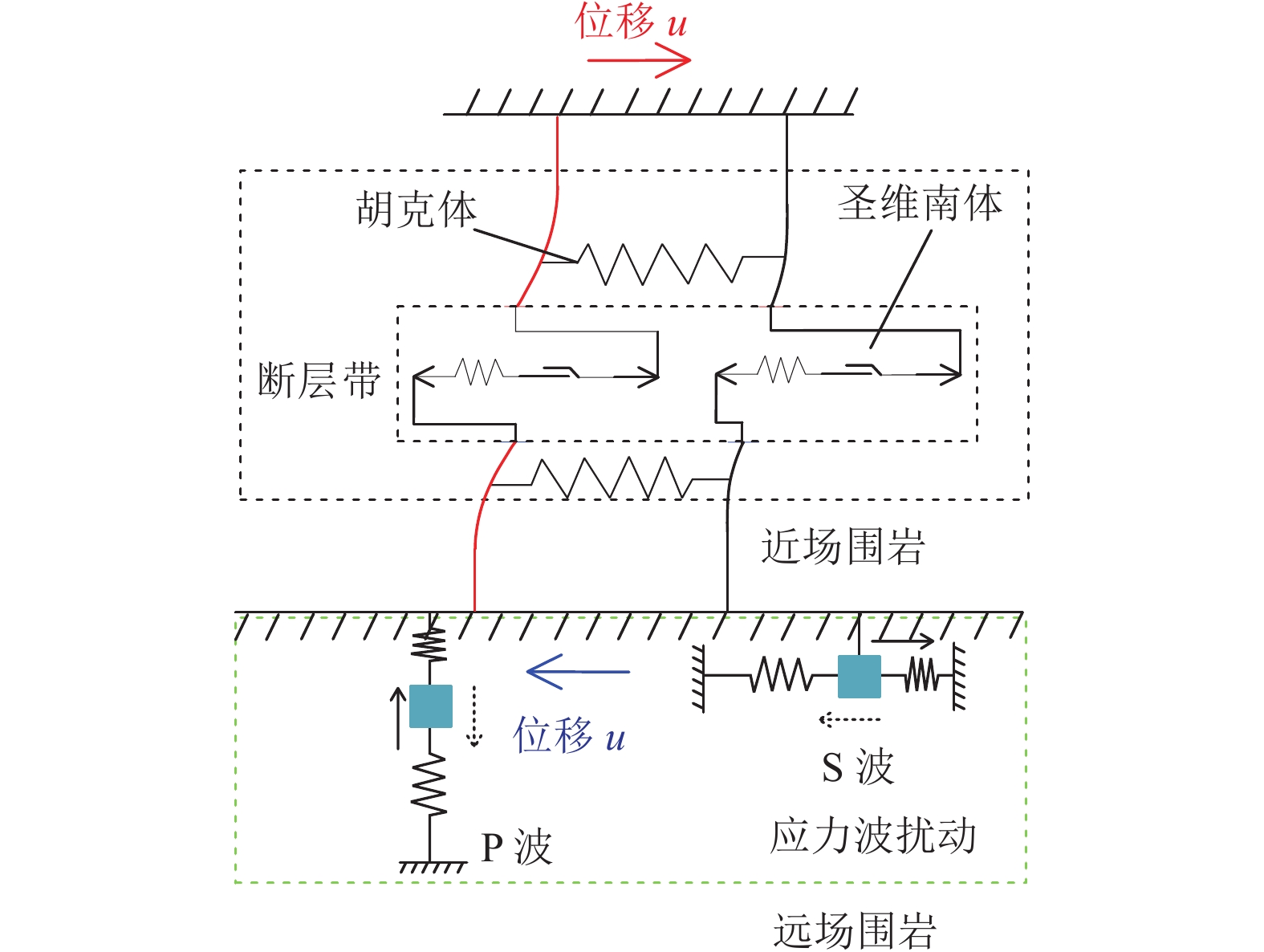
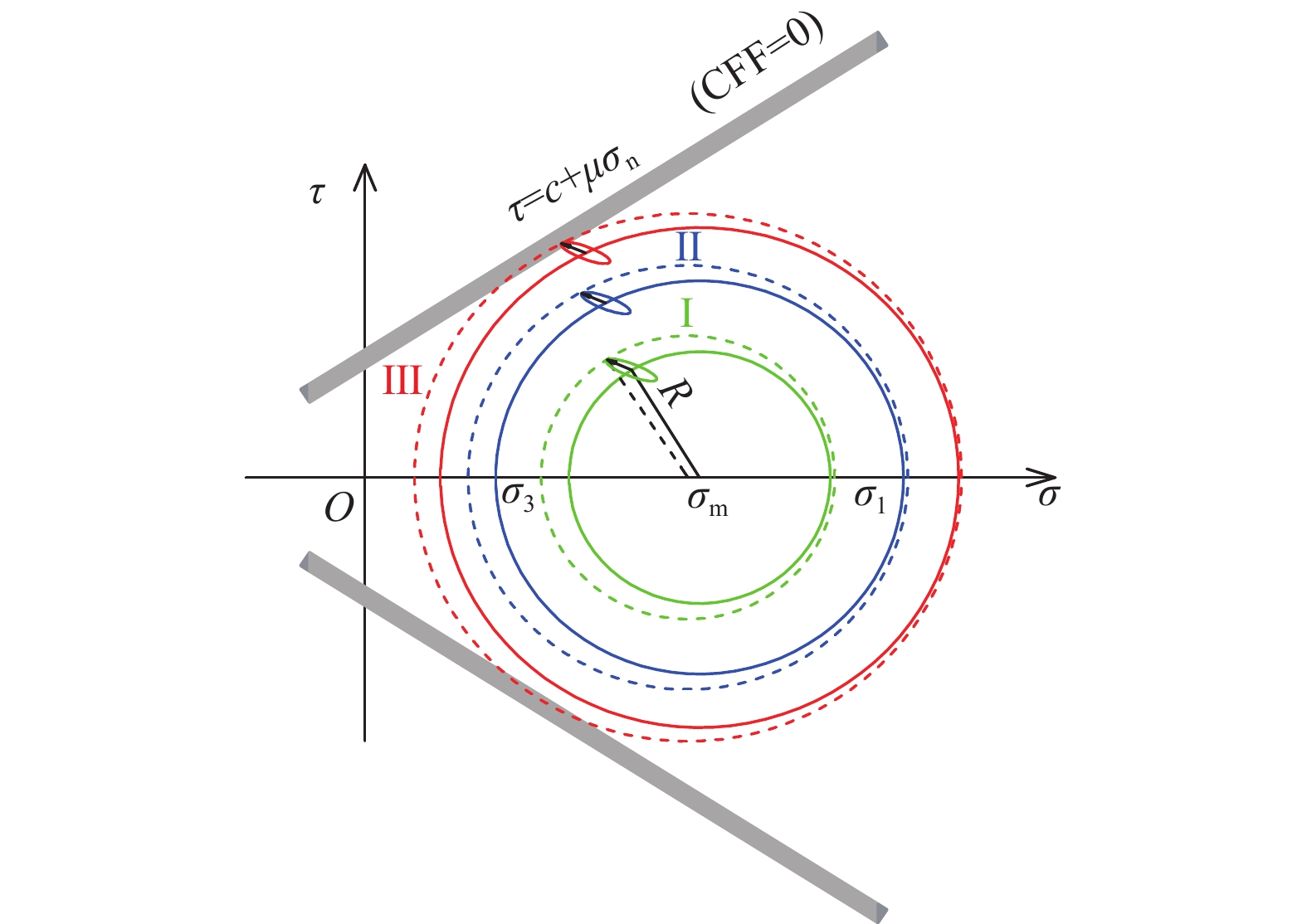
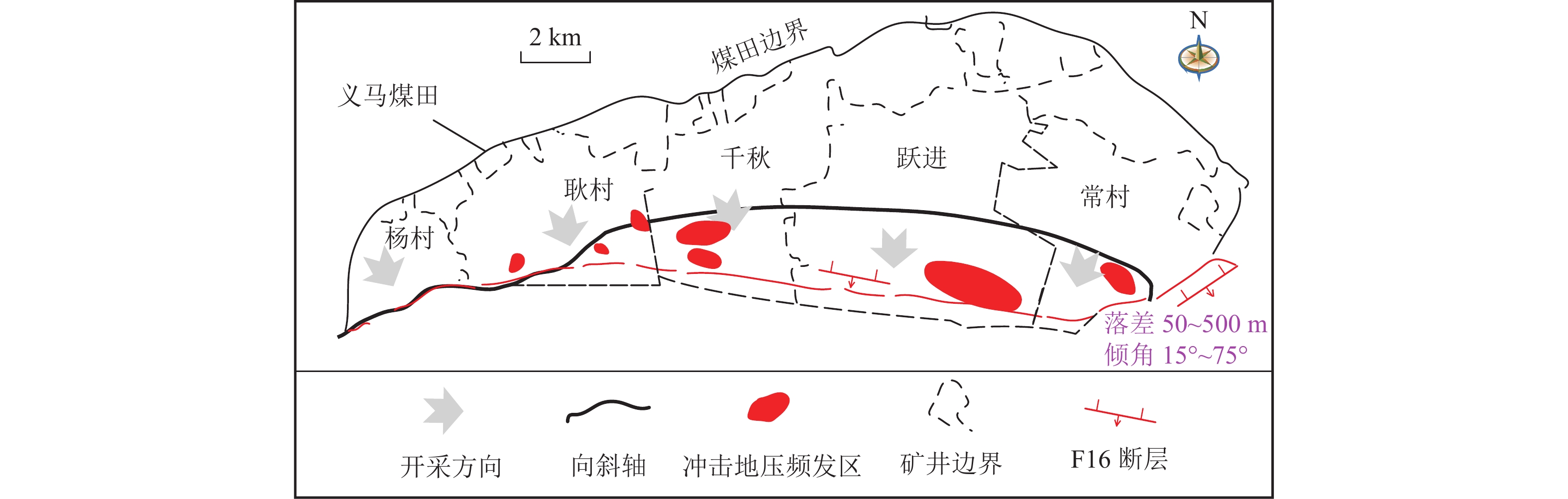
Mechanism of thrust fault slip under the disturbance of stress waves induced by coal mining
-
摘要:目的
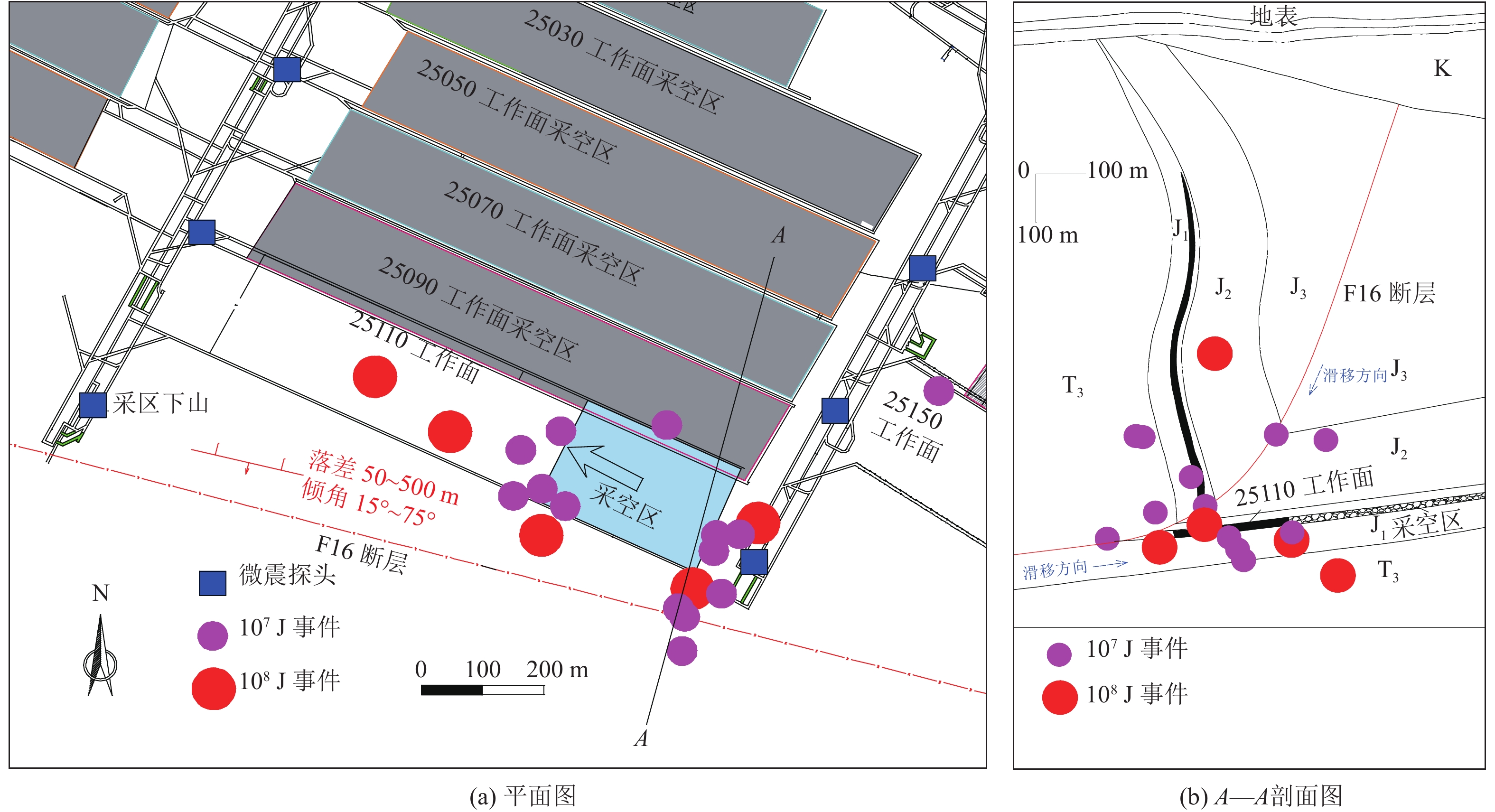
煤矿开采中,人工爆破、顶板垮断等震源激发应力波易诱发断层失稳并导致冲击地压等灾害。
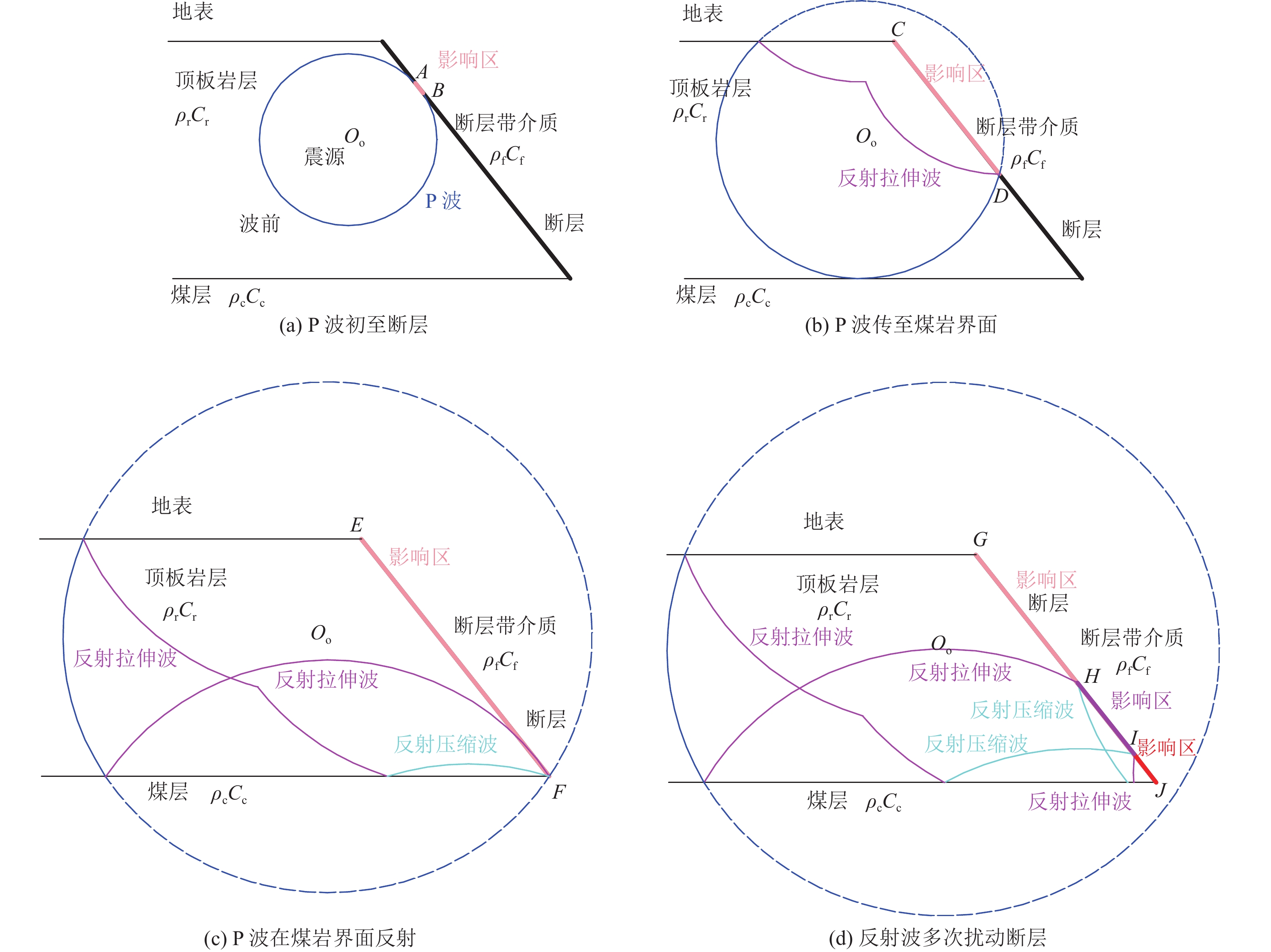
方法以河南义马矿区F16逆冲断层为研究对象,通过开展断层动光弹实验、数值模拟实验和理论分析,对应力波在断裂结构中的传播规律和应力波作用下断层摩擦能演化特征进行了研究,探讨了震源位置及能量对逆冲断层滑移的扰动规律,阐释了应力波扰动下逆冲断层失稳机理和失稳类型。
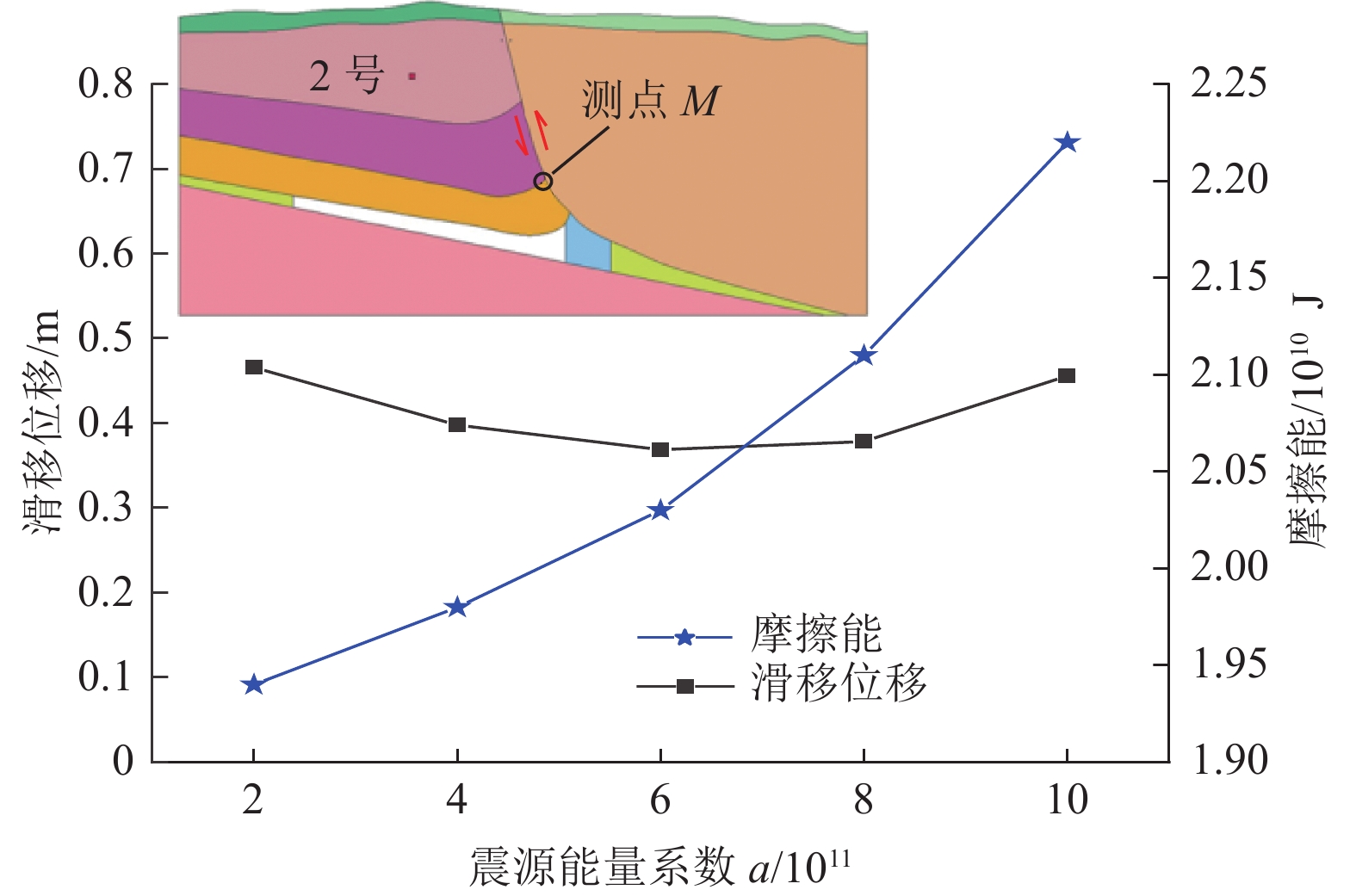
结果和结论研究结果表明:(1)应力波传播会被断层阻隔,并造成断层活化加剧、摩擦能迅速增大。(2)震源应力波能量增大可加强断层自锁效应,当能量超过一定阈值时断层才会解锁。(3)应力波自上至下分区扰动断层并造成断层滑移,其滑移模式受初始应力状态和应力波扰动强度影响。(4)初始高水平静载和强应力波扰动是断层失稳的必要条件。研究成果对断层型灾害防控技术发展具有重要的指导意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveThe seismic sources, such as roof collapse and artificial blasting, in coal mining may induce stress waves, which will cause the surrounding faults lose its stability and thus cause the dynamic disasters such as rockbursts etc.
MethodsThe propagation law of stress waves in the fracture structure and the evolution characteristics of friction energy under the action of stress waves were studied through dynamic photoelastic experiment, numerical simulation and theoretical analysis based on the thrust fault F16 in Henan Yima mining area. Meanwhile, the disturbance law of the location of seismic source and energy to the slip of thrust fault was discussed, and the mechanism and type of thrust fault slip under the disturbance of stress waves were elaborated. [Results and Conclusions] The results show that: (1) The propagation of stress waves will be blocked by fault, which will lead to the intensification of fault activation and the rapid rise of friction energy. (2) The increase of source stress wave energy can strengthen the self-locking effect of fault, and the fault will be unblocked when the energy exceeds a certain threshold. (3) The stress waves will disturb the fault by area from top to bottom, thereby resulting in fault slip, and the slip model of a fault is influenced by its initial stress state and the disturbance intensity of stress waves. (4) High initial static stress and strong disturbance of stress waves are the necessary conditions for fault slips. Generally, the research results have important guiding significance for the development of fault disaster prevention and control technology.
-
Keywords:
- stress wave /
- thrust fault /
- photoelastic experiment /
- mechanical model /
- rock burst /
- coal mining
-
-
表 1 煤岩体物理力学性质
Table 1 Physical and mechanical properties of coal and rock mass
岩层分类 岩性组成 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 屈服应力/MPa 失效应变 表土层 黄土 1 830 20 0.40 5 0.90 中侏罗统岩层 砾岩、粉砂岩 2 600 26 0.15 35 0.90 晚侏罗统岩层 粗砾岩 2 600 42 0.20 52 0.90 2-3煤 煤 1 350 10 0.34 14 0.80 晚三叠统岩层 石英砂岩 2 700 48 0.20 67 0.90 表 2 断层界面性质
Table 2 Mechanical properties of fault interface
静摩擦
因数动摩擦
因数黏性摩擦
系数黏性阻尼
系数启动
时间/μs结束
时间/µs0.4 0.2 1.5×107 20 0 1.0×1020 表 3 JWL方程参数
Table 3 Parameters in JWL equation
a b R1 R2 ω E0/J 2.0×1011~
1.0×10126.710×104 4.5 1.1 0.35 8.0×106 表 4 数值模拟实验方案
Table 4 Numerical simulation scheme
因素分类 方案参数 震源位置 1号震源,煤层上方800 m 2号震源,煤层上方600 m 3号震源,煤层上方400 m 4号震源,煤层上方200 m 震源能量参数 a=2×1011 a=4×1011 a=6×1011 a=8×1011 a=1×1012 -
[1] CAI Wu,DOU Linming,LI Zhenlei,et al. Mechanical initiation and propagation mechanism of a thrust fault:A case study of the Yima section of the Xiashi-Yima thrust (north side of the Eastern Qinling Orogen,China)[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2015,48(5):1927−1945. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-014-0666-x
[2] 齐庆新,李一哲,赵善坤,等. 矿井群冲击地压发生机理与控制技术探讨[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):141−150. QI Qingxin,LI Yizhe,ZHAO Shankun,et al. Discussion on the mechanism and control of coal bump among mine group[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):141−150.
[3] 王宏伟,姜耀东,邓代新,等. 义马煤田复杂地质赋存条件下冲击地压诱因研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(增刊2):4085−4092. WANG Hongwei,JIANG Yaodong,DENG Daixin,et al. Investigation on the inducing factors of coal bursts under complicated geological environment in Yima mining area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017,36(Sup.2):4085−4092.
[4] 王浩,赵毅鑫,牟宗龙,等. 综放工作面采动诱发逆断层张剪失稳特征及矿震活动规律分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(10):2573−2581. WANG Hao,ZHAO Yixin,MU Zonglong,et al. Characteristics of seismic activity and tensile-slip features of fault under stress and displacement disturbance in full-mechanized workface[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(10):2573−2581.
[5] 王宏伟,王刚,张越,等. 动压影响下断层构造应力场和能量场分布特征[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(10):183−189. WANG Hongwei,WANG Gang,ZHANG Yue,et al. Stress field and energy field distribution characteristics of faults under dynamic pressure[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(10):183−189.
[6] 姜耀东,王涛,赵毅鑫,等. 采动影响下断层活化规律的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2013,42(1):1−5. JIANG Yaodong,WANG Tao,ZHAO Yixin,et al. Numerical simulation of fault activation pattern induced by coal extraction[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2013,42(1):1−5.
[7] 潘一山,王来贵,章梦涛,等. 断层冲击地压发生的理论与试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1998(6):642−649. PAN Yishan,WANG Laigui,ZHANG Mengtao,et al. The theoretical and testing study of fault rock burst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1998(6):642−649.
[8] 张宁博,欧阳振华,赵善坤,等. 基于粘滑理论的断层冲击地压发生机理研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2016,12(增刊2):894−898. ZHANG Ningbo,OUYANG Zhenhua,ZHAO Shankun,et al. Research on the occurrence mechanism of fault rock-burst based on the stick-slip theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2016,12(Sup.2):894−898.
[9] 张宁博,赵善坤,邓志刚,等. 动静载作用下逆冲断层力学失稳机制研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(6):1186−1192. ZHANG Ningbo,ZHAO Shankun,DENG Zhigang,et al. Mechanical instability mechanism of thrust fault under static and dynamic loading[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2019,36(6):1186−1192.
[10] 李振雷,窦林名,蔡武,等. 深部厚煤层断层煤柱型冲击矿压机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(2):333−342. LI Zhenlei,DOU Linming,CAI Wu,et al. Fault-pillar induced rock burst mechanism of thick coal seam in deep mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(2):333−342.
[11] 潘一山,王凯兴. 岩体间超低摩擦发生机理的摆型波理论[J]. 地震地质,2014,36(3):833−844. PAN Yishan,WANG Kaixing. Pendulum-type waves theory on the mechanism of anomalously low friction between rock masses[J]. Seismology and Geology,2014,36(3):833−844.
[12] 李利萍,李卫军,潘一山. 冲击扰动对超低摩擦型冲击地压影响分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(1):111−120. LI Liping,LI Weijun,PAN Yishan. Influence of impact disturbance on anomalously low friction rock bursts[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(1):111−120.
[13] 黄元敏,马胜利,缪阿丽,等. 正应力扰动对断层滑移失稳影响的实验研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(3):931−940. HUANG Yuanmin,MA Shengli,MIAO Ali,et al. Effect of normal stress perturbation on frictional instability:An experimental study[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(3):931−940.
[14] 黄元敏,马胜利,缪阿丽,等. 剪切载荷扰动对断层摩擦影响的实验研究[J]. 地震地质,2009,31(2):276−286. HUANG Yuanmin,MA Shengli,MIAO Ali,et al. Effect of shear loading perturbation on frictional behavior:An experimental study[J]. Seismology and Geology,2009,31(2):276−286.
[15] 张宁博,单仁亮,赵善坤,等. P波、S波扰动下逆冲断层卸载滑移实验研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(4):693−701. ZHANG Ningbo,SHAN Renliang,ZHAO Shankun,et al. Experiment study of thrust fault rupture with unloading effect under P-wave and S-wave disturbance[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2022,39(4):693−701.
[16] SCHOLZ C H. The mechanics of earthquakes and faulting[M]. Cambridgeshire,UK:Cambridge University Press,2018.
[17] HUBBERT M K. Role of fluid pressure in mechanics of overthrust faulting,1. Mechanics of fluid-filled porous solids and its application to overthrust faulting[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America,1959,70:115−166. DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1959)70[115:ROFPIM]2.0.CO;2
[18] 王宏伟,王晴,石瑞明,等. 煤矿冲击地压与断层构造失稳的多物理场互馈机制研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(2):762−790. WANG Hongwei,WANG Qing,SHI Ruiming,et al. A review on the interaction mechanism between coal bursts and fault structure instability from the perspective of multi physical field[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(2):762−790.
[19] 王思维,李建春. 节理接触面积比对压缩波传播影响的动光弹实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(5):939−947. WANG Siwei,LI Jianchun. Dynamic photoelastic experimental study on the influence of joint contact area ratio on stress wave propagation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(5):939−947.
[20] GABUCHIAN V,ROSAKIS A J,BHAT H S,et al. Experimental evidence that thrust earthquake ruptures might open faults[J]. Nature,2017,545(7654):336−339. DOI: 10.1038/nature22045
[21] LU Caiping,LIU Bin,LIU Biao,et al. Anatomy of mining-induced fault slip and a triggered rockburst[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and Environment,2019,78(7):5147−5160. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-019-01464-8
[22] HILL D P. Dynamic Stresses,Coulomb failure,and remote triggering-corrected[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,2012,102(6):2313−2336. DOI: 10.1785/0120120085







 下载:
下载: