-
摘要:
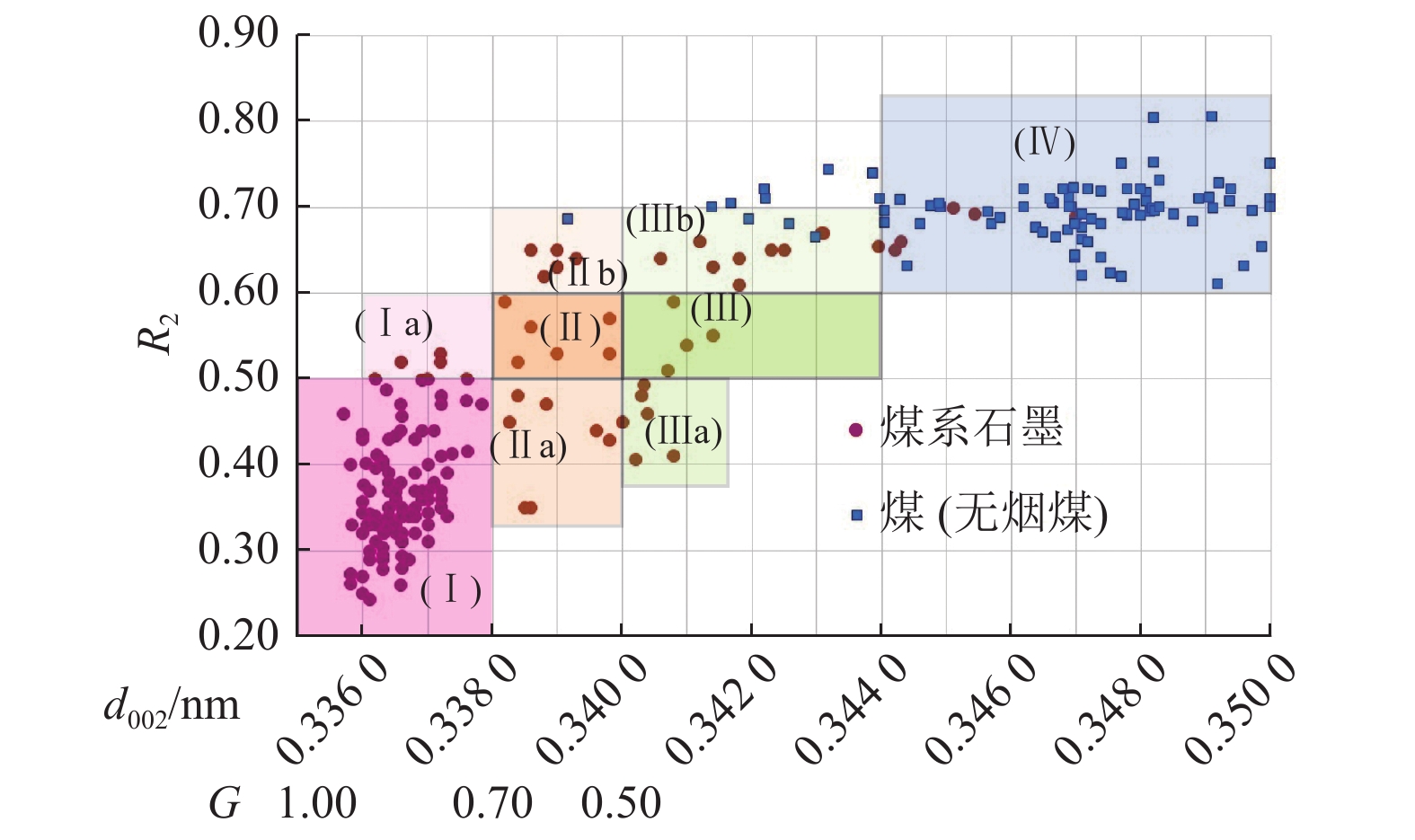
煤系石墨的鉴别及其类型划分,是矿产地质勘查和资源开发利用的前提条件和基础性工作,制定煤系石墨鉴定标准应遵循科学性、系统性、适用性和可操作性的原则。煤石墨化作用与煤化作用是连续递进加跃变的演化过程,煤系石墨的大分子结构阶跃性演化和物质组成非均质性等特点,造成矿种鉴别的复杂性。为制定科学实用的鉴定标准,从成矿机制研究和资源评价需求出发,按照矿石总体石墨化程度由高至低,划分了煤系石墨一号、二号、三号等3种类型;在前期工作的基础上,补充了110多组实测数据,修改完善了由初步鉴定指标和精确鉴定指标构成的煤系石墨鉴定指标体系。初步鉴定指标包括挥发分产率Vdaf和最大反射率Rmax,用于资源评价和地质勘查阶段初步区分煤与煤系石墨;精确鉴定指标包括晶面间距d002及其等效的石墨化度G、拉曼光谱参数R2,用以精确鉴别煤与煤系石墨,并划分煤系石墨类型。基于涵盖我国主要煤系石墨矿山500余组样品实测数据统计分析结果,确定了煤系石墨类型划分指标:煤系石墨一号,0.335 4 nm≤d002<0.338 0 nm(G>0.70)、R2<0.50;煤系石墨二号,0.338 0 nm≤d002<0.340 0 nm(G>0.50~0.70)、R2值范围0.50~0.60;煤系石墨三号,0.340 0 nm≤d002<0.344 0 nm(G>0~0.50),R2值范围0.50~0.60。根据上述指标,建立了煤系石墨鉴定模板,主要煤系石墨矿山样品测试数据表明,该鉴定模版具有实用性和可操作性。
Abstract:The identification and classification of coal-measure graphite are the precondition and basic work of mineral geological exploration, as well as resource exploitation and utilization. The preparation of identification standards of coal-measure graphite should follow the principles of science, systematicness, applicability and operability. Coal graphitization and coalification is a continuous progression plus jump process, and the characteristics of coal-measure graphite, including the step evolution of macromolecular structure and the heterogeneity of material composition, leads to the complexity of ore identification. In order to establish the scientific and practical identification standards, and from the study of metallogenic mechanism and the demand of resource evaluation, coal-measure graphite was divided into three types: No.1, No.2 and No.3, according to the graphitization degree of the ore as a whole ranges from high to low. On the basis of the previous work, more than 110 groups of measured data were added, and the identification index system of coal-measure graphite composed of the preliminary and precise identification indexes was modified and perfected. The preliminary identification indexes, including the volatile yield Vdaf and the maximum reflectivity Rmax, are used to roughly distinguish coal and coal-measure graphite in the stage of resource evaluation and geological exploration. The precise identification indexes, including the interplanar spacing d002, its equivalent graphitization degree G, and Raman spectrum parameter R2, are used to accurately distinguish coal and coal-measure graphite, and to classify the types of coal-measure graphite. Besides, the classification indexes of coal-measure graphite were determined based on the statistical analysis results of the measured data of over 500 groups of samples from the main coal-measure graphite mines in our country, including No.1 coal-measure graphite with 0.335 4 nm ≤ d002 < 0.338 0 nm (G > 0.70) and R2 < 0.50; No.2 coal-measure graphite with 0.338 0 nm ≤ d002 < 0.340 0 nm (G>0.50−0.70) and R, 0.50−0.60; and No. 3 coal-measure graphite with 0.340 0 nm ≤ d002 < 0.344 0 nm (G>0−0.50) and R, 0.50−0.60. Thus, an identification template of coal-measure graphite was established based on the above indexes, which was practical and operable according to the test data of samples from the main coal-measure graphite mines.
-
Keywords:
- coal-measure graphite /
- identification standard /
- index /
- classification /
- identification template
-
电磁随钻测量(EM-MWD)可利用极低频电磁信号将井底的地质和工程参数实时传输到地面,便于掌握钻进工况以及时调整钻井参数,达到辅助控制井眼轨迹的效果[1]。EM-MWD具备结构简单、传输速率高、信号可靠、不受循环介质性质及泵开关状态限制等优势[2-4],在泡沫、空气、欠平衡及漏失地层钻井中发挥着不可替代的作用[5-6]。EM-MWD信号在传输过程中不断衰减,尤其在低电阻率地层流失严重[7],导致其应用效果和测量深度严重受限。近年来,改善EM-MWD应用效果,突破其测量深度限制成为钻探领域的研究热点。
目前,针对提高EM-MWD测量深度的研究主要包括地面信号处理技术[8-9]、延伸天线技术[10-11]、中继传输技术[12-13]和邻井接收信号技术[14]等。其中,信号处理技术提高EM-MWD测量深度的作用有限,未取得突破性进展;延伸天线技术中,设备的装卸复杂费时,成本较高;中继传输技术易受到深井长套管的制约;邻井接收信号对井况要求较高,应用场景有限。B. Peter等[15]提出在套管外敷绝缘涂层以减少信号在地层流失,增大EM-MWD信号传输深度,应用效果较好,但未对套管外敷绝缘涂层适用的地层电阻率范围及涂层特性对信号强度的具体影响规律进行深入研究。
鉴于此,笔者分析了EM-MWD工作原理,建立了套管外敷绝缘涂层后的EM-MWD传输信道有限元模型并进行仿真实验,以确定套管外绝缘涂层适用的地层电阻率范围及绝缘涂层厚度和电阻率对接收信号强度的影响规律,以期为合理运用该技术以优化EM-MWD应用效果进而突破其应用井深提供理论依据。
1 EM-MWD工作原理
EM-MWD主要分为井下信号发射与地面信号接收两部分,其工作原理如图1所示。
采用绝缘短节将井下钻柱隔开,构成发射信号的对称偶极子天线,传感器采集完井下参数后,由井下仪器将参数转化为电信号施加在绝缘短节隔开的上下钻柱上以激发电磁信号[16],电磁信号则通过钻杆、钻井液、套管和地层组成的传输信道传输至地面[17],信号传输轨迹与方向如图1中虚线和箭头所示。地面获取到以钻杆为电极,和距井口一定距离的接地电极接收到的两路信号,二者电势差可表征信号强度,经过地面仪器对信号的滤波、放大和解码等处理,可实现实时获取井下信息以调整井眼轨迹的功能[16]。EM-MWD发射部分激发的超低频信号在传输至地面的过程中,由于地层是开放性介质,对于信号的衰减程度有很大影响。
基于麦克斯韦方程组得到的电磁波趋肤深度公式:
$$ \delta =\sqrt{\frac{\rho }{ {\text{π}} f\mu }} $$ (1) 式中:
$ \delta $ 为趋肤深度,m; f为频率,Hz;ρ为电阻率,Ω·m;μ可近似用真空磁导率来表示,H/m,为定值。由此可得出电磁波传输深度主要受控于信号频率和传播介质电阻率。在EM-MWD的应用中,基于前人的研究成果,地层电阻率过低与过高都不利于电磁信号的传输,其中,地层电阻率越小,信号衰减越严重[7],即电磁信号易经套管引导泄漏进入低电阻率地层中,导致地面的接收信号强度微弱。本文基于传播介质电阻率较低的情况,针对套管外绝缘涂层特性对EM-MWD信号的增强效果展开研究,信号频率不参与讨论。
2 仿真模型建立与求解
2.1 模型建立
在建立模型前,作出如下假设:地层为仅有水平分层的均质地层;钻杆、套管和井眼轴线重合;钻杆、套管及地层等以井眼轴线对称;钻柱全部为钻杆。以底部钻杆内侧作为坐标系原点,分别建立了钻杆、绝缘短节、环空钻井液、套管、套管外绝缘涂层及水平分层地层。模型如图2所示。
基于ANSYS有限元分析软件建立仿真模型,综合考虑实际钻井参数、有限元模型计算精度及EM-MWD中绝缘短节常用长度及位置,整个模型长宽均设为2 000 m,井深2 000 m,下部钻杆长10 m,绝缘短节长1 m,钻杆壁厚2 cm,环空厚度5 cm,套管深1 800 m,套管壁厚3 cm,套管外绝缘涂层厚度2 mm,其长度与所应用的地层厚度一致,即敷满所应用地层的套管外。为研究套管外绝缘涂层在不同电阻率地层的应用效果,将地层水平分为深度不等的4层。地层厚度的设计一方面考虑到地层的不均匀分层,另一方面侧重于信号传输流经的主要地层,地层1为地表层,地层4为信号发射所在地层,故将这两处地层设计的较薄,地层2与地层3作为信号传输的主要地层,故设计成较厚的地层。4层地层厚度由上至下分别为200、800、600、400 m。
模型中各介质电阻率的设置参考常见介质电阻率,见表1。绝缘材料电阻率范围人为可控,将绝缘短节与套管外绝缘涂层电阻率设置为1×107 Ω·m。钻柱、套管制造材料主要为钢材,电阻率值设为1×10−7 Ω·m。钻井液电阻率以应用较广泛的水基钻井液电阻率为参考,取值为1 Ω·m。为分析不同电阻率地层的电势分布,地层电阻率的设置以常见的岩石电阻率为参考,并考虑到实验对不同电阻率地层的要求。将中部的地层2作为低电阻率地层,电阻率设为0.1 Ω·m,其相邻地层取较高的电阻率,地层1电阻率设为100 Ω·m,地层3电阻率设为20 Ω·m,地层4套管下入较浅,且为信号源发射所在地层,电阻率取中间数量级,为1 Ω·m。
表 1 常见介质电阻率Table 1. Resistivities of common medium介质 电阻率/(Ω·m) 钢铁 9.78×10−8 钻井液 10−1~105 黏土 0.1~10 煤层 20~106 页岩 50~200 砂岩 10~1000 上述各地层电阻率、套管外绝缘涂层厚度及电阻率均为初始值,在下文实验设计中若作自变量时将不断改变。
2.2 网格划分
有限元仿真模型中,网格划分与计算结果的精度和效率密切相关[18]。网格单元设置为PLANE230单元,钻杆、绝缘短节、钻井液、套管和绝缘涂层与整个模型相差几个数量级,采用小单元尺寸以保证网格精密,并对绝缘短节与绝缘涂层区域网格进行加密。对于大面积的地层模块,则采用较稀疏的大尺寸网格以提高计算效率。仿真模型网格疏密分布如图3所示。
2.3 电压加载与求解
在绝缘短节处的上部钻杆和下部钻杆上施加电势差为1 V的电压载荷,采用直接求解方法,求解后在后处理模块中获得不同实验条件下的地层电势云图及模型各节点的电势数据,取地面处钻杆的电势及距钻杆100 m处地面(接收电极处)的电势作为地面接收到的两路信号。两路电势差为恒压发射下地面接收信号强度,EM-MWD在应用时一般为恒功率发射,故将实验数据换算为5 W恒功率下的电势差,以表征地面接收信号强度。
3 仿真结果分析
3.1 绝缘涂层对地层中电势分布影响
图4为无套管外绝缘涂层的地层电势云图,从蓝色区域到红色区域,电势逐渐升高。由图可知,高电势从绝缘短节上部沿钻杆向地面传播,但在地层2处,高电势向地层中扩散。将地层2处的套管外敷绝缘涂层后,得到图5的地层电势分布图,可见高电势沿钻杆向地面传播过程中,始终集中在井眼附近,而地层中电势较低。
这是因为:信号沿低电阻率的钻杆从井底传向井口,高电势主要分布在井眼周围,但由于地层2电阻率较低,仅为0.1 Ω·m,高电势在此处向地层中大幅流失。在地层2处套管外敷绝缘涂层后,高电势流经此处时受到高电阻率的绝缘涂层阻隔,因此被收束在井眼附近,避免了地面无法接收到有效信号的问题。
3.2 绝缘涂层在不同地层中应用效果
将套管外绝缘涂层分别应用在信号流经的主要地层(地层1、地层2、地层3)套管外敷上绝缘涂层,长度与所应用地层的厚度一致,并分别以绝缘涂层所应用的地层的电阻率为自变量(当某地层电阻率作自变量时,其余地层电阻率保持初始值不变),得到绝缘涂层在不同地层应用时地面接收信号强度的变化,如图6所示。
由图6可见,所有曲线都呈先升高后降低的趋势,在各地层套管外应用绝缘涂层得到的信号强度曲线均高于未应用绝缘涂层的曲线,随着地层电阻率增大,绝缘涂层对信号的增强作用(同色曲线差值)呈先略微增大,后快速减小的趋势,当地层电阻率超过1×103 Ω·m时,套管外绝缘涂层对信号的增强效果保持稳定。
在地层电阻率较低时,信号衰减严重,而地层电阻率较大会导致电磁波难以注入到地层中[7],故图6中曲线均呈现先升高后降低的趋势。在3个地层中应用套管外敷绝缘涂层均能在一定程度上增强接收信号,但由于地层2和地层3电阻率较大,有无绝缘涂层对信号强度的影响较小,而地层2是电阻率最小的地层,套管外绝缘涂层在此地层套管外应用时,信号的增强效果显著优于其他地层。随着地层电阻率增大,同色曲线差值呈先略微增大,后快速减小的趋势,这是因为:绝缘涂层对信号的阻隔作用可减少其在低电阻率地层的大幅流失,对地面接收信号的增强幅度明显,但由于地层电阻率过低,信号仍然存在一定衰减,故随地层电阻率增大,绝缘涂层对信号的增强幅度也略有增大,而高电阻率地层本身可避免信号大幅衰减,绝缘涂层进一步增强信号的作用有限,因此在地层电阻率较高时其应用效果不佳,导致同色曲线差值快速减小。
3.3 绝缘涂层电阻率对信号强度的影响
分别在各地层套管外敷绝缘涂层并改变涂层电阻率,得到接收信号强度随套管外绝缘涂层电阻率变化的趋势,如图7所示。
由图7可得,接收信号强度随绝缘涂层电阻率的增大而增大,但绝缘涂层电阻率大于1×104 Ω·m时,对接收信号的增强效果才较为明显;当绝缘涂层电阻率达到1×107 Ω·m时,地面接收信号强度达到峰值,之后几乎不再继续增强;此外,绝缘涂层在地层2套管外应用时,对信号的增强作用同样显著优于其他地层。
涂层电阻率需达到一定值才能起到绝缘作用,达到阻隔信号大量流入地层的效果。信号除了在低电阻率地层流失,也会在传输过程中产生不可避免的损耗,因此,绝缘涂层对信号的增强作用是有一定限度的。
3.4 绝缘涂层厚度对信号强度的影响
分别在各地层套管外敷绝缘涂层并改变涂层厚度,得到接收信号强度随套管外绝缘涂层厚度变化的趋势,如图8所示。
由图8可得,接收信号强度随绝缘涂层厚度的增大而增大,但当绝缘涂层厚度达到7 mm时,地面接收信号强度趋于稳定,几乎不再随涂层厚度继续增强,且绝缘涂层在地层2套管外的应用效果依旧显著优于其他地层。
套管外绝缘涂层越厚,对信号的阻隔效果越好,但当厚度达到一定值,绝缘涂层对接收信号的增强效果达到峰值,信号强度便逐渐趋于稳定。
3.5 绝缘涂层长度对信号强度的影响
基于上述仿真结果,绝缘涂层在低电阻率地层有较为明显的效果。因此,针对低电阻率的地层2,在套管外分别由上向下和由下至上敷绝缘涂层,并逐渐增加绝缘涂层长度,得到接收信号强度随套管外绝缘涂层长度变化的趋势,如图9所示。
由图9可见,接收信号强度随套管外绝缘涂层长度的增加而增加,至敷满地层2处套管时达到最强,且在地层2处由下至上在套管外敷绝缘涂层效果略微好于由上至下,但总体基本一致,这是因为地层2底部离发射源较近,电磁信号更强,因此由下至上敷绝缘涂层对信号的增强略微明显于由上至下,但信号衰减的主控因素是无涂层的低电阻率地层的厚度,电磁信号会在未涂绝缘层的那部分地层流失,因而两条曲线趋势基本一致。在应用中,为保证绝缘涂层对EM-MWD信号的增强效果,应将绝缘涂层长度与低电阻率地层段的长度保持一致。
从整体来看,不同电阻率和不同厚度的套管外绝缘涂层在低电阻率的地层2中的应用效果都显著强于其他地层。在现场应用中,要考虑到绝缘涂层适用地层、涂层工艺和成本等因素,确定套管外涂绝缘层最佳厚度、电阻率和长度。
4 结 论
a. 建立了有限元仿真模型,并探明了套管外绝缘涂层技术适用地层以及该技术关键参数对EM-MWD接收信号强度的影响规律,为优化EM-MWD应用效果及突破其测量井深限制提供了一种新思路,对套管外绝缘涂层技术的现场应用具有指导意义。
b. 根据模拟仿真的结果,套管外绝缘涂层在较低电阻率的地层中应用可有效减少EM-MWD信号的衰减,显著增强地面接收信号。接收信号随套管外绝缘涂层电阻率的增大而呈现先微弱增强,后快速增强,最后保持稳定的趋势;随涂层厚度增加,接收信号逐渐增强,随后保持稳定;在低电阻率地层应用中,接收信号随套管外绝缘涂层长度的增加而不断增强。
c. 基于以上初步成果,后续将开展室内实验、现场试验及更深入的研究工作,为套管外绝缘涂层技术的合理运用提供更可靠的指导意见。
-
表 1 煤系石墨测试分析方法
Table 1 Testing and analysis methods of coal-measure graphite
大类 方法 成分分析 (1) 光学显微镜观察:石墨组分鉴别
(2) 工业分析:固定碳、挥发分
(3) 元素分析:C、H结构分析 (1) 反射率测试
(2) X射线衍射分析
(3) 激光拉曼光谱分析
(4) 扫描电镜
(5) 透射电镜物化性质分析 电学性质、热分析、密度、孔隙率、机械
性质等表 2 煤系石墨鉴定指标
Table 2 Identification index of coal-measure graphite
类型 初步鉴定指标 精确鉴定指标 Vdaf/% Rmax/% d002/nm 石墨化度G① R2② 煤系
石墨一号 <5.0 >6.0 <0.3380~0.3354 >0.70 <0.50 二号 <0.3400~0.3380 >0.50~0.70 0.50~0.60 三号 <0.3440~0.3400 >0~0.50 煤 ≥0.3440 ≤0 >0.60 注:① G=(0.3440 nm−d002)/(0.3440 nm−0.3354 nm);② R2=AD1/(AD1+AD2+AG),其中AD1、AD2、AG分别为D1、D2和G峰面积。 -
[1] 孙升林,吴国强,曹代勇,等. 煤系矿产资源及其发展趋势[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2014,26(11):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.11.01 SUN Shenglin,WU Guoqiang,CAO Daiyong,et al. Mineral resources in coal measures and development trend[J]. Coal Geology of China,2014,26(11):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.11.01
[2] 曹代勇,张鹤,董业绩,等. 煤系石墨矿产地质研究现状与重点方向[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(5):317−327. CAO Daiyong,ZHANG He,DONG Yeji,et al. Research status and key orientation of coal−based graphite mineral geology[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2017,24(5):317−327.
[3] 曹代勇,王路,刘志飞,等. 我国煤系石墨研究及资源开发利用前景[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.001 CAO Daiyong,WANG Lu,LIU Zhifei,et al. The research status and prospect of coal–based graphite in China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):1−11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.001
[4] 王德利,任辉,张宇航,等. 我国煤系石墨资源开发利用现状及对策建议探讨[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2022,34(6):8−10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.06.02 WANG Deli,REN Hui,ZHANG Yuhang,et al. Probe into coal measures graphite resources exploitation and utilization status quo in China and countermeasures proposal[J]. Coal Geology of China,2022,34(6):8−10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.06.02
[5] 董业绩,曹代勇,王路,等. 地质勘查阶段煤系石墨与无烟煤的划分指标探究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(1):8−12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.01.002 DONG Yeji,CAO Daiyong,WANG Lu,et al. Indicators for partitioning graphite and anthracite in coal measures during geological exploration phase[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(1):8−12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.01.002
[6] CAO Daiyong,ZHANG He,DONG Yeji,et al. Nanoscale microscopic features and evolution sequence of coal–based graphite[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2017,17(9):6276−6283. DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2017.14403
[7] LI Kuo,RIMMER S M,LIU Qinfu. Geochemical and petrographic analysis of graphitized coals from central Hunan,China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,195:267−279. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.06.009
[8] 刘钦甫,袁亮,李阔,等. 不同变质程度煤系石墨结构特征[J]. 地球科学,2018,43(5):1663−1669. LIU Qinfu,YUAN Liang,LI Kuo,et al. Structure characteristics of different metamorphic grade coal−based graphites[J]. Earth Science,2018,43(5):1663−1669.
[9] WANG Lu,CAO Daiyong,PENG Yangwen,et al. Strain−induced graphitization mechanism of coal−based graphite from Lutang,Hunan Province,China[J]. Minerals,2019,9(10):617. DOI: 10.3390/min9100617
[10] 冯杨伟,吕录仕. 陕西凤县石炭系煤系石墨矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国煤炭,2018,44(7):44−48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2018.07.008 FENG Yangwei,LYU Lushi. Analysis of geological characteristics and genesis of Carboniferous coal–based graphite deposit in Fengxian County,Shaanxi Province[J]. China Coal,2018,44(7):44−48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2018.07.008
[11] 王路,曹代勇,丁正云,等. 闽西南地区煤成石墨的控制因素与成矿区带划分[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(8):2865−2871. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0690 WANG Lu,CAO Daiyong,DING Zhengyun,et al. Controlling factors and metallogenic belts of coal−based graphite in the south−western Fujian Province[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(8):2865−2871. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0690
[12] 丁正云,曹代勇,王路,等. 福建漳平可坑矿区煤系石墨赋存规律研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(2):198−205. DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.02.018 DING Zhengyun,CAO Daiyong,WANG Lu,et al. Study on occurrence regularity of coal–based graphite in Kekeng mining area in Zhangping,Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(2):198−205. DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.02.018
[13] 李阳,王路,曹代勇,等. 江西崇义矿煤成石墨的发现及其地质意义[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(5):79−85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.011 LI Yang,WANG Lu,CAO Daiyong,et al. The discovery and geological significance of coal–formed graphite in Chongyi coal mine in Jiangxi Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(5):79−85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.011
[14] 陈泉霖,程乔,邓瑞锦,等. 福建煤系石墨资源状况和开发前景[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):12−17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.002 CHEN Quanlin,CHENG Qiao,DENG Ruijin,et al. Status and development prospect of the coal−based graphite resources in Fujian Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):12−17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.002
[15] 莫佳峰,赵训林,朱文卿,等. 湖南省煤系石墨成矿规律与找矿方向探讨[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):18−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.003 MO Jiafeng,ZHAO Xunlin,ZHU Wenqing,et al. Metallogenic law and prospecting direction of coal−based graphite in Hunan Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):18−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.003
[16] 程乔,陈泉霖,曹代勇,等. 福建省煤系石墨成矿模式初步探讨[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2021,33(11):11−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.11.03 CHENG Qiao,CHEN Quanlin,CAO Daiyong,et al. Preliminary discussion on coal measures graphite minerogenic mode in Fujian Province[J]. Coal Geology of China,2021,33(11):11−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.11.03
[17] 曹代勇,魏迎春,李阳,等. 煤系石墨鉴别指标厘定及分类分级体系构建[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1833−1846. CAO Daiyong,WEI Yingchun,LI Yang,et al. Determination of identification index and construction of classification and classification system of coal measures graphite[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(6):1833−1846.
[18] 曹代勇,刘志飞,王安民,等. 构造物理化学条件对煤变质作用的控制[J]. 地学前缘,2022,29(1):439−448. DOI: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.12.11 CAO Daiyong,LIU Zhifei,WANG Anmin,et al. Control of coal metamorphism by tectonic physicochemical conditions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2022,29(1):439−448. DOI: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.12.11
[19] 秦勇. 中国高煤级煤的显微岩石学特征及结构演化[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 1994. [20] KWIECIŃSKA B,PETERSEN H I. Graphite,semi−graphite,natural coke,and natural char classification:ICCP system[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2004,57:99−116. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2003.09.003
[21] RODRIGUES S,MARQUES M,SUÁREZ–RUIZ I,et al. Microstructural investigations of natural and synthetic graphites and semi–graphites[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2013,111:67−79. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.06.013
[22] BUSECK P R,BEYSSAC O. From organic matter to graphite:Graphitization[J]. Elements,2014,10(6):421−426. DOI: 10.2113/gselements.10.6.421
[23] CAO Daiyong,WANG Lu,DING Zhengyun,et al. Characterization of the heterogeneous evolution of the nanostructure of coal–based graphite[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2021,21(1):670−681. DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2021.18726
[24] 王路. 煤系石墨的构造–热成矿机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2020. WANG Lu. Study on the tectonic–thermal metallogenic mechanism of the coal–based graphite[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2020.
[25] 李久庆,秦勇,陈义林. 超无烟煤中石墨微晶产出状态与成因[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):27−33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.004 LI Jiuqing,QIN Yong,CHEN Yilin. Occurrence and origin of graphite microcrystal in meta–anthracite[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):27−33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.004
[26] 李阔,刘钦甫,张帅,等. 煤系石墨显微组分与结构特征[J]. 矿物学报,2021,41(1):101−108. LI Kuo,LIU Qinfu,ZHANG Shuai,et al. Characteristics of microscopically distinguishable components and structures of the coaly graphite[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2021,41(1):101−108.
[27] 曹代勇, 宁树正, 郭爱军, 等. 中国煤田构造格局与构造控煤作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017. [28] 杨起, 吴冲龙, 汤达祯, 等. 中国煤变质作用[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1996. [29] OBERLIN A. Carbonization and graphitization[J]. Carbon,1984,22(6):521−541. DOI: 10.1016/0008-6223(84)90086-1
[30] 郑辙. 煤基石墨微结构的高分辨电镜研究[J]. 矿物学报,1991,11(3):214−218. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.03.004 ZHENG Zhe. HRTEM studies of microstructures of coal–based graphite[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1991,11(3):214−218. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.03.004
[31] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中国煤炭分类: GB/T 5751—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [32] International Standard. Classification of coals: ISO 11760: 2018[S]. Switzerland: ISO Copyright Office, 2018.
[33] FRANKLIN R E. The structure of graphitic carbons[J]. Acta Crystallographica,1951,4(3):253−261. DOI: 10.1107/S0365110X51000842
[34] 李焕同,曹代勇,张卫国,等. 高煤级煤石墨化轨迹阶段性的XRD和Raman光谱表征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(8):2491−2498. LI Huantong,CAO Daiyong,ZHANG Weiguo,et al. XRD and Raman spectroscopy characterization of graphitization trajectories of high−rank coal[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021,41(8):2491−2498.
-
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 杨烨,许强,李娟,姜雅怡. 二连盆地伊和高勒地区赛汉组砂岩型铀成矿条件. 铀矿地质. 2024(02): 216-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 来强,张欣熠,韩效忠,谷懿. 无人直升机航空伽马能谱测量在砂岩型铀矿调查评价中的应用. 内蒙古石油化工. 2024(05): 1-5 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蒋喆,韩效忠,胡航,来强,郭鹏,李紫楠. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗恩格日音铀矿床Th地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的指示. 地质通报. 2024(06): 926-937 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周舰,李占春,王常东,林天发,唐国龙,余弘龙,于兵,吴燕清,董小宇. 二连盆地乌尼特坳陷砂岩型铀成矿古水文地质条件分析. 矿产勘查. 2024(S1): 390-399 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘晓雪,赵丽君,俞礽安,汤超. 二连盆地陆海地区砂岩型铀矿岩石地球化学特征及地质意义. 华北地质. 2024(03): 36-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 董燕,王美玲,陈彬,时志强. 中国北方侏罗系烧变岩露头区白色砂岩特征与成因分析. 古地理学报. 2024(06): 1325-1337 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 许强,秦明宽,李娟,杨烨,李西得,林效宾. 二连盆地伊和高勒地区下白垩统赛汉组沉积特征. 铀矿地质. 2022(01): 1-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 韩效忠,林中湘,吴兆剑,蒋喆,殷栋法,王行军,季辉. 中—新生代盆地煤铀协同勘查及对策建议. 地质论评. 2022(03): 945-954 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 蒋喆,韩效忠,胡航,来强,郭鹏. 二连盆地恩格日音砂岩型铀矿床U-Ra平衡特征、影响因素及其地质意义. 中国煤炭地质. 2022(10): 37-42+59 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘鑫扬. 二连盆地砂岩型铀矿找矿方向探讨. 铀矿地质. 2021(01): 51-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 潘宏峰,刘成东,万建军,赵严. 内蒙古巴彦乌拉铀矿床地质特征. 中国金属通报. 2021(04): 116-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 林效宾,李西得,刘武生. 二连盆地铀矿床成矿类型及时空分布特征. 铀矿地质. 2021(06): 1013-1026 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 俞礽安,吴兆剑,司马献章,韩效忠,李紫楠,文思博,涂家润. 二连盆地马尼特坳陷南缘赛汉塔拉组砂岩碎屑锆石年龄及其地质意义. 地球科学. 2020(05): 1609-1621 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 蒋喆,韩效忠,胡航,吴兆剑,李紫楠,来强,郭鹏. 二连盆地恩格日音砂岩型铀矿床地质特征及成矿作用初探. 大地构造与成矿学. 2020(04): 742-753 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 吴兆剑,韩效忠,林中湘,李紫楠,季辉,殷栋法,蒋喆,胡航. 中国北方主要中新生代盆地构造沉积气候演化及其成煤、铀意义. 大地构造与成矿学. 2020(04): 710-724 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 韩效忠,吴兆剑,林中湘,蒋喆,胡航,殷栋法,季辉,李紫楠. 浅论中国北方主要产铀盆地含矿目标层沉积相对砂岩型铀矿的制约. 大地构造与成矿学. 2020(04): 697-709 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 杨崇根. 二连盆地马尼特坳陷铀成矿地质条件分析. 甘肃科技. 2020(24): 10-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)








 下载:
下载: