Optimum selection of favorable areas for multi-layer CBM mining and reservoir characterstics in North Yunnan and Guizhou exploration area
-
摘要:
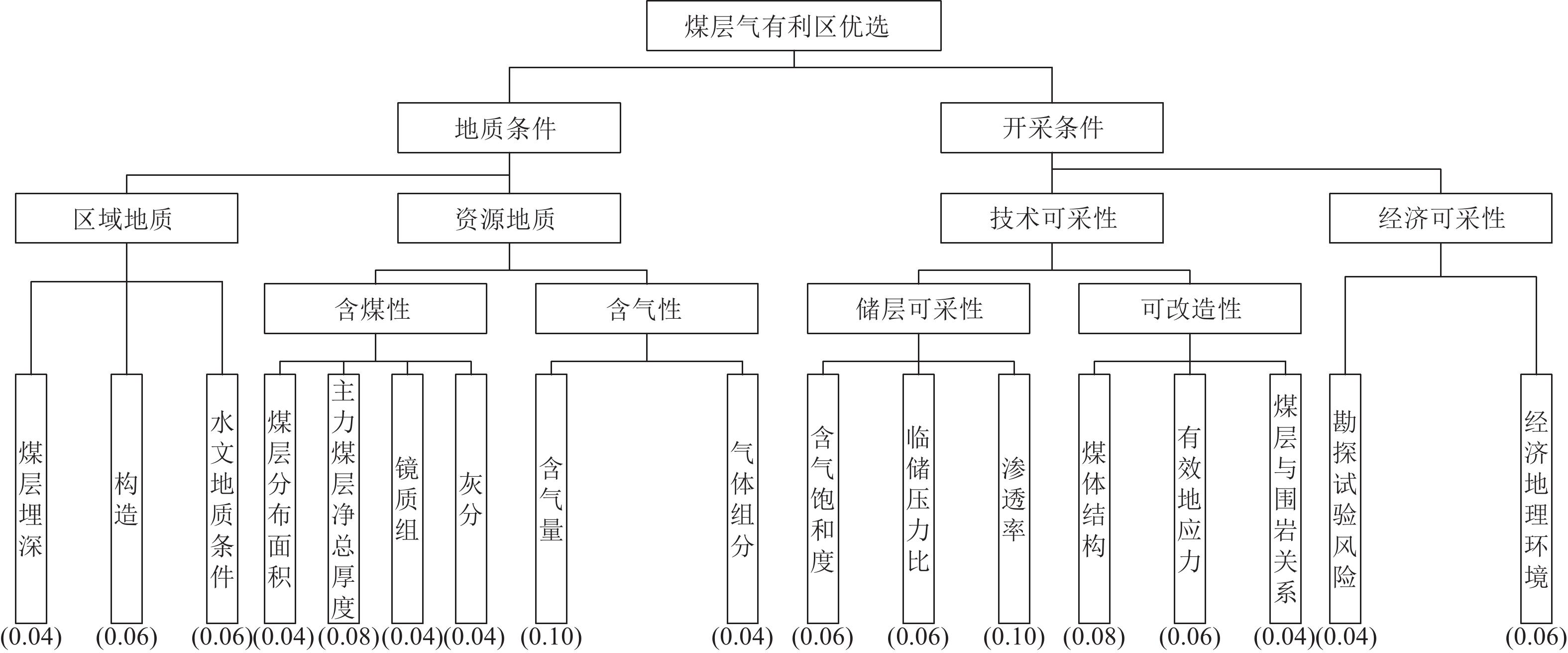
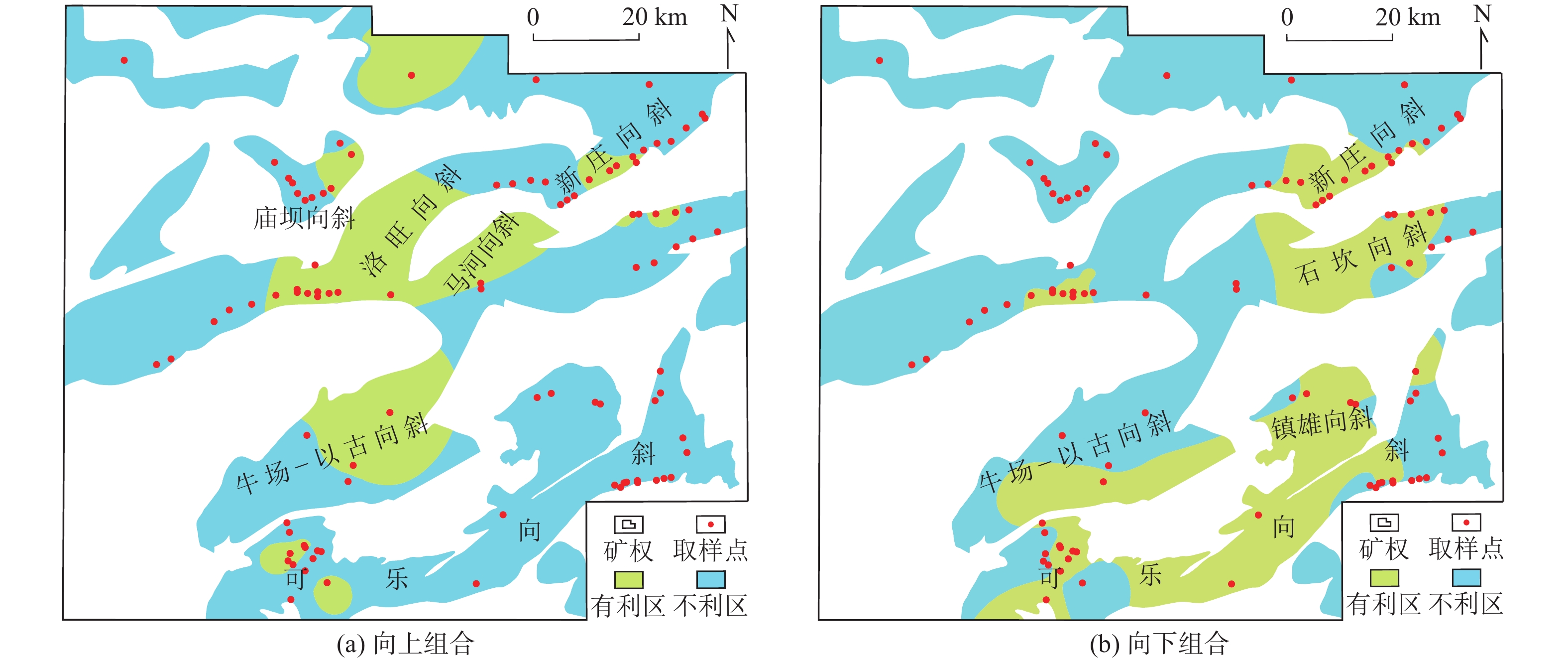
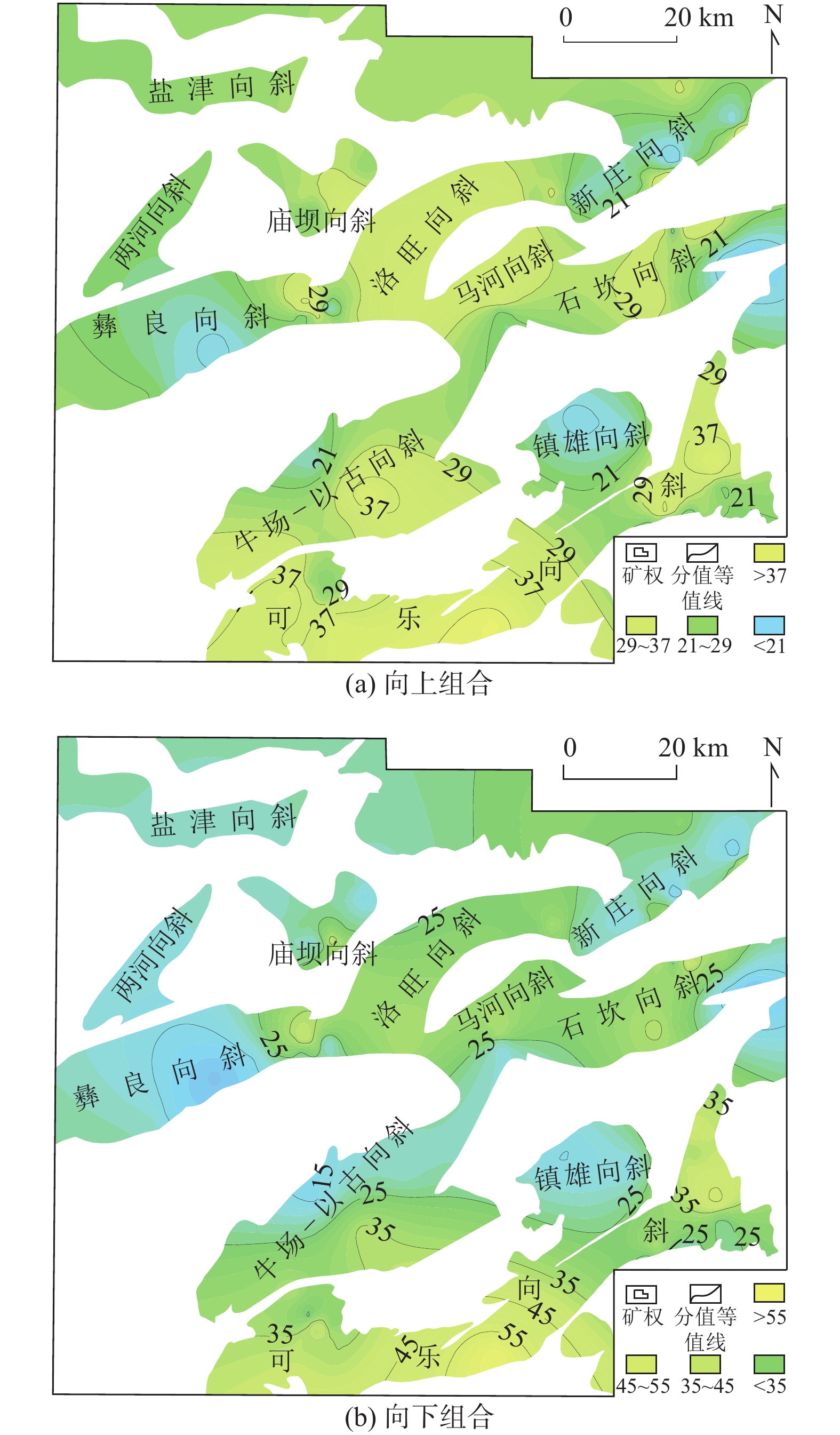
滇黔北探区赋煤向斜众多,多薄煤层发育,含气量较高,煤层气资源丰富,是筠连外围重要的拓展区块。基于大量煤田孔及煤层气试验井,分析煤层气地质条件,建立多层合采有利区优选评价方法:多层次模糊数学+关键指标法。首先,基于层次递阶优选构建评价模型并确定关键指标,明确关键指标为合采系数、煤体结构、含气量,其中,合采系数由最优合采跨度及合采累计煤厚构成,并给出关键指标的定量评价表,然后,运用模糊数学计算公式,得到储层评分结果,最终获得多层合采有利区优选结果。结果显示:研究区晚二叠世龙潭组/宣威组煤层最多可达到20层以上,可采煤层一般3层左右,煤层总厚度一般在6 m以上,煤层层数及煤层厚度由东南向西北逐渐减少或减薄。大部分区域主力煤层为C5(M11)煤层,厚度一般在2 m以上,其灰分质量分数平均为27.73%,为中灰煤,煤级主要为贫煤–无烟煤。各向斜主力煤层含气性差异性较大,含气量最大可达到30.53 m3/t。研究区煤体结构以原生结构煤和碎裂结构煤为主。以C5(M11)煤层分别向上或向下合采计算合采系数,由此形成了两个合采层段,多层合采Ⅰ类有利区主要位于研究区可乐向斜中西部,牛场–以古向斜南部,镇雄向斜南部,庙坝向斜东南部,洛旺向斜中西部,石坎向斜中西部。
Abstract:Due to the abundance of coal-bearing synclines, multiple seams and high gas content, the exploration area in North Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces is an important expansion block in the periphery of Junlian County. Based on a large number of coalfield holes and test wells, the geological conditions of CBM are analyzed, and the optimization and evaluation method of multi-layer favorable area is established, i.e. multi-level fuzzy mathematics plus key indicators. Firstly, the evaluation model is constructed based on hierarchical optimization, and the key indicators are determined as co-mining coefficient, coal structure and gas content. The co-mining coefficient is composed of the optimal co-mining span and the cumulative coal thickness, and the quantitative evaluation table of the key indicators is given. Then, the fuzzy mathematics calculation formula is used to obtain the reservoir score results, guiding the optimization of multi-layer co-mining favorable areas. The results show that the coal seam of Longtan Formation/Xuanwei Formation in Late Permian in the study area can reach up to more than 20 layers, and the recoverable coal seam is generally about 3 layers with the total thickness of more than 6 m. From southeast to northwest, coal seams pinch out and the number of layers gradually decreases. In most areas, the main coal seam is C5 (M11), with a thickness of more than 2 m and an average ash content of 27.73%, belonging to medium ash coal, and the coal rank is mainly lean coal–anthracite. The gas content of main coal seams in each syncline varies significantly, and the maximum gas content can reach 30.53 m3/t. The coal structure in the study area is dominated by primary structure coal and fractured structure coal. The co-mining coefficient is calculated by the upward or downward co-mining of seam C5 (M11), thus forming two co-mining layers. The multi-layer co-mining type I favorable area is mainly located in the central and western Kele syncline, the south of Niuchang-Yigu syncline, the south of Zhenxiong syncline, the southeast of Miaoba syncline, the central and western Luowang syncline, and the central and western Shikan syncline.
-
-
表 1 煤层气勘探阶段有利区评价参数
Table 1 Evaluation parameters of favorable areas in CBM exploration stage
评价参数xij 权重Wi Ⅰ类区
(0.7<xij≤1.0)Ⅱ类区
(0.3<xij≤0.7)Ⅲ类区
(0<xij≤0.3)煤层含气量(空气干燥基)/(m3·t–1) 0.26 ≥12 8~12 ≤8 煤体结构 0.27 原生结构煤或碎裂煤 碎粒–糜棱煤 合采系数 0.23 ≥0.08 <0.08 表 2 研究区典型向斜煤层群发育情况统计
Table 2 Statistics on the development of typical syncline coal seam groups in the study area
向斜 评价单元 含煤地层 煤系厚度/m 煤层总
厚度/m煤层层数 可采
煤层数可采煤层
总厚度/m可乐 辅处 宣威组 51.04~112.32 2.08 0~12 4 1.90 结构 龙潭–长兴组 78.90~278.05 6.52 5~21 5 4.88 财神 龙潭–长兴组 171.52~355.94 6.42 3~22 5 2.88 青场 龙潭–长兴组 203.53~260.52 6.42 3~12 3 2.38 牛场–以古 牛场–以古 龙潭–长兴组 156.00~181.00 6.08 9~18 3 3.90 大银煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 201.00 5.40 6~19 2 2.47 镇雄 兴远煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 206.69 8.70 6~19 2 3.29 天平煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 254.66 7.61 3~10 3 5.00 长岭1号 龙潭–长兴组 180.00 9.36 11~27 3 4.49 朱家湾 龙潭–长兴组 190.00 9.36 14~25 5 5.81 塘房煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 182.50 7.00 14~29 3 3.90 新庄 观音山煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 109.00~178.00 10.18 2~16 2 4.12 墨黑煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 118.00~175.00 5.81 12~21 1 2.03 玉京山煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 135.00~182.00 7.62 3~19 3 3.17 大井沟煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 151.00~183.00 4.29 4~16 1 1.42 石坎 石坎煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 166.00 8.01 4~13 4 4.31 马河 马河煤矿 龙潭–长兴组 132.00 5.00 3~9 3 3.66 庙坝 庙坝煤矿 宣威组 173.00 3.38 6 3 2.96 洛旺 塘房煤矿 宣威组 120.00~170.00 4.80 2~10 2 2.60 桃子湾煤矿 宣威组 120.00~170.00 4.80 2~10 2 2.60 西段普查 龙潭–长兴组 208.14 8.40 9~18 3 5.63 彝良 荞山勘查区 宣威组 184.59 2.82 3~10 1 1.31 表 3 主要向斜主力煤层C5(M11)含气性概况(基准:空气干燥基)
Table 3 General situation of gas content of main synclinal main seam C5 (M11) (Air dried basis)
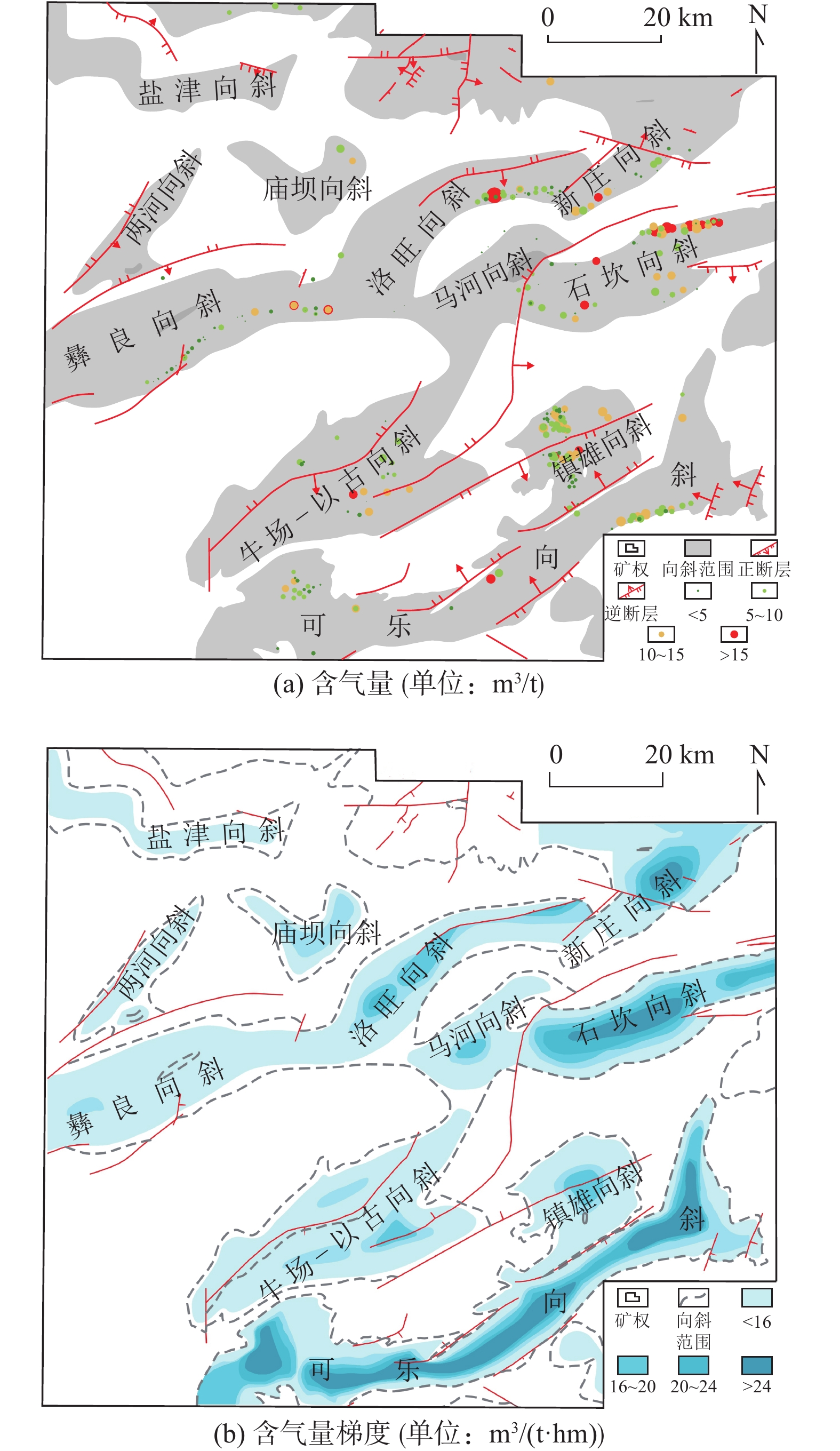
向斜 预估风化带
深度/m平均
埋深/m平均甲烷
体积分数/%平均含气量/
(m3·t−1)平均含气梯度/
(m3·t−1·hm−1)最大含气量/
(m3·t−1)数据个数 彝良 400 595.28 83.54 7.19 1.21 11.75 23 洛旺 300 607.67 91.35 9.56 1.57 17.88 15 牛场–以古 200 575.68 91.93 9.15 1.59 16.96 129 镇雄 100 318.48 94.88 7.78 2.44 16.43 76 石坎 200 728.24 85.97 13.58 1.86 21.71 44 马河 200 588.83 91.13 10.37 1.76 18.04 50 新庄 200 578.88 90.64 9.32 1.61 30.53 43 可乐 100 382.28 90.87 8.82 2.31 18.26 40 表 4 研究区不同评价单元综合得分
Table 4 Comprehensive scores of different evaluation units in the study area
评价单元 向上得分 向下得分 综合得分 彝良向斜 16.37 13.76 15.06 镇雄向斜 17.82 19.19 18.51 新庄向斜 22.25 22.51 22.38 庙坝向斜 26.54 23.20 24.87 石坎向斜 23.28 26.98 25.13 洛旺向斜 26.83 28.48 27.66 牛场–以古向斜 29.60 26.32 27.96 可乐向斜 29.72 33.42 31.57 -
[1] 单衍胜,毕彩芹,迟焕鹏,等. 六盘水地区杨梅树向斜煤层气地质特征与有利开发层段优选[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(1):122−129. SHAN Yansheng,BI Caiqin,CHI Huanpeng,et al. Geological characteristics of coalbed methane and optimization for favorable productive intervals of Yangmeishu syncline in Liupanshui area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2018,29(1):122−129.
[2] 毕彩芹,单衍胜,朱韩友,等. 四川南部地区川高参1井获煤层气高产工业气流[J]. 中国地质,2018,45(5):1076−1077. DOI: 10.12029/gc20180515 BI Caiqin,SHAN Yansheng,ZHU Hanyou,et al. Industrial gas production of CBM obtained by Well CGC1 in southern Sichuan[J]. Geology in China,2018,45(5):1076−1077. DOI: 10.12029/gc20180515
[3] 魏元龙,孙钊,龙萃芸,等. 贵州省煤层气勘探开发形势与产业支持政策研究[J]. 煤炭经济研究,2021,41(8):69−74. WEI Yuanlong,SUN Zhao,LONG Cuiyun,et al. Coalbed methane exploration and development situation and industrial support policy in Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Economic Research,2021,41(8):69−74.
[4] LI Song,TANG Dazhen,PAN Zhejun,et al. Evaluation of coalbed methane potential of different reservoirs in western Guizhou and eastern Yunnan,China[J]. Fuel,2015,139:257−267. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.054
[5] QIN Yong,MOORE T A,SHEN Jian,et al. Resources and geology of coalbed methane in China:A review[J]. International Geology Review,2018,60(5/6):777−812.
[6] JU Wei,LI Zhaoliang,SUN Weifeng,et al. In–situ stress orientations in the Xiagou tight oil reservoir of Qingxi oilfield,Jiuxi Basin,northwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2018,98:258−269. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.020
[7] 高彩霞. 川渝滇黔晚二叠世层序−古地理与聚煤规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2015. GAO Caixia. Sequence−palaeogeography and coal−accumulation of Late Permian in Chuan−Yu−Dian−Qian, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2015.
[8] 刘冰. 蜀南地区及邻区晚二叠世煤系煤层气地质条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. LIU Bing. Research on geological conditions of coal and coalbed methane in Late Permian, Shunan and peripheral areas[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[9] 邵龙义,高彩霞,张超,等. 西南地区晚二叠世层序−古地理及聚煤特征[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(5):856−866. SHAO Longyi,GAO Caixia,ZHANG Chao,et al. Sequence–palaeogeography and coal accumulation of Late Permian in southwestern China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2013,31(5):856−866.
[10] 邵龙义,王学天,张家强,等. 滇东北地区煤层气富集特征及勘探目标优选[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(9):17−27. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.003 SHAO Longyi,WANG Xuetian,ZHANG Jiaqiang,et al. CBM accumulation characteristics and exploration target selection in northeastern Yunnan,China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(9):17−27. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.003
[11] 康高峰,王辉,王巨民,等. 滇东北晚二叠世沉积体系与层序地层格架下的聚煤特征[J]. 地质通报,2009,28(1):91−98. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.012 KANG Gaofeng,WANG Hui,WANG Jumin,et al. Research on coal–accumulation features in Late Permian sedimentary system and sequence stratigraphic framework,northeastern Yunnan,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2009,28(1):91−98. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.012
[12] 李聪聪,孙顺新,张光超,等. 滇东北上二叠统可采煤层变化规律及控制因素[J]. 中国地质,2014,41(6):2110−2121. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.024 LI Congcong,SUN Shunxin,ZHANG Guangchao,et al. Variation regularity and control factors of the Upper Permian mineable coal seams in northeastern Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China,2014,41(6):2110−2121. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.024
[13] 张军建,韦重韬,陈玉华,等. 多煤层区煤层气开发优选评价体系分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(9):13−17. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2017.09.003 ZHANG Junjian,WEI Chongtao,CHEN Yuhua,et al. Analysis on optimized evaluation system of coalbed methane development in multi seams area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(9):13−17. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2017.09.003
[14] 毕彩芹,胡志方,汤达祯,等. 煤系气研究进展与待解决的重要科学问题[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(2):402−423. BI Caiqin,HU Zhifang,TANG Dazhen,et al. Research progress of coal measure gas and some important scientific problems[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(2):402−423.
[15] 吴财芳,刘小磊,张莎莎. 滇东黔西多煤层地区煤层气“层次递阶”地质选区指标体系构建[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(6):1647−1653. WU Caifang,LIU Xiaolei,ZHANG Shasha. Construction of index system of“hierarchical progressive”geological selection of coalbed methane in multiple seam area of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(6):1647−1653.
[16] 金军, 杨兆彪, 秦勇, 等. 贵州省煤层气开发进展、潜力及前景[J/OL]. 煤炭学报, 2021: 1–13 [2022-02-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2190.TD.20211223.1615.004.html. JIN Jun, YANG Zhaobiao, QIN Yong, et al. Progress, potential and prospects of CBM development in Guizhou Province[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021: 1–13 [2022-02-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2190.TD.20211223.1615.004.html.
[17] 秦勇,吴建光,李国璋,等. 煤系气开采模式探索及先导工程示范[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2513−2522. QIN Yong,WU Jianguang,LI Guozhang,et al. Patterns and pilot project demonstration of coal measures gas production[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2513−2522.
[18] 郭晨,秦勇,易同生,等. 煤层气合采地质研究进展述评[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(3):42−57. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.10.0573 GUO Chen,QIN Yong,YI Tongsheng,et al. Review of the progress of geological research on coalbed methane co−production[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022,50(3):42−57. DOI: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.10.0573
[19] LI Song,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. Advanced characterization of physical properties of coals with different coal structures by nuclear magnetic resonance and X−ray computed tomography[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2012,48:220−227.
[20] 陈跃,汤达祯,许浩,等. 基于测井信息的韩城地区煤体结构的分布规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(8):1435−1442. CHEN Yue,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. The distribution of coal structure in Hancheng based on well logging data[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(8):1435−1442.
[21] 谢学恒,樊明珠. 基于测井响应的煤体结构定量判识方法[J]. 中国煤层气,2013,10(5):27−29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2013.05.007 XIE Xueheng,FAN Mingzhu. Quantitative identification of deformed coals based on logging response[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2013,10(5):27−29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2013.05.007
[22] 杨兆彪,李洋阳,秦勇,等. 煤层气多层合采开发单元划分及有利区评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(3):559−568. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2019.03.14 YANG Zhaobiao,LI Yangyang,QIN Yong,et al. Development unit division and favorable area evaluation for joint mining coalbed methane[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2019,46(3):559−568. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2019.03.14
[23] 朱超. 临兴地区煤系气开发地质单元[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. ZHU Chao. Geological units of coal measure gas development in Linxing area, Shanxi, China[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019.
[24] 杨兆彪, 何金先, 鞠玮, 等. 川南–滇东地区煤层(系)气成藏条件及富集规律研究[R]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.








 下载:
下载: