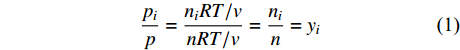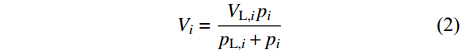Experimental study on CO2-enhanced coalbed methane production and its simultaneous storage
-
摘要:
长期以来针对CO2-ECBM已做了大量研究工作,然而有限的工业试验没能达到预期目的,使得这一煤层气强化技术推广应用欠缺。近些年随着各国碳中和路线的制定,CO2封存逐渐受到重视,煤储层可否作为CO2的封存空间、可否实现CO2驱替CH4和封存同步进行,又重新回归人们的视野。为此,以新疆准南区块目标煤层样为研究对象,采用不同CO2与CH4混合比例气体进行煤的吸附/解吸实验,探索混合气体比例对CO2-ECBM和CO2吸附封存潜力的影响。结果表明,随着混合气体CO2比例减少,CH4驱替效果降低,其中40%CH4+60%CO2混合气体的CO2残余量最多,在解吸至0.7 MPa时已有83.05%的CH4产出,而83.62%的CO2吸附残余在煤中,表明其CO2吸附封存潜力最佳。根据道尔顿分压分体积理论和Langmuir方程,对降压解吸阶段各混合气体解吸量与解吸率进行理论计算,结果显示,随混合气体CO2含量减少,煤中CO2的残余率、残余量以及CH4最终解吸率均降低。理论计算与实验中CH4解吸率和CO2残余量随混合气体组成变化趋势基本一致,表明混合气体中CO2占比越高,越有利于最大限度地提升CH4采收率以及煤储层CO2吸附封存潜力。研究认识为CO2-ECBM和煤储层CO2封存现场应用提供理论依据,为这一技术的推广应用提供实验支撑。
Abstract:Abstract: Experimental study on CO2-enhanced coalbed methane production and its simultaneous storage Abstract: For a long time, a lot of work has been done on CO2-enhanced coalbed methane (CO2-ECBM), but the limited industrial trials failed to achieve the expected purpose, which prevented the promotion and application of CBM enhancement technology. In recent years, with the establishment of carbon neutrality routes in different countries, CO2 geological storage has gradually gained attention, and the questions of whether coal reservoirs can be treated as CO2 storage space and whether simultaneous CO2 displacing CH4 and storage can be achieved have returned to the spotlight. In this study, using the coal samples from Xinjiang Zhunnan coal region, the adsorption/desorption experiments of coal were carried out with different mixture ratios of CO2 and CH4 to explore the effects of gas composition on CO2-ECBM, as well as CO2 adsorptive storage potential. The results show that, the CH4 displacement effect decreases as the CO2 ratio of the mixed gas decreasing, among which the CO2 residual volume of 40% CH4+60% CO2 mixture is the highest, corresponding to 83.05% CH4 production and 83.62% CO2 storage by adsorption as the experimental pressure drops to 0.7 MPa during desorption processes. This indicates that its CO2 adsorptive storage potential is the best. The desorption volume and rate of each mixed gas during different depressurization and desorption stages were calculated according to the Dalton’s law for partial pressure and partial volume, as well as the Langmuir’s equation. The results indicate that, as the CO2 ratio of the mixed gas decreases, the CO2 residual rate and volume, as well as the final CH4 desorption rate, were decrease. The predicted trends of CH4 desorption rate and CO2 residual volume with gas mixture composition are generally consistent with those obtained by the experiments, indicating that high proportion of CO2 in the gas mixture enhances CH4 recovery, as well as CO2 adsorptive storage potential of the coal reservoir. This study can provide not only theoretical basis for the field application of CO2-ECBM and CO2 storage, but also experimental supports for the promotion of this technology.
-
Keywords:
- coalbed methane /
- CO2-ECBM /
- CO2 displacing CH4 /
- CO2 synchronous storage /
- adsorption/desorption
-
煤层气是在煤化过程中生成并储存在煤储层中的以CH4为主要成分的一种非常规天然气,与煤相比是一种相对清洁、高效的能源[1-2]。通过向煤层注入CO2强化CH4采收率(CO2-ECBM)被认为是提高煤层气生产效率以及减少CO2排放的有效技术手段之一[3]。国内外在这一方面的大量研究主要集中在基础理论上,大多以CH4/CO2在煤中的吸附/解吸实验为主体,从不同的影响因素进行拓展研究[4-6]。不同矿区、不同煤阶煤对CH4/CO2吸附能力存在一定差异,但均可证明,受煤亲CH4能力低于亲CO2能力的影响,注入CO2驱替CH4这一行为是可行的,可以将CH4的采收率从以往的20%~60%提升到90%以上[7-11]。然而,大部分实验没有考虑分压对混合气体各组分吸附的影响,同时没有充分考虑煤吸附CO2和CH4能力的差异,以及注入CO2的费用问题和CO2封存的碳交易效益,使得注入的CO2量难以满足最佳驱替CH4效果,致使这一技术裹足不前[12]。国内外先后在这一领域进行了一些工程试验,但效果不尽人意,没有得到大规模推广。
美国于1995年在圣胡安盆地的Allison区块进行了世界上第一个CO2-ECBM先导试验,经过5年注入3.36×105 t的CO2,产出气体中CO2占比仅由注入前的4%增大至6%,表明注入的大量CO2被封存在煤储层中;而CO2-ECBM将CH4采收率由注入前的77%提高至95%[13]。2004年8月—2005年6月,波兰上西里西亚盆地RECOPOL项目共注入CO2约760 t,其中692 t CO2在工程结束后被储存在煤层中,然而CH4产气量比CO2注入前仅略有提高。以该项目的MS-3井为例,该井产出气体组分中CO2、CH4平均体积分数分别为40%和60%[14]。2004年,中国在沁水盆地南部TL-003井3号煤层开展了CO2-ECBM试验。沁水盆地平均煤层气资源丰度1×108 m3/km2,3号煤层平均含气量为11.94 m3/t。试验共注入192.8 t的CO2,使CH4采收率提高10.2%[15-16]。2011—2012年,在鄂尔多斯盆地东缘的柳林煤层气区块进行CO2-ECBM项目,目标煤层平均含气量为10.72 m3/t,共注入超过460 t CO2[17]。国内外进行的CO2-ECBM试验都反映出,少量CO2注入量虽然提高了CH4采收率,然而并没有实现CO2封存量最大化以及CH4采收率最佳化的需求[18]。综上可知,以往试验存在的问题有两个方面,一是CO2注入量远远不足以克服因CH4与CO2的吸附能力差异所需的最低驱替分压;二是CO2注入困难导致其扩散范围有限。
尽管Gunter于1991年就提出了煤储层封存CO2这个概念,但当时并没有引起人们的重视,更没有把CO2-ECBM与其同步封存结合起来[13]。碳中和的实现除了节能降耗增加低碳能源比例,降低化石燃料消耗外,最关键的抓手是CCUS(CO2封存捕捉与利用),就目前的技术而言,CO2的商业化利用可能还需要重大的技术突破,封存是近期有望作为一种切实可行的减排途径[19],煤储层中封存CO2逐渐被重视,而如何高效封存还需要进一步探索[20]。CO2在煤层中封存是一个复杂的地质过程,其可行性受煤储层物性、气体圈闭性等多种因素影响,而煤对CO2的吸附能力是影响煤储层CO2吸附封存潜力的重要因素[24]。另外,考虑商业化运行成本问题,能否在驱替煤层气产出的同时实现CO2的同步封存,既不降低煤层气的质,又能够实现驱替和封存最大化,是这一技术产业化的关键。据此,笔者通过对比煤对CO2和CH4吸附能力差异、吸附混合气体后降压解吸过程中解吸气体浓度、解吸率以及CO2残余率的变化,并结合分压分体积理论,探讨混合气体比例对CO2-ECBM和CO2吸附封存潜力的影响,通过研究,以期为强化煤层气产出和CO2最佳注入量预测提供一种新方法,并为这一技术的推广应用提供实验支撑。
1 实验与方法
1.1 实验样品与装置
选用新疆准南区块42号煤层煤样作为实验样品,煤层埋深750 m左右,煤层压力梯度平均为0.82 MPa/100 m,储层压力约6 MPa,煤的工业分析和元素分析结果见表1。将煤破碎、筛分出粒径为60~80目(0.18~0.25 mm)的样品备用,采用如图1所示实验装置对煤样进行CH4和CO2的混合气体吸附/解吸实验。实验阶段通过恒温水浴箱保持实验温度恒定为25℃,分别研究CH4和CO2的纯气体吸附特征,以及体积分数配比分别为30%CH4+70%CO2、40%CH4+60%CO2、50%CH4+50%CO2、60%CH4+40%CO2和70%CH4+30%CO2的混合气体吸附/解吸特征。实验过程中,采用气相色谱检测仪(GC-4000A)对不同阶段降压解吸气体进行组分测试。检测器为热导(TCD),10阶程序升温,升温速率0.1~40.0℃/min;TDX-01色谱柱,载气为氦气。使用排水集气法进行煤层气含量测试,解吸仪中的液体为饱和碳酸氢钠溶液。
表 1 新疆煤样工业分析和元素分析结果Table 1. Industrial analysis and elemental analysis results of coal samples in Xinjiang样品来源
工业分析w/%
元素分析w/%镜质体最大反射率Rmax/% Mad Aad Vad FCad C H N (O+S) 新疆准南区块 1.82 2.83 38.08 57.27 79.71 4.77 1.03 14.49 0.67 1.2 实验步骤
(1) 将60~80目(0.18~0.25 mm)的煤样放入105℃的烘箱中干燥24 h,去除煤体原始含气。将烘干后的煤样放入煤样罐中,并加入蒸馏水使煤样处于饱水状态,拧紧煤样罐封盖,记录加入的煤粉和蒸馏水的质量。向煤样罐中通入不具有吸附性的氦气至1 MPa,压力在6 h内保持不变则视为气密性良好。
(2) 向参考罐通入氦气至2~3 MPa,连通参考罐与煤样罐,待压力平衡后采集一组数据,重复2~3次计算煤样罐自由空间体积。之后多次注水并测试,由此尽量减小煤样罐中的自由体积并降低游离气对气体吸附、解吸特性分析的影响,使实验数据能够更准确地反映解吸气体。随后使用真空泵对煤样罐进行抽真空处理。
(3) 向煤样罐内注入单一气体或混合气体,根据原位煤储层压力,注入压力设定为6 MPa左右。通过质量流量计分别测试注入煤样罐的CH4和CO2体积,吸附平衡过程持续48 h。
(4) 每隔0.5 MPa打开一次四通阀并进行煤中气体解吸,计量并收集解吸气体,随后使用气相色谱仪测试解吸气体组分(CH4和CO2)。为确保解吸过程稳定进行,煤样罐出口端流量通过瓦斯解吸仪限制在300 mL/min以内,且每次解吸完成后平衡压力24 h。重复该步骤直至压力降低至0 MPa。根据注入量与解吸气中CH4和CO2的解吸量计算出CH4与CO2的残余量。考虑到以目前的开采技术不可能抽采出全部煤层气,故CO2也不能全部封存,因此设定CO2残余率达到80%、CH4采收率达到80%为实验研究的一个理想数值。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 煤吸附CO2和CH4特征
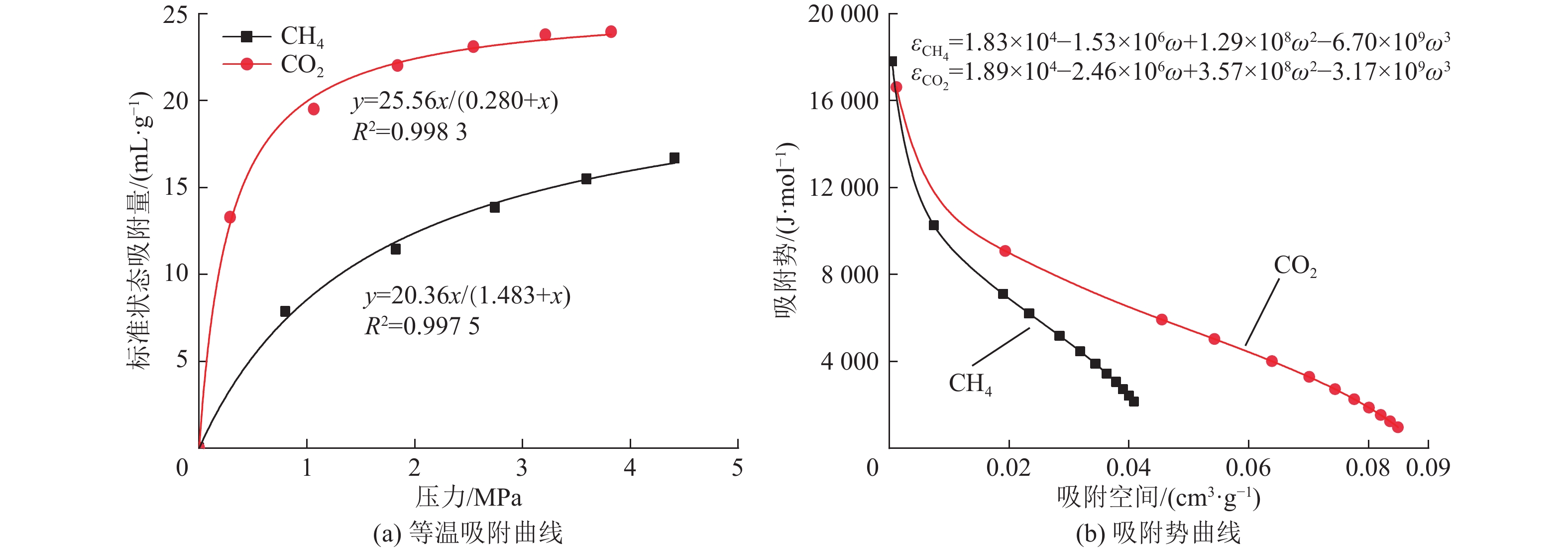
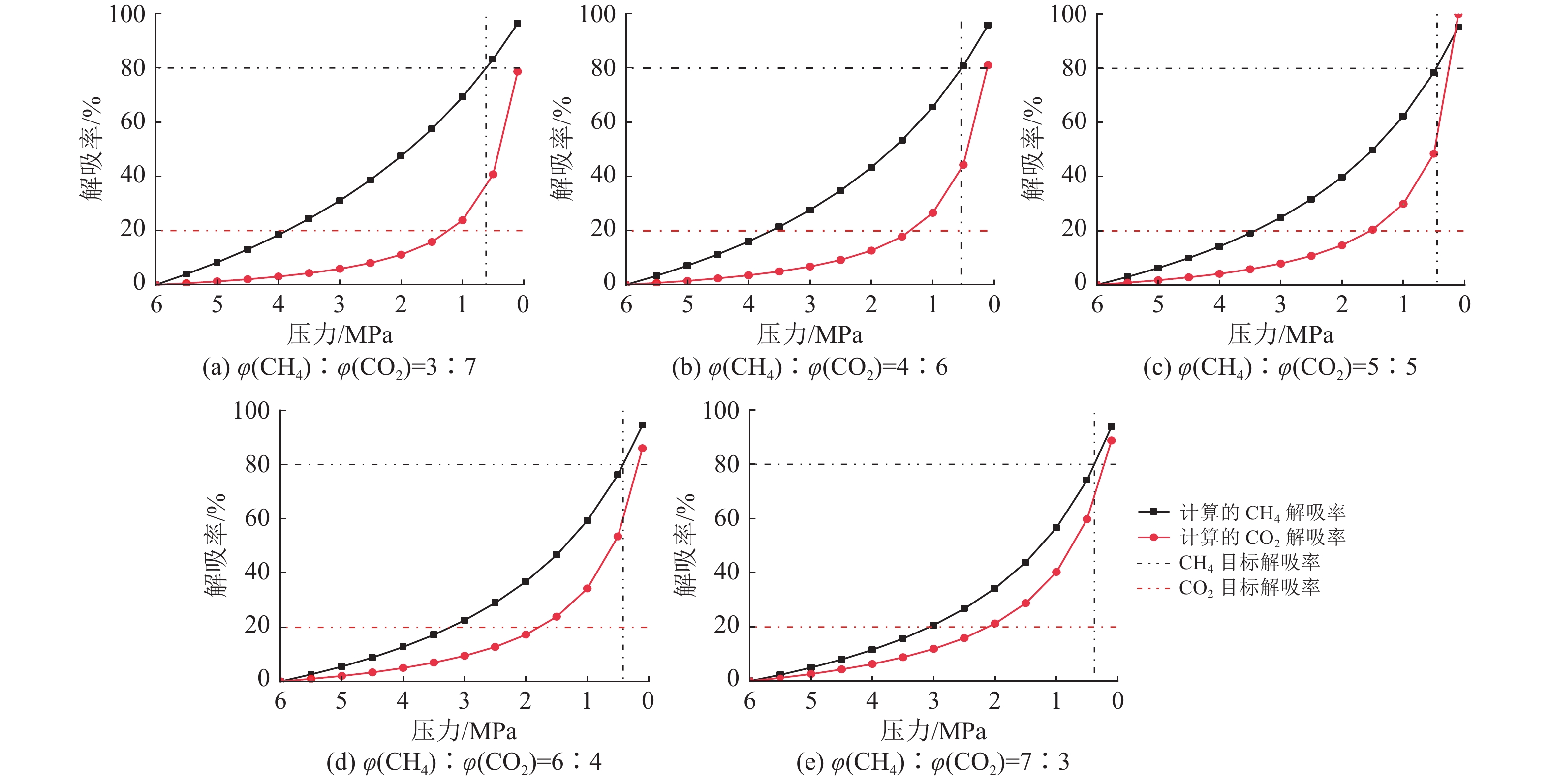
通过煤对CH4和CO2单一气体的等温吸附实验可知(图2a),CO2和CH4的Langmuir体积(VL)分别为25.56 cm3/g和20.36 cm3/g,Langmuir压力(pL)分别为0.28 MPa和1.48 MPa。CO2的VL是CH4的1.26倍,而CH4的pL是CO2的5.29倍。同时,运用Polanyi吸附势理论对CH4和CO2的吸附特性进行表征(图2b),结果显示CO2的吸附势(ε)和吸附空间(ω)均大于CH4,且随压力增加逐渐增大[11]。由此可见,该煤样对CO2的吸附能力大于CH4,使得整个解吸过程中CH4的解吸优先于CO2,且高压阶段更明显。
2.2 降压解吸混合气体CH4与CO2浓度变化特征
CH4与CO2混合气体降压解吸阶段,30%CH4+70%CO2、40%CH4+60%CO2和50%CH4+50%CO2实验组,在压力高于2.5 MPa的解吸过程中,CH4解吸气体浓度随压力降低而逐渐增大,CO2气体浓度则趋于降低;在压力低于2.5 MPa的解吸阶段,前两个实验组的解吸气体中CH4浓度都呈现先缓后急的降低趋势;而50%CH4+50%CO2实验组的CH4组分浓度逐渐上升,在1 MPa时才开始下降。60%CH4+40%CO2和70%CH4+30%CO2实验组在整个解吸过程中,CH4浓度都处于缓慢下降状态。对比5组实验可以发现,解吸气浓度的变化过程虽然各自表现出差异,但当压力低于0.7 MPa时,CH4组分浓度都开始大幅度下降,CO2组分浓度上升(表2,图3)。这与新疆煤样的纯CH4和CO2等温吸附曲线(图2a)所表现出的,当解吸压力低于1 MPa时,CO2才开始大量解吸现象是一致的。引起50%CH4+50%CO2%实验组现象异常的原因可能是50%CH4+50%CO2%混合气体的AHI(面积滞后指数)是所有实验组中最高的,解吸滞后引起该实验组解吸过程中CH4组分浓度降低存在滞后现象[21]。由等温吸附曲线和吸附势特性曲线可以看出,在高压阶段CO2与CH4的竞争吸附更强烈,解吸气体中CH4浓度缓慢增加;而到达低压解吸阶段后,竞争吸附效应逐渐减弱,同时煤中大部分CH4气体已解吸产出使得其分压逐渐降低,进而CO2解吸浓度随解吸压力的降低趋于增大[22]。上述分析表明,任何浓度比例,产出气体中CH4的浓度均高于CO2,表明煤中CO2驱替CH4作用普遍存在,这也符合研究区煤的吸附特性曲线(图2b)。
表 2 不同比例混合气体吸附解吸实验数据Table 2. Data for adsorption and desorption experiments on mixed gases气体成分配比 平衡压力
段/MPaCH4解吸
体积分数/%CO2解吸
体积分数/%CH4分压/
MPaCO2分压/
MPaCH4解吸
率/%CO2解吸
率/%CH4解吸
量/mLCO2解吸
量/mL30%CH4+70%CO2 4.50~4.00 65.71 34.29 2.63 1.37 12.97 3.15 97.25 50.75 4.00~3.50 67.02 32.98 2.35 1.15 22.53 05.35 71.71 35.29 3.50~3.00 67.31 32.69 2.02 0.98 37.61 08.76 113.08 54.92 3.00~2.50 69.51 30.49 1.74 0.76 51.04 11.51 100.79 44.21 2.50~2.00 62.02 37.98 1.24 0.76 60.72 14.27 72.56 44.44 2.00~1.50 53.35 46.65 0.80 0.70 73.10 19.31 92.83 81.17 1.50~1.00 50.20 49.80 0.50 0.50 84.61 24.64 86.34 85.66 1.00~0.70 41.50 58.50 0.29 0.41 88.98 27.51 32.79 46.22 0.70~0.20 31.94 68.06 0.06 0.14 96.73 35.21 58.13 123.87 0.20~0 18.99 81.01 0 0 98.86 39.44 15.95 68.05 40%CH4+60%CO2 5.50~5.00 68.94 31.06 3.45 1.55 11.92 3.90 166.83 75.17 5.00~4.50 75.25 24.75 3.39 1.11 19.87 5.81 111.37 36.63 4.50~4.00 79.27 20.73 3.17 0.83 25.70 6.92 81.65 21.35 4.00~3.50 80.37 19.63 2.81 0.69 32.42 8.11 94.03 22.97 3.50~3.00 81.22 18.78 2.44 0.56 39.09 9.23 93.40 21.60 3.00~2.50 83.19 16.81 2.08 0.42 46.04 10.25 97.33 19.67 2.50~2.00 83.23 16.77 1.66 0.34 55.08 11.58 126.51 25.49 2.00~1.50 81.91 18.09 1.23 0.27 64.62 13.11 133.51 29.49 1.50~1.00 81.47 18.53 0.81 0.19 73.52 14.58 124.65 28.35 1.00~0.70 79.41 20.59 0.56 0.14 83.05 16.38 133.41 34.59 0.70~0.20 67.66 32.34 0.14 0.06 97.11 21.27 196.89 94.11 0.20~0 22.75 77.25 0 0 98.24 24.04 15.70 53.30 50%CH4+50%CO2 4.70~3.90 65.47 34.53 2.55 1.35 20.53 12.07 225.87 119.13 3.90~3.50 70.48 29.52 2.47 1.03 28.03 15.57 82.46 34.54 3.50~3.00 71.32 28.68 2.14 0.86 35.10 18.74 77.74 31.26 3.00~2.50 71.61 28.39 1.79 0.71 46.56 23.80 126.03 49.97 2.50~2.00 72.79 27.21 1.46 0.54 54.43 27.08 86.62 32.38 2.00~1.50 79.76 20.24 1.20 0.30 64.36 29.89 109.27 27.73 1.50~1.00 83.55 16.45 0.84 0.16 74.01 32.01 106.11 20.89 1.00~0.60 74.77 25.23 0.45 0.15 84.27 35.87 112.90 38.10 0.60~0.20 60.17 39.83 0.12 0.08 94.45 43.37 111.92 74.08 0.20~0 21.97 78.03 0 0 96.60 51.91 23.73 84.27 60%CH4+40%CO2 7.70~7.00 83.96 16.04 5.88 1.12 11.27 3.23 135.27 25.84 7.00~6.50 81.58 18.42 5.30 1.20 18.35 5.63 84.92 19.17 6.50~6.00 79.66 20.34 4.78 1.22 24.34 7.92 71.92 18.36 6.00~5.50 81.26 18.74 4.47 1.03 30.70 10.12 76.32 17.60 5.50~5.00 80.64 19.36 4.03 0.97 37.03 12.40 75.93 18.23 5.00~4.50 80.41 19.59 3.62 0.88 43.13 14.63 73.18 17.83 4.50~4.00 80.07 19.93 3.20 0.80 49.47 17.00 76.08 18.94 4.00~3.50 79.56 20.44 2.78 0.72 56.02 19.52 78.60 20.19 3.50~3.00 78.90 21.10 2.37 0.63 61.50 21.72 65.77 17.59 3.00~2.50 77.70 22.30 1.94 0.56 67.61 24.35 73.28 21.03 2.50~2.00 76.29 23.71 1.53 0.47 73.57 27.13 71.52 22.23 2.00~1.50 74.64 25.36 1.12 0.38 79.45 30.13 70.59 23.98 1.50~1.00 72.02 27.98 0.72 0.28 85.13 33.43 68.14 26.47 1.00~0.70 66.58 33.42 0.47 0.23 90.37 37.38 62.91 31.58 0.70~0.40 54.11 45.89 0.22 0.18 94.79 43.00 53.03 44.97 0.40~0.20 35.01 64.99 0.07 0.13 96.83 48.69 24.51 45.49 0.20~0 17.00 83.00 0 0 97.61 54.37 9.32 45.48 70%CH4+30%CO2 7.00~6.30 93.62 6.38 5.90 0.40 8.43 1.34 59.04 4.02 6.30~5.50 93.68 6.32 5.15 0.35 19.86 3.14 80.00 5.40 5.50~5.00 92.00 8.00 4.60 0.40 25.00 4.18 35.96 3.13 5.00~4.50 93.29 6.71 4.20 0.30 31.00 5.19 42.02 3.02 4.50~4.00 93.48 6.52 3.74 0.26 36.20 6.04 36.38 2.54 4.00~3.50 93.18 6.82 3.26 0.24 42.44 7.10 43.69 3.20 3.50~3.00 89.12 10.88 2.67 0.33 47.56 8.56 35.81 4.37 3.00~2.50 92.61 7.39 2.32 0.18 53.87 9.73 44.18 3.53 2.50~2.00 91.15 8.85 1.82 0.18 59.07 10.91 36.42 3.50 2.00~1.60 91.69 8.31 1.40 0.13 66.98 12.58 55.32 5.01 1.60~1.20 90.48 9.52 1.09 0.10 72.98 14.06 42.03 4.42 1.20~0.90 88.47 11.53 0.80 0.10 78.26 15.66 36.97 4.82 0.90~0.60 83.43 16.57 0.50 0.10 84.56 18.58 44.08 8.75 0.60~0.20 74.86 25.14 0.15 0.05 89.80 22.69 36.68 12.32 0.20~0 58.74 41.26 0 0 92.27 26.73 17.27 12.13 2.3 CH4与CO2混合气体解吸率
降压解吸结束后,各实验组CH4最终解吸率分别为98.86%、98.24%、96.60%、97.61%、92.27%,随注入的混合气体中CH4浓度增大趋于降低,但均取得了良好的驱替效果。然而,不同实验组CO2的解吸率存在较大差异,随注入气体中CO2浓度降低,CO2解吸率分别为39.44%、24.04%、51.91%、54.37%、26.73%,呈先降后增再降趋势(表2,图4)。如果以CH4解吸率80%和CO2残余率80%为期望值,注入气体的CH4浓度为40%和70%的实验组在压力降低至1 MPa左右后CH4解吸率均达到80%以上,此时从表2中可知,且CO2残余率分别约为84.52%和82.88%,此时压力分别为0.83 MPa和0.71 MPa,能够满足高效的CH4驱替和CO2同步吸附封存的要求。然而,其他3个实验组在甲烷解吸率达到80%时,CO2残余率均低于80%,分别为78.02%、66.06%、69.87%,此时压力分别为0.79、1.48、0.71 MPa,表明CO2吸附封存潜力较差。另外,随注入气体中CO2浓度降低,其最终残余量分别为1115、1637、588、432、220 mL,可见CH4体积分数为40%的实验组CO2残余量最多(表2)。因此40%CH4+60%CO2实验组的驱替CH4效果最好以及CO2吸附封存潜力最佳,如果以此时结束排采,废弃压力也是比较高的。
2.4 竞争吸附和分压对CH4与CO2混合气体吸附/解吸的理论计算方法
为了探讨竞争吸附和分压对CH4和CO2混合气体吸附/解吸的影响,并为CO2-ECBM和CO2吸附封存的混合气体最佳比例预测提供方法,根据道尔顿分压分体积理论和Langmuir方程对降压解吸阶段各混合气体解吸量与解吸率进行计算。首先,计算不同混合气体比例下各气体分压,其中混合气体比例与上述实验保持一致(表2);之后,将气体分压代入Langmuir方程计算不同压力下煤中CH4和CO2各自的吸附量;最后,根据不同压力点气体吸附量,计算得到不同解吸阶段气体的解吸量,并根据累计解吸量与解吸总量计算解吸率(图5)。
道尔顿分压分体积理论式如下:
$$ \frac{{{p_{{i}}}}}{p} = \frac{{{n_{{i}}}RT/v}}{{nRT/v}} = \frac{{{n_{{i}}}}}{n} = {y_{{i}}} $$ (1) 式中:pi为混合气体中组分i的分压;p为混合气体的总压力;yi为气体混合物中i组分物质的量比例分数,即摩尔分数;T为温度;ni和n分别为第i组分浓度和总浓度;R为气体常数,取值8.314 J/(mol·k);v为气体体积。
Langmuir方程为:
$$ {V_{{i}}} = \frac{{{V_{{{{\rm{L}},i}}}}{p_{{i}}}}}{{{p_{{{{\rm{L}},i}}}} + {p_{{i}}}}} $$ (2) 式中:Vi为i组分吸附量;pL,i为i组分Langmuir压力;VL,i为i组分Langmuir体积。
计算结果显示,随注入气体CH4浓度增大,各计算组CH4最终解吸率趋于降低,依次为96.38%、95.75%、95.12%、94.50%、93.89%;而CO2最终解吸率则趋于增大,依次为78.67%、80.98%、83.43%、86.04%、88.82%(图5)。另外,各计算组在CH4解吸率达到80%以上时,CO2的残余率随注入气体中CO2占比增加而降低,依次为59.26%、55.75%、51.57%、46.53%、25.87%;且此时对应的压力值分别为0.66、0.54、0.45、0.42、0.38 MPa,而压力值越高越有利CH4驱替和CO2吸附封存,以吸附气体总量1 000 mL为基准,各计算组CO2残余量分别为415、335、258、186、78 mL。由此可知,注入气体CO2比例越大,CH4解吸率和CO2残余量就越高,CO2驱替CH4能力就越强、CO2吸附封存潜力就越大。然而在CH4解吸率达到80%时,各计算组中CO2残余率均明显低于80%的预期值。上述计算结果与实验结果存在差异,造成这种差异的原因可能是:(1) 理论计算没有考虑气体溶解,而由于CH4溶解度远低于CO2,导致实验解吸完成后仍有部分CO2溶解在水中,造成CO2残余率偏高,计算的CO2残余率则较低;(2)理论计算中认为各压力点气体浓度保持不变,而实验过程中气体浓度随时变化,这就使得在相同压力点下理论计算与实验中气体分压存在一定差异,进而导致各气体吸附量的不同,但驱替和封存的总体变化趋势是一致的。在储层压力允许的条件下(注入后气体的临界解吸压力要低于储层压力),注入的CO2越多越有利于CH4产出,CO2同步吸附封存的潜力就越大,越易在较高的废弃压力下完成煤层气开发和CO2同步吸附封存。
3 结 论
a. 煤样对CO2的吸附能力远高于CH4,使得在任何混合气体浓度比下,解吸气体中CH4浓度均明显高于CO2,煤中CO2驱替CH4作用普遍存在。
b. 在实验条件下,当气体压力降低至0.7 MPa,混合气体比例为40%CH4+60%CO2和70%CH4+30%CO2时,煤中CO2残余率与CH4解吸率均达到80%,而两者CO2残余量分别是不同混合气体比例中的最高值与最低值,表明实验条件下40%CH4+60%CO2的混合气体比例具有最佳的CH4驱替效果和CO2同步吸附封存潜力。
c. 依据道尔顿分压分体积定律和Langmuir方程的理论计算结果,随混合气体中CO2占比增大,煤中CH4解吸率和CO2残余量增加,CO2吸附封存潜力随之提升。因此,在储层压力允许的条件下,混合气体中CO2比例越高越有利于提高CH4的采收率和CO2吸附封存潜力。
-
表 1 新疆煤样工业分析和元素分析结果
Table 1 Industrial analysis and elemental analysis results of coal samples in Xinjiang
样品来源
工业分析w/%
元素分析w/%镜质体最大反射率Rmax/% Mad Aad Vad FCad C H N (O+S) 新疆准南区块 1.82 2.83 38.08 57.27 79.71 4.77 1.03 14.49 0.67 表 2 不同比例混合气体吸附解吸实验数据
Table 2 Data for adsorption and desorption experiments on mixed gases
气体成分配比 平衡压力
段/MPaCH4解吸
体积分数/%CO2解吸
体积分数/%CH4分压/
MPaCO2分压/
MPaCH4解吸
率/%CO2解吸
率/%CH4解吸
量/mLCO2解吸
量/mL30%CH4+70%CO2 4.50~4.00 65.71 34.29 2.63 1.37 12.97 3.15 97.25 50.75 4.00~3.50 67.02 32.98 2.35 1.15 22.53 05.35 71.71 35.29 3.50~3.00 67.31 32.69 2.02 0.98 37.61 08.76 113.08 54.92 3.00~2.50 69.51 30.49 1.74 0.76 51.04 11.51 100.79 44.21 2.50~2.00 62.02 37.98 1.24 0.76 60.72 14.27 72.56 44.44 2.00~1.50 53.35 46.65 0.80 0.70 73.10 19.31 92.83 81.17 1.50~1.00 50.20 49.80 0.50 0.50 84.61 24.64 86.34 85.66 1.00~0.70 41.50 58.50 0.29 0.41 88.98 27.51 32.79 46.22 0.70~0.20 31.94 68.06 0.06 0.14 96.73 35.21 58.13 123.87 0.20~0 18.99 81.01 0 0 98.86 39.44 15.95 68.05 40%CH4+60%CO2 5.50~5.00 68.94 31.06 3.45 1.55 11.92 3.90 166.83 75.17 5.00~4.50 75.25 24.75 3.39 1.11 19.87 5.81 111.37 36.63 4.50~4.00 79.27 20.73 3.17 0.83 25.70 6.92 81.65 21.35 4.00~3.50 80.37 19.63 2.81 0.69 32.42 8.11 94.03 22.97 3.50~3.00 81.22 18.78 2.44 0.56 39.09 9.23 93.40 21.60 3.00~2.50 83.19 16.81 2.08 0.42 46.04 10.25 97.33 19.67 2.50~2.00 83.23 16.77 1.66 0.34 55.08 11.58 126.51 25.49 2.00~1.50 81.91 18.09 1.23 0.27 64.62 13.11 133.51 29.49 1.50~1.00 81.47 18.53 0.81 0.19 73.52 14.58 124.65 28.35 1.00~0.70 79.41 20.59 0.56 0.14 83.05 16.38 133.41 34.59 0.70~0.20 67.66 32.34 0.14 0.06 97.11 21.27 196.89 94.11 0.20~0 22.75 77.25 0 0 98.24 24.04 15.70 53.30 50%CH4+50%CO2 4.70~3.90 65.47 34.53 2.55 1.35 20.53 12.07 225.87 119.13 3.90~3.50 70.48 29.52 2.47 1.03 28.03 15.57 82.46 34.54 3.50~3.00 71.32 28.68 2.14 0.86 35.10 18.74 77.74 31.26 3.00~2.50 71.61 28.39 1.79 0.71 46.56 23.80 126.03 49.97 2.50~2.00 72.79 27.21 1.46 0.54 54.43 27.08 86.62 32.38 2.00~1.50 79.76 20.24 1.20 0.30 64.36 29.89 109.27 27.73 1.50~1.00 83.55 16.45 0.84 0.16 74.01 32.01 106.11 20.89 1.00~0.60 74.77 25.23 0.45 0.15 84.27 35.87 112.90 38.10 0.60~0.20 60.17 39.83 0.12 0.08 94.45 43.37 111.92 74.08 0.20~0 21.97 78.03 0 0 96.60 51.91 23.73 84.27 60%CH4+40%CO2 7.70~7.00 83.96 16.04 5.88 1.12 11.27 3.23 135.27 25.84 7.00~6.50 81.58 18.42 5.30 1.20 18.35 5.63 84.92 19.17 6.50~6.00 79.66 20.34 4.78 1.22 24.34 7.92 71.92 18.36 6.00~5.50 81.26 18.74 4.47 1.03 30.70 10.12 76.32 17.60 5.50~5.00 80.64 19.36 4.03 0.97 37.03 12.40 75.93 18.23 5.00~4.50 80.41 19.59 3.62 0.88 43.13 14.63 73.18 17.83 4.50~4.00 80.07 19.93 3.20 0.80 49.47 17.00 76.08 18.94 4.00~3.50 79.56 20.44 2.78 0.72 56.02 19.52 78.60 20.19 3.50~3.00 78.90 21.10 2.37 0.63 61.50 21.72 65.77 17.59 3.00~2.50 77.70 22.30 1.94 0.56 67.61 24.35 73.28 21.03 2.50~2.00 76.29 23.71 1.53 0.47 73.57 27.13 71.52 22.23 2.00~1.50 74.64 25.36 1.12 0.38 79.45 30.13 70.59 23.98 1.50~1.00 72.02 27.98 0.72 0.28 85.13 33.43 68.14 26.47 1.00~0.70 66.58 33.42 0.47 0.23 90.37 37.38 62.91 31.58 0.70~0.40 54.11 45.89 0.22 0.18 94.79 43.00 53.03 44.97 0.40~0.20 35.01 64.99 0.07 0.13 96.83 48.69 24.51 45.49 0.20~0 17.00 83.00 0 0 97.61 54.37 9.32 45.48 70%CH4+30%CO2 7.00~6.30 93.62 6.38 5.90 0.40 8.43 1.34 59.04 4.02 6.30~5.50 93.68 6.32 5.15 0.35 19.86 3.14 80.00 5.40 5.50~5.00 92.00 8.00 4.60 0.40 25.00 4.18 35.96 3.13 5.00~4.50 93.29 6.71 4.20 0.30 31.00 5.19 42.02 3.02 4.50~4.00 93.48 6.52 3.74 0.26 36.20 6.04 36.38 2.54 4.00~3.50 93.18 6.82 3.26 0.24 42.44 7.10 43.69 3.20 3.50~3.00 89.12 10.88 2.67 0.33 47.56 8.56 35.81 4.37 3.00~2.50 92.61 7.39 2.32 0.18 53.87 9.73 44.18 3.53 2.50~2.00 91.15 8.85 1.82 0.18 59.07 10.91 36.42 3.50 2.00~1.60 91.69 8.31 1.40 0.13 66.98 12.58 55.32 5.01 1.60~1.20 90.48 9.52 1.09 0.10 72.98 14.06 42.03 4.42 1.20~0.90 88.47 11.53 0.80 0.10 78.26 15.66 36.97 4.82 0.90~0.60 83.43 16.57 0.50 0.10 84.56 18.58 44.08 8.75 0.60~0.20 74.86 25.14 0.15 0.05 89.80 22.69 36.68 12.32 0.20~0 58.74 41.26 0 0 92.27 26.73 17.27 12.13 -
[1] MANAB M,SANTANU M. A review of experimental research on enhanced coal bed methane (ECBM) recovery via CO2 sequestration[J]. Earth–Science Reviews,2018,179:392−410.
[2] 桑树勋,王冉,周效志,等. 论煤地质学与碳中和[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(1):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.001 SANG Shuxun,WANG Ran,ZHOU Xiaozhi,et al. Review on carbon neutralization associated with coal geology[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(1):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.01.001
[3] 桑树勋. 二氧化碳地质存储与煤层气强化开发有效性研究述评[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(5):1−9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.001 SANG Shuxun. Research review on technical effectiveness of CO2 geological storage and enhanced coalbed methane recovery[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(5):1−9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.001
[4] FAN Chaojun,ELSWORTH D,LI Sheng,et al. Modelling and optimization of enhanced coalbed methane recovery using CO2/N2 mixtures[J]. Fuel,2019,253:1114−1129. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.158
[5] YU Hongguan,YUAN Jian,GUO Weijia,et al. A preliminary laboratory experiment on coalbed methane displacement with carbon dioxide injection[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2008,73(2):156−166. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.04.005
[6] 张松航,张守仁,唐书恒,等. 无烟煤中甲烷和二氧化碳混合气吸附运移规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(2):544−555. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.XR20.1746 ZHANG Songhang,ZHANG Shouren,TANG Shuheng,et al. Adsorption and transport of methane and carbon dioxide mixture in anthracite[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(2):544−555. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.XR20.1746
[7] 郑贵强. 不同煤阶煤的吸附、扩散及渗流特征实验和模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012. ZHENG Guiqiang. Experimental and simulation study on the sorption, diffusion and seepage characters in different–ranked coals[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
[8] 李伟. CO2–ECBM中煤储层结构对CH4和CO2吸附/解吸影响的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2018. LI Wei. Influences of coal reservoir structure on adsorption/desorption of CH4 and CO2 associated with CO2–ECBM[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018.
[9] WANG Qianqian,ZHANG Dengfeng,WANG Haohao,et al. Influence of CO2 exposure on high–pressure methane and CO2 adsorption on various rank coals:Implications for CO2 sequestration in coal seams[J]. Energy & Fuels,2015,29(6):3785−3795.
[10] ZHANG Xiaogang,RANJITH P G. Experimental investigation of effects of CO2 injection on enhanced methane recovery in coal seam reservoirs[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization,2019,33:394−404. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.06.019
[11] 苏现波,陈润,林晓英,等. 吸附势理论在煤层气吸附/解吸中的应用[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(10):1382−1389. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.10.012 SU Xianbo,CHEN Run,LIN Xiaoying,et al. Application of adsorption potential theory in the fractionation of coalbed gas during the process of adsorption/desorption[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2008,82(10):1382−1389. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.10.012
[12] XIE Heping,LI Xiaochun,FANG Zhiming,et al. Carbon geological utilization and storage in China:Current status and perspectives[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2014,9(1):7−27. DOI: 10.1007/s11440-013-0277-9
[13] WHITE C M,SMITH D H,JONES K L,et al. Sequestration of carbon dioxide in coal with enhanced coalbed methane recovery:A review[J]. Energy & Fuels,2005,19(3):659−724.
[14] BERGEN F V, KRZYSTOLIK P, WAGENINGEN N V, et al. Production of gas from coal seams in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin in Poland in the post–injection period of an ECBM pilot site[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2009, 77(1/2): 175–187.
[15] WONG S, MACDONALD D, ANDREI S, et al. Conceptual economics of full scale enhanced coalbed methane production and CO2 storage in anthracitic coals at South Qinshui Basin, Shanxi, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2010, 82(3–4): 280–286.
[16] 叶建平,张兵,WONG S. 山西沁水盆地柿庄北区块3#煤层注入埋藏CO2提高煤层气采收率试验和评价[J]. 中国工程科学,2012,14(2):38−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.02.006 YE Jianping,ZHANG Bing,WONG S. Test of and evaluation on elevation of coalbed methane recovery ratio by injecting and burying CO2 for 3# coal seam of north section of Shizhuang,Qinshui Basin,Shanxi[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2012,14(2):38−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.02.006
[17] CONNELL L D,PAN Z,CAMILLERI M,et al. Description of a CO2 enhanced coal bed methane field trial using a multi–lateral horizontal well[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2014,26:204−219. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.04.022
[18] 陈浮,于昊辰,卞正富,等. 碳中和愿景下煤炭行业发展的危机与应对[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1808−1820. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2021.0368 CHEN Fu,YU Haochen,BIAN Zhengfu,et al. How to handle the crisis of coal industry in China under the vision of carbon neutrality[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(6):1808−1820. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2021.0368
[19] 王双明,申艳军,孙强,等. “双碳”目标下煤炭开采扰动空间CO2地下封存途径与技术难题探索[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):45−60. WANG Shuangming,SHEN Yanjun,SUN Qiang,et al. Underground CO2 storage and technical problems in coal mining area under the“dual carbon”target[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):45−60.
[20] 降文萍,崔永君. 深部煤层封存CO2的地质主控因素探讨[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2010,22(11):1−6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2010.11.01 JIANG Wenping,CUI Yongjun. A discussion on main geologic controlling factors of CO2 sequestration in deep coal seams[J]. Coal Geology of China,2010,22(11):1−6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2010.11.01
[21] ZHANG Songhang,TANG Shuheng,LI Zhongcheng,et al. Competitive sorption and diffusion of methane and carbon dioxide mixture in carboniferous−permian anthracite of South Qinshui Basin,China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2020,13(24):1292. DOI: 10.1007/s12517-020-06303-9
[22] 王向浩,王延忠,张磊,等. 高、低煤阶CO2与CH4竞争吸附解吸置换效果分析[J]. 非常规油气,2018,5(3):46−51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2018.03.007 WANG Xianghao,WANG Yanzhong,ZHANG Lei,et al. Research on CO2,CH4 competitive adsorption,desorption and replacement effect of high and low rank coal[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas,2018,5(3):46−51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2018.03.007
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 郑永旺,崔轶男,李鑫,肖翠,郭涛,张登峰. 深层高阶煤层CO_2-ECBM技术研究与应用启示——以沁水盆地晋中地区为例. 石油实验地质. 2025(01): 143-152 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张瑜. 碳中和目标下二氧化碳能源开发现状及展望. 化学工程师. 2025(02): 69-72+52 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邓小鹏,相建华. 东曲矿8号煤CO_2和CH_4竞争吸附特性分子模拟研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(03): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 司小昆. 封闭空间煤心固碳过程CO_2吸附-运移特征. 煤矿安全. 2024(04): 26-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 薛恩思. CO_2-ECBM过程中煤层渗透率演化规律. 煤矿安全. 2024(04): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 宋平,崔晨光,张记刚,刘凯,邓振龙,谭龙,禹希科. 玛湖凹陷上乌尔禾组强敏感油藏CO_2同步吞吐试验. 新疆石油地质. 2024(03): 355-361 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 金毅,李娅妮,宋慧波,赵梦余,杨运航,陈泽楠. 分形界面吸附行为初探. 煤田地质与勘探. 2024(05): 1-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 马亮,邓广哲,王守印,蔚斐,高亮,袁超. 碳封存超临界CO_2螺旋管换热器传热规律. 西安科技大学学报. 2024(03): 467-477 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 车永芳. 二氧化碳驱替煤层气技术发展现状分析. 煤质技术. 2024(05): 67-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 肖智勇,王刚,刘杰,邓华锋,姜枫,郑程程. 热–流–固耦合作用下含水煤层渗透率模型建立及应用研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(12): 3044-3057 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 苏现波,王乾,于世耀,赵伟仲,王小明,毕彩芹,陈明,王一兵,孙长彦,伏海蛟,邹成龙,张双斌,黄津,谢相军. 基于低负碳减排的深部煤系气一体化开发技术路径. 石油学报. 2023(11): 1931-1948 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 朱磊,刘成勇,古文哲,盛奉天,袁超峰. 双碳目标下“煤基固废-CO_2”协同充填封存技术构想. 矿业安全与环保. 2023(06): 16-21+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)







 下载:
下载: