Vertical variability of hydrogeological characteristics of Luohe Formation by double packer system pumping test
-
摘要:
为了精细探查鄂尔多斯盆地巨厚洛河组水文地质条件并定量评价其含水层段富水性垂向变异特征,提出采用导水系数进行含水层富水性评价,给出了导水系数法富水性7级分级标准;采用双Packer系统对陕西高家堡井田DJ1、DJ2钻孔洛河组垂向10个固定厚度层段进行抽水试验并计算水文地质参数,采用综合富水性指数法对洛河组垂向分层并对比分析其垂向分层水文地质特征。结果显示:(1) 提出导水系数富水性分级标准,即T≤1 m2/d、1 m2/d<T≤10 m2/d、10 m2/d<T≤50 m2/d、50 m2/d<T≤100 m2/d、100 m2/d<T≤200 m2/d、200 m2/d<T≤400 m2/d、T>400 m2/d依次表示富水性极弱、弱、中等、强、很强、特强、极强。(2) 采用综合富水性指数法将洛河组垂向上划分为上段、中上段、中下段和下段4个含水层段。(3) 洛河组垂向分层水文地质特征存在差异。中上段和中下段厚度相对较大,分别为122.20~124.30 m和113.30~148.70 m,岩性以砂岩类地层为主,渗透系数K分别为0.598 9~0.708 5 m/d和0.111 5~0.211 5 m/d,导水系数T分别为65.60~116.94 m2/d和11.05~30.89 m2/d,均相对较大,富水性中等至很强,为主要含水层段;上段和下段厚度相对较小,分别为20.45~35.20 m和57.60~91.19 m,岩性为砂泥岩互层,渗透系数K分别为0.064 6 m/d和0.005 1~0.009 0 m/d,导水系数T分别为1.58 m2/d和0.34~0.66 m2/d,均相对较小,富水性极弱至弱,为次要含水层段。(4)导水系数在多个含水层段之间具有确定的换算关系,采用导水系数法评价显示洛河组含水层段富水性在垂向上存在显著差异,现场应用效果良好。
Abstract:To investigate the hydrogeological conditions of the thick Luohe Formation in Ordos Basin and quantitatively evaluate vertical variation characteristics of its aquifer’ s water-rich, proposes the method of using the coefficient of transmissibility to evaluate the water-rich of the aquifer, and give the seven level classification standard of water-rich by the method of determining coefficient of transmissibility. The double-packer system was used to carry out the pumping tests of 10 vertical sections of fixed thickness of the Luohe Formation in the DJ1 and DJ2 boreholes in the Gaojiabao mine field, shaanxi, and the hydrogeological parameters were calculated. Using the comprehensive water-rich index method to stratify the Luohe Formation vertically and analyze its hydrogeological characteristics vertically. The results show that: (1) The water-rich standards of coefficient of transmissibility are given; when T≤1 m2/d, 1 m2/d<T≤10 m2/d, 10 m2/d<T≤50 m2/d, 50 m2/d<T≤100 m2/d, 100 m2/d<T≤200 m2/d, 200 m2/d<T≤400 m2/d and T>400 m2/d, the water-rich is very weak, weak, medium, strong, very strong, especially strong, and extremely strong. (2) The Luohe Formation is vertically divided into four aquifers including the upper, middle-upper, middle-lower and lower aquifers by the comprehensive water-rich index method. (3) The Luohe Formation vertical hydrogeological characteristics are different. The middle-upper and middle-lower formation are the main aquifers, which are dominated by sandstone strata and relatively thick (122.20-124.30 m and 113.30-148.70 m, respectively), the permeability coefficient K (0.598 9-0.708 5 m/d and 0.111 5-0.211 5 m/d, respectively) and coefficient of transmissibility T (65.60-116.94 m2/d and 11.05-30.89 m2/d, respectively) have relatively large values, and the water-rich are from medium to very strong; The upper and lower formation are the secondary aquifers, which are dominated by sand-mudstone strata and relatively small (20.45-35.20 m and 57.60-91.19 m, respectively), the permeability coefficient K (0.064 6 m/d and 0.005 1-0.009 0 m/d, respectively) and coefficient of transmissibility T (1.58 m2/d and 0.34-0.66 m2/d, respectively) have relatively small values, and the water-rich are from very weak to weak. (4) The coefficient of transmissibility has a definite calculation relationship among multiple aquifers. The coefficient of transmissibility method is used to evaluate the vertical water-rich of the Luohe Formation, and there are significant differences. Therefore, the application was successful.
-
-
表 1 导水系数富水性分级标准
Table 1 Classification standard of water-rich by coefficient of transmissibility
含水层富水性等级 导水系数T/(m2·d−1) 极弱 T≤1 弱 1<T≤10 中等 10<T≤50 强 50<T≤100 很强 100<T≤200 特强 200<T≤400 极强 T>400 表 2 抽水试验工程量统计
Table 2 Completion of pumping tests
类型 孔号 层位 抽水次数 完整井
抽水DJ1 洛河组 1 DJ2 洛河组 1 DJ4 洛河组 1 DJ4 直罗组和延安组 1 非完整
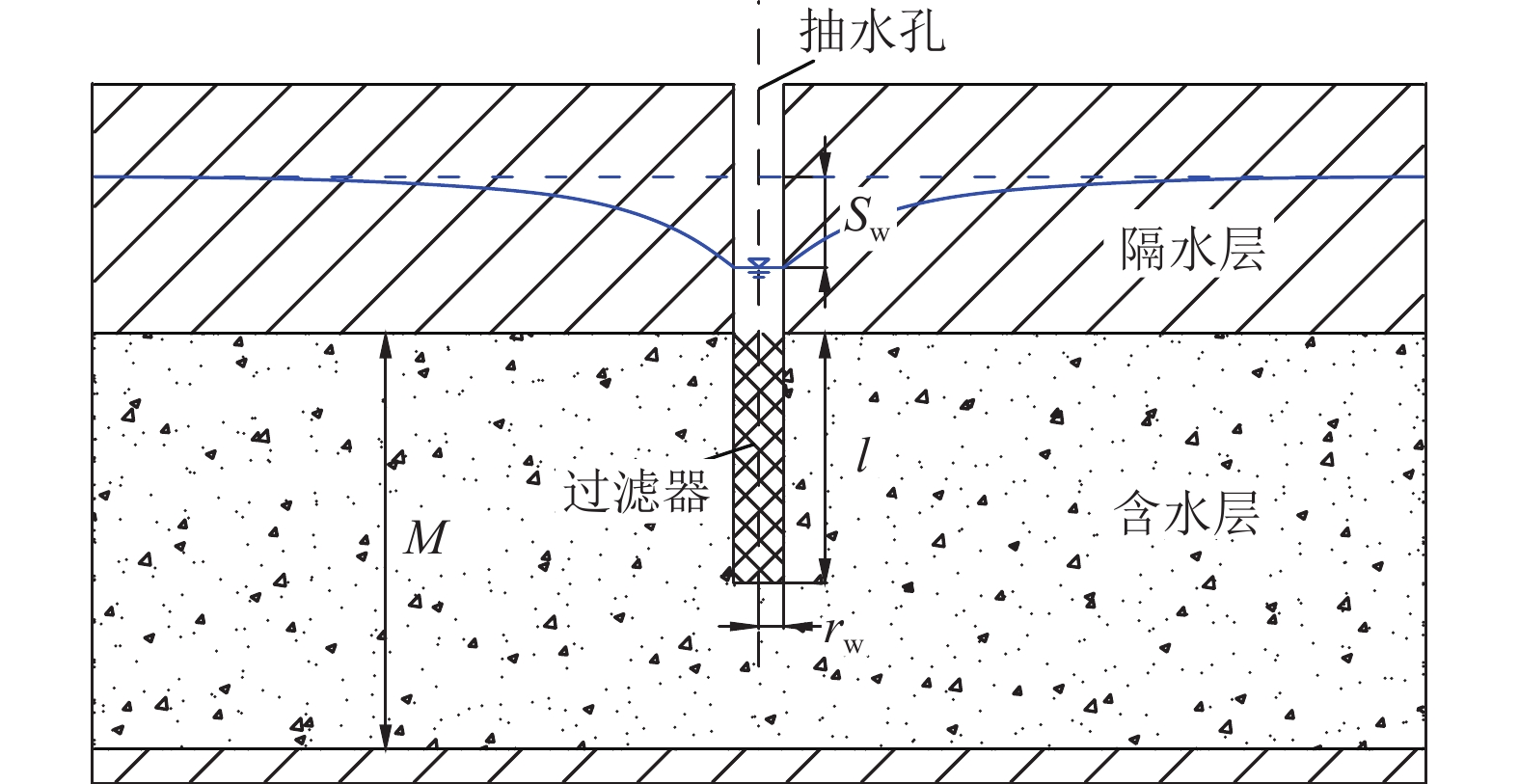
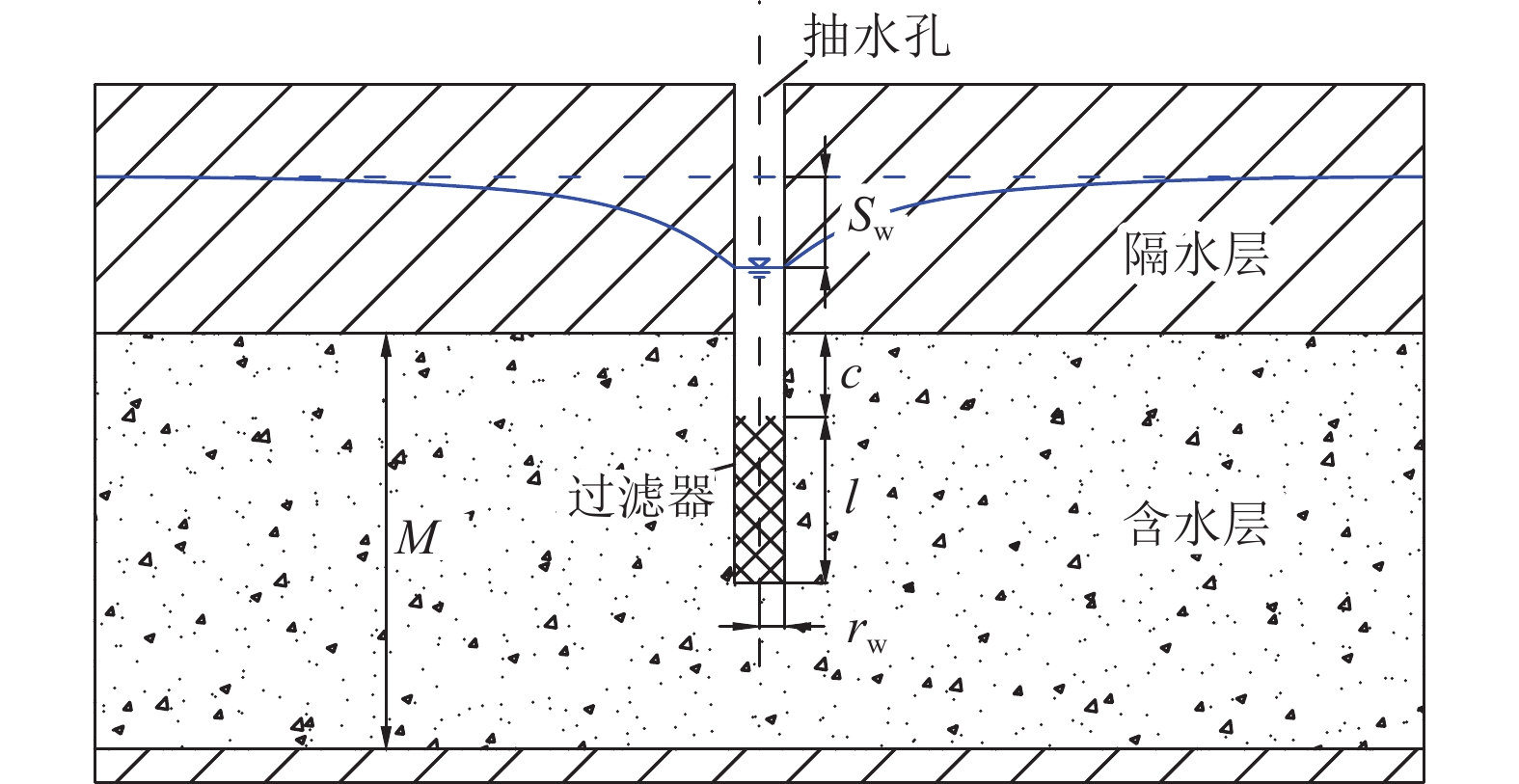
井抽水DJ3 洛河组上部层段 1 DJ3 洛河组下部层段 1 双Packer
分层抽水
(非完整井)DJ1 洛河组10个层段 10 DJ2 洛河组上部8个层段 8 DJ3 洛河组下部2个层段 2 合计 26 注:DJ2孔第9、第10层抽水试验变更至DJ3孔完成。 表 3 DJ1、DJ2/DJ3钻孔双Packer分层抽水试验成果
Table 3 Results of pumping tests using the double packer in DJ1, DJ2/DJ3 boreholes
钻孔 序号 抽水层段 孔径
/m初始水位
埋深/m恢复水位
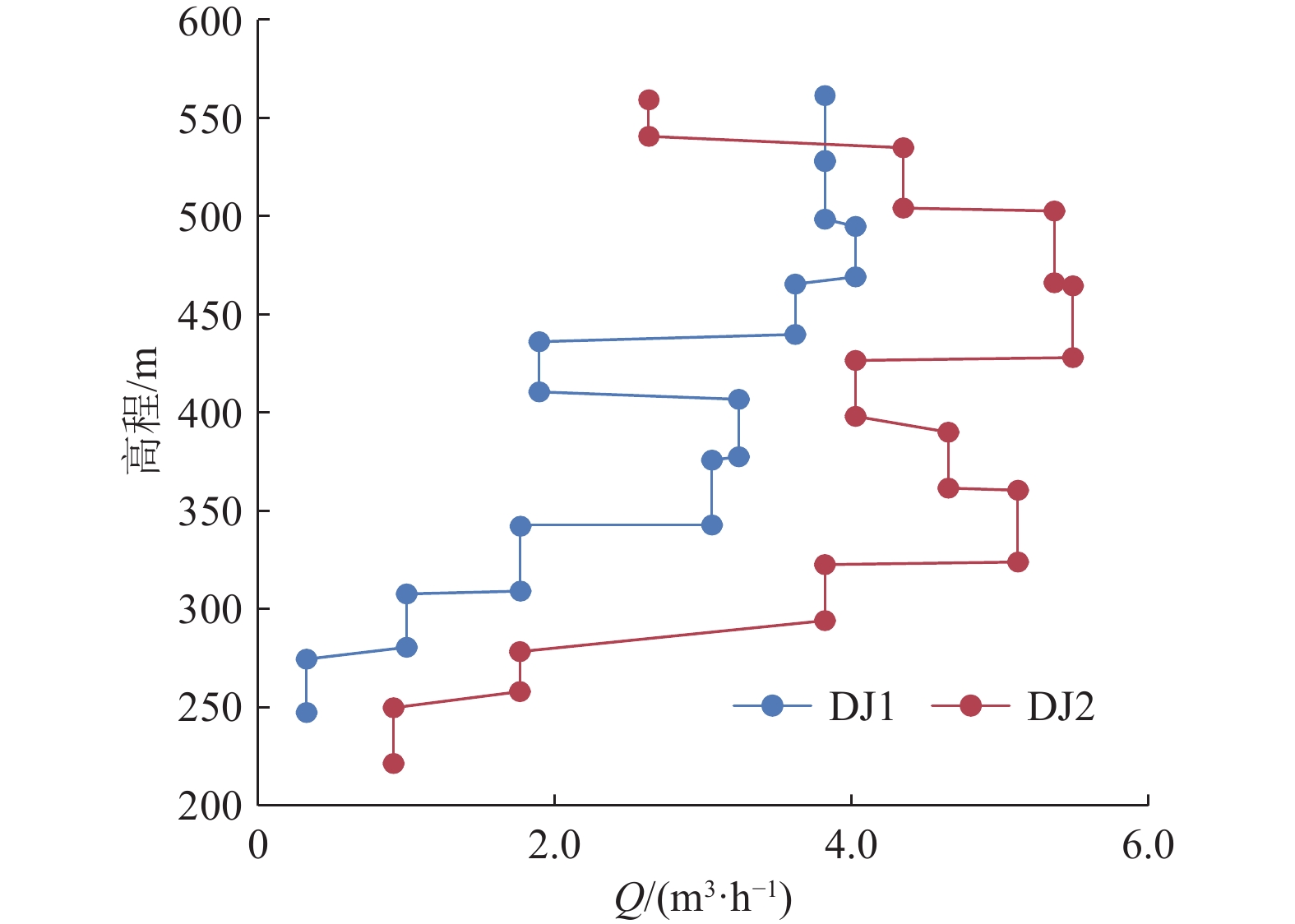
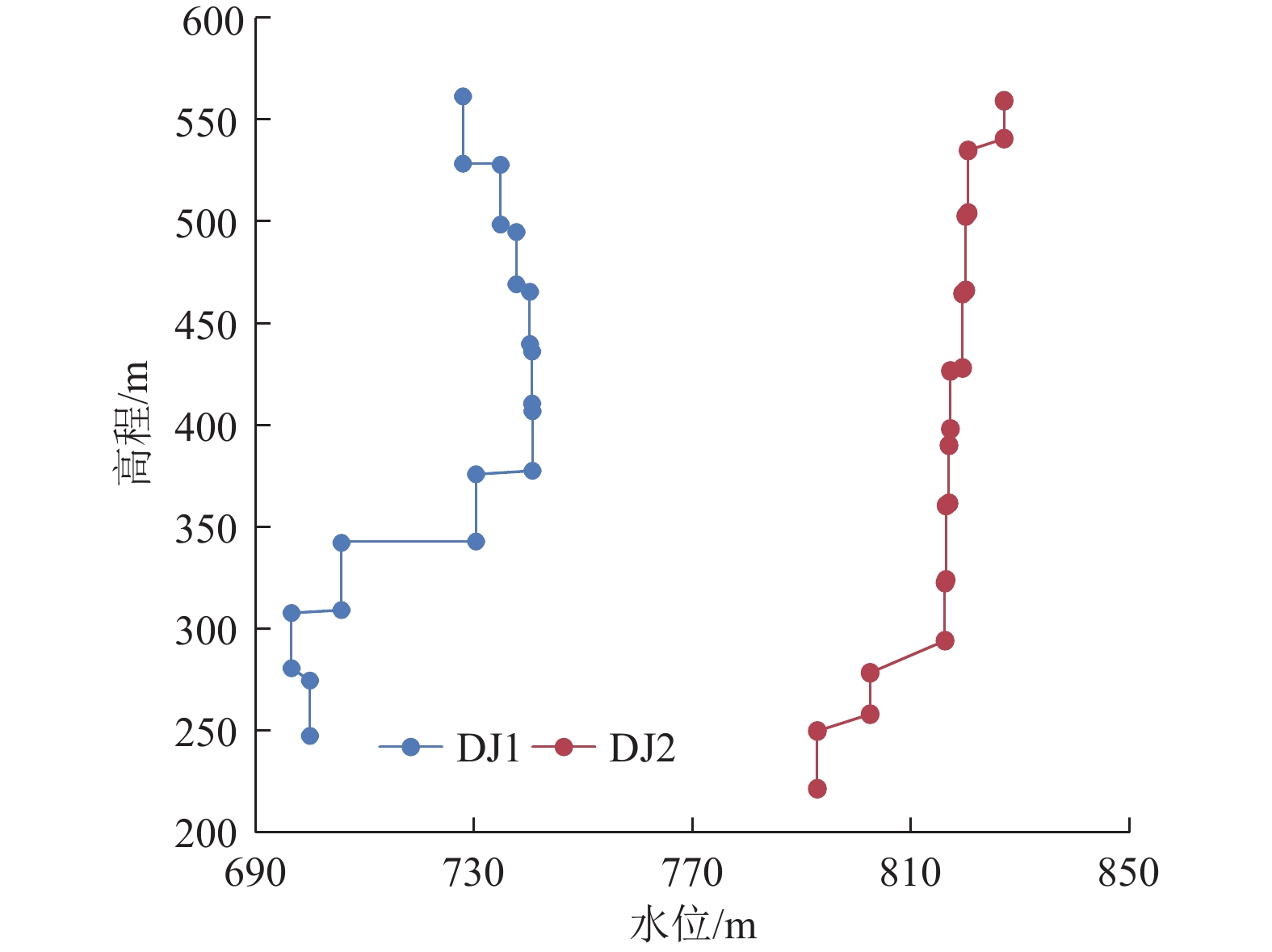
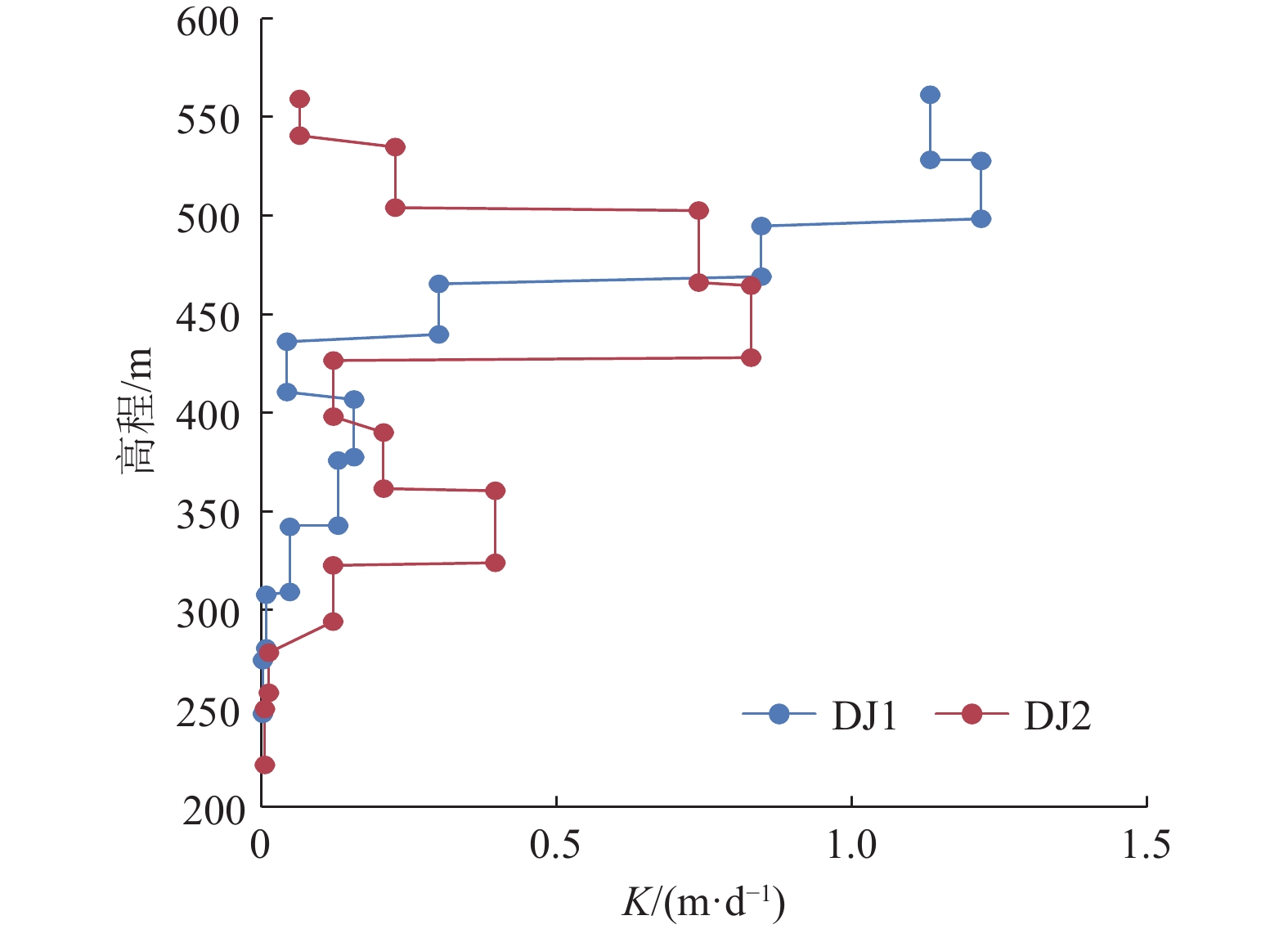
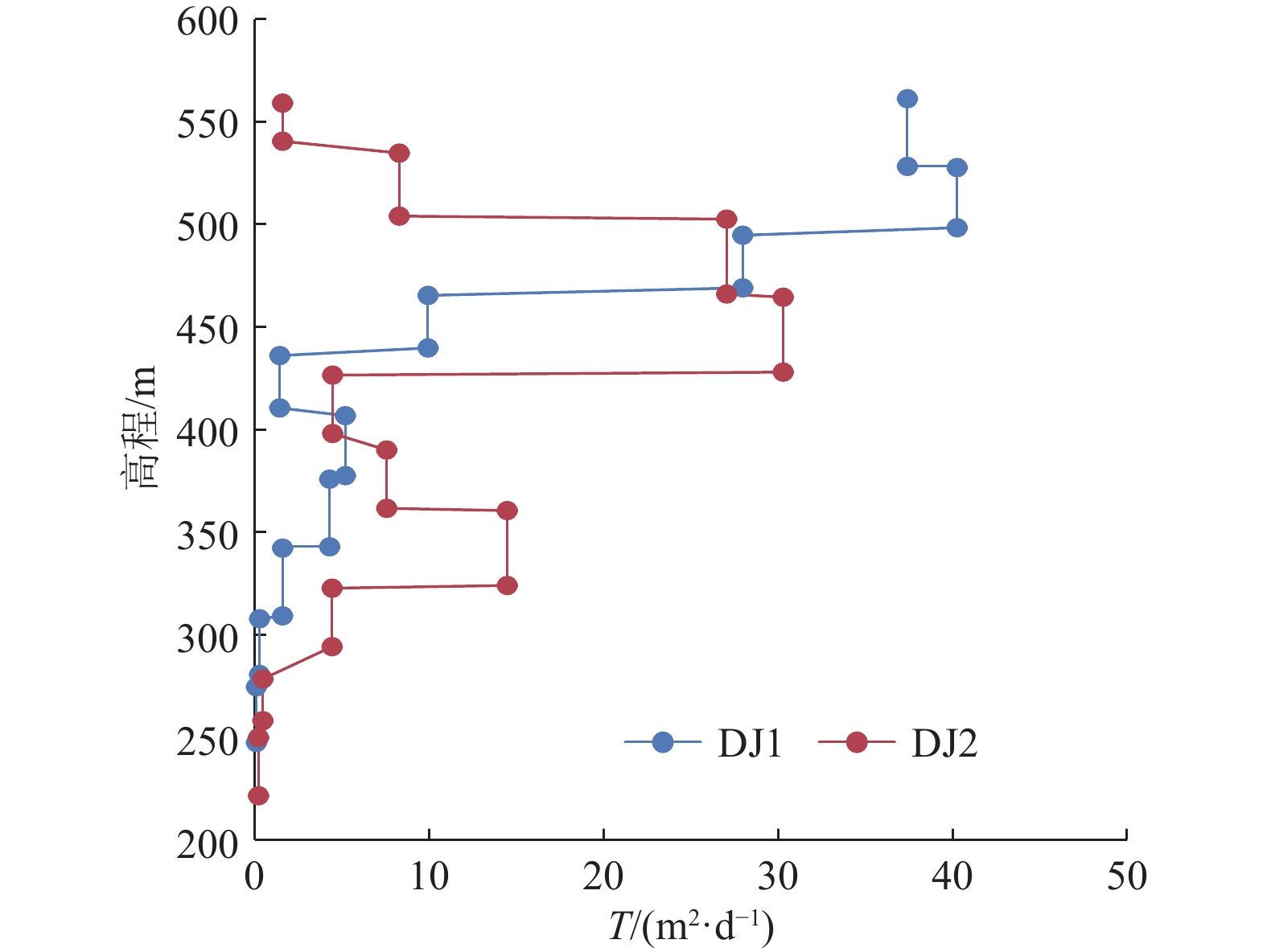
埋深/m试验序次 Q/(m3·h–1) Sw/m T/(m2·d–1) K/(m·d–1) 起始埋深/m 截止埋深/m 厚度/m DJ1 1 465.85 498.86 33.01 0.085 7 299.19 297.65 1 13.7513 11.45 26.45 0.801 4 2 11.6608 6.58 39.03 1.182 5 3 4.6649 2.20 46.70 1.414 8 平均 37.40 1.132 9 2 499.42 532.43 33.01 0.085 7 292.30 291.17 1 13.7513 8.08 36.84 1.116 2 2 10.0742 5.26 41.46 1.256 1 3 5.0569 2.58 42.43 1.285 5 平均 40.25 1.219 2 3 528.75 561.76 33.01 0.085 7 289.41 288.04 1 14.4943 11.53 27.06 0.819 7 2 10.0742 7.72 28.09 0.850 9 3 5.0569 3.79 28.72 0.870 0 平均 27.96 0.846 9 4 558.08 591.09 33.01 0.085 7 286.71 286.93 1 13.0313 29.34 9.53 0.288 7 2 9.1886 19.63 10.04 0.304 2 3 4.6649 9.83 10.18 0.308 4 平均 9.92 0.300 5 5 587.39 620.40 33.01 0.085 7 286.54 286.51 1 6.8180 107.59 1.36 0.041 1 2 4.8586 71.85 1.45 0.043 9 3 2.4480 35.72 1.47 0.044 5 平均 1.42 0.043 1 6 616.62 649.63 33.01 0.085 7 285.84 286.47 1 11.6608 49.83 5.00 0.151 6 2 8.0827 33.14 5.21 0.158 0 3 4.1123 16.55 5.31 0.160 9 平均 5.18 0.156 8 7 651.34 684.35 33.01 0.085 7 287.99 296.80 1 11.0095 56.77 4.14 0.125 5 2 7.5614 37.66 4.29 0.129 9 3 3.9373 19.01 4.42 0.134 0 平均 4.28 0.129 8 8 684.99 718.00 33.01 0.085 7 313.27 321.43 1 6.3626 90.89 1.49 0.045 3 2 4.4762 60.19 1.59 0.048 1 3 2.3198 29.64 1.67 0.050 6 平均 1.58 0.048 0 9 719.43 752.62 33.19 0.085 7 324.52 330.57 3.6011 292.54 0.26 0.007 9 10 746.58 779.77 33.19 0.085 7 327.20 307.19 1.1714 322.85 0.08 0.002 3 DJ2 1 531.42 555.81 24.39 0.085 7 263.03 263.57 1 9.4784 128.12 1.54 0.063 2 2 7.3084 97.37 1.56 0.064 1 3 4.6649 59.91 1.62 0.066 5 平均 1.58 0.064 6 2 550.01 586.52 36.51 0.085 7 269.76 270.16 1 15.6535 42.61 8.16 0.223 5 2 10.9901 29.45 8.29 0.227 1 3 5.8979 15.66 8.37 0.229 2 平均 8.27 0.226 6 3 588.00 624.51 36.51 0.085 7 270.36 270.59 1 19.3194 15.77 26.91 0.737 1 2 13.3884 10.89 27.01 0.739 7 3 7.0607 5.70 27.21 0.745 3 平均 27.04 0.740 7 4 626.08 662.59 36.51 0.085 7 270.70 271.17 1 19.7694 14.65 29.50 0.808 1 2 14.1199 10.18 30.32 0.830 6 3 7.5614 5.33 31.02 0.849 5 平均 30.28 0.829 4 5 664.05 700.56 36.51 0.085 7 271.48 273.40 1 14.4943 72.59 4.35 0.119 2 2 9.7844 47.07 4.53 0.124 1 3 4.8586 23.77 4.46 0.122 1 平均 4.45 0.121 8 6 692.50 729.01 36.51 0.085 7 272.75 273.66 1 16.7468 47.19 7.73 0.211 7 2 11.6608 37.71 6.73 0.184 4 3 5.8979 15.67 8.20 0.224 5 平均 7.55 0.206 9 7 730.11 766.62 36.51 0.085 7 273.71 274.19 1 18.4370 28.32 14.16 0.387 8 2 12.6803 18.92 14.58 0.399 2 3 6.3482 9.42 14.66 0.401 4 平均 14.46 0.396 1 8 767.94 804.45 36.51 0.085 7 274.23 274.38 1 13.7513 69.74 4.28 0.117 3 2 9.1886 45.08 4.43 0.121 3 3 4.6649 22.23 4.56 0.124 9 平均 4.42 0.121 2 DJ3 9 796.44 833.02 36.58 0.085 7 279.70 280.33 6.3482 304.38 0.45 0.012 4 10 824.79 861.37 36.58 0.085 7 272.91 289.99 3.2825 346.55 0.20 0.005 6 表 4 洛河组综合富水性指数法垂向分层结果
Table 4 Vertical aquifers of Luohe Formation stratified by comprehensive water-rich index
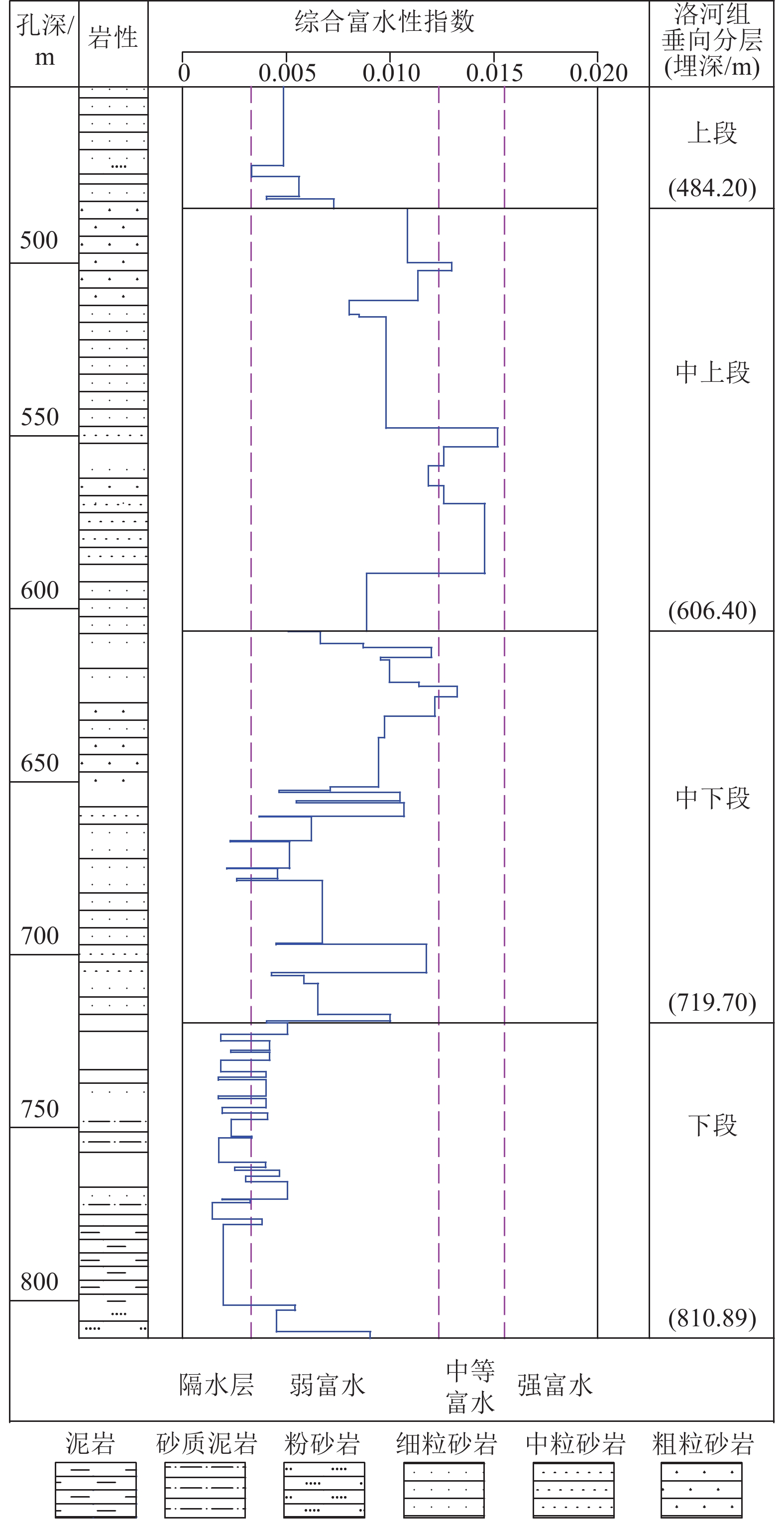
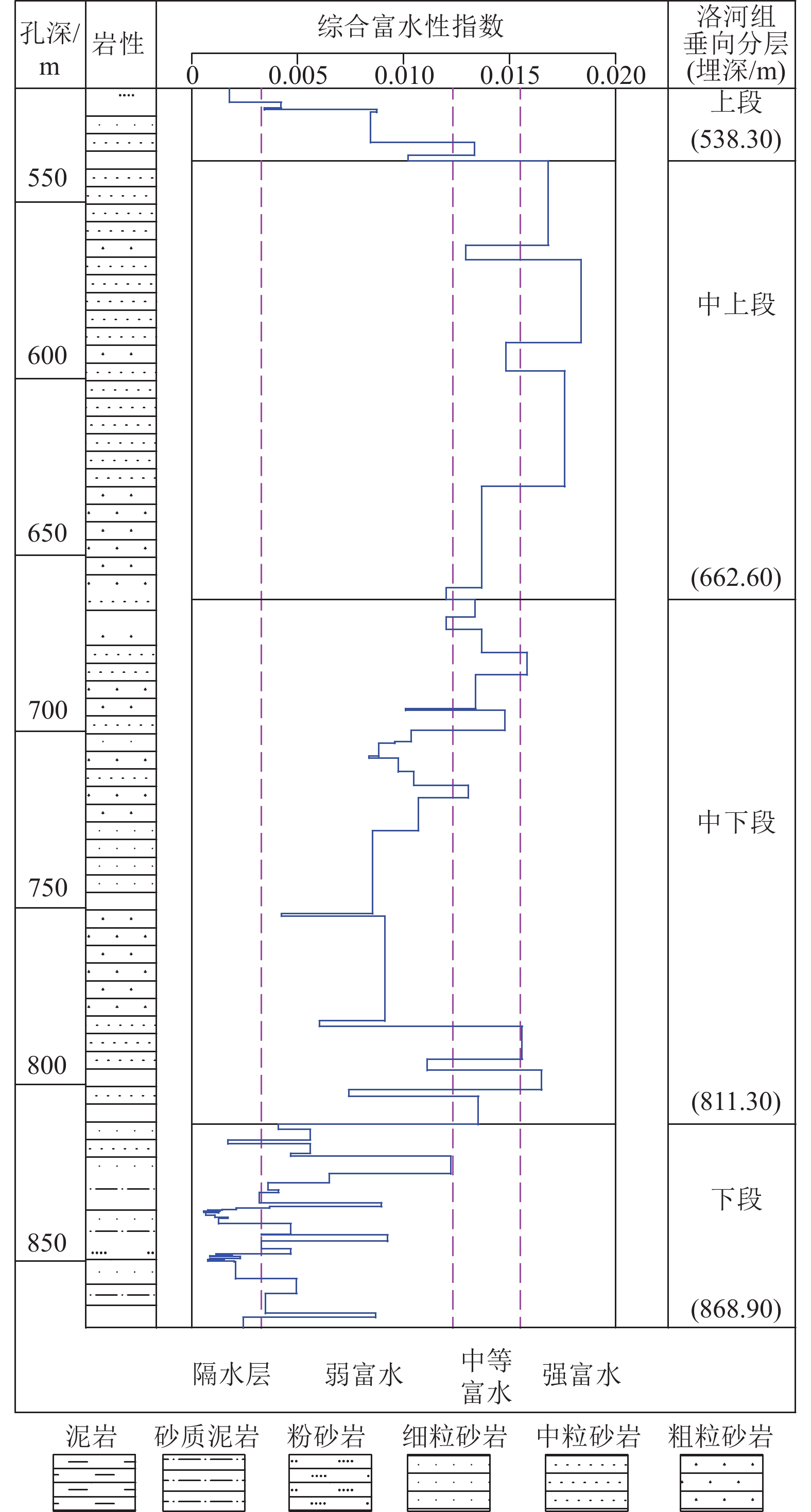
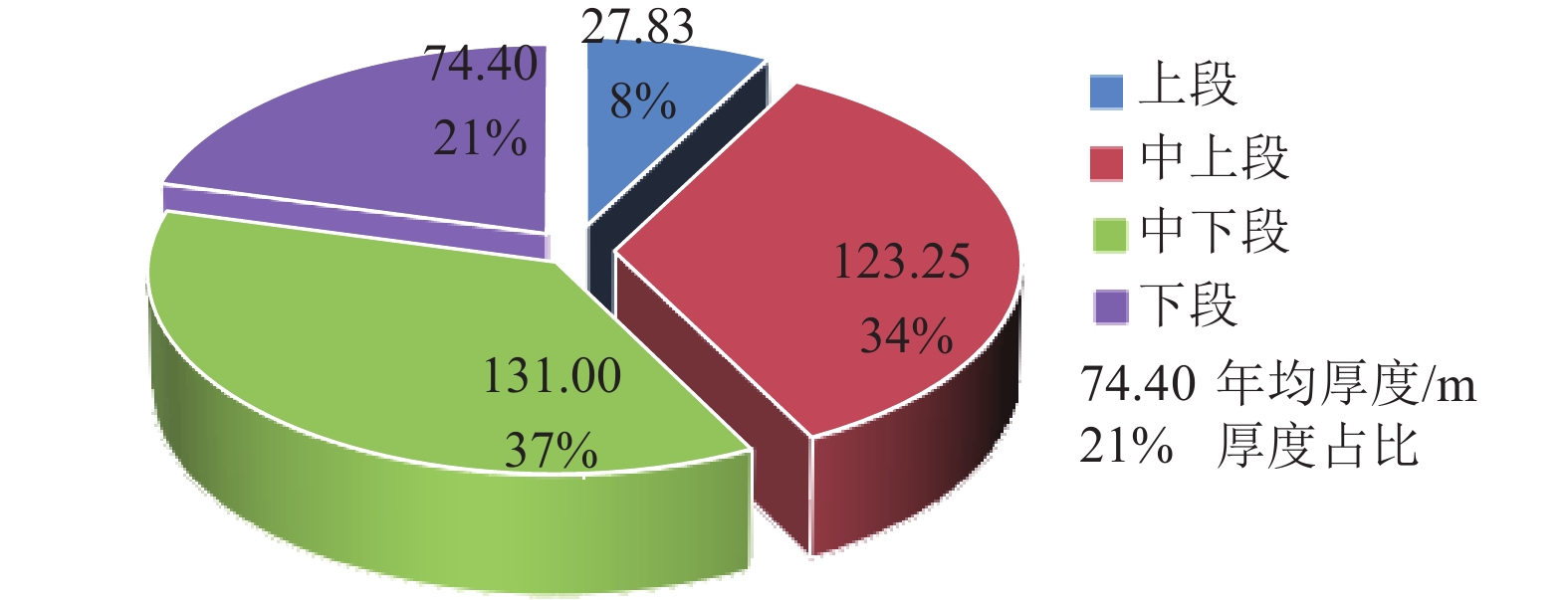
单位:m 钻孔 洛河组
厚度上段
厚度中上段
厚度中下段
厚度下段
厚度DJ1 361.89 35.20 122.20 113.30 91.19 DJ2 351.05 20.45 124.30 148.70 57.60 均值 356.47 27.83 123.25 131.00 74.40 表 5 洛河组垂向分层渗透系数计算结果
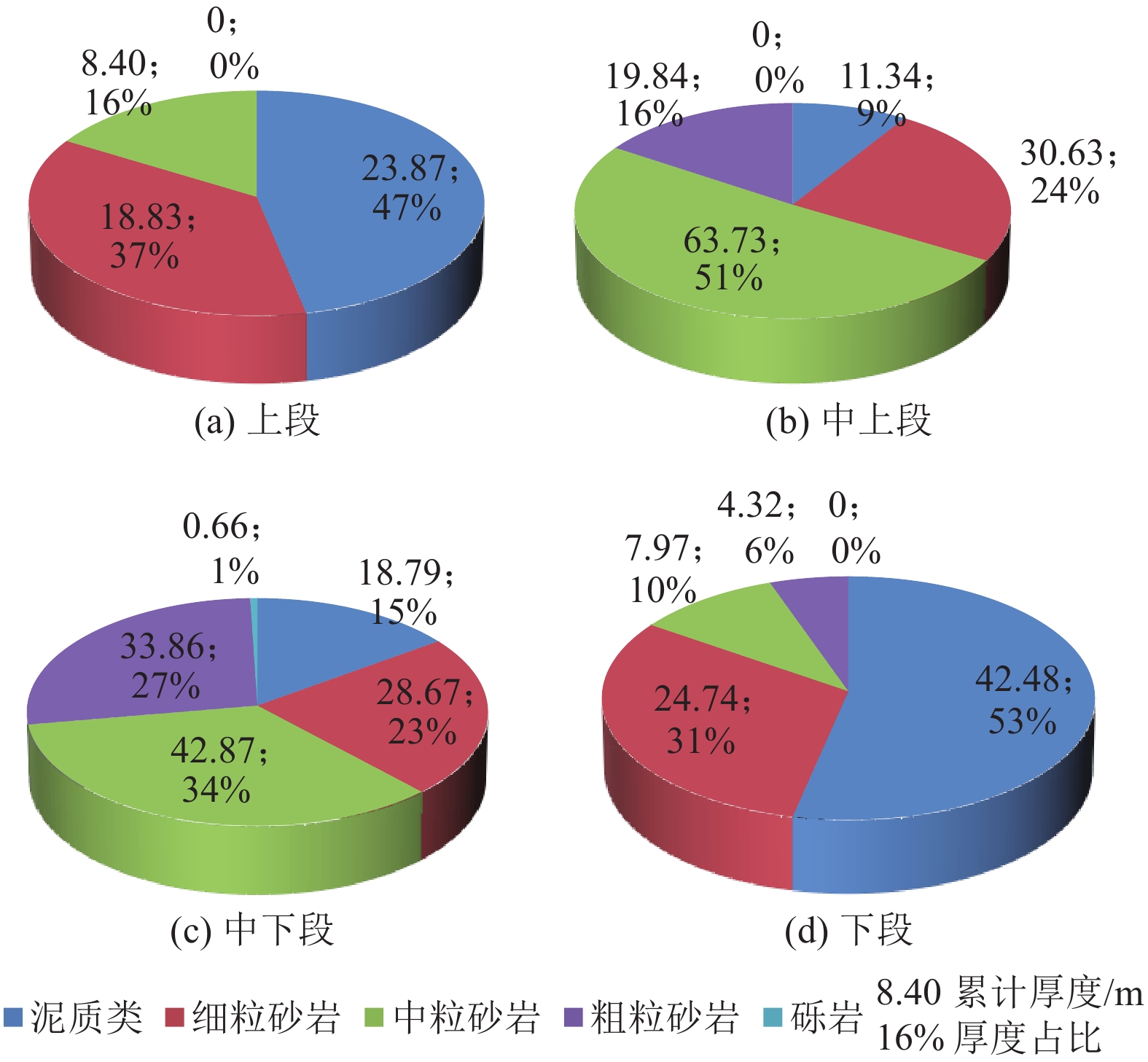
Table 5 Calculation results of permeability coefficient of each aquifer in Luohe Formation
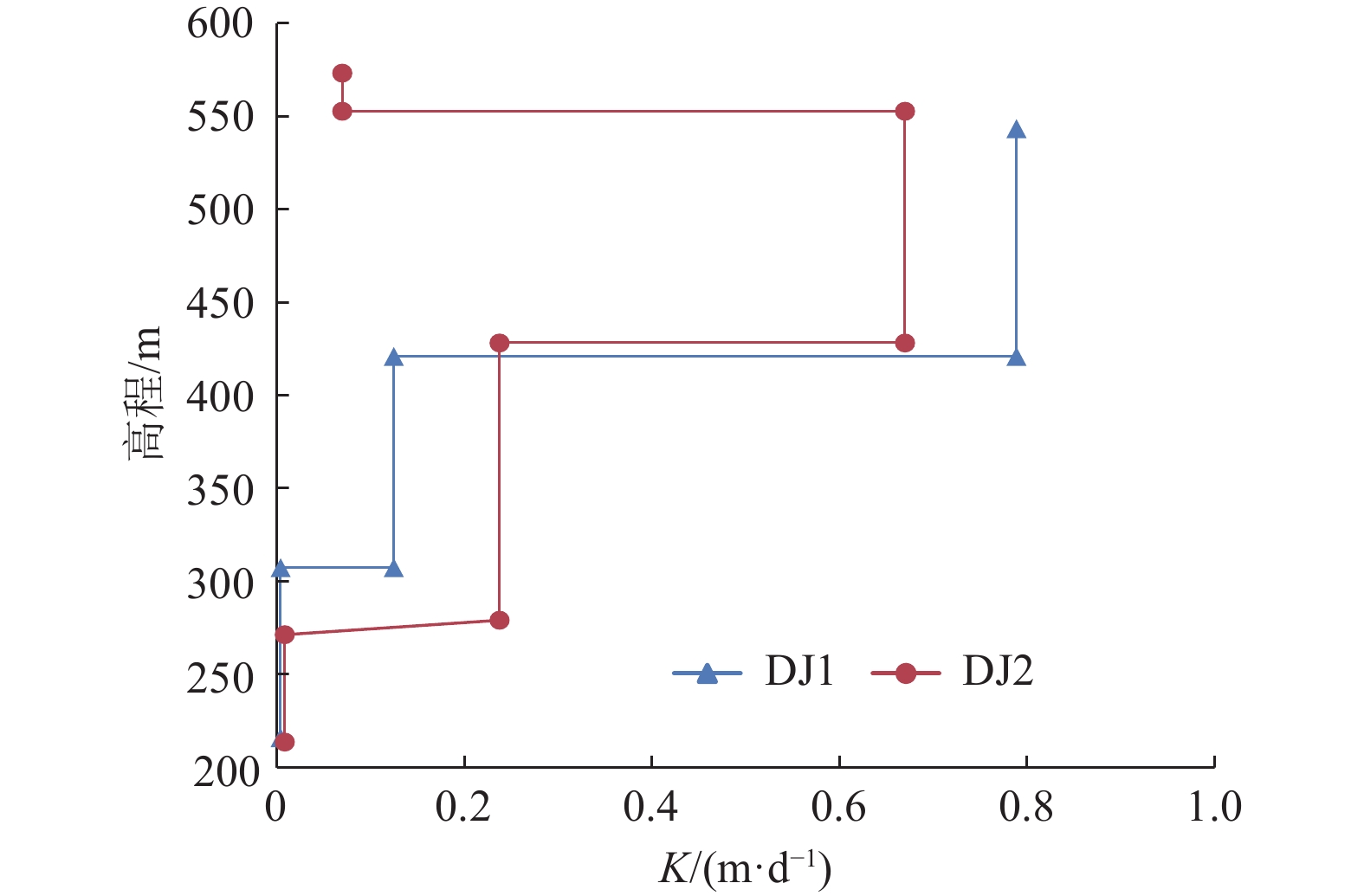
垂向层段 渗透系数计算结果/(m·d–1) DJ1钻孔 DJ2钻孔 均值 上段 0.064 6 0.064 6 中上段 0.708 5 0.598 9 0.653 7 中下段 0.111 5 0.211 5 0.161 5 下段 0.005 1 0.009 0 0.007 1 表 6 洛河组垂向分层导水系数计算结果
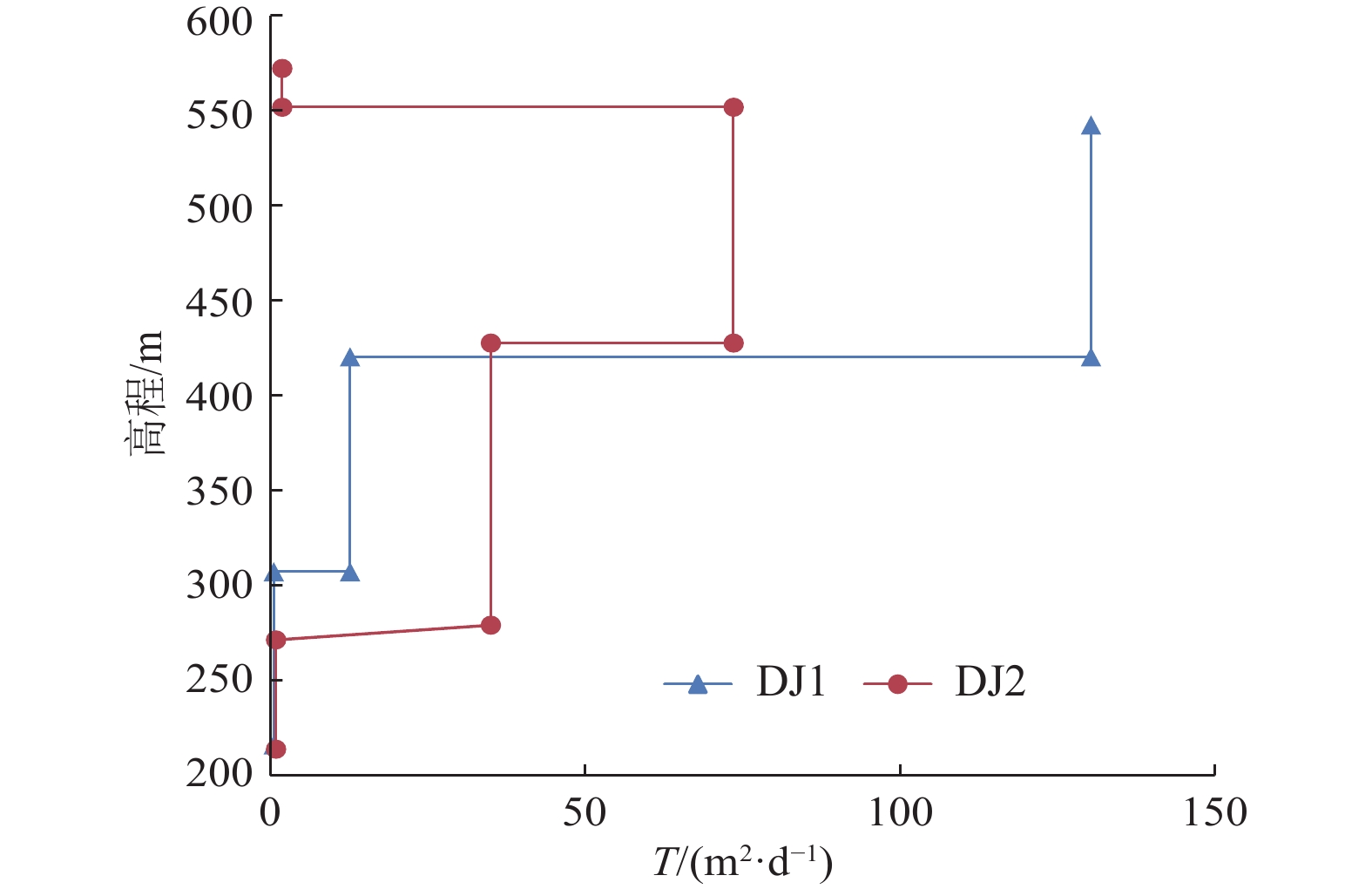
Table 6 Calculation results of coefficient of transmissibility of each aquifer in Luohe Formation
垂向层段 导水系数计算值/(m2·d−1) 富水性 DJ1钻孔 DJ2钻孔 均值 上段 1.58 1.58 弱 中上段 116.94 65.60 91.27 强−很强 中下段 11.05 30.89 20.97 中等 下段 0.34 0.66 0.50 极弱 表 7 洛河组全段导水系数
Table 7 Results of coefficient of transmissibility of Luohe Formation
钻孔 洛河组全段导水系数计算值/(m2·d–1) 富水性 DJ1 128.32 很强 DJ2 98.72 强 -
[1] 侯光才,林学钰,苏小四,等. 鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地地下水系统研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2006,36(3):391−398. DOI: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2006.03.013 HOU Guangcai,LIN Xueyu,SU Xiaosi,et al. Groundwater system in Ordos Cretaceous Artisan Basin (CAB)[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2006,36(3):391−398. DOI: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2006.03.013
[2] 李云峰,冯建国,王玮,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地白垩系含水层系统分析[J]. 西北地质,2004,37(1):90−96. LI Yunfeng,FENG Jianguo,WANG Wei,et al. The groundwater system analysis of Cretaceous system of Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology,2004,37(1):90−96.
[3] 董书宁,姬亚东,王皓,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪煤田典型顶板水害防控技术与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2367−2375. DONG Shuning,JI Yadong,WANG Hao,et al. Prevention and control technology and application of roof water disaster in Jurassic coal field of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2367−2375.
[4] 刘英锋,王新. 黄陇侏罗纪煤田顶板水害防治问题及对策探讨[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2013,33(4):431−435. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2013.04.010 LIU Yingfeng,WANG Xin. Water hazard prevention and control in Huanglong Jurassic Coalfield[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2013,33(4):431−435. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2013.04.010
[5] 杨国栋. 永陇矿区麟北郭家河煤矿离层水形成典型地质条件与防治关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2019. YANG Guodong. Study on typical geological conditions and key prevention technologies for separated water in Guojiahe Coal Mine[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[6] 乔伟,王志文,李文平,等. 煤矿顶板离层水害形成机制、致灾机理及防治技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(2):507−522. QIAO Wei,WANG Zhiwen,LI Wenping,et al. Formation mechanism,disaster–causing mechanism and prevention technology of roof bed separation water disaster in coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(2):507−522.
[7] 张培森,朱慧聪,吴玉华,等. 我国煤矿离层涌突水致灾机理及其防控关键技术研究进展[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(4):1057−1070. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0329 ZHANG Peisen,ZHU Huicong,WU Yuhua,et al. State–of–the–art of mechanism of water inrush from bed separation and key technology of prevention and pre−control in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(4):1057−1070. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0329
[8] 李超峰,虎维岳,刘英锋. 洛河组含水层垂向差异性研究及保水采煤意义[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(3):848−857. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.6021 LI Chaofeng,HU Weiyue,LIU Yingfeng. Vertical hydrogeological characteristics of Luohe aquifer and its significance of water−preserved coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(3):848−857. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.6021
[9] 李超峰,虎维岳. 回采工作面顶板复合含水层涌水量时空组成及过程预测方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):1−13. LI Chaofeng,HU Weiyue. Prediction method of mine water inflow regime from a layered extra–thick aquifer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):1−13.
[10] 李超峰. 煤层顶板含水层涌水危险性评价方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(增刊1):384−392. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.1634 LI Chaofeng. Method for evaluating the possibility of water inrush from coal seam roof aquifer[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(Sup.1):384−392. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.1634
[11] 侯光才, 张茂省, 刘方, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地地下水勘查研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008. [12] 徐中华. 鄂尔多斯盆地南区保安群地下水水化学特征及演化机理[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010. XU Zhonghua. Study on hydrochemical characteristic and evolution mechanism of Bao’ an group groundwater of the Ordos Cretaceous Artesian Basin south[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010.
[13] 杨郧城,侯光才,张茂省,等. 双Packer系统在鄂尔多斯盆地地下水勘查中的应用[J]. 西北地质,2005,38(1):113−115. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.01.016 YANG Yuncheng,HOU Guangcai,ZHANG Maosheng,et al. Applications of double Packer system to exploration of the groundwater in Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology,2005,38(1):113−115. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.01.016
[14] 马思锦,汤献敏. Packer系统在地下水勘查中的应用[J]. 陕西地质,2009,27(2):75−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2009.02.011 MA Sijin,TANG Xianmin. Application of Packer system on exploration of groundwater[J]. Geology of Shaanxi,2009,27(2):75−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2009.02.011
[15] 刘英锋, 李超峰. 陕西彬长胡家河矿业有限公司矿井首采区水文地质补充勘探报告[R]. 西安: 中煤科工集团西安研究院有限公司, 2014. [16] 李超峰. 彬长矿区巨厚洛河组垂向差异性研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2018,37(4):131−133. DOI: 10.13301/j.cnki.ct.2018.04.051 LI Chaofeng. Vertical differences of thick Luohe Formation in Binchang mining area[J]. Coal Technology,2018,37(4):131−133. DOI: 10.13301/j.cnki.ct.2018.04.051
[17] 李超峰. 采煤工作面顶板巨厚层状含水层涌水量预测研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2019. LI Chaofeng. Prediction theory and method of water inflow from roof thick layered aquifer of coal mining face[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2019.
[18] 李超峰. 水力联系系数法定量评价含水层之间水力联系[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(6):1801−1810. LI Chaofeng. Hydraulic connection coefficient and quantitative evaluation of hydraulic connection between aquifers[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(6):1801−1810.
[19] 李超峰,姬亚东. 揭露两个含水层混合井初始混合水位形成机理研究[J]. 地下水,2021,43(4):25−28. DOI: 10.19807/j.cnki.DXS.2021-04-007 LI Chaofeng,JI Yadong. Formation mechanism of initial water level in a mixed well of two aquifers[J]. Groundwater,2021,43(4):25−28. DOI: 10.19807/j.cnki.DXS.2021-04-007
[20] 纪传豪. 对岩层含水性图编制原则的几点意见[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1959(3):14−15. JI Zhuanhao. Opinions on the principles for compiling water–rich maps of formations[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1959(3):14−15.
[21] 沈树荣. 读“对岩层含水性图编制原则的几点意见”[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1959(10):24−27. SHEN Shurong. Read “Opinions on the principles for compiling water–rich maps of formations”[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1959(10):24−27.
[22] 国家技术监督局. 矿区水文地质工程地质勘探规范: GB 12719—1991[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1991. [23] 国家安全生产监督管理总局, 国家煤矿安全监察局. 煤矿防治水规定[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2009. [24] 国家煤矿安全监察局. 煤矿防治水细则[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2018. [25] 李超峰. 基于导水系数的含水层富水性评价方法[J]. 地下水, 2023, 45(5): 15−17. LI Chaofeng. Evaluation method of water–rich of aquifers based on transmissivity[J]. Groundwater, 2023, 45(5): 15−17.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 付金磊,林华颖,衡献伟,张书金,陈蒙磊. 顺层瓦斯抽采长钻孔封孔深度分析:以贵州黔北矿区抽采工程为例. 科学技术与工程. 2025(08): 3513-3520 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 段会军. 破碎松软复合煤体高效螺旋钻进技术试验研究. 能源与环保. 2024(04): 228-233+242 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋昱播. 复杂软弱煤层条件下高转速大扭矩钻探装备设计及试验研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(06): 200-205 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈冬冬. 彬长矿区中硬煤层长钻孔分段水力压裂瓦斯抽采技术. 煤炭工程. 2023(07): 72-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 金元甲,马凯,张亚洲,马钱钱. 定向孔抽采特性对布孔参数响应变化规律研究. 矿业安全与环保. 2023(06): 120-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王心龙,孙平贺,赵明哲,王靖源,邢世宽. 管道穿越对煤系土河床冲刷深度的影响. 煤田地质与勘探. 2022(06): 118-124 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 李迎喜. 复杂软弱煤层条件下高速螺旋复合钻进技术研究及实践. 煤矿安全. 2022(08): 87-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 徐毅豪,秦汝祥,贾明乐,刘忠平,张成功. 煤层瓦斯测压下向钻孔自动排水实验装置研制. 矿业安全与环保. 2022(04): 176-180+186 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陆晓东,荣鹏,左宇军,林健云. 开采扰动下底板巷道应力演化规律及围岩稳定性研究. 矿业研究与开发. 2022(11): 102-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张春华,张子健,年军,焦登铭. 大直径双钻孔强化抽采瓦斯效应及效果分析. 煤田地质与勘探. 2021(06): 273-280 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载: