(4):68−78.
[16] 王军,解振华. 浅埋工作面过空巷煤基混凝土墩柱支护研究与应用[J]. 中国煤炭,2023,49(增刊2):226−232. WANG Jun. Research and application of coal-based concrete pier column support in shallow-buried mining face[J]. China Coal,2023,49(Sup.2):226−232.
[17] 段计伟. 窄煤柱沿空掘巷非对称支护力学特征与支护参数研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2024,51(1):147−153. DUAN Jiwei. Study on mechanical characteristics and supporting parameters of asymmetric support in gob-side entry driving with narrow coal pillar[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2024,51(1):147−153.
[18] 谢学斌,李德玄,孔令燕. 基于弹性薄板理论的矿壁稳定性分析模型及应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(4):698−706. XIE Xuebin,LI Dexuan,KONG Lingyan. Stability analysis model of ore wall based on elastic thin plate theory and its application[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(4):698−706.
[19] 邵春瑞,李俊清,赵宝友. 综放工作面过密集空巷群高水充填技术研究及应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(6):57−63. SHAO Chunrui,LI Junqing,ZHAO Baoyou. High water filling technology for fully mechanized top-coal caving face crossing close-set abandoned roadway groups[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(6):57−63.
[20] 钱鸣高,许家林. 煤炭工业发展面临几个问题的讨论[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2006,23(2):127−132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2006.02.001 QIAN Minggao,XU Jialin. Discussion of several issues concerning the development of coal industry in China[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2006,23(2):127−132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2006.02.001
[21] 冯强,刘炜炜,伏圣岗,等. 基于弹性地基梁采场坚硬顶板变形与内力的解析计算[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2017,34(2):342−347. FENG Qiang,LIU Weiwei,FU Shenggang,et al. Analytical solution for deformation and internal force of hard roof in stope based on elastic foundation beam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2017,34(2):342−347.
[22] 刘雨涛,李其振,王鹏伟. 高瓦斯突出煤层原位充填沿空留巷技术研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2020,47(1):45−50. LIU Yutao,LI Qizhen,WANG Pengwei. Study on gob-side entry retaining technology of in situ filling in high gassy outburst coal seam[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2020,47(1):45−50.
[23] 刘迅. 沿空巷道侧采空区上方基本顶断裂位置研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2017,44(5):40−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2017.05.010 LIU Xun. Study on fracture position of main roof above gob-side entry[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2017,44(5):40−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2017.05.010
[24] 钱鸣高,石平五,许家林. 矿山压力与岩层控制[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2010. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王栋晨,孙华清,冯伟斌,王代峰,秦艳华,陈井龙,吕金龙,李然,曹峰. 综放工作面过空巷超前支护技术研究与应用. 中国煤炭. 2025(01): 132-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 问永忠,贾澎涛,杨鸿宇,张龙刚. 基于TCN-GRU-DAB模型的工作面矿压智能预测研究. 中国煤炭. 2025(02): 102-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王军. 松软厚煤层孤岛工作面回采巷道支护技术研究. 陕西煤炭. 2024(12): 118-121+137 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)








 下载:
下载: