Analysis and jet drilling test of coiled tubing drilling string for underground coal mine
-
摘要:
由于可连续起下钻、不间断循环等优势,连续管钻井已成为近年来发展最快的石油钻井技术之一,开发煤矿井下连续管钻进技术是煤矿实现“少人化”甚至“无人化”钻探的重要技术途径。针对该技术在煤矿井下应用存在的管柱优选、钻进方法等关键问题,提出了连续管射流定向钻进方法,根据煤矿井下钻探用泥浆泵能力和孔深设计,分析了不同管径、不同弯曲比(r0/Rb)连续管流体摩阻;采用数值模拟方法,分析了不同连续管管径与钻孔孔径比(管孔比rc)情况下近水平钻进管柱屈曲形态及与孔壁接触应力;通过旋转射流水力学参数研究和破岩效果实验,给出了最佳射流钻头参数:通过连续管射流定向钻进实验,分析了射流定向钻进造斜规律,不同流量、钻进速度与钻孔孔径的关系。结果表明:ø19~ø31.75 mm连续管的弯曲半径可满足煤矿坑道空间要求;连续管流体摩阻的主要影响因素为管径和流量,在井下常用泥浆泵流量200 L/min、压力31.5 MPa、钻孔深度200 m情况下,ø31.75 mm连续管为最佳管柱方案;管孔比rc=0.454时,连续管与孔壁接触应力稳定,压应力呈线性变化;采用ø34.5 mm/5×1.0 mm(5个孔径1.0 mm的喷嘴)喷射钻头+ø40 mm液力换向器+ø31.75 mm连续管钻具组合钻进,平均增倾角能力0.67 (°)/m,平均降倾角能力为0.61 (°)/m,平均增/减方位能力0.45 (°)/m;通过控制射流流量和钻进速度,钻孔直径可控制在ø70 mm左右;研究成果为煤矿井下连续管钻进技术与装备的开发提供了理论基础。
Abstract:Due to continuous tripping, uninterrupted circulation and other technical advantages, coiled tubing drilling has become one of the fastest developing oil-drilling-technologies in recent years. Developing the coiled tubing drilling technology for underground coal mine is an essential technical means to realize “less humanized” or even “unhumanized” coal drilling. Aiming at solving the key problems existing in the application of this technology in underground coal mine, such as pipe string optimization and drilling method, the coiled tubing jet directional drilling method was proposed. According to the mud pump capacity and borehole depth design for underground coal mine drilling, the fluid friction resistance of coiled tubing with different diameters and bending ratios (r0/Rb) was analyzed. Numerical simulation was used to analyze the buckling morphology of horizontal drilling string and the contact stress with borehole wall at different ratios of coiled tubing diameter to borehole diameter (rc). Besides, the optimum jet bit parameters were given through the study on rotary jet hydraulic parameters and rock breaking effect test. Specifically, the deviation rule of jet directional drilling, as well as the relationship of different flow rate, drilling speed and borehole diameter, were studied based on the coiled tubing jet directional drilling test. The results show that the bending radius ø19 mm‒ø31.75 mm of coiled tubing can meet the space requirements of coal mine tunnel.Tubing diameter and flow rate are the main factors affecting the fluid friction resistance of coiled tubing. Under the conditions of a flow rate of 200 L/min, a pressure of 31.5 MPa and a drilling depth of 200 m, ø31.75 mm coiled tubing is preferred for the optimal drilling string scheme. When the tube hole ratio is rc=0.454, the contact stress between the coiled tubing and borehole wall is stable and the compressive stress changes linearly. Drilling with ø34.5 mm/5×1.0 mm jet bit + ø40 mm hydraulic commutator + ø31.75 mm coiled tubing assembly, the average inclination increase capacity was 0.67 (°)/m, the average inclination decrease capacity was 0.61 (°)/m, and the average azimuth increase/decrease capacity was 0.45 (°)/m. By controlling the jet flow rate and drilling speed, the borehole diameter can be controlled around ø70 mm. Generally, the research results could provide a theoretical foundation for the development of coiled tubing drilling technology and equipment in underground coal mine.
-
我国浅部煤炭资源逐渐减少甚至枯竭,未来煤炭资源开采集中于浅部延伸至深部阶段[1-2]。随着煤炭开采深度的不断增加,煤层瓦斯压力和瓦斯含量不断增加,瓦斯抽采是预防瓦斯灾害和促进瓦斯利用的有效途径[3-4]。煤矿井下瓦斯抽采以施工钻孔抽采为主,钻孔的瓦斯抽采效果直接影响矿井瓦斯灾害的治理效果[5-6]。随着抽采时间的增加,瓦斯抽采钻孔发生塌孔、堵孔的现象显著增加,导致钻孔抽采功能部分或者完全失效,瓦斯抽采效率降低[7-9]。在石油天然气开采过程中也面临类似的难题,油管结垢降低了油气田开采量和开采效率。进入开采中后期时,油气田长时间进行聚驱、水驱、复合驱等作业,使得地面集输系统和地层等输运通道都出现一定程度的结垢现象[10]。随着开采工作持续进行,结垢量增加,可能造成管道堵塞、井下作业装置难以取出等情况,严重影响油气田的正常运作和经济效益。因此,采取有效的解堵除垢措施对解决瓦斯抽采钻孔塌孔问题、提高瓦斯抽采效率、改善油气田生产效率及提高综合开发效益具有重大意义。
自驱旋转射流技术以其无损、操作简单、无污染等优点逐渐成为一种新兴的解堵除垢技术。自驱钻头作为其执行装置,其性能优劣直接决定了自进和解堵除垢能力。合理设计的自驱钻头具有优异的射流动力特性,因而研发高性能自驱钻头是国内外学者研究的重心。20世纪40年代,国外油井开发中采用了喷嘴组合的钻头结构设计。自此,水力学在喷射式钻头上的应用开始发展。C. Landers等[11]提出了应用最为广泛的自进式多孔钻头,刘玉洲等[12]将钻头结构改进后应用于煤层气开发领域,利用自进式钻头在煤层内完成径向水平钻孔,形成新的瓦斯流动通道,提高煤层气产量。针对瓦斯抽采钻孔塌孔、堵孔问题,刘勇等[13]提出采用自进式旋转钻头修复失效钻孔的方法,其利用钻头后置喷嘴反冲力作为动力,自行至钻孔堵塞段处,前置喷嘴形成水射流对堵塞物进行破碎并将其与水混合返出孔外,实现清孔排渣、钻孔修复的目的。现场实验结果表明:进行钻孔修复后,瓦斯抽采浓度提高2.09倍,瓦斯抽采流量提高2.74倍,大大提高了瓦斯抽采效率。喷嘴的角度和布置方式影响射流速度,进而影响钻头的自进力和破岩能力。贺乐昌[14]对多孔射流钻头冲击射流流场进行研究,研究结果表明:正向喷嘴采用交错型布局方式,可以保证水力射孔孔径,减少射流能量耗散。董惠娟等[15]在此基础上建立了射流钻头内部流场模型,研究了压力、围压、喷嘴直径等因素对射流钻头破岩钻孔能力的影响,为射流钻头结构优化提供依据。郭瑞昌等[16]建立了多孔式射流钻头流场计算模型,分析了射流钻头内外不同区域的流场分布情况和局部流动特性,发现反向喷嘴较大的流线转角导致射流在流道内产生流动的分离与附壁现象,大大增加了反向喷嘴的局部阻力系数。修复理论是自驱旋转射流技术工程应用的基础。针对已有的修复理论计算长钻孔修复参数时误差较大的问题,刘勇等[17]基于变质量牛顿定律建立了钻孔修复运动方程,通过系统阻力测试实验明确综合摩擦因素k的理论值需要用系数进行修正。但综合摩擦因素理论值存在误差的原因尚不清晰。多股射流导致管道内流场发生变化,自驱钻头和高压软管受力与管道内流场结构直接相关。目前对于自驱钻头流场结构研究多针对喷头部分,缺乏多股射流共同作用下管道内流场变化影响自进力和返水阻力的研究。
笔者以管道内多股射流共同作用下流场结构特性为研究对象,通过数值模拟和实验相结合的方法揭示综合摩擦因素理论值存在误差的原因,分析后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比和系统压力等因素对自驱钻头自进力的影响规律,明确自进力影响因素的主次关系,以期为自驱钻头的参数优化设计提供理论依据。
1 数值模拟
1.1 几何模型
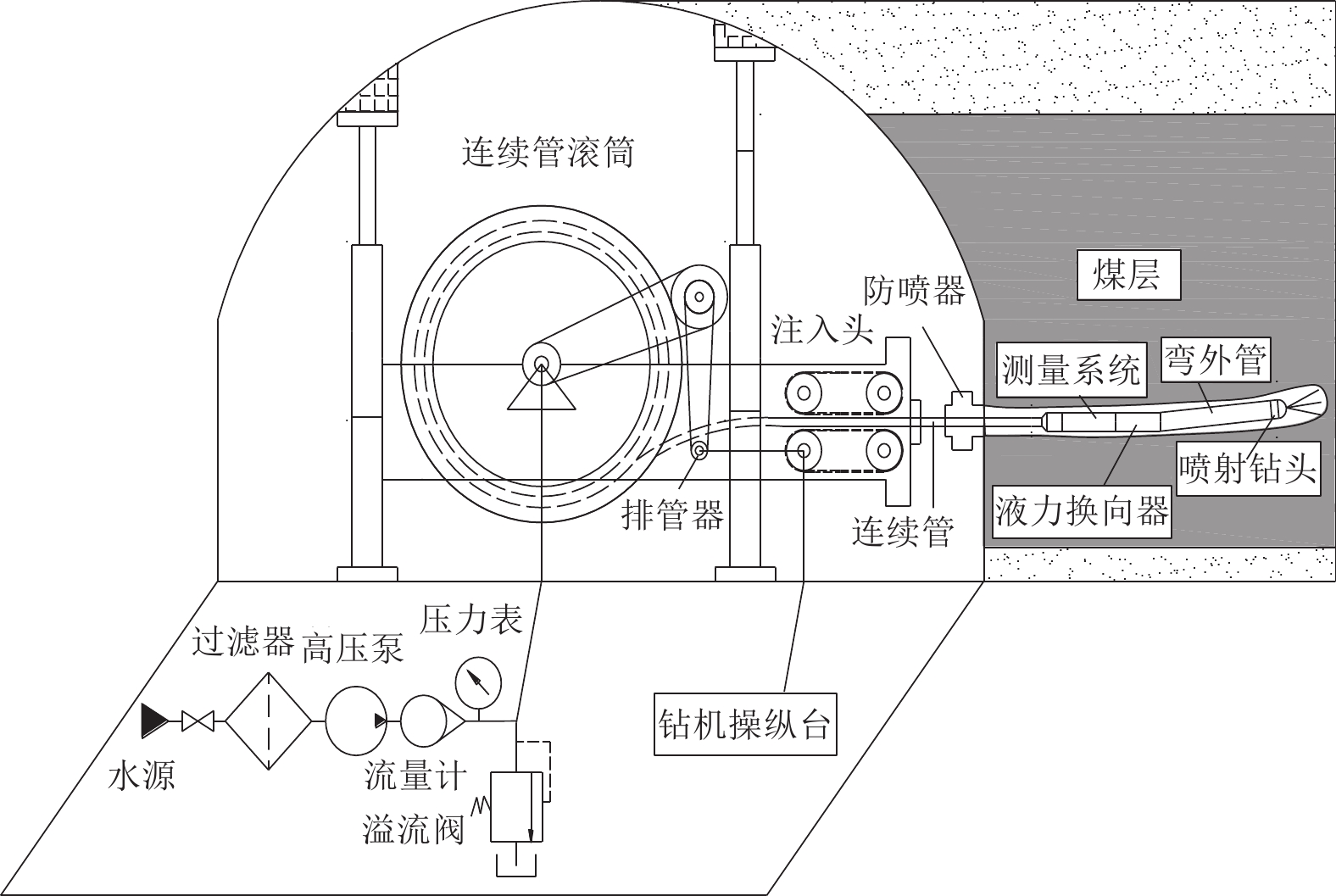
水射流自驱钻头修复钻孔装置主要由高压柱塞泵、软管卷盘和自驱钻头组成,如图1所示。自驱钻头是系统运动和破煤动力输出的关键装置。高压水射流从钻头后置喷嘴喷出,提供系统前进动力;从前置喷嘴喷出,提供破煤动力;破碎煤渣随返水排出孔外,实现钻孔修复。
为分析管道内流场变化对自进力和返水阻力的影响规律,结合图1中高压软管与管道接触情况,利用SpaceClaim建立自驱钻头在管道中运动时的物理模型,物理模型总长度为1.1 m,如图2所示。自驱钻头由旋转体和喷头组成,总长度为158 mm,外径为40 mm,流体入口直径为16 mm,高压软管外径为28 mm。自驱钻头前端为喷头,用于安装喷嘴,流体通过高压软管进入自驱钻头,前置喷嘴射流用于解堵除垢,后置喷嘴射流用于提供推力和旋转转矩。钻头前端为3个直径1 mm喷嘴,与钻头中轴线夹角分别为35°、30°、10°,后置喷嘴直径为1.5 mm。
1.2 控制方程
水为不可压缩流体,自驱钻头运动过程中,流体与管道之间的传热对流场的影响可以忽略不计。因此,进行管道内流场数值模拟时,不考虑传热,基本控制方程包括连续方程、Navier-Stokes方程。
不可压缩流体连续方程表达式[18]为:
$$ \frac{{\partial {v_x}}}{{\partial x}} + \frac{{\partial {v_y}}}{{\partial y}} + \frac{{\partial {v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}} = 0 $$ (1) 式中:
${{{v}}_x}$ 、${{{v}}_y}$ 、${{{v}}_{\textit{z}}}$ 分别为流体在x、y、z方向上的速度。对于不可压缩黏性流体Navier-Stokes方程,在空间直角坐标系中的表达式[18]为:
$$ \frac{{{\rm{d}}{v_x}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = {f_x} - \frac{{\partial p}}{{\rho \partial x}} + \upsilon \left( {\frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_x}}}{{\partial {x^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_x}}}{{\partial {y^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_x}}}{{\partial {{\textit{z}}^2}}}} \right) $$ (2) $$ \frac{{{\rm{d}}{v_y}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = {f_y} -\frac{{\partial p}}{{\rho\partial y}} + \upsilon \left( {\frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_y}}}{{\partial {x^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_y}}}{{\partial {y^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_y}}}{{\partial {{\textit{z}}^2}}}} \right) $$ (3) $$ \frac{{{\rm{d}}{v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = {f_{\textit{z}}} - \frac{{\partial p}}{{\rho\partial {\textit{z}}}} + \upsilon \left( {\frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{\partial {x^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{\partial {y^2}}} + \frac{{{\partial ^2}{v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{\partial {{\textit{z}}^2}}}} \right) $$ (4) 式中:
$\dfrac{{{\rm{d}}{v_x}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}$ 、$\dfrac{{{\rm{d}}{v_y}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}$ 、$\dfrac{{{\rm{d}}{v_{\textit{z}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}$ 分别为流体在x、y、z方向上的加速度;$\upsilon $ 为运动黏度;$\rho $ 为流体密度;$x$ 、$y$ 、$\textit{z}$ 分别为流体质点在$t$ 时刻的空间坐标;${f_x}$ 、${f_y}$ 、${f_z}$ 为体积力在x、y、z方向上的分量;$p$ 为压力。1.3 湍流模型
自驱钻头后置射流与钻头内部流体流动方向相反,存在较大的流线转角,导致后置喷嘴入口处局部流线严重弯曲,并且射流速度较高,诱导流场内产生涡旋。采用标准k-ε湍流模型进行管道内流场数值模拟会产生较大的误差。因此,本文采用RNG k-ε湍流模型进行数值模拟。与标准k-ε湍流模型相比,RNG k-ε湍流模型中的ε传输方程中多了一个R项,使RNG k-ε湍流模型能更加精确地模拟大应变和大流线弯曲度的流体流动问题[19]。
1.4 网格划分及边界条件
管道内部流场结构相对复杂,所以采用Fluent Meshing进行网格划分,并在壁面划分边界层网格,如图2所示。分别对流体模型的不同部分划分网格,网格最小边长为0.2 mm,网格总数为910 217,在喷嘴出口等流场变化剧烈的地方采用0.2 mm网格进行划分。模拟过程中喷头以不同转速进行旋转,因此对喷头部分进行局部加密来保证模拟效果。
边界条件设置如图2所示,包括入口、出口、壁面以及充满水的流动区域。钻头流体入口边界条件设置为压力入口,根据实际工况条件确定计算压力值,出口设置为压力出口,出口压力为大气压,壁面设置为无滑移的固定壁面。
1.5 数值模拟方案
后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比(管道内径为D1,高压软管外径为D2,(D1−D2)/D1定义为环空比)和系统压力影响管道内的流场结构,从而影响自驱钻头自进力。依次改变后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比、系统压力,其他条件不变,进行多因素逐项数值模拟,数值模拟方案见表1。
表 1 多因素逐项数值模拟方案Table 1. Scheme of multi-factor numerical simulation by item编号 后置喷嘴倾角/(°) 转速/(r·min−1) 环空比 压力/MPa 1 20 600 0.63 25 2 25 600 0.63 25 3 30 600 0.63 25 4 35 600 0.63 25 5 40 600 0.63 25 6 45 600 0.63 25 7 20 0 0.63 25 8 20 300 0.63 25 9 20 900 0.63 25 10 20 1200 0.63 25 11 20 900 0.44 25 12 20 900 0.53 25 13 20 900 0.69 25 14 20 900 0.75 25 15 20 900 0.53 10 16 20 900 0.53 15 17 20 900 0.53 20 选用自进力大小作为指标评价自驱钻头性能优劣,根据多因素逐项数值模拟结果,由自进力影响因素的全部水平组合中,选取部分有代表性的水平组合:系统压力15、20、25 MPa,后置喷嘴倾角20°、25°、35°,转速600、900、1 200 r/min,环空比0.44、0.53、0.63。根据上述水平组合,正交数值模拟4个因素的水平见表2,正交数值模拟方案见表3。
表 2 正交数值模拟因素水平Table 2. Factors and levels of orthogonal numerical simulation水平 系统压力/MPa 后置喷嘴倾角/(°) 转速/(r·min−1) 环空比 1 15 20 600 0.44 2 20 25 900 0.53 3 25 35 1 200 0.63 表 3 正交数值模拟方案Table 3. Orthogonal numerical simulation scheme编号 系统压力/MPa 后置喷嘴倾角/(°) 转速/(r·min−1) 环空比 1 15 20 600 0.44 2 15 25 900 0.53 3 15 35 1 200 0.63 4 20 20 900 0.63 5 20 25 1 200 0.44 6 20 35 600 0.53 7 25 20 1 200 0.53 8 25 25 600 0.63 9 25 35 900 0.44 2 模拟结果与分析
2.1 流场基本结构特性
图3为管道内基本流场分布情况。根据流场分布,可分为前置射流区、后置射流区、涡旋区、返流区4个区域。前置射流为3个角度不同的射流组成的射流束,后置射流区由2个射流组成。前置射流和后置射流冲击壁面会形成一次涡旋,诱导周围流体进入涡旋,没有卷入一次涡旋的流体撞击壁面后分离形成二次涡旋。涡旋的形成导致钻孔内产生复杂的涡旋区。当涡旋能量不足以诱导流体产生新的涡旋时,钻孔内流场趋于稳定,形成返流区。
2.2 多因素逐项数值模拟结果与分析
2.2.1 后置喷嘴倾角的影响
自驱钻头多股高速射流快速喷射,产生反冲力的同时在钻头区域产生局部低压区,由于压力梯度作用,使自驱钻头产生压差力。反冲力和压差力是自驱钻头实现自进的主要动力。后置喷嘴倾角在一定程度上决定着自驱钻头的自进力。因此,选择合适的后置喷嘴倾角对提高自驱钻头的自进力有积极的作用。
前置喷嘴的个数、直径和倾角不变,并固定后置喷嘴个数和直径。入口压力为25 MPa,环空比为0.63,后置喷嘴倾角分别为20°、25°、30°、35°、40°、45°,自进力和返水阻力变化情况如图4所示。由图4可知,随着后置喷嘴倾角由20°增加至45°,自进力逐渐减小,但后置喷嘴倾角为30°时自进力小于其他条件下自进力。
自驱钻头多股射流冲击壁面后速度迅速衰减,并开始沿壁面横向发展,从而形成壁面射流区,其主要由顺流(管道出口方向)区域和逆流(管道底部方向)区域组成。低速返流受到高速射流的卷吸作用以及管道内壁与喷嘴之间有限空间的限制,产生尺度不一的涡旋,涡旋不断进行分裂、变形、卷吸和合并,形成大小不一的涡旋并随机运动[20],如图5所示。
涡旋的发展和射流的卷吸作用影响自驱钻头前后压力梯度,从而影响压差力。图6为不同后置喷嘴倾角条件下喷头后端至前端42 mm范围内压力变化,从喷头后端至前端,压力先增大后减小。后置喷嘴高速射流喷射过程中,射流周围形成低压区,喷头后端压力较低。射流冲击壁面后,在射流两侧形成大小不一的涡旋。由图5区域Ⅰ可知,前置射流形成的涡旋与后置射流形成的涡旋发生碰撞,涡旋碰撞时对流体的挤压作用导致压力升高(图6,A阶段)。前后涡旋发生碰撞后,流体向喷头两侧流动,在前置射流的卷吸作用下,喷头前端压力降低(图6,B阶段)。由于涡旋结构交替形成、发展,喷头两侧涡旋结构不一致,导致压力出现波动(图6,C阶段)。后置喷嘴倾角小于30°时,壁面射流以顺流为主,随着后置喷嘴角度增加,逆流速度增加,射流右侧涡旋速度增大,涡旋碰撞后压力峰值随之增加。由图6可知,随着后置喷嘴倾角增加,喷头前后压力梯度增加,导致压差力增大。自驱钻头自进力主要由轴向射流反冲力和压差力组成,当后置喷嘴倾角大于30°时,压差力大于因后置喷嘴倾角增加而减小的轴向射流反冲力。因此,后置喷嘴倾角30°时自进力小于其他后置喷嘴倾角条件下自进力。
流体从高压软管与钻孔壁之间的环空返回时,在高压软管近壁区存在速度梯度很大的流动,产生流体对壁面的切应力,对高压软管的运动产生返水阻力[17]。根据文献[17]的研究,返水阻力是综合摩擦因素的重要组成部分,采用出口处流速代替返流速度计算返水阻力导致综合摩擦因素理论值出现误差。射流冲击壁面后,水流被限制在管道和自驱钻头之间的环形空间流动,产生水流拖曳力。水流拖曳力的方向与流体流动方向一致。由图4可知,入口压力一定时,后置喷嘴倾角影响返水阻力的大小。后置喷嘴倾角发生改变时涡旋区随之改变(图5)。涡旋区导致流体流动方向发生改变,从而影响返水阻力。采用出口处流速代替返水速度计算返水阻力时未考虑涡旋区的影响,因此综合摩擦因素理论值需要用系数进行修正。
2.2.2 转速的影响
转速是影响射流速度和涡旋范围的重要参数。设置系统压力为25 MPa,转速分别为0、300、600、900、1 200 r/min,对管道内流场进行数值模拟。后置射流旋转冲击过程中产生封隔作用,阻碍钻头后方流体回流至低压区域。环空比一定时,射流旋转速度越大,封隔作用越强。同时,射流处于旋转状态时,射流流动特征会发生偏转。同一压力条件下,旋转速度不同,射流受旋转的影响程度也不同,从而导致不同的流动规律。图7为后置喷嘴射流轴心位置速度变化,随着旋转速度增加,射流速度衰减程度加剧。
射流的旋转会强化射流与周围流体的掺混作用,加速射流能量的消耗和速度的衰减,从而影响涡旋结构和范围[21]。如图8所示,随着喷头旋转速度的增加,射流冲击壁面形成的壁面射流区速度降低,导致后置射流诱导形成的一次涡旋范围逐渐减小。一次涡旋(标记为D)形成过程中诱导周围流体进入,没有卷入一次涡旋的流体撞击壁面后分离形成二次涡旋(标记为E)。涡旋速度与环空直径成反比,旋转体上方涡旋速度大于高压软管上方涡旋速度。如图8所示,旋转速度为900 r/min和1 200 r/min时,一次涡旋与二次涡旋在旋转体上方发生碰撞挤压,导致压力梯度增加。在射流封隔作用和涡旋碰撞挤压作用下,自驱钻头前后压力梯度增加。转速增加有利于钻头自进,但过高的转速会加剧射流速度衰减,不利于破碎堵塞物。因此,设计自驱钻头时应考虑转速对射流速度衰减的影响,提高自进力和解堵效率。
2.2.3 环空比的影响
图9为系统压力25 MPa、后置喷嘴倾角为20°时环空比对自进力的影响规律,环空比从0.44增加至0.75,自驱钻头的自进力逐渐下降。从数值模拟结果(图10)可以看出,自驱钻头外径固定时,环空比越小,钻头前后压力梯度越大。射流冲击壁面过程中卷吸流体,产生尺度不一的涡旋,在管道底部形成低压区域。后置射流旋转冲击过程中产生封隔作用,阻碍钻头后方流体回流至低压区域。系统压力一定时,后置射流的封隔能力有限,当环空比超过后置射流的封隔范围时,钻头后方流体对被射流卷吸的流体进行补充,从而导致钻头前后压力梯度减小。入口压力和后置喷嘴倾角不变的情况下,环空比为0.44时,自驱钻头和管道间环空直径较小,后置射流的封隔作用较强,阻碍流体回流,导致射流卷吸的流体无法得到补充,自驱钻头前后压力梯度较大。随着环空比增大,后置射流封隔作用逐渐减弱,在射流的卷吸作用下,钻头后方低速流体回流至低压区域,对被射流卷吸的部分流体进行补充,从而导致自驱钻头前后压力梯度减小,自驱钻头的自进力降低;当环空比继续增大至0.75时,后置射流的封隔作用基本失效,自驱钻头前后压力梯度较小。因此,存在最优的环空比,使自驱钻头的自进力最大。
2.2.4 系统压力的影响
图11为后置喷嘴倾角20°、环空比0.53时系统压力对喷头、旋转体和高压软管受力的影响。由图11可知,系统各部分受力与系统压力近似呈线性关系。高压软管主要受到返水阻力,其大小与返水流速有关。环空比一定时,系统压力增加,返流速度增加,高压软管受到的返水阻力增大。涡旋区域和压力梯度的变化影响系统各部分受力。以旋转体受力为例,当系统压力由10 MPa增加至25 MPa时,旋转体受力由16.97 N增加至40.32 N。由数值分析结果(图12)可知,在旋转体后端至前端100 mm范围内,随着系统压力由10 MPa增加至25 MPa,旋转体上方环空压力最小值由73.73 kPa降低至32.38 kPa,旋转体前后压力梯度逐渐增大。压力梯度增大导致旋转体受到的压差力增加。后置喷嘴喷出的高速流体对周围流体形成卷吸,使后置喷嘴出口附近局部压力降低[22]。同时,多股后置射流旋转冲击过程中共同作用形成封隔作用,阻碍流体回流至低压区域。压力梯度作用提高了自驱钻头的自进力。随着系统压力的增加,射流卷吸效果和封隔作用增强,低压区压力逐渐降低,压力梯度形成的推力增大,有利于提高自进力。
2.3 正交数值模拟结果与分析
根据极差的大小可以判断后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比、系统压力对自进力的影响程度。各影响因素中对应不同水平的数值模拟结果的最大值与最小值之差定义为极差。Ki表示任意列上水平号为i时所对应的结果之和,计算9个数值模拟方案的极差结果见表4。从表4可以看出,环空比的极差最大,为300.07,所以影响自进力的最主要因素是环空比;其次是系统压力,极差为111.87;转速的极差为60.42,其对自进力的影响小于环空比和系统压力;后置喷嘴倾角对自进力的影响相对其他几个因素较小。因此得到自进力影响因素主次关系为:环空比>系统压力>转速>后置喷嘴倾角。
表 4 正交数值模拟结果Table 4. Orthogonal numerical simulation results编号/参数 压力/MPa 后置喷嘴
倾角/(°)转速/(r·min−1) 环空比 自进力/N 1 15 20 600 0.44 124.16 2 15 25 900 0.53 60.92 3 15 35 1 200 0.63 32.17 4 20 20 900 0.63 43.07 5 20 25 1 200 0.44 146.74 6 20 35 600 0.53 67.00 7 25 20 1 200 0.53 123.35 8 25 25 600 0.63 50.68 9 25 35 900 0.44 155.09 K1 217.25 290.58 241.84 425.99 K2 256.81 258.34 259.08 251.27 K3 329.12 254.26 302.26 125.92 极差 111.87 36.32 60.42 300.07 3 自进力测试实验
3.1 实验装置
自进力测试实验装置主要由柱塞泵、高压软管、模拟管道、自驱钻头、数显式推拉力计组成,如图13所示。柱塞泵额定压力为35 MPa,额定排量为100 L/min。实验用自驱钻头前置喷嘴为3个直径1 mm喷嘴,前置喷嘴与钻头中轴线夹角分别为35°、30°、10°;后置喷嘴为2个直径1.5 mm喷嘴,与钻头中轴线夹角分别为20°、25°、30°、35°、40°、45°。
3.2 实验方法
实验装置如图13所示。模拟管道水平放置并固定,连接高压软管的自驱钻头放置于模拟管道内,将测试线一端与自驱钻头连接,另一端与数显式推拉力计连接。拉力计固定并确保测试线水平放置。启动柱塞泵,自驱钻头产生推力,拉力计示数即为自进力。
自驱钻头后置喷嘴沿周向呈一定偏心角,高速射流喷射时对钻头施加扭矩实现旋转。实验所用自驱钻头使用阻尼液控制转速,钻头偏心角和射流压力一定时,通过更换不同黏度的阻尼液调整转速。选用VC6236P型高精度数显转速计(图14)进行转速测试实验,测试时利用激光监测被测物体表面的反光纸即可得到转速数值。
分别改变后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比、系统压力,进行自进力测试实验,实验方案与正交数值模拟方案一致(表3)。
3.3 实验结果与分析
自进力作为衡量自驱钻头结构优劣的关键指标,其大小直接影响自进效果。为验证数值模拟结果的正确性,开展不同条件下自进力测试实验,将自进力的实验结果与数值模拟结果进行对比,如图15所示。由图15可知,自驱钻头自进力实验值和仿真值的变化规律较为一致。在进行数值模拟时,假设自驱钻头和高压软管在管道中的位置固定,但在实验过程中,自驱钻头的旋转过程导致钻头和高压软管的位置发生改变,从而影响管道内的流场和自进力。因此,在相同条件下,自驱钻头自进力仿真值与实验值存在一定误差。由图15可知,自进力数值模拟结果与实验结果之间的最大误差为24.24 N,验证了通过数值模拟结果分析后置喷嘴倾角、转速、环空比和系统压力对自驱钻头自进力影响规律的正确性。
4 结 论
a. 反冲力和压差力是自驱钻头实现自进的主要动力,涡旋挤压碰撞作用和射流卷吸作用导致自驱钻头产生压差力。增大后置喷嘴倾角或提高转速均会增强涡旋挤压碰撞作用,导致钻头所受压差力增加,从而提高自驱钻头自进力。
b. 后置射流旋转冲击过程中产生封隔作用,阻碍钻头后方流体回流至低压区域。提高转速、系统压力或减小环空比均会导致后置射流的封隔作用增强,致使自驱钻头所受压差力增加,有利于提高自驱钻头的自进力。
c. 涡旋区导致水流拖曳力方向发生改变,从而影响返水阻力。采用出口处流速代替返流速度计算返水阻力时忽略了涡旋区的影响,因此综合摩擦因素理论值需要采用系数进行修正。
d. 环空比、系统压力、转速和后置喷嘴倾角影响自驱钻头自进力,极差分别为300.07、111.87、60.42、36.32,影响因素主次关系为:环空比>系统压力>转速>后置喷嘴倾角。
e. 由于计算机运算能力的限制,数值模拟所用模型尺寸较小,无法充分分析钻孔内全孔段流场结构特征及其对管道受力的影响;本文实验设备尚需改进,无法开展大倾角钻孔条件下相关实验。后续拟开展大倾角钻孔条件下数值模拟和实验研究。
-
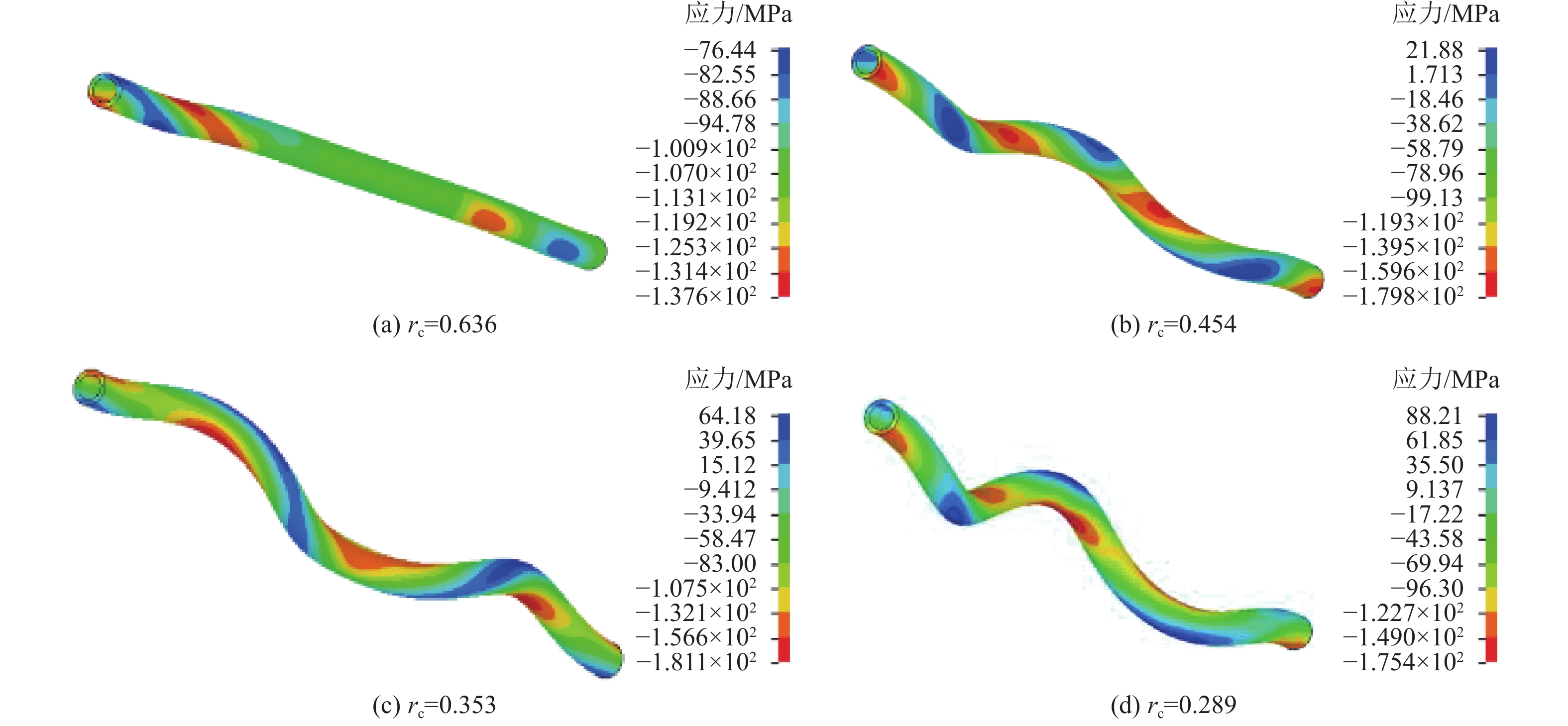
表 1 连续管最小弹性弯曲直径
Table 1 Minimum elastic bending diameter of coiled tubing
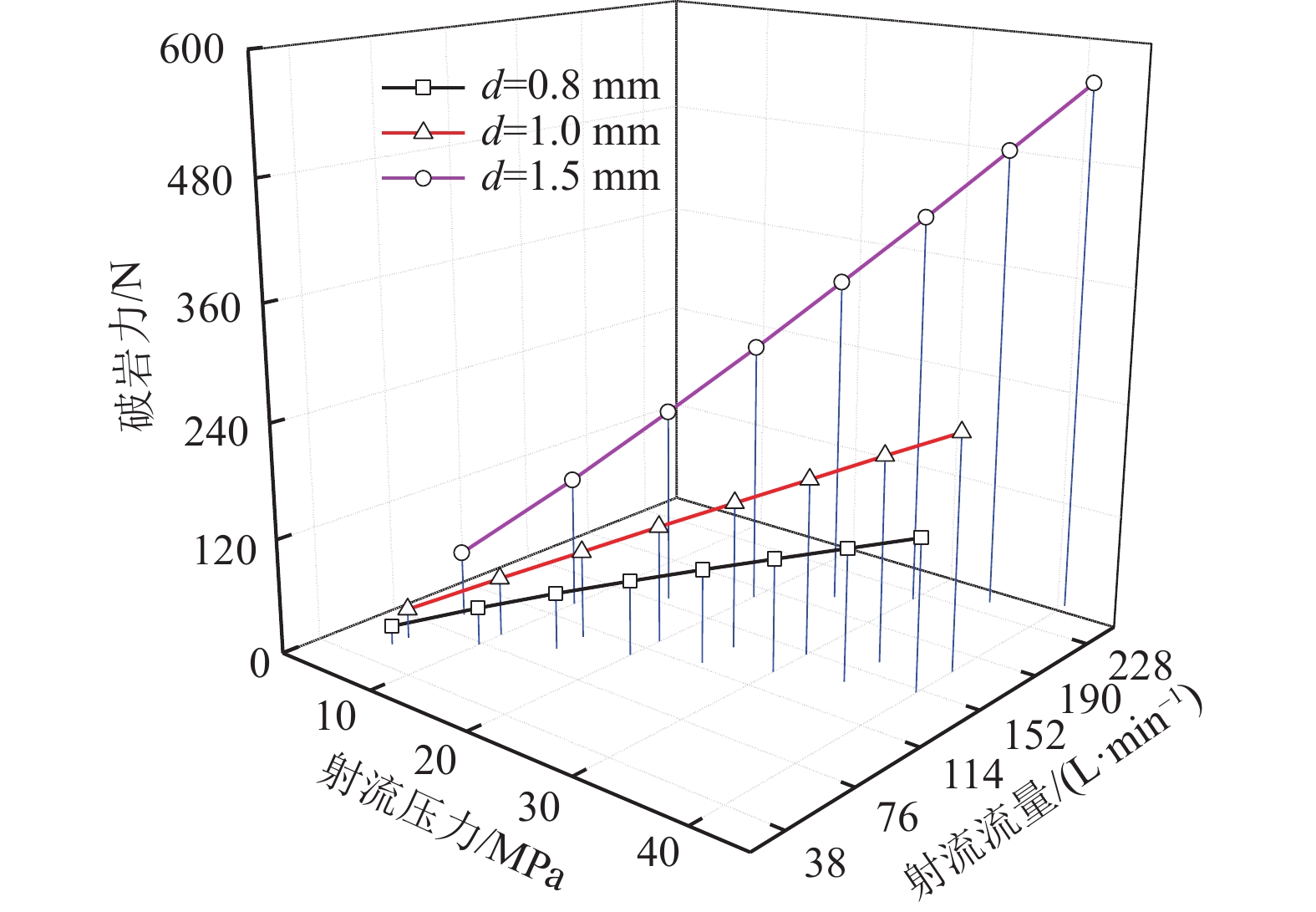
管径/mm 最小弹性弯曲半径/mm 19.00 643 25.40 857 31.75 1 072 38.10 1 286 44.45 1 501 表 2 不同喷嘴不同流量时破岩力
Table 2 Rock-breaking force at different flow rates of nozzles
射流压力/
MPad=0.8 mm d=1.0 mm d=1.5 mm 流量/
(L·min−1)破岩力/
N流量/
(L·min−1)破岩力/
N流量/
(L·min−1)破岩力/
N5 52.6 19.7 61.0 30.8 90.4 69.4 10 74.4 39.5 86.3 61.6 127.8 138.7 15 91.1 59.2 105.7 92.5 156.6 208.1 20 105.2 78.9 122.1 123.3 180.8 277.4 25 117.6 98.6 136.5 154.1 202.1 346.8 30 128.8 118.4 149.5 184.9 221.4 416.1 35 139.1 138.1 161.5 215.8 239.2 485.5 40 148.8 157.8 172.7 246.6 255.7 554.8 表 3 煤试样配方及强度实验结果
Table 3 Coal sample formula and strength test results
试样 试样配方比例
(水泥∶石膏∶煤粉)单轴抗压
强度/MPa备注 1 1.5∶1.5∶1 11.6 温度:20~25℃
湿度:95%
养护:14 d2 11.8 3 12.9 4 11.4 5 12.8 表 4 采用的实验设备和材料
Table 4 Test equipment and material adopted
名称 规格/型号 性能参数 数量 钻机 ZDY650 给进力25 kN 1 台 测斜仪 YHD2-1000 倾角误差±0.2°
方位误差±1.5°1台 高压泵 JN250 30.5 MPa、250 L/min 1台 喷射钻头 ø34.5 mm 喷嘴直径1.0 mm 2只 连续管 1.25寸 31.75 mm 50 m 液力换向器 40 mm 单次换向60° 1只 固定角弯管 40 mm 1.25° 1根 表 5 实验钻孔
Table 5 Test boreholes
孔号 工具
面/(°)钻孔测量测点倾角/方位角/(°) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 0 5 7 7.1 8.6 9.2 9.6 9.4 9.5 2 0 6 7.8 8.6 9.5 10.3 10.3 10.4 10.5 3 0 3.5 3.4 5.5 6.8 8.1 7.9 8.1 8.5 4 0 5.3 6 6.5 8 8.9 9.1 9.7 10 5 180 −1 −1.2 −2.4 −2.2 −2.9 −4.5 −5 −5.2 6 180 −1 −1.1 −2.45 −2.25 −3.1 −4.6 −5.11 −5.3 7 180 −0.9 −0.6 −1.3 −2 −2.6 −3.8 −4.66 −5.2 8 270 53 53 52.2 51.2 50.8 50.3 50.1 50 9 270 97 97 96 95.8 96.1 94.8 94.6 93.6 10 270 125 126 125 124 123 122 122 121 注:0°、180°为倾角;270°为方位角。 表 6 不同射流流量、钻进速度下钻孔孔径
Table 6 Borehole diameter under different jet flow rates and drilling speed
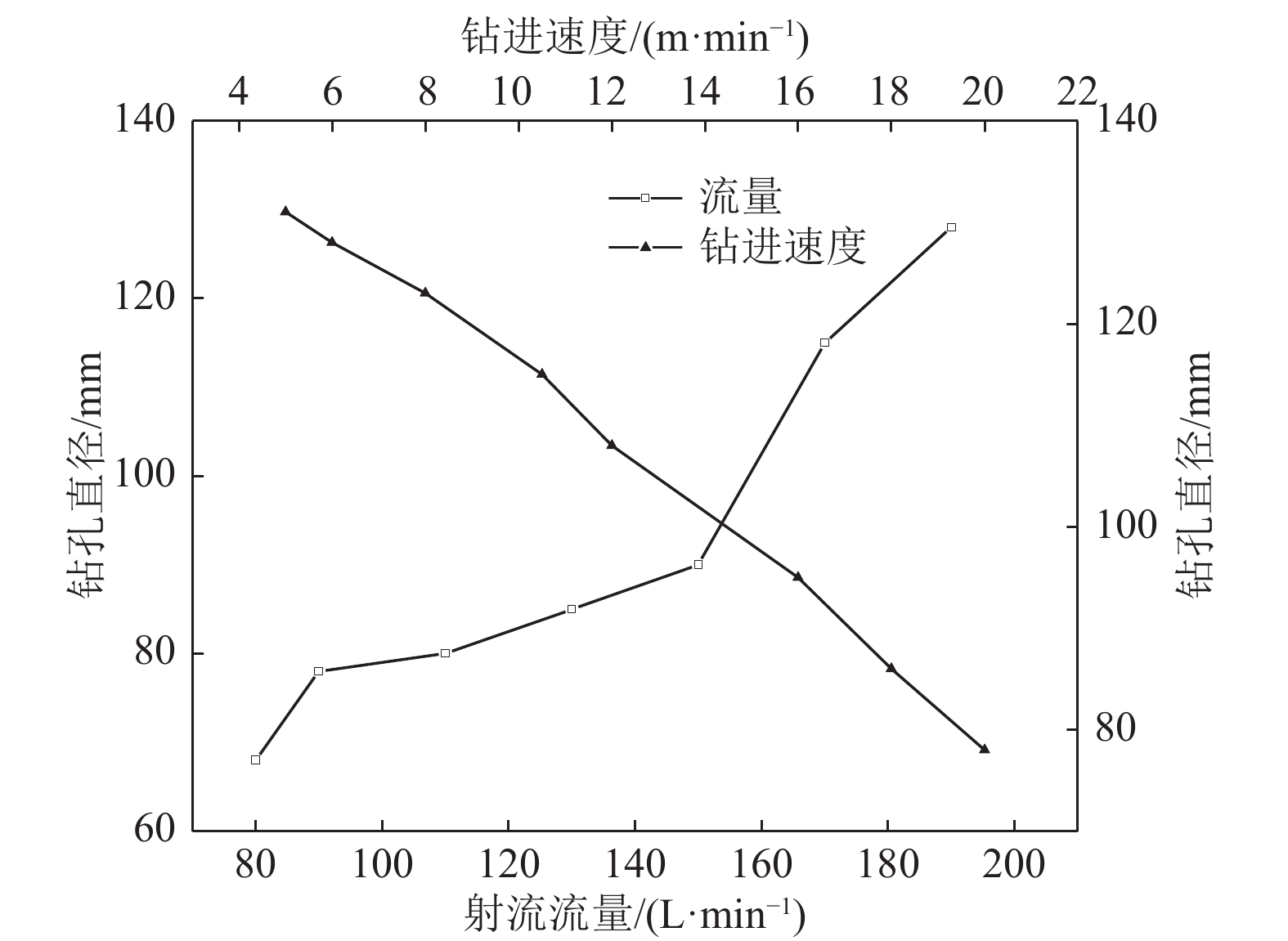
流量/(L·min−1) 钻孔孔径
/mm钻进速度
/(m·min−1)钻孔孔径
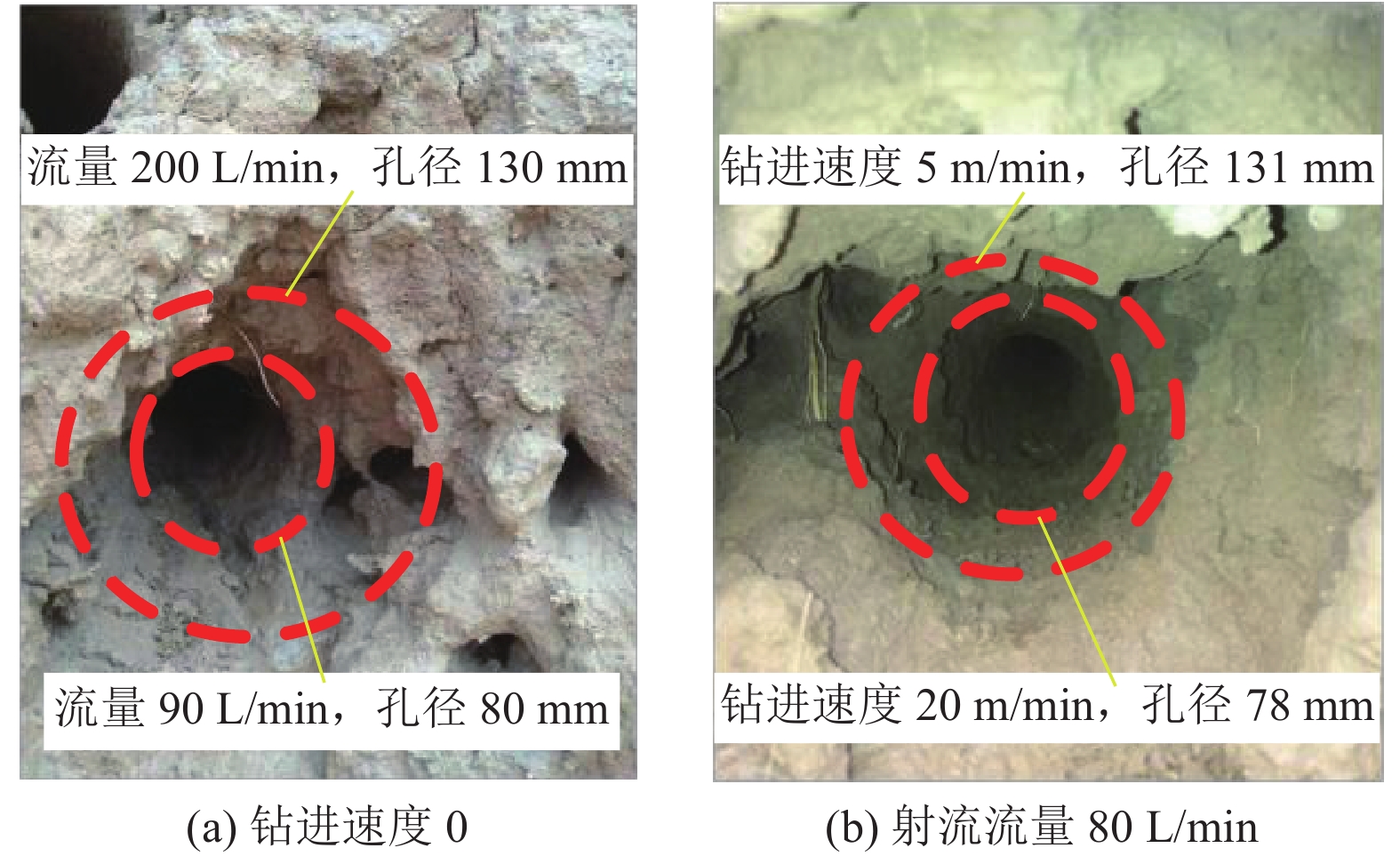
/mm80 68 5 131 90 78 6 128 110 80 8 123 130 85 10 115 150 90 12 108 170 115 16 95 190 128 18 86 200 130 20 78 -
[1] 姚宁平,王毅,姚亚峰,等. 我国煤矿井下复杂地质条件下钻探技术与装备进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(2):1−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.001 YAO Ningping,WANG Yi,YAO Yafeng,et al. Progress of drilling technologies and equipments for complicated geological conditions in underground coal mines in China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(2):1−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.001
[2] 石智军,姚克,姚宁平,等. 我国煤矿井下坑道钻探技术装备40年发展与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(4):1−34. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.04.001 SHI Zhijun,YAO Ke,YAO Ningping,et al. 40 years of development and prospect on underground coal mine tunnel drilling technology and equipment in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(4):1−34. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.04.001
[3] 王清峰,陈航. 瓦斯抽采智能化钻探技术及装备的发展与展望[J]. 工矿自动化,2018,44(11):18−24. DOI: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.17370 WANG Qingfeng,CHEN Hang. Development and prospect on intelligent drilling technology and equipment for gas drainage[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2018,44(11):18−24. DOI: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.17370
[4] 杨林. 煤矿井下瓦斯抽采钻孔机器人研究现状及关键技术[J]. 煤矿机械,2018,39(8):60−62. DOI: 10.13436/j.mkjx.201808022 YANG Lin. Research status and key technology of underground gas drainage drilling robot in coal mine[J]. Coal Mine Machinery,2018,39(8):60−62. DOI: 10.13436/j.mkjx.201808022
[5] RAMOS A B,FAHEL R A,CHAFFIN M,et al. Horizontal slim−hole drilling with coiled tubing:An operator ’s experience[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1992,44(10):1119−1125. DOI: 10.2118/23875-PA
[6] KRUEGER S, GRAY K, KILLIP D. Fifteen years of successful coiled tubing re–entry drilling projects in the Middle East: Driving efficiency and economics in maturing gas fields: SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference & Exhibition[C]. Dubai, 2013.
[7] 张文平. 连续管钻井水力轴向振动降摩减阻机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019. ZHANG Wenping. Research on the mechanism of friction reduction of the hydraulic axial vibration in coiled tubing drilling[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019.
[8] 李根生,宋先知,黄中伟,等. 连续管钻井完井技术研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 石油科学通报,2016,1(1):81−90. LI Gensheng,SONG Xianzhi,HUANG Zhongwei,et al. Research progress and prospects of well drilling and completion with coiled tubing[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin,2016,1(1):81−90.
[9] 任经纬. 连续油管作业管柱力学分析[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017. REN Jingwei. Mechanical analysis of coiled tubing operation string[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017.
[10] 张帅,张燕萍,郭慧娟. 国内外连续管钻井技术发展现状[J]. 石油矿场机械,2019,48(6):77−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2019.06.015 ZHANG Shuai,ZHANG Yanping,GUO Huijuan. Development status of continuous pipe drilling technology in China and abroad[J]. Oil Field Equipment,2019,48(6):77−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2019.06.015
[11] SOE S, LAGAT C, EVANS B, et al. The coiled tubing drilling rig for mineral exploration[C]//SPE/ICo TA Coiled Tubing and Well Intervention Conference and Exhibition. 2018: 3–7.
[12] 赵章明. 连续油管工程技术手册[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011. [13] 赵广慧,梁政. 连续油管内流体压力损失研究进展[J]. 钻采工艺,2008,31(6):41−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2008.06.014 ZHAO Guanghui,LIANG Zheng. Research on pressure loss of fluid in coiled tubing[J]. Drilling & Production Technology,2008,31(6):41−44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2008.06.014
[14] 王弥康,林日亿,张毅. 管内单相流体沿程摩阻系数分析[J]. 油气储运,1998,17(7):22−26. WANG Mikang,LIN Riyi,ZHANG Yi. Analysis on frictional resistance coefficient of single–phase fluid inside pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation,1998,17(7):22−26.
[15] 周博,管锋,周传喜,等. 连续管钻井系统摩阻计算方法与试验研究[J]. 石油机械,2015,43(2):22−26. DOI: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2015.02.006 ZHOU Bo,GUAN Feng,ZHOU Chuanxi,et al. Calculation and experimental study of friction resistance in coiled tubing drilling system[J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2015,43(2):22−26. DOI: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2015.02.006
[16] 袁发勇, 马卫国. 连续管水平井工程技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. [17] SAS–JAWORSKY II A,REED T D. Predicting friction pressure losses in coiled tubing operations[J]. World Oil,1997,218(9):141−146.
[18] 马沈岐,吴雅丽,任瑞玲. 煤矿瓦斯抽采钻进钻具级配技术[J]. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程),2009,36(9):28−31. MA Shenqi,WU Yali,REN Ruiling. Drilling tool grading technique for gas drainage drilling[J]. Exploration Engineering (Rock & Soil Drilling and Tunneling),2009,36(9):28−31.
[19] 李根生,黄中伟,李敬彬. 水力喷射径向水平井钻井关键技术研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2017,45(2):1−9. LI Gensheng,HUANG Zhongwei,LI Jingbin. Study of the key techniques in radial jet drilling[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques,2017,45(2):1−9.
[20] 董小龙. 连续油管径向旋转喷射钻进的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2014. DONG Xiaolong. Study on radial rotary jet drilling of coiled tubing[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2014.
[21] 毕刚,李根生,屈展,等. 自进式旋转射流钻头破岩效果[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(5):680−687. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201605012 BI Gang,LI Gensheng,QU Zhan,et al. Rock breaking efficiency of the self–propelled swirling jet bit[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(5):680−687. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201605012
[22] 刘勇,陈长江,刘笑天,等. 高压水射流破岩能量耗散与释放机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(10):2609−2615. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0514 LIU Yong,CHEN Changjiang,LIU Xiaotian,et al. Mechanism on energy dissipation and release of rock breakage with high pressure water jets[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(10):2609−2615. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0514
[23] 林柏泉,王瑞,乔时和. 高压气液两相射流多级脉动破煤岩特性及致裂机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):124−130. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.4305 LIN Baiquan,WANG Rui,QIAO Shihe. Characteristics and mechanism of multistage fluctuation of coal–breaking caused by high–pressure gas–liquid two–phase jet[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(1):124−130. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.4305
[24] 徐洋. 水力喷射径向钻孔工艺射流参数研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2012. XU Yang. Jet parameters research of hydraulic injection radial drilling technology[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2012.
[25] 肖宋强. 自旋转射流流场特性及破煤岩成孔机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. XIAO Songqiang. Flow characteristics and rock–breaking mechanism by water jets generated by a self−rotatory bit[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019.
[26] 雷顺,高富强,王晓卿. 煤体单轴抗压强度统计与分级研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(3):64−70. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.007 LEI Shun,GAO Fuqiang,WANG Xiaoqing. Study on statistics and classification of uniaxial compressive strength of coal[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(3):64−70. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.007
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 武强,朱慧聪,胡辰睿,魏新疆,侯柱平,肖璇,刘学,李俊杰,赵佳,程一帆,杨亮,邢一迪,曾一凡. 我国煤层水害基本架构及发展情势. 煤炭工程. 2024(10): 12-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨忠,李晓龙. 带压开采煤层底板破坏深度研究. 能源与环保. 2022(05): 306-310 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王兴明,刘英锋,南生辉,郭康,尚荣. 奥灰承压水上采场底板沿工作面倾向破坏特征分析. 煤炭科学技术. 2022(12): 206-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 姬东,汪万里,崔风,白振华. 综采放顶煤工作面常见问题及处理方法. 陕西煤炭. 2021(02): 103-106+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 任辰锋. 构建煤矿水害“十位一体”防治技术体系理论与实践. 能源科技. 2021(02): 22-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李晓龙. 煤矿井下水砂突涌钻孔封孔技术研发与应用. 煤田地质与勘探. 2021(04): 192-197 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 赵双全. 层次分析法在工作面底板突水影响因素分析的应用. 现代矿业. 2020(04): 200-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵利军,曹恒,朱马别克·达吾力. 复合隔水条件下煤层群涌水控制因素及对瓦斯赋存的影响. 中国安全生产科学技术. 2020(07): 55-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 曹思文,张民,张振国,朱术云. 下组煤某工作面带压开采奥灰突水危险性探究. 采矿技术. 2020(05): 98-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王高峰. 厚煤层综放开采底板水害探查技术. 自动化应用. 2020(09): 136-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 侯俊华,孟凡贞,冯鲁顺. 东滩煤矿采区构造复杂程度及突水危险性分区对比探究. 现代矿业. 2020(09): 191-194+211 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 王志荣,宋沛,温震洋,陈玲霞. 裂隙性储层水平井起裂行为的控制. 工程科学学报. 2020(11): 1449-1456 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)








 下载:
下载: