Geological adaptability analysis and operational parameter optimization for staged fracturing horizontal wells in coal seam roof
-
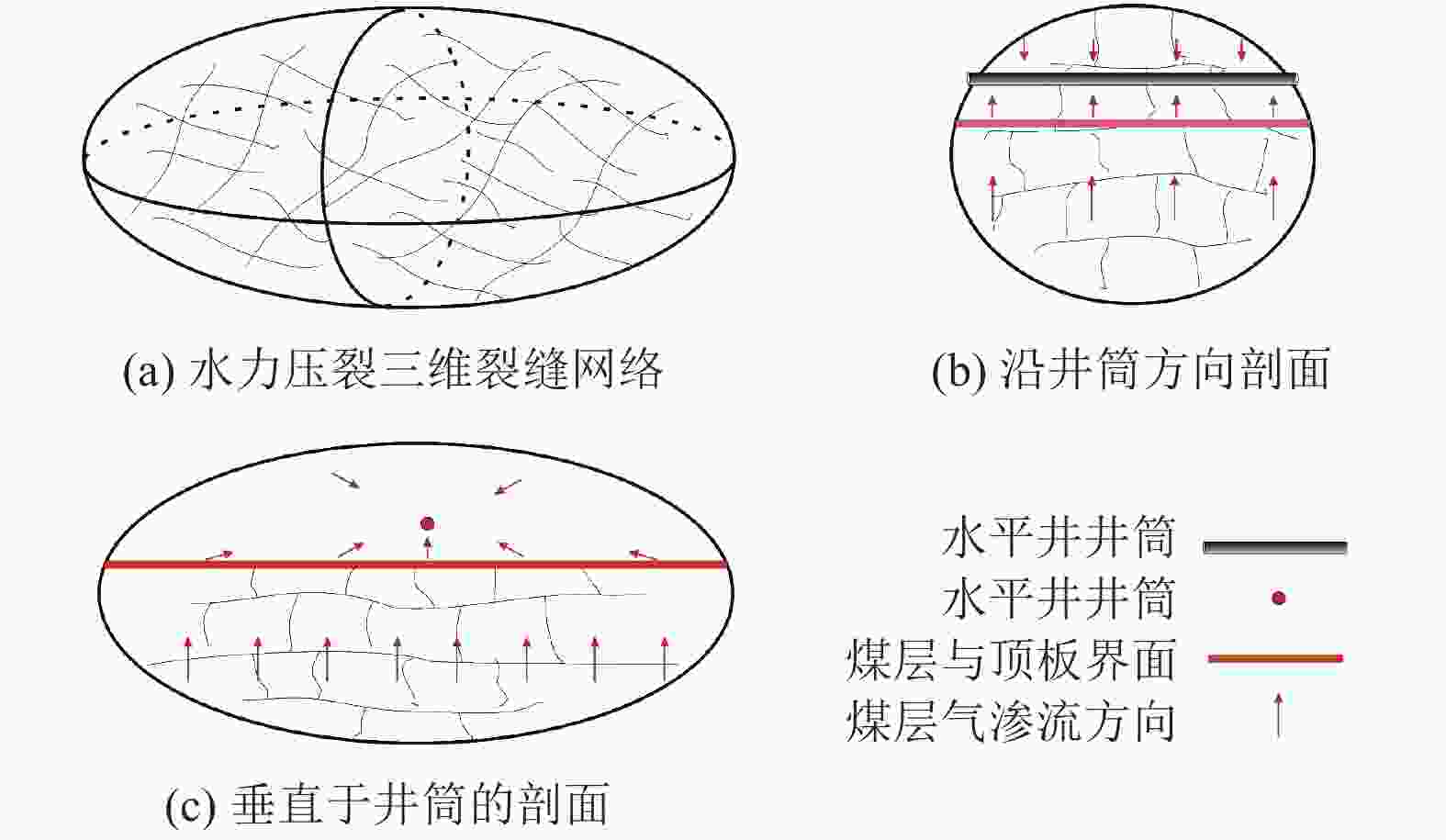
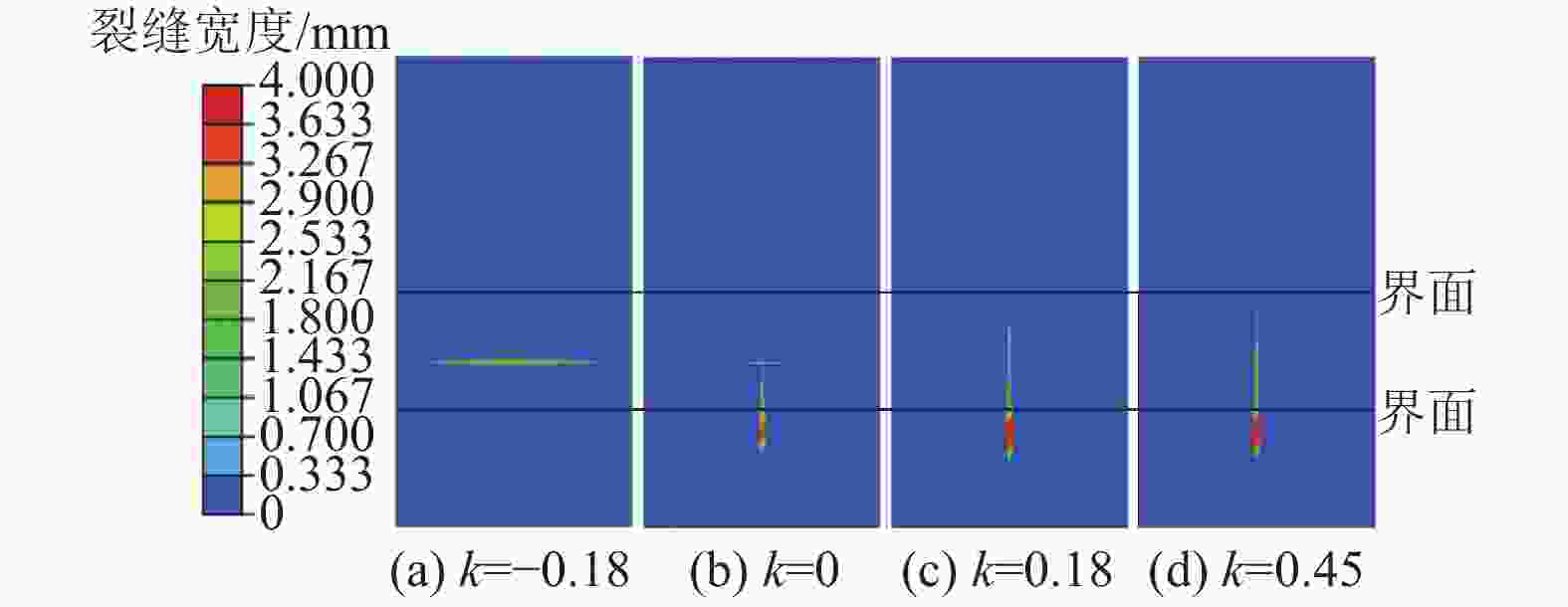
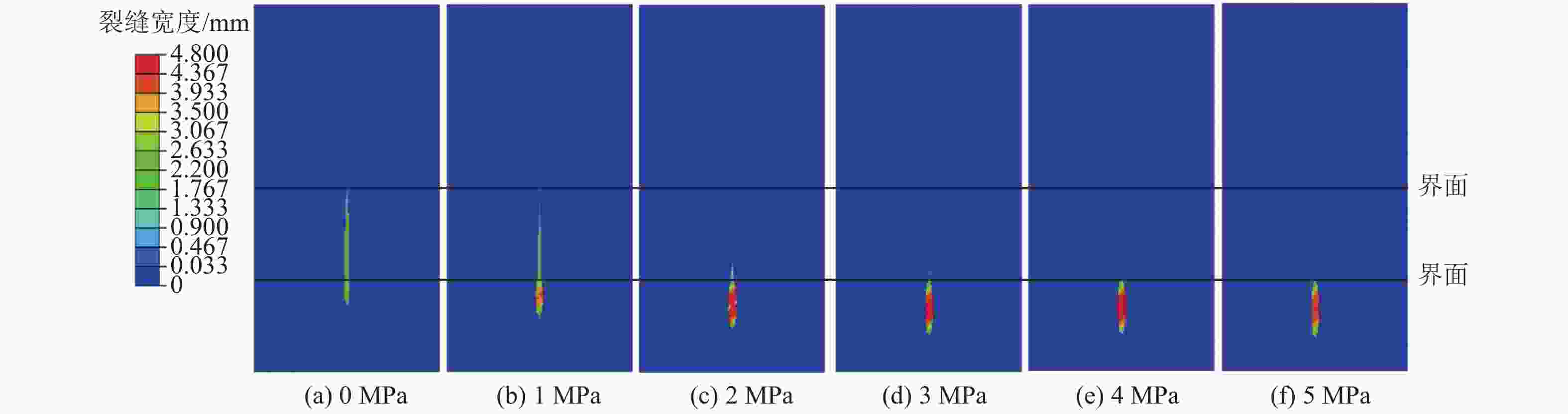
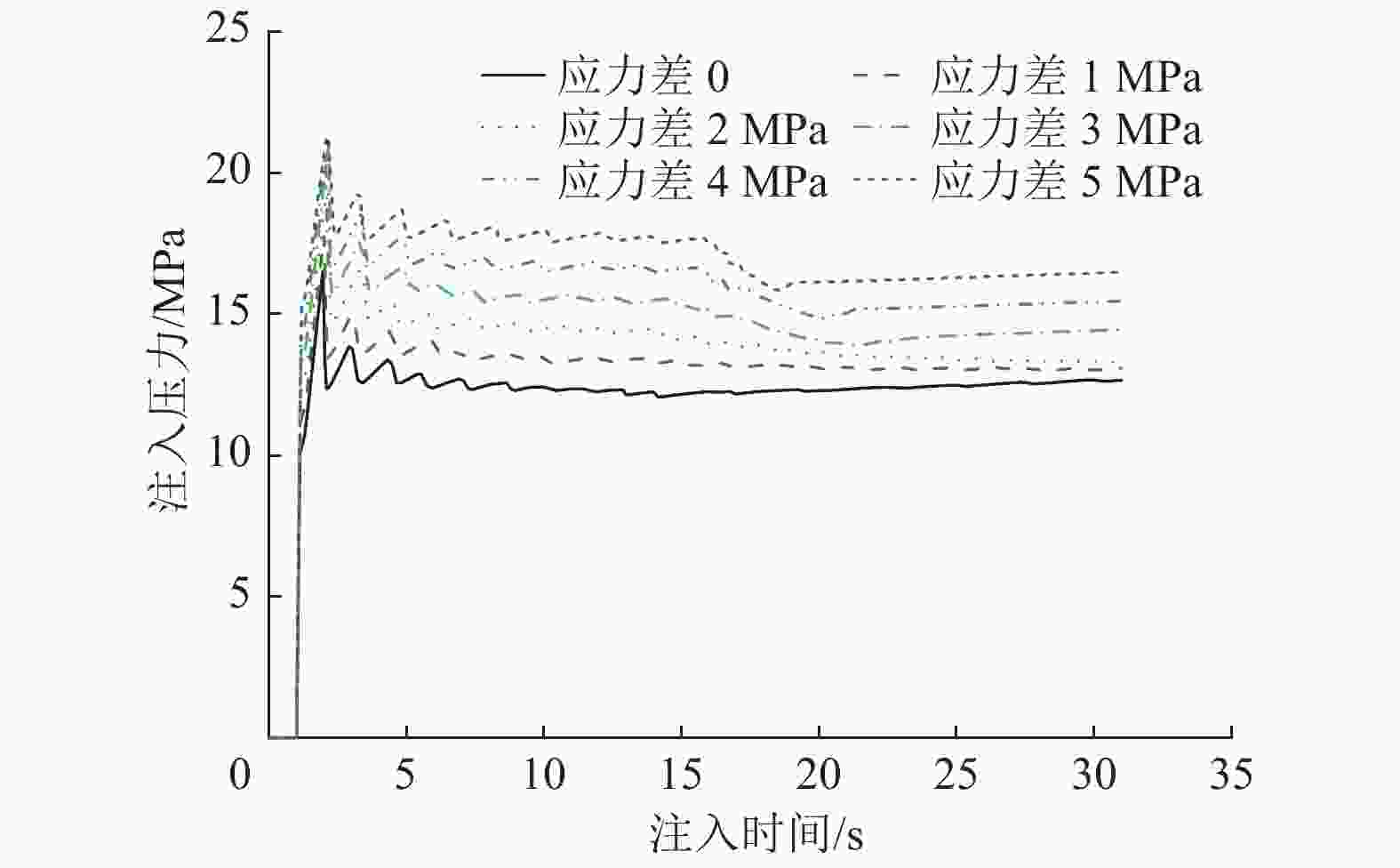
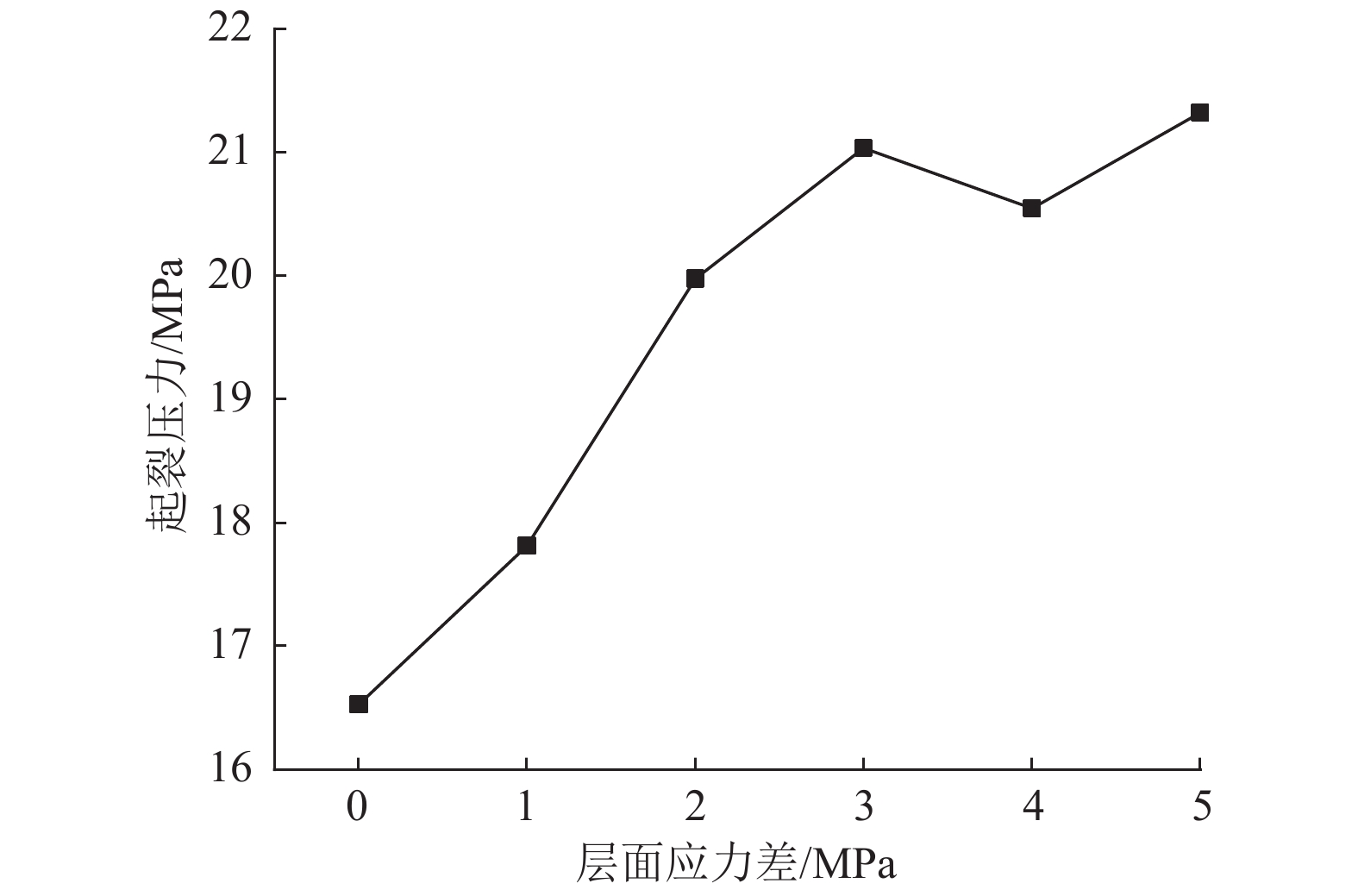
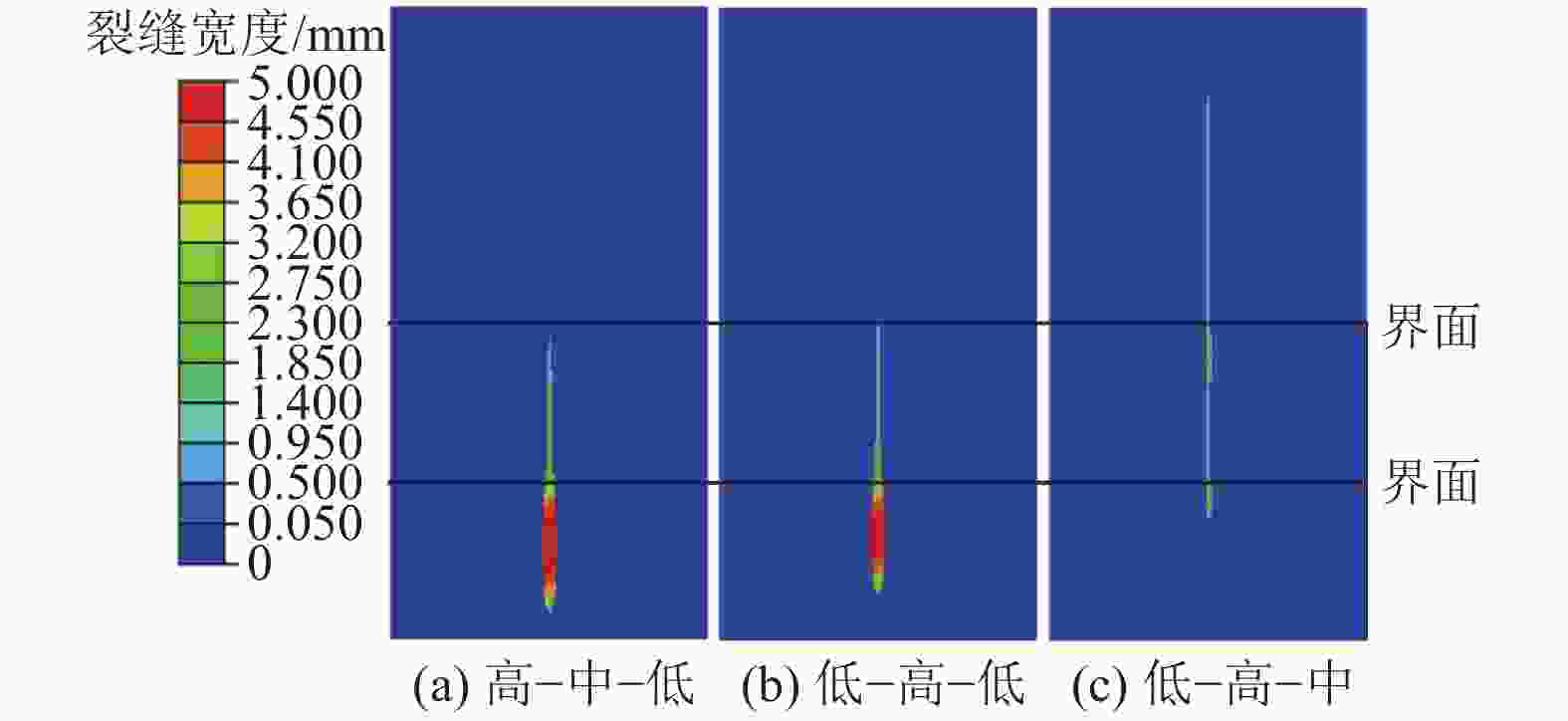
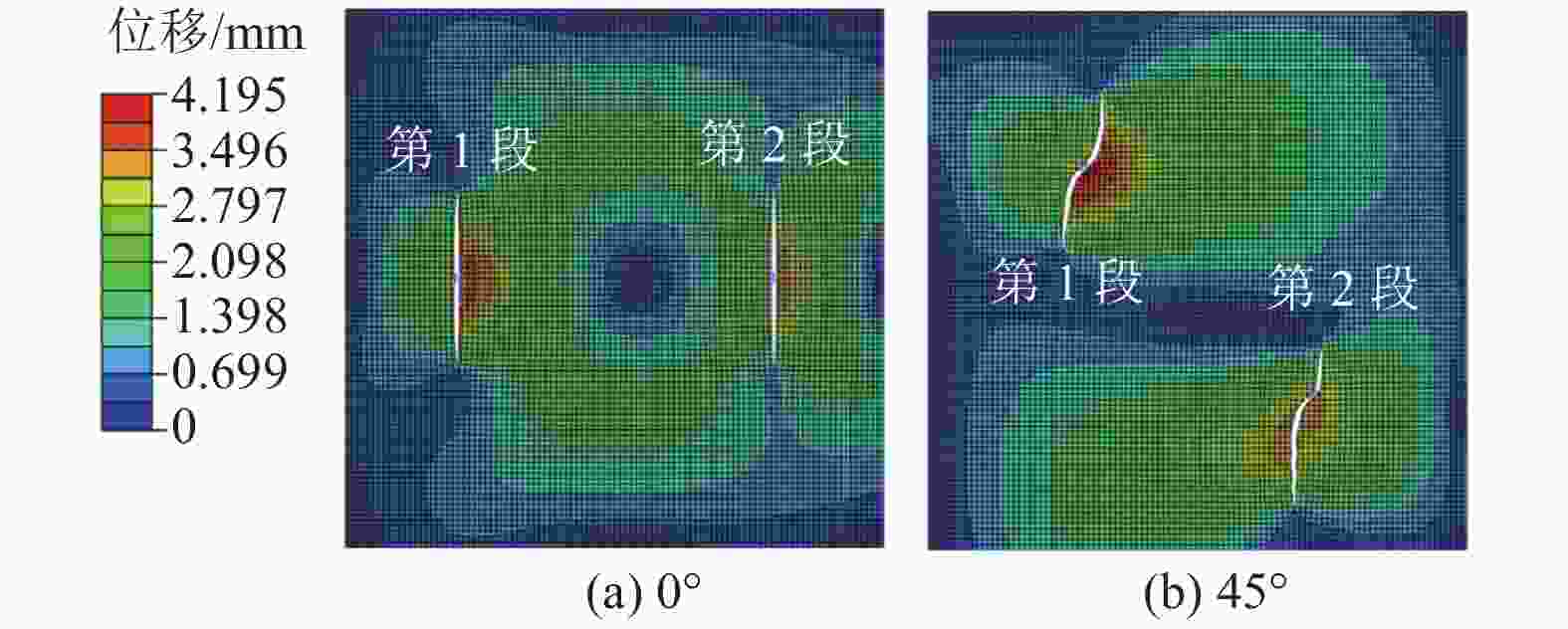
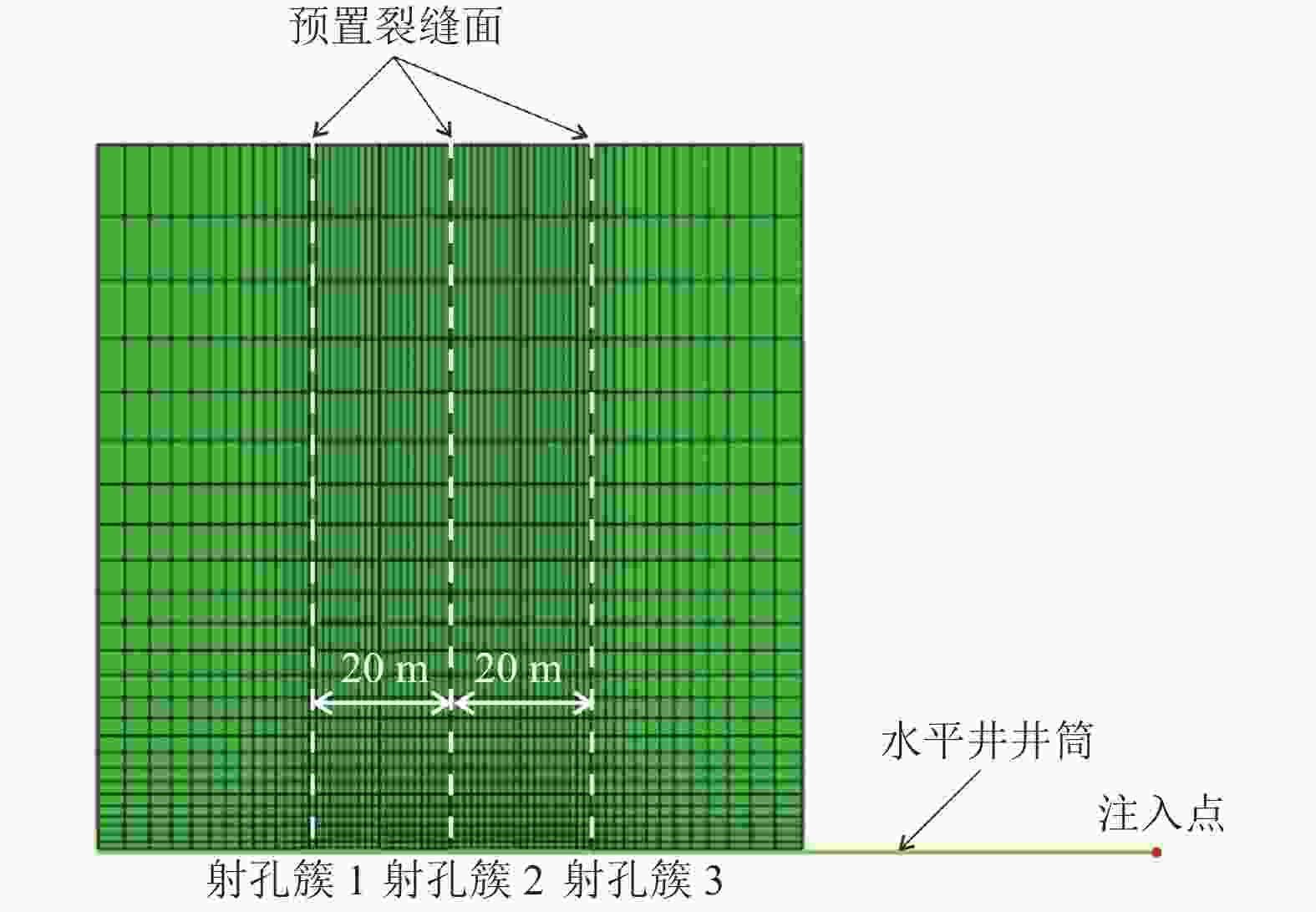
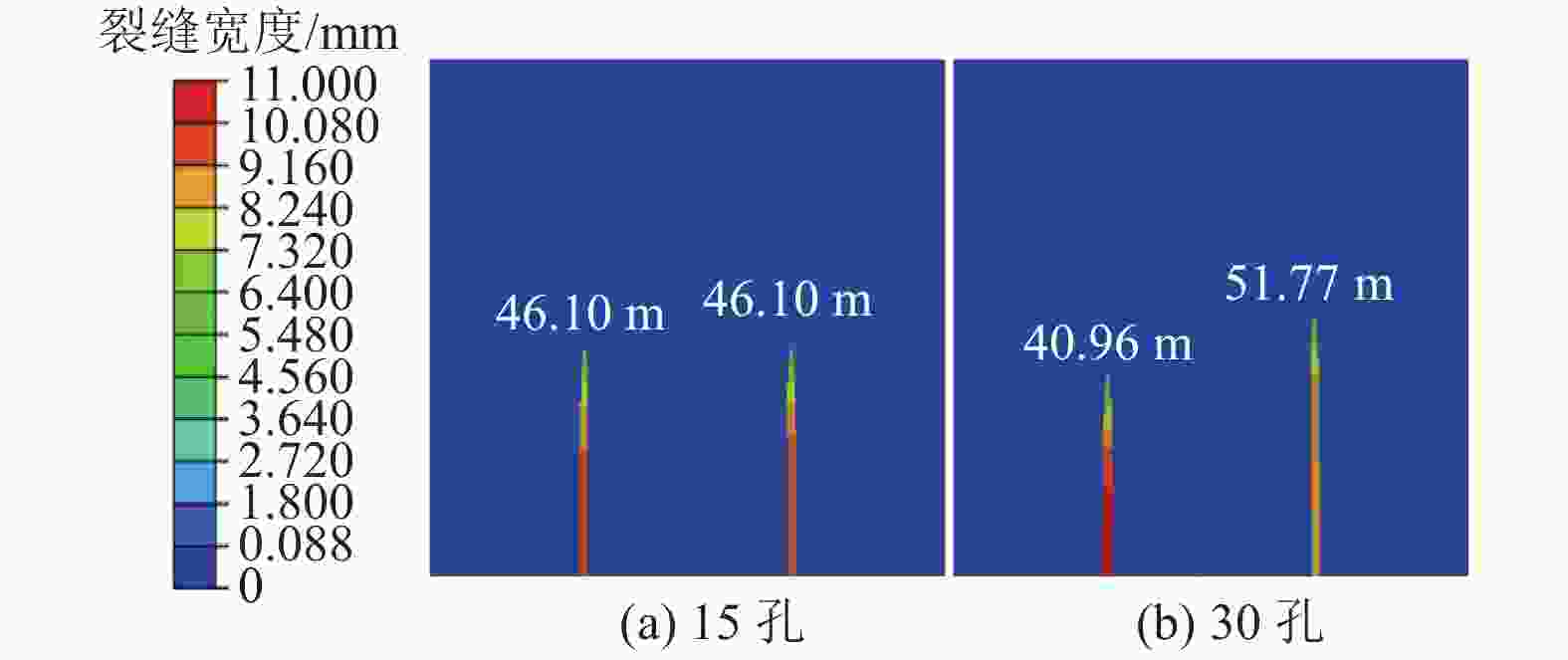
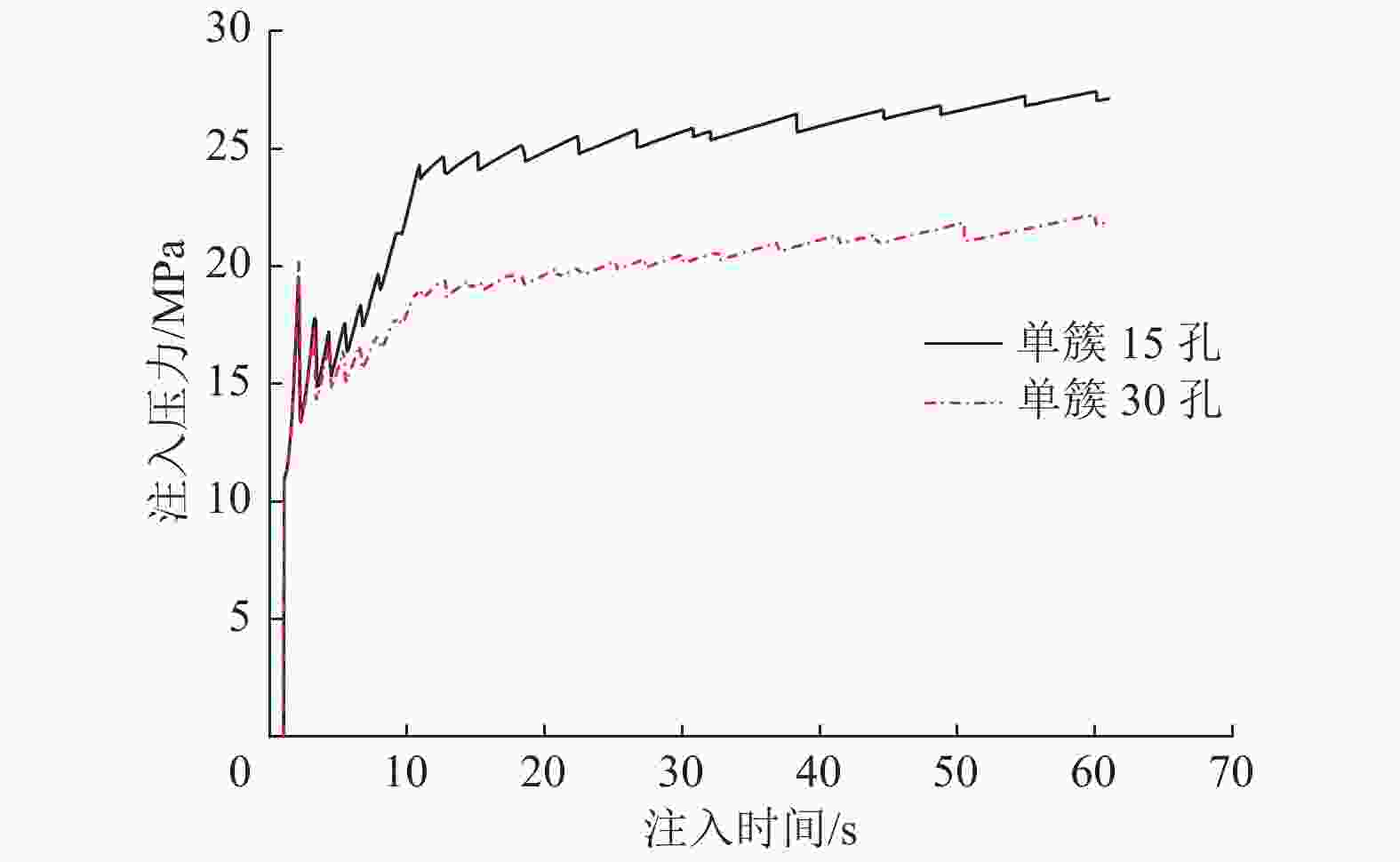
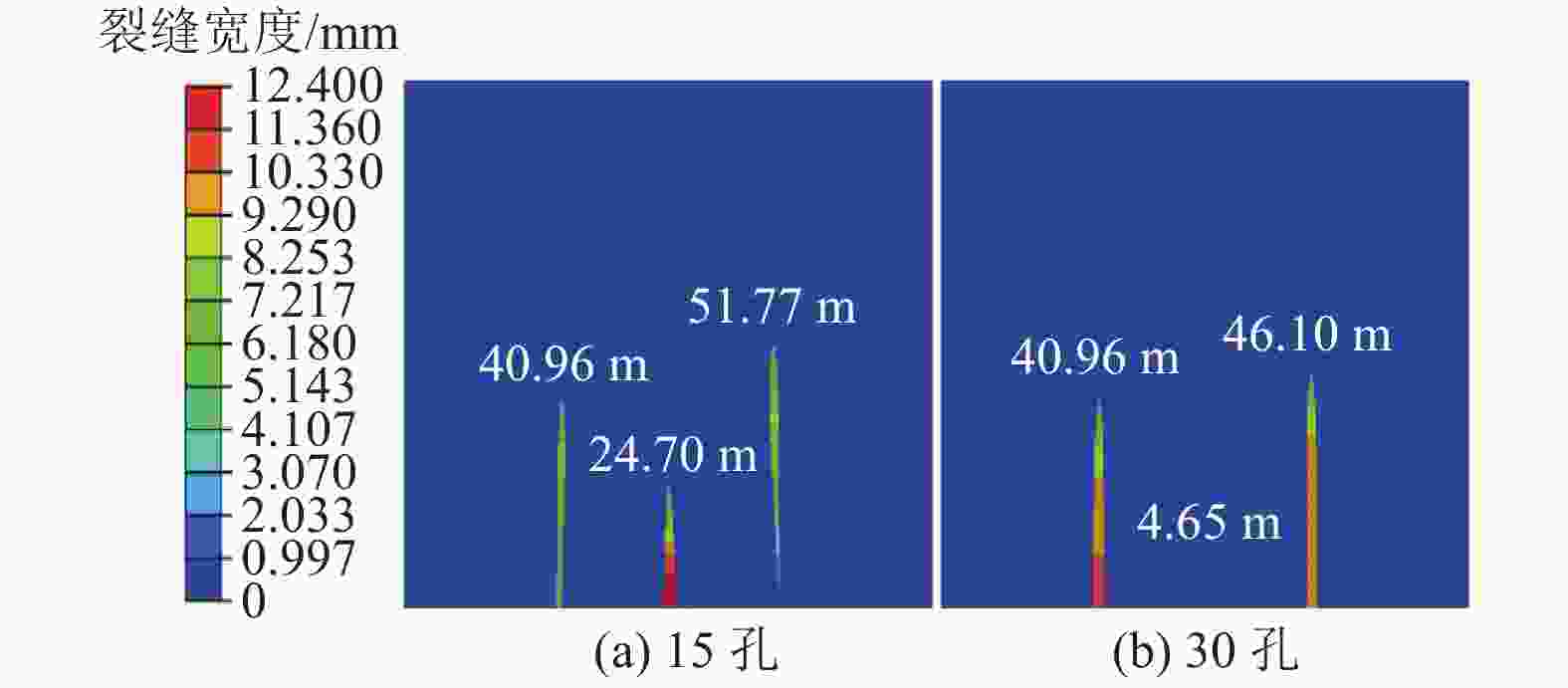
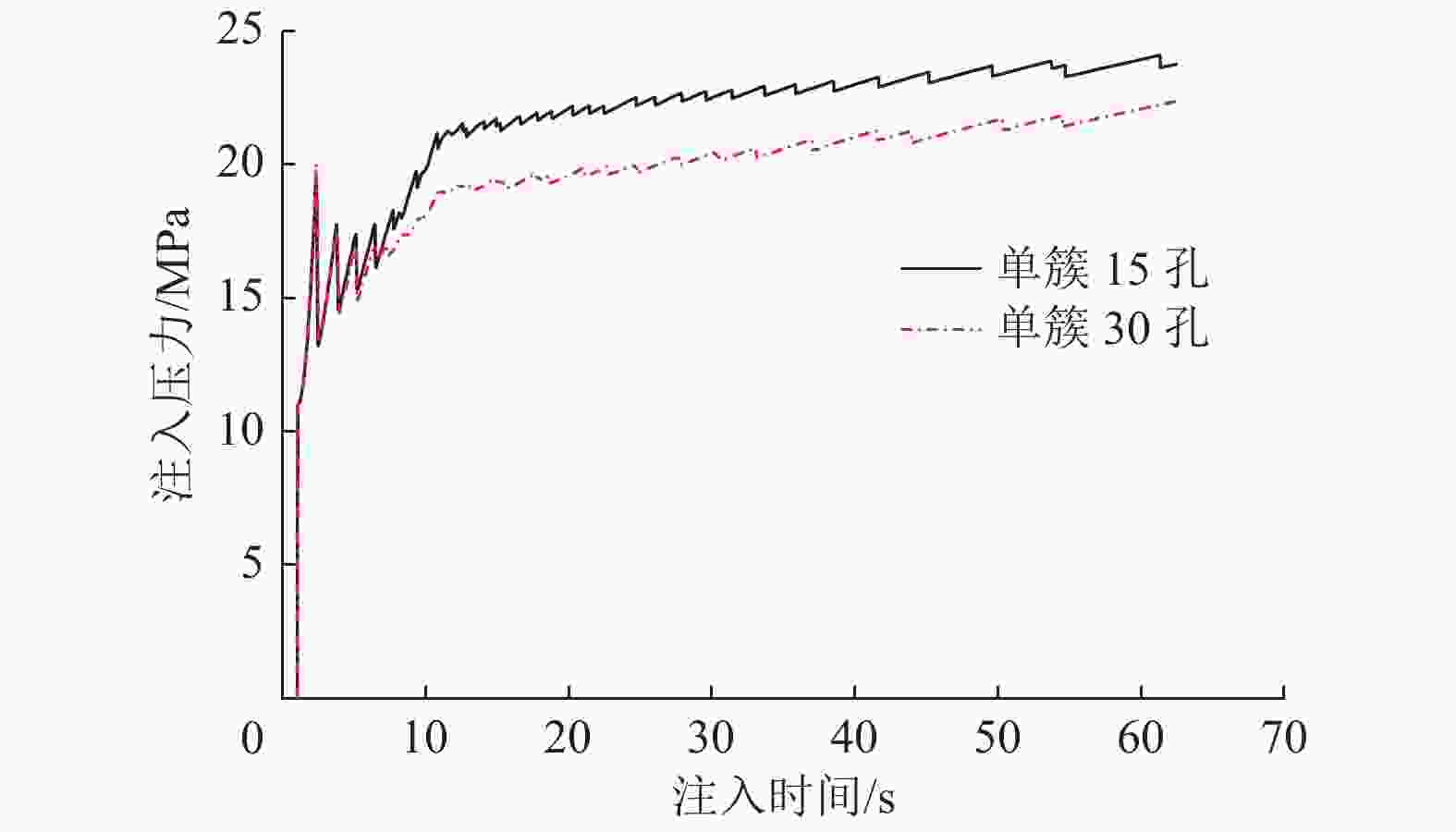
摘要: 煤层顶板分段压裂水平井是实现碎软低渗煤层煤层气高效抽采的有效技术。依托“十三五”国家科技重大专项课题,围绕煤层顶板分段压裂水平井煤层气高效抽采技术,采用理论分析、数值模拟等手段,对比不同地应力状态下裂缝的穿层扩展形态,研究水平井布井方位与最小水平主应力方向夹角对裂缝转向扩展的影响,分析多簇射孔条件下裂缝的竞争扩展现象。结果表明:(1)煤层顶板分段压裂水平井技术应用于碎软低渗煤层煤层气开发具有避免钻井液污染储层、提高水平井钻井施工安全性、提高固井质量、提高压裂改造效果、控制煤粉产出等优势。(2)地应力是裂缝穿层扩展的关键控制因素。为保证裂缝穿层扩展,垂向应力需大于最小水平主应力,顶板最小水平主应力需大于煤层,并且层间应力差为1~3 MPa时,既能够保证裂缝的穿层扩展效果,也能避免裂缝的起裂和延伸压力过高;“上覆岩层–顶板–煤层”应力剖面为“低–高–中”型时,水平井与煤层顶面的距离对于裂缝的穿层扩展效果影响较大;推荐水平井水平段与煤层顶面距离小于2.0 m。(3)水平井布井方位与最小水平主应力方向夹角越大,裂缝转向半径和转向距离越大,在压裂段间距相同的条件下,夹角为45°时缝间干扰程度比夹角为0°时强,不利于后续压裂段裂缝扩展,建议水平井布井方位与最小水平主应力方向夹角±15°以内。(4)对于分段多簇压裂,缝间应力干扰、压裂液流动摩阻、射孔孔眼摩阻共同导致各射孔簇裂缝非均匀扩展,可通过限流压裂、裂缝暂堵等手段促进裂缝均匀扩展。(5)工程试验取得了良好的产气效果,裂缝延伸特征与理论研究吻合度高。研究成果可为煤层顶板水平井的施工参数优化设计和推广应用提供借鉴。Abstract: The technique of staged fracturing horizontal wells in coal seam roof is effective for efficient extraction of coalbed methane (CBM) in broken soft and low-permeability coal seams. With the help of the major national science and technology projects of the 13th Five Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development, the efficient extraction technology of CBM by staged fracturing horizontal wells in coal seam roof was studied. By using theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, the fracture propagation patterns in different in-situ stress states were compared, and the influence of the angle between the horizontal well layout orientation and the minimum horizontal principal stress on the fracture deflection and propagation was studied. The competitive propagation phenomenon of fractures under the condition of multi-cluster perforation was also analyzed. The results show that: (1) the staged fracturing horizontal well in coal seam roof applied to CBM development in broken, soft and low-permeability coal seams can avoid contamination of reservoirs by drilling fluid, improve the safety in horizontal well drilling, cementing, and the effect of fracturing transformation, and controlling the output of coal fine. (2) In-situ stress is the key controlling factor for fracture propagation. In order to ensure the crack propagation through the bedding plane interface, the vertical stress must be greater than the minimum horizontal stress, and the minimum horizontal stress of the roof must be greater than that of the coal seam. The interlayer stress difference of 1-3 MPa can not only ensure the effect of through-layer propagation of fractures, but also avoid excessive fracture initiation and extension pressure. When the stress profile of “overlying rock-roof-coal seam” is “low-high-medium” type, the distance between the horizontal well and the top surface of the coal seam has a great influence on fracture propagation. It is recommended that the distance between the horizontal section of the horizontal well and the top surface of the coal seam should be less than 2.0 m. (3) The larger the angle between the horizontal well and the minimum horizontal stress, the greater the fracture turning radius and turning distance. With the same fracturing spacing, the fracture interference is stronger at an angle of 45° than at an angle of 0°, which is not conducive to the propagation of subsequent fractures. It is recommended that the angle between the horizontal well and the minimum horizontal stress should be within ± 15°. (4) For staged multi-cluster fracturing, the fracture stress interference, fracturing fluid flow friction, and perforation friction jointly lead to non-uniform propagation of fractures for each perforation cluster, which can be controlled by using limited entry fracturing, temporary plugging, etc., to promote the uniform propagation of fractures. (5) The pilot test has achieved good gas production, and the fracture extension characteristics are in good agreement with the theoretical research. The research results can provide reference for the optimization design and application of operational parameters of horizontal wells in the coal seam roof.
-
表 1 模型计算参数
Table 1 Simulation model parameters
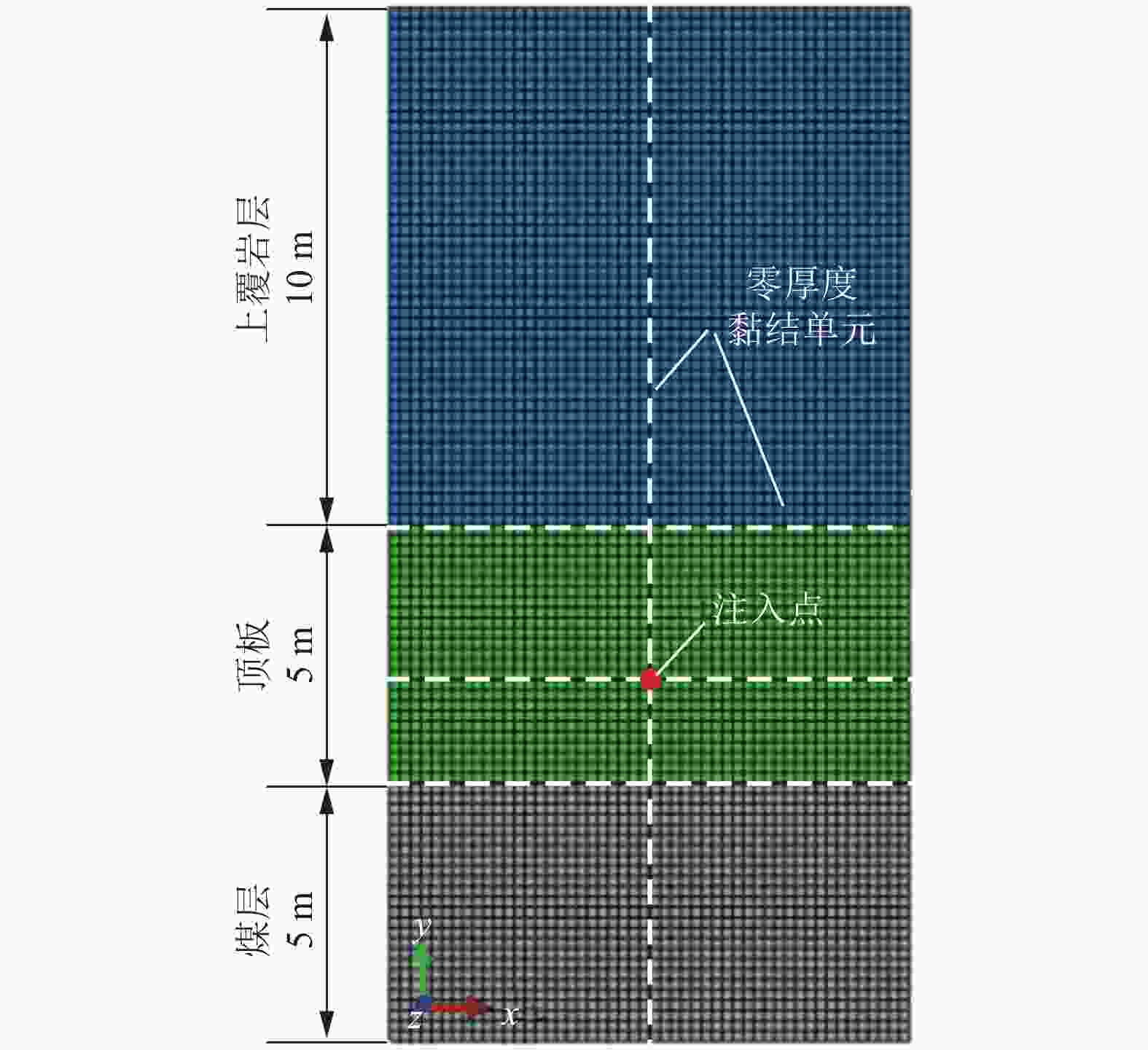
参数 上覆岩层 顶板 煤层 抗拉强度/MPa 1.50 1.00 0.50 弹性模量/GPa 4.50 3.00 1.00 泊松比 0.25 0.30 0.35 渗透率/10−3 μm2 0.01 0.01 0.10 地层孔隙率/% 2 2 9 煤层孔隙压力/MPa 6 6 6 垂向地应力/MPa 16 16 16 最小水平主应力/MPa 14 13 12 最大水平主应力/MPa 12 11 10 表 2 水平井压裂裂缝微地震监测结果
Table 2 Microseismic monitoring results of horizontal well hydraulic fracturing
裂缝参数 第3段 第7段 1357~1360 m 1317~1320 m 947~950 m 裂缝长度/m 左翼长度 43 46 100 右翼长度 未检测到有效裂缝 68 74 裂缝高度/m 11 16 12 裂缝方位 SW 70° NE 49° NE 45° 裂缝产状 垂直 垂直 垂直 -
[1] 周守为,朱军龙. 助力“碳达峰、碳中和”战略的路径探索[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(12):1−8. ZHOU Shouwei,ZHU Junlong. Exploration of ways to helping“Carbon Peak and Neutrality”strategy[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(12):1−8.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.12.001 [2] 孙海萍,张胜军,徐立昊,等. “双碳”目标下中国油气行业低碳发展措施与路径探讨[J]. 油气与新能源,2021,33(5):27−31. SUN Haiping,ZHANG Shengjun,XU Lihao,et al. Discussion on low−carbon development measures and paths of China’s oil and gas industry under the goals of “Dual Carbon”[J]. Petroleum and New Energy,2021,33(5):27−31. [3] 刘合,梁坤,张国生,等. 碳达峰、碳中和约束下我国天然气发展策略研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2021,23(6):33−42. LIU He,LIANG Kun,ZHANG Guosheng,et al. China’s natural gas development strategy under the constraints of carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2021,23(6):33−42. [4] 张道勇,朱杰,赵先良,等. 全国煤层气资源动态评价与可利用性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(6):1598−1604. ZHANG Daoyong,ZHU Jie,ZHAO Xianliang,et al. Dynamic assessment of coalbed methane resources and availability in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(6):1598−1604. [5] 张群. 关于我国煤矿区煤层气开发的战略性思考[J]. 中国煤层气,2007,4(4):3−5. ZHANG Qun. Strategic thinking on coal mine methane development in China[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2007,4(4):3−5.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2007.04.001 [6] 申宝宏,刘见中,雷毅. 我国煤矿区煤层气开发利用技术现状及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(2):1−4. SHEN Baohong,LIU Jianzhong,LEI Yi. Present status and prospects of coalbed methane development and utilization technology of coal mine area in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(2):1−4. [7] 桑树勋,周效志,刘世奇,等. 应力释放构造煤煤层气开发理论与关键技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2531−2543. SANG Shuxun,ZHOU Xiaozhi,LIU Shiqi,et al. Research advances in theory and technology of the stress release applied extraction of coalbed methane from tectonically deformed coals[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2531−2543. [8] 姜波,琚宜文. 构造煤结构及其储层物性特征[J]. 天然气工业,2004,24(5):27−29. JIANG Bo,JU Yiwen. Tectonic coal structure and its petrophysical features[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2004,24(5):27−29.. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.05.009 [9] 董夔,贾建称,巩泽文,等. 淮北许疃矿构造煤孔隙结构及压敏效应[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(2):58−65. DONG Kui,JIA Jiancheng,GONG Zewen,et al. Study on pore structure and pressure−sensitive effect of tectonic coal in Huaibei Xutuan mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(2):58−65. [10] LI Ming,JIANG Bo,LIN Shoufa,et al. Tectonically deformed coal types and pore structures in Puhe and Shanchahe coal mines in western Guizhou[J]. Mining Science and Technology(China),2011,21:353−357. [11] HOU Quanlin,LI Huijun,FAN Junjia,et al. Structure and coalbed methane occurrence in tectonically deformed coals[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2012,55(11):1755−1763.. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4493-1 [12] PAN Jienan,ZHU Haitao,HOU Quanlin,et al. Macromolecular and pore structures of Chinese tectonically deformed coal studied by atomic force microscopy[J]. Fuel,2015,139:94−101.. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.039 [13] 张群, 姜在炳, 李彬刚, 等. 一种煤层气分段压裂水平井强化抽采方法: CN103967472B[P]. 2016-08-31. [14] 张群, 姜在炳, 李彬刚, 等. 碎软低渗煤层顶板或底板分段压裂水平井煤层气抽采方法: CN112983385B[P]. 2021-08-10. [15] 巫修平. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂裂缝扩展规律及机制研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2017.WU Xiuping. Research on control mechanism of fracture propagation of multi−stage hydraulic fracturing horizontal well in roof of broken soft and low permeable coal seam[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2017. [16] 张群,葛春贵,李伟,等. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂煤层气高效抽采模式[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):150−159. ZHANG Qun,GE Chungui,LI Wei,et al. A new model and application of coalbed methane high efficiency production from broken soft and low permeable coal seam by roof strata−in horizontal well and staged hydraulic fracture[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(1):150−159. [17] 李彬刚. 芦岭煤矿碎软低渗煤层高效抽采技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(4):81−84. LI Bingang. Technology of CBM extraction in the crushed and soft coal seam in Luling coal mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2017,45(4):81−84.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.04.014 [18] 许耀波,朱玉双,张培河. 紧邻碎软煤层的顶板岩层水平井开发煤层气技术[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(9):70−75. XU Yaobo,ZHU Yushuang,ZHANG Peihe. Application of CBM horizontal well development technology in the roof strata close to broken−soft coal seams[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(9):70−75.. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.009 [19] 方良才,李贵红,李丹丹,等. 淮北芦岭煤矿煤层顶板水平井煤层气抽采效果分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(6):155−160. FANG Liangcai,LI Guihong,LI Dandan,et al. Analysis on the CBM extraction effect of the horizontal wells in the coal seam roof in Luling coal mine in Huaibei[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(6):155−160.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.06.021 [20] 姜在炳,李浩哲,方良才,等. 紧邻碎软煤层顶板水平井分段穿层压裂裂缝延展机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(Sup.2):922−931. JIANG Zaibing,LI Haozhe,FANG Liangcai,et al. Fracture propagation mechanism of staged through−layer fracturing for horizontal well in roof adjacent to broken−soft coal seams[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(Sup.2):922−931. [21] 巩泽文,贾建称,许耀波,等. 基于测井信息的煤层顶板水平井抽采煤层气技术[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(2):83−91. GONG Zewen,JIA Jiancheng,XU Yaobo,et al. The coal seam roof strata−in horizontal well CBM gas drainage technology based on logging information[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(2):83−91. [22] 许耀波. 应力干扰下煤层顶板水平井穿层分段压裂规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(4):11−18. XU Yaobo. Layer−penetrating staged fracturing law of horizontal wells within roof of coal seams under stress interference[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(4):11−18.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.002 [23] 胡焮彭,赵永哲,徐堪社,等. 黔北矿区煤层顶板水平井钻井关键技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(1):227−232. HU Xinpeng,ZHAO Yongzhe,XU Kanshe,et al. The key technology for drilling horizontal well in coal seam roof in Qianbei mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(1):227−232.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.031 [24] 方佳伟,韩保山,周加佳,等. 基于工作面全覆盖的地面瓦斯高效抽采模式研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(3):81−85. FANG Jiawei,HAN Baoshan,ZHOU Jiajia,et al. Surface efficient gas extraction mode based on full coverage of working face[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(3):81−85.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.03.012 [25] 李浩哲,姜在炳,舒建生,等. 水力裂缝在煤岩界面处穿层扩展规律的数值模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(2):106−113. LI Haozhe,JIANG Zaibing,SHU Jiansheng,et al. Numerical simulation of layer−crossing propagation behavior of hydraulic fractures at coal−rock interface[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(2):106−113.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.017 [26] 张东亮. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井条带瓦斯预抽技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(4):72−76. ZHANG Dongliang. Strip gas pre−pumping technology in horizontal well of broken soft and low permeability coal seam roof[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2019,50(4):72−76. [27] 巫修平,张群. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂裂缝扩展规律及控制机制[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(2):268−276. WU Xiuping,ZHANG Qun. Research on controlling mechanism of fracture propagation of multi−stage hydraulic fracturing horizontal well in roof of broken soft and low permeability coal seam[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2018,29(2):268−276. [28] 李浩哲,姜在炳,范耀. 基于裂缝尖端应力强度因子的裂缝穿层行为分析[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2019,34(1):76−82. LI Haozhe,JIANG Zaibing,FAN Yao. Analysis of crack across−layer extension behavior based on stress intensity factor at crack tip[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition),2019,34(1):76−82. [29] 成巧耘,李波波,李建华,等. 考虑支撑剂压实和嵌入作用的滑脱效应及渗流机制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(5):88−97. CHENG Qiaoyun,LI Bobo,LI Jianhua,et al. Slippage effect and the seepage mechanism considering the compaction and embedding action of proppant[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(5):88−97. [30] 唐方璇. 松软煤层支撑裂缝导流能力影响因素研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2018.TANG Fangxuan. Study on influence factors of fracture proppants conductivity in soft coal seam[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2018. [31] 雷毅,武文宾,陈久福. 松软煤层井下水力压裂增透技术及应用[J]. 煤矿开采,2015,20(1):105−107. LEI Yi,WU Wenbin,CHEN Jiufu. Technology of underground permeability improvement of soft coal−seam with hydrofracture and its application[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2015,20(1):105−107. [32] 雷毅. 松软煤层井下水力压裂致裂机理及应用研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2014.LEI Yi. Study on mechanism and application of hydraulic fracturing in soft seam underground mine[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2014. [33] 郑同社. 水力压裂煤储层卸压增透技术的适用性分析[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,32(5):536−539. ZHENG Tongshe. Adaptability analysis of technique to improve gas permeability of coal seam by hydraulic fracturing[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University(Natural Science),2013,32(5):536−539. [34] 康红普,伊丙鼎,高富强,等. 中国煤矿井下地应力数据库及地应力分布规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):23−33. KANG Hongpu,YI Bingding,GAO Fuqiang,et al. Database and characteristics of underground in−situ stress distribution in Chinese coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):23−33. [35] 许耀波,郭盛强. 软硬煤复合的煤层气水平井分段压裂技术及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(4):1169−1177. XU Yaobo,GUO Shengqiang. Technology and application of staged fracturing in coalbed methane horizontal well of soft and hard coal composite coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(4):1169−1177. [36] OLSEN T N, BRENIZE G, FRENZEL T. Improvement processes for coalbed natural gas completion and stimulation[C]. SPE 84122, 2003. [37] OLSEN T N, BRATTON T R, DONALD A, et al. Application of indirect fracturing for efficient stimulation of coalbed methane[C]. SPE 107985, 2007. [38] 郭建春,赵志红,路千里,等. 深层页岩缝网压裂关键力学理论研究进展[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(1):102−117. GUO Jianchun,ZHAO Zhihong,LU Qianli,et al. Research progress in key mechanical theories of deep shale network fracturing[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(1):102−117. [39] 赵金洲,王强,胡永全,等. 多孔眼裂缝竞争起裂与扩展数值模拟[J]. 天然气地球科学,2020,31(10):1343−1354. ZHAO Jinzhou,WANG Qiang,HU Yongquan,et al. Numerical simulation of multi−hole fracture competition initiation and propagation[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2020,31(10):1343−1354. [40] 周彤,张士诚,陈铭,等. 水平井多簇压裂裂缝的竞争扩展与控制[J]. 中国科学:技术科学,2019,49(4):469−478. ZHOU Tong,ZHANG Shicheng,CHEN Ming,et al. Competitive propagation of multi−fractures and their control on multi−clustered fracturing of horizontal wells[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica,2019,49(4):469−478.. doi: 10.1360/N092018-00059 [41] 程万,蒋国盛,周治东,等. 水平井中多条裂缝同步扩展时裂缝竞争机制[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(12):4448−4456. CHENG Wan,JIANG Guosheng,ZHOU Zhidong,et al. Fracture competition of simultaneous propagation of multiple hydraulic fractures in a horizontal well[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(12):4448−4456. [42] WU Kan,OLSON J,BALHOFF M T,et al. Numerical analysis for promoting uniform development of simultaneous multiple−fracture propagation in horizontal wells[J]. SPE Production & Operations,2016,32(1):41−50. [43] MURPHREE C, KINTZING M, ROBINSON S, et al. Evaluating limited entry perforating & diverter completion techniques with ultrasonic perforation imaging & fiber optic DTS warmbacks[C]. SPE 199712, 2020. [44] SOMANCHI K, BREWER J, REYNOLDS A. Extreme limited entry design improves distribution efficiency in plug−n−perf completions: Insights from fiber−optic diagnostics[C]. SPE 184834, 2017. [45] 陈钊,王天一,姜馨淳,等. 页岩气水平井段内多簇压裂暂堵技术的数值模拟研究及先导实验[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(增刊1):158−163. CHEN Zhao,WANG Tianyi,JIANG Xinchun,et al. Numerical simulation study and pilot test of multi−cluster fracturing and temporary plugging technology in the horizontal hole section of shale−gas horizontal wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(Sup.1):158−163. -









 下载:
下载: