Accumulation mode of middle-low rank coalbed methane in Houxia Basin,Xinjiang
-
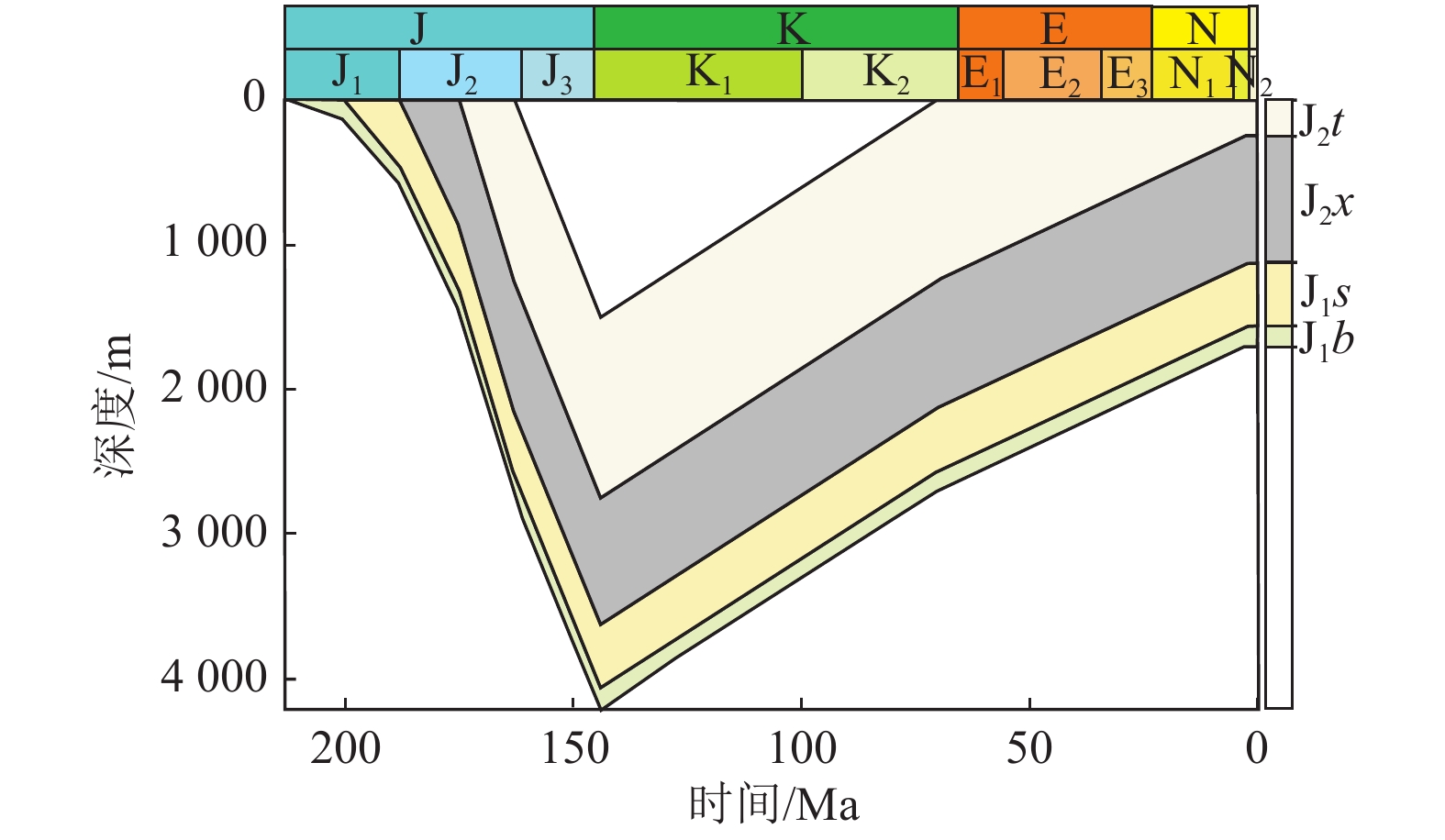
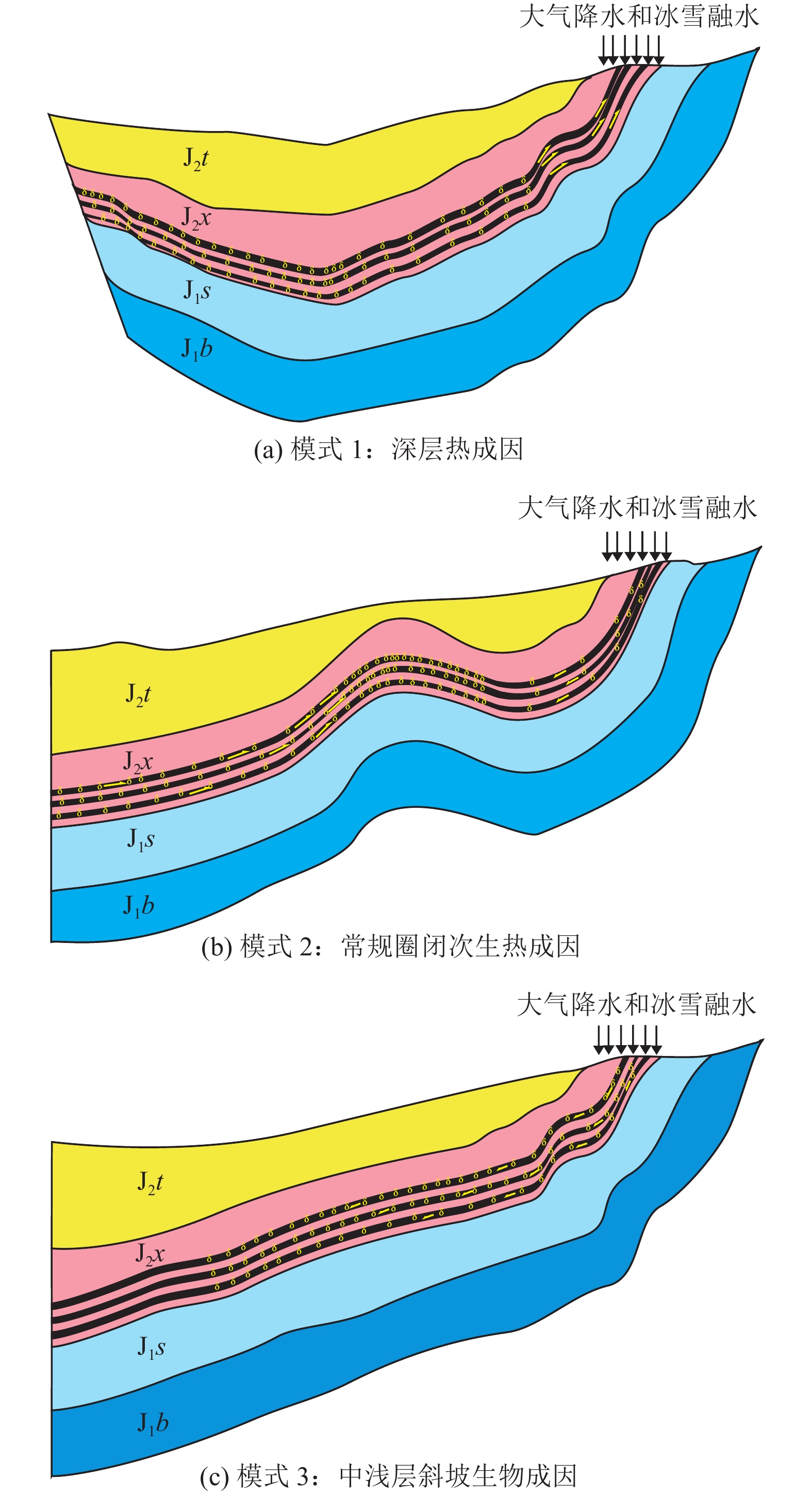
摘要: 低阶煤层气在国外有规模开发成功的案例,我国低阶煤层气资源丰富,但其勘探开发进展缓慢。新疆后峡盆地煤层气勘探程度较低,为进一步认识后峡盆地中–低阶煤煤层气成藏条件,指导勘探实践,根据研究区内地震、地质及已钻探井的煤岩分析化验和排采生产资料进行总结分析。结果表明,该区构造较为复杂,煤层厚度较大(4.1~24.3 m),发育较稳定,含气量差异较大(1.16~12.30 m3/t),物性较好,渗透率(1.61~13.30)×10−3 μm2,渗透性较好;并且存在热成因、次生热成因、混合成因及生物成因4种煤层气成因类型,结合构造演化、水文地质及煤层顶底板保存条件,形成了深层热成因、常规圈闭次生热成因及中浅斜坡生物气3种成藏模式,每一种成藏模式代表了不同的煤层气富集过程。认为研究区中–低阶煤煤层气在匹配的构造、水文及顶底板封盖条件下能够形成有利的资源富集区;3种成藏模式中,深层热成因及常规圈闭次生热成因成藏模式更有利于聚集成藏,其对应的区域是今后勘探开发有利区。Abstract: There are successful cases of large-scale CBM development of low-rank coal abroad. Though China is rich in low-rank CBM resources, their exploration and development progress is slow. Considering the low exploration degree and for the purpose of further understanding the accumulation conditions of medium-low rank CBM and guiding exploration practice in Houxia Basin, seismic and geological analysis, as well as coal petrography analysis and drainage production data of drilled wells are carried out in the study area. The results show that the coal seams are characterized by complex structure, large thickness (4.1-24.3 m), stable development, large difference in gas content (1.16-12.30 m3/t), good physical properties and large permeability (1.61-13.30)×10−3 μm2. There are four genetic types of CBM: thermal origin, secondary thermal origin, mixed origin and biological origin. Under this condition, combined with structural evolution, hydrogeology and preservation conditions of the coal seam roof and floor, three accumulation models of deep thermal origin, secondary thermal origin of conventional traps and medium shallow slope biogenic gas are formed. Each mode represents the concentration processes of different types CBM. It is considered that the medium-low rank CBM in this study area can form a favorable resource concentration area under the matched structural, hydrological, and roof and floor sealing conditions. Among the accumulation modes, deep thermal origin and secondary thermal origin of conventional traps are more favorable for accumulation, and the corresponding areas are favorable for future exploration and development.
-
据不完全统计,我国华北型石炭–二叠纪煤田煤层受底板岩溶水害威胁的煤炭资源储量高达570亿t。煤层底板高承压含水层水害已经成为新时期我国煤炭资源安全高效开采的主要制约因素[1]。目前,采用注浆技术对底板隔水层加固和含水层改造是煤层底板水害防治的主要手段[2]。
以往煤层底板含水层注浆改造一直采用常规直孔注浆,但由于钻孔钻遇含水层孔段较短,需要布置较为密集的钻孔来达到改造目的[3-6],而且必须依托井巷工程实施[7]。同时,注浆工艺也面临注浆盲区大、目标位置不准确、注浆效果差等问题,使巷道掘进过程中水害难以高效探查与治理。2008年,董书宁等[8]首次提出利用水平定向钻孔进行煤层底板注浆加固的理念,发明煤层底板注浆加固水平定向钻孔的施工方法,大幅增加有效注浆孔段长度,提高钻孔揭露裂隙带、含水体面积,减小注浆盲区,提高注浆改造效率[9]。另外,利用水平定向钻注浆可扩大单孔探查或注浆面积,减少钻进机械搬运工程,降低钻探工程对矿井生产进度影响,对煤层底板进行超前探查和治理[10]。
2011年,中煤科工西安研究院(集团)有限公司(简称西安研究院)首次将水平定向钻技术引入到煤层底板水害超前注浆治理中,在河南能化集团赵固一矿11151工作面成功完成现场底板注浆加固试验。随后,超前区域治理理念在河北邯邢矿区、安徽淮北矿区煤层底板水害治理中大面积推广应用,并迅速发展到断层、陷落柱等导水构造治理,形成了集超前区域探查与面状治理于一体的煤层底板水害超前区域治理技术[11-12]。该技术先后在河北峰峰矿区九龙、陕西焦坪矿区桑树坪[13]、安徽淮北矿区朱庄等煤矿[14] 成功应用,并进一步推广至安徽皖北[15]和淮南[16]、山东黄河北[17]、河北邯邢[18]、河南焦作[19]等大水矿区,取得了良好的治理效果,使水平定向钻技术广泛应用于矿井水害防治工程[20]。但在工程实践中,普遍面临水平定向钻孔浆液运移规律不明、钻遇隐伏导水通道判识与治理难度高、注浆效果检验技术不可靠等问题,且井下定向钻机钻进能力无法满足高强度、高水压灰岩含水层钻进和安全需求。
因此,针对上述问题,笔者聚焦水平孔浆液运移规律、超前区域注浆改造模式和分类标准、灰岩地层水平定向钻高效钻进工艺、隐伏导水通道超前判识治理、底板水害超前治理关键参数控制工艺、注浆效果检验与评价等方面进行深入研究,形成煤层底板水害超前区域治理技术体系,以期为现场工程实践提供重要的理论和技术支撑。
1 煤矿底板水害超前区域治理理念与技术体系
针对华北型煤田煤层底板石炭–二叠系太原组薄层灰岩或奥陶系灰岩(简称奥灰)岩溶含水层突水威胁,突破常规井下直孔注浆的“被动式”局部工作面防治理念,采用水平定向钻从地面或井下对底板岩溶含水层进行超前区域(多个工作面)注浆改造,实现底板水害的“主动式”防治。该技术有效避免了井下施工位置限制和影响采掘作业等问题,通过多个工作面整体超前治理实现了水文地质条件的区域性改变,避免了井下局部单个工作面改造后的绕流现象。
煤层底板超前区域治理技术涉及采矿工程、水文地质、工程地质、钻探工程等专业学科,是一项复杂的系统工程,面临众多技术难题,包括注浆层位选择、灰岩地层水平孔高效钻进工艺、隐伏导水通道判识、关键注浆参数控制工艺、注浆效果评价技术等,必须进行超前区域注浆治理改造模式、水平孔倾斜裂隙浆液扩散规律、注浆效果评价方法等理论研究,开发相关关键技术,才能为煤层底板超前区域治理提供理论和技术支撑。西安研究院经过近10年的研究开发和工程实践,创建了煤层底板水害超前区域治理的理论框架和关键技术(图1)。具体包括煤层底板水害超前区域治理模式分类和选择准则,实现超前区域的精准治理;形成灰岩地层水平定向钻高效钻进工艺和隐伏导水通道超前判识治理技术,实现坚硬灰岩地层钻孔施工和隐伏通道的精准探查和治理;形成底板水害超前治理关键参数控制工艺,实现超前区域治理关键注浆参数的科学确定;提出多指标的注浆效果定性与定量相结合的检验与评价方法。
2 煤矿底板水害超前区域治理关键技术
2.1 治理模式分类和选择准则
2.1.1 模式分类
现阶段,我国煤层底板水害超前区域治理工程已经形成了定向钻进、常规钻进、径向射流结合的施工方式,及薄层太原组灰岩和厚层奥陶系灰岩的含水层治理模式,其具体定义为以底板水害防治与带压开采为目标,考虑基础水文地质条件、治理区地面施工条件、治理层位选择和钻孔钻进方式,从工程施工方案选择角度构建技术可靠、经济合理的注浆治理技术与方案的组合体系[21-22]。
1) 指 标
超前区域治理模式分类指标包括施工位置、层位选择、钻进方式。其中施工位置可选取地面钻孔施工结合地面浆液、井下钻孔施工结合地面浆液、井下钻孔施工结合井下浆液3种配置方案;改造层位包括太原组薄层灰岩含水层和奥陶系巨厚灰岩含水层;钻进方式包括定向钻进和径向射流2种钻进方式。
2) 模 式
采用交叉分类原则对各指标进行交叉组合分类,当3个指标连接形成闭合环路径时,可提炼形成治理模式,据此得到5种超前区域治理模式(表1)。
施工位置C 层位选取L 钻进方式D 治理模式M 地面施工C1 厚层灰岩L1 定向钻进D1 C1L1D1地面定向钻进厚层灰岩改造模式M1 井下施工C2 厚层灰岩L1 定向钻进D1 C2L1D1井下定向钻进厚层灰岩改造模式M2 地面施工C1 薄层灰岩L2 定向钻进D1 C1L2D1地面定向钻进薄层灰岩改造模式M3 井下施工C2 薄层灰岩L2 定向钻进D1 C2L2D1井下定向钻进薄层灰岩改造模式M4 地面施工C1 厚层灰岩L1 径向射流D2 C1L1D2地面径向射流厚层灰岩改造模式M5 3) 亚类模式
定向钻进过程中利用侧向分支孔可形成4种钻孔布设形态,包括扫帚状(S1)、鱼骨状(S2)、梳状(S3)、叉状(S4);径向射流在治理层位利用射流工艺可形成梅花状(S5)布孔形态。另外,根据钻孔探查情况采用不同注浆材料,常见超前区域注浆材料包括碎石骨料(G1)、河沙骨料(G2)、粉煤灰(G3)、水泥(G4)。根据超前区域探查改造模式结合施工设计中钻孔形态、注浆材料分类,可综合确定治理模式亚类(表2)。
表 2 超前区域治理注浆改造亚类模式[21]Table 2. Subgroup mode of grouting transformation in advanced regional control[21]治理模式(M) 钻孔形态(S) 注浆材料(G) 亚类分类 C1L1D1地面厚层灰岩定向钻孔改造模式 扫帚状(S1)
鱼骨状(S2)
梳状(S3)
叉状(S4)碎石骨料(G1)
河沙骨料(G2)
水泥−粉煤灰(G3)
纯水泥(G4)C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G1/G2/G3)
C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G1/G2/G4)
C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G2/G3)
C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G2/G4)
C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G3)
C1L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G4)C2L1D1井下厚层灰岩定向钻孔改造模式 扫帚状(S1)
鱼骨状(S2)
梳状(S3)
叉状(S4)水泥−粉煤灰(G3)
纯水泥(G4)C2L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G3)
C2L1D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G4)C1L2D1地面薄层灰岩定向钻孔改造模式 扫帚状(S1)
梳状(S3)
叉状(S4)碎石骨料(G1)
河沙骨料(G2)
水泥−粉煤灰(G3)
纯水泥(G4)C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G1/G2/G3)
C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G1/G2/G4)
C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G2/G3)
C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G2/G4)
C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G3)
C1L2D1-(S1/S3/S4)(G4)C2L2D1井下薄层灰岩定向钻孔改造模式 扫帚状(S1)
鱼骨状(S2)
梳状(S3)
叉状(S4)水泥−粉煤灰(G3)
纯水泥(G4)C2L2D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G3)
C2L2D1-(S1/S2/S3/S4)(G4)C1L1D2地面厚层灰岩径向射流改造模式 梅花状(S5) 水泥−粉煤灰(G3)
纯水泥(G4)C1L1D2-S5(G3)
C1L1D2-S5(G3)2.1.2 模式选择准则
根据前文内容,可得到各判识指标选择标准:(1)地面有施工条件优先考虑地面施工;(2)煤层埋深大于800 m时地面施工钻探成本高,优先考虑井下施工;(3)煤层底板所承受水压大于6 MPa时,井下孔口装置难以保障施工安全,必须选用地面施工;(4)煤层埋深小于240 m时,地面定向钻孔施工难以实现造斜,优先考虑地面径向射流;(5)煤层底板有薄层灰岩地层结构,优先考虑改造薄层灰岩;(6)薄层、厚层灰岩顶部改造后需满足突水系数的要求。依据该选择准则体系,建立煤层底板灰岩含水层超前区域探查改造模式选择流程(图2)。
2.2 超前注浆定向钻孔高效钻进工艺
煤层底板超前注浆加固定向钻孔钻进时需要综合采用螺旋钻杆回转钻进、稳定组合钻具定向钻进和螺杆钻具随钻测量定向钻进等多种耦合工艺[23]。定向钻孔施工时按钻孔结构及施工工艺的不同可分为套管段施工、目的层位与套管之间层段施工、定向造斜段施工和透孔钻进施工等。钻进时,首先采用螺旋钻杆回转钻进工艺进行套管段施工,成功下入套管并试压合格;然后采用稳定组合钻具定向钻进工艺钻至目的层位,使钻孔倾角略为增加,以减少后期定向钻进倾角调整难度;再使用螺杆钻具随钻测量定向钻进完成定向造斜段和稳斜段施工,使钻孔按设计轨迹在目的岩层中延伸直至达到设计要求。
2.2.1 套管段
套管部位钻孔施工采用回转钻进成孔工艺,为确保套管顺利下入孔内,要求钻孔轨迹平直,孔内沉渣少,为此可采用螺旋钻进工艺配套稳定组合钻具和取心钻进工艺技术进行套管段施工。
2.2.2 回转钻进段
如果目的层位与套管之间岩层坚硬且较稳定,为缩短造斜段的距离,确保钻孔轨迹平滑可在回转钻进阶段利用稳定器组合钻具实施钻孔造斜;如果目的层位与套管之间岩层不稳定,钻进过程中需尽量缩短此段的钻孔长度,为此需对钻孔进行保直钻进。
2.2.3 定向钻进
井下硬岩层定向钻进过程中,造斜率是轨迹控制过程中衡量底部导向钻具组合造斜能力的重要指标,也是实施导向钻进工艺的重要依据。井下定向钻进普遍采用单弯螺杆马达,其配套的导向钻具长度较短、刚性较大、变形较小,可采用几何法计算煤矿井下导向钻具造斜率。
井下硬岩定向钻进轨迹控制宜采用复合定向钻进工艺。在钻进过程中钻杆柱“有滑有转”,以回转稳斜钻进为主、滑动造斜钻进为辅,典型轨迹控制方法如图3所示,当实钻轨迹与设计轨迹之间偏差达到一定值后,调整孔底螺杆马达造斜工具的指向(即工具面)、滑动给进,连续造斜改变钻孔前进方向,获得理想钻孔姿态参数后回转稳斜钻进,在水平面和垂直剖面内控制实钻轨迹围绕设计轨迹延伸。
2.3 隐伏导水通道超前判识治理技术
煤层底板隐伏导水通道是发生底板突水事故的主要因素之一,也是超前区域治理过程中的主要治理对象。综合采用钻进过程中岩屑录井、钻时录井、钻液漏失量、压水试验、随钻伽马、注浆参数等判识指标,能够验证地面物探疑似通道并在区域上探查隐伏导水通道发育情况,形成钻进过程中隐伏导水通道判识的主要指标、变化规律、通道类型等,科学判识通道导水性,为超前区域治理提供基础依据。
2.3.1 类型与特征
基于淮北、淮南、黄河北、邢台等华北型煤田矿区各矿井揭露的隐伏导水构造情况的分析和总结,得到矿井隐伏导水通道特征为:类型多样,且呈现隐伏断层、陷落柱及裂隙等构造类型组合出水事故特征;褶曲轴部裂隙相对发育,含水层富水性强,隔水层相对薄弱;多发育于煤层底板,发育层位低,位置不明,充填较松散、胶结差,导水性较好;隐蔽性好,可探测性差等。
华北型煤田开采主要受断层、陷落柱和岩溶裂隙构造的充水影响,根据岩溶含水层特征及钻探过程中所能探查的构造精度、种类和性质,可得到隐伏导水通道分类,即岩溶裂隙,包括封闭溶隙、弱连通溶隙、强连通溶隙;断层,包括隔水断层、弱导水断层、导水断层;陷落柱,包括全充水强导水型、边缘充水导水型、不导水(微弱导水)陷落柱。
2.3.2 判识指标
隐伏导水通道的存在是造成煤层底板突水事故的主要因素之一,是超前区域治理的主要对象。对我国多个矿区超前区域治理钻探、注浆成果进行统计,总结出岩屑录井、钻时录井、冲洗液消耗量、压水试验、注浆参数和随钻伽马6个隐伏导水通道的判识指标。其中,岩屑录井和钻时录井用于判识构造通道发育情况,冲洗液消耗量、压水试验和注浆参数用于判识通道的导水性,随钻伽马作为孔内地球物理探查方法,对所判识的隐伏导水通道进行验证和预判。
分析隐伏导水通道判识指标得到,定向钻进过程中,岩屑录井共有3种曲线类型,即岩屑渐变型(岩屑-Ⅰ型)、岩屑突变无岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅱ型)、岩屑突变有岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅲ型);钻时录井曲线共有3种曲线类型,即钻时渐变型(钻时-Ⅰ型)、钻时突变未放空型(钻时-Ⅱ型)、钻时突变放空型(钻时-Ⅲ型)。根据不同构造形态特征得到灰岩含水层中判识指标的多元组合(表3)。
表 3 多元信息通道判识组合Table 3. Combination of multiple information channel identification序号 岩屑录井形态 钻时录井形态 判识构造类型 1 岩屑渐变型(岩屑-Ⅰ型) 钻时渐变型(钻时-Ⅰ型) 穿层,非构造 2 无变化形态 钻时突变未放空型(钻时-Ⅱ型) 小型岩溶裂隙(隙宽<10 cm) 3 无变化形态 钻时突变放空型(钻时-Ⅲ型) 大型岩溶裂隙(隙宽>10 cm) 4 岩屑突变无岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅱ型) 钻时突变未放空型(钻时-Ⅱ型) 小型断层 5 岩屑突变无岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅱ型) 钻时突变放空型(钻时-Ⅲ型) 大中型断层 6 岩屑突变有岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅲ型) 钻时突变未放空型(钻时-Ⅱ型) 胶结良好陷落柱 7 岩屑突变有岩爆型(岩屑-Ⅲ型) 钻时突变放空型(钻时-Ⅲ型) 胶结较差陷落柱 2.3.3 判识方法
根据我国现阶段主要治理区钻孔施工揭露情况统计,确定“冲洗液消耗量中钻液漏失量大于30 m3/h,压水试验渗透率大于10 Lu,单位注浆量大于10 t/m”可作为地层通道导水性判识标准。基于多因素建立综合判识标准,对通道的导水性能进行分区,得出不同构造类型的导水性能类型。根据上述3因素进行通道导水性分区,可分为8个小区(图4)。
2.4 底板水害超前治理关键参数控制工艺
由于煤层底板岩溶裂隙含水层超前区域注浆具有隐蔽性特征,注浆实践中缺少对浆液扩散的有效控制,致使存在施工周期长、注浆量大、注浆效果不可靠等问题。基于超前区域注浆特点,关键注浆参数控制结合受注地层特征、注浆材料、浆液性能、浆液扩散规律[24]、底板注浆改造要求和工艺等因素,系统分析注浆材料及浆液选配和调控、注浆终结标准、钻孔布置间距和方向、注浆控制因素等[25]。
(1) 奥陶系灰岩顶部垂向渗透性存在明显差异,存在渗透性随深度增加而增大的变化趋势;细观空隙的总数量中以闭合裂隙和微张裂隙数量占比为主,两者开度均值分别稳定在120和420 μm,宽张裂隙和中张裂隙在总裂隙面积中占主要比例,具有较好的贯通性和延展性;在奥灰顶部超前区域注浆过程中可采用水泥−粉煤灰浆液或水泥−黏土浆液进行“垫底式”充填注浆,再采用颗粒较细小的水泥浆液对微小裂隙和闭合裂隙进行升压注浆和劈裂注浆[26-28]。
(2) 水泥浆液、水泥−粉煤灰浆液、水泥−黏土浆液的凝结时间主控因素为水玻璃掺量,黏度的主控因素分别为水玻璃掺量、水灰比、水灰比,结石率的主控因素分别为水灰比、水灰比、水玻璃掺量,强度的主控因素为水灰比;根据各因素极差大小进行排序,得到各因素对实验结果的敏感性,由大到小为:裂隙开度>裂隙倾角>水灰比>注浆压力,即裂隙开度对浆液扩散距离影响程度高于裂隙倾角,浆液水灰比高于注浆压力[29-31]。
(3) 关于注浆压力、稳压时间和钻孔间距确定,可通过分析不同条件下水平孔倾斜单裂隙浆液扩散距离特征曲线,得到不同浆液水灰比、受注地层条件和注浆压力下的浆液扩散距离,结合注浆设备额定工作能力约束,得到符合注浆设备工作能力的水平孔间距,同时也得到对应钻孔间距的注浆压力和稳压时间,通过与岩体起裂压力对比可得到合理的注浆终结压力,最后得到对应稳压时间和水平注浆孔间距的注浆终结压力标准,该标准能够满足注浆设备能力和水平注浆孔间距要求,也可有效保证注浆覆盖范围和注浆效果[32]。
(4) 水平分支孔布设方向可根据受注地层地应力方向尽量保持钻孔轨迹与最大主应力方向垂直、与最小主应力方向平行。注浆过程中浆液扩散可根据浆液性能和扩散距离敏感性特征通过调控浆液水灰比、注浆压力和注浆时间达到注浆终结压力和稳压时间标准。
综合上述控制因素和原则,结合底板超前区域注浆工艺和要求,形成煤层底板水害超前区域治理关键注浆参数控制技术(图5)[33]。
2.5 检验与评价
注浆效果评价为煤层底板超前区域治理技术的重要组成部分。准确地进行注浆效果评价,不但可以有效保证矿井采掘安全,还可为超前区域治理工程布设提供指导,进一步优化注浆孔布设及注浆工艺。
2.5.1 定性评价方法
灰色关联分析是灰色系统方法之一,已广泛应用于经济学、社会学和环境等各个领域。它的基本思想是根据2个数据序列几何形状的相似性来确定它们之间的关系度。根据几何形状建立了关系分析模型[34],断线之间的几何形状越近,关系度就越大。灰色关联分析可综合注浆量、钻井液漏失量、伽马值、水温、平均渗透率、注浆段长度等多种注浆因素,通过关联、分组、综合评分进行效果检验。具体注浆中分析和整理注浆点的注浆量、钻井液漏失量、伽马值、水温、平均渗透率、注浆段长度、奥灰含水层水压和隔水层厚度等数据,并灰色关联度计算,通过各个参数的灰色关联度确定其评价结果的权重。然后计算得到突水风险评估的综合权重系数、综合分数并完成突水风险评价图。
2.5.2 定量评价标准
注浆效果检查方法有钻探、物探和注浆特征分析法等,主要以定性评价方法为主。而以冲洗液消耗量、钻孔涌水量、渗透率和改造层厚度4个指标为研究对象,可建立超前区域治理技术的注浆效果定量评价分析方法[35]。
根据多个矿区注浆改造施工技术经验,当冲洗液消耗量为均匀消耗时,且消耗量不大于1 L/(min·m),表明注浆效果良好;根据多个矿区注浆改造施工技术经验,当井下检查孔为均匀出水且每钻进100 m段内涌水量小于5 m3/h时,表明注浆效果良好;当每个层段的渗透率均不大于1 Lu时,表明注浆效果良好。在地层结构预测准确的前提下,只要轨迹偏差、注浆结束标准均满足设计要求时,且在该注浆层段内,渗透率、钻孔涌水量、冲洗液消耗量均达到注浆良好标准时,表明改造层厚度达到设计要求。
2.5.3 孔中物探检验设备及配套工艺
电磁波在地下岩层中传播时,由于各种岩石、矿物电性参数(电阻率、介电常数等)不同,对电磁波能量的吸收有一定差异,电阻率较低的岩石、矿物具有较大的吸收作用。另外,伴随着断裂构造或空洞所出现的界面,能够对电磁波产生折射、反射等作用,也会造成电磁波能量的损耗。因此,可研究各种岩层及地质构造对电磁波传播的影响(包括吸收、反射、二次辐射等作用)所造成的各种异常进行地质解释,从而判识地质构造。基于上述原理,为实现注浆效果检验,制造了孔中无线电波透视装备,其工作原理如图6所示。
发射机是孔中电磁波透视仪的建场设备,供出稳定、具有较强功率且符合本安要求的电磁波信号是发射机的主要技术指标。接收机接收的信号范围为纳伏到微伏级,按探测设计要求可选择接收探测频率信号。接收机由模拟板、控制板、电源板和面板组成,接收机采用本安型防爆设计,孔中接收天线采用多级放大设计,使孔中接收信号通过天线放大处理,实现电磁波信号的高性能接收。具体检验钻孔可在工作面巷道底板施工定向钻,采取“一对二”施工方式,具体施工方式如图7所示。
2.5.4 综合检验技术
超前区域治理工程中可采用孔间电磁波透视仪对前一注浆序次进行效果检验并补充分支孔进行及时补充注浆。在治理完成后,综合单个钻孔漏失量、注浆量、水温、平均渗透率等指标,采用关联分析、综合评分定性评价整个治理区注浆效果。在孔间物探确定的浆液充填较差区、定性评价的注浆效果较差区施工井下注浆效果检查钻孔,评价注浆效果,并对效果较差区域进行补充注浆,由此形成了注浆效果检验综合评价装备技术体系(图8)。
3 工程应用
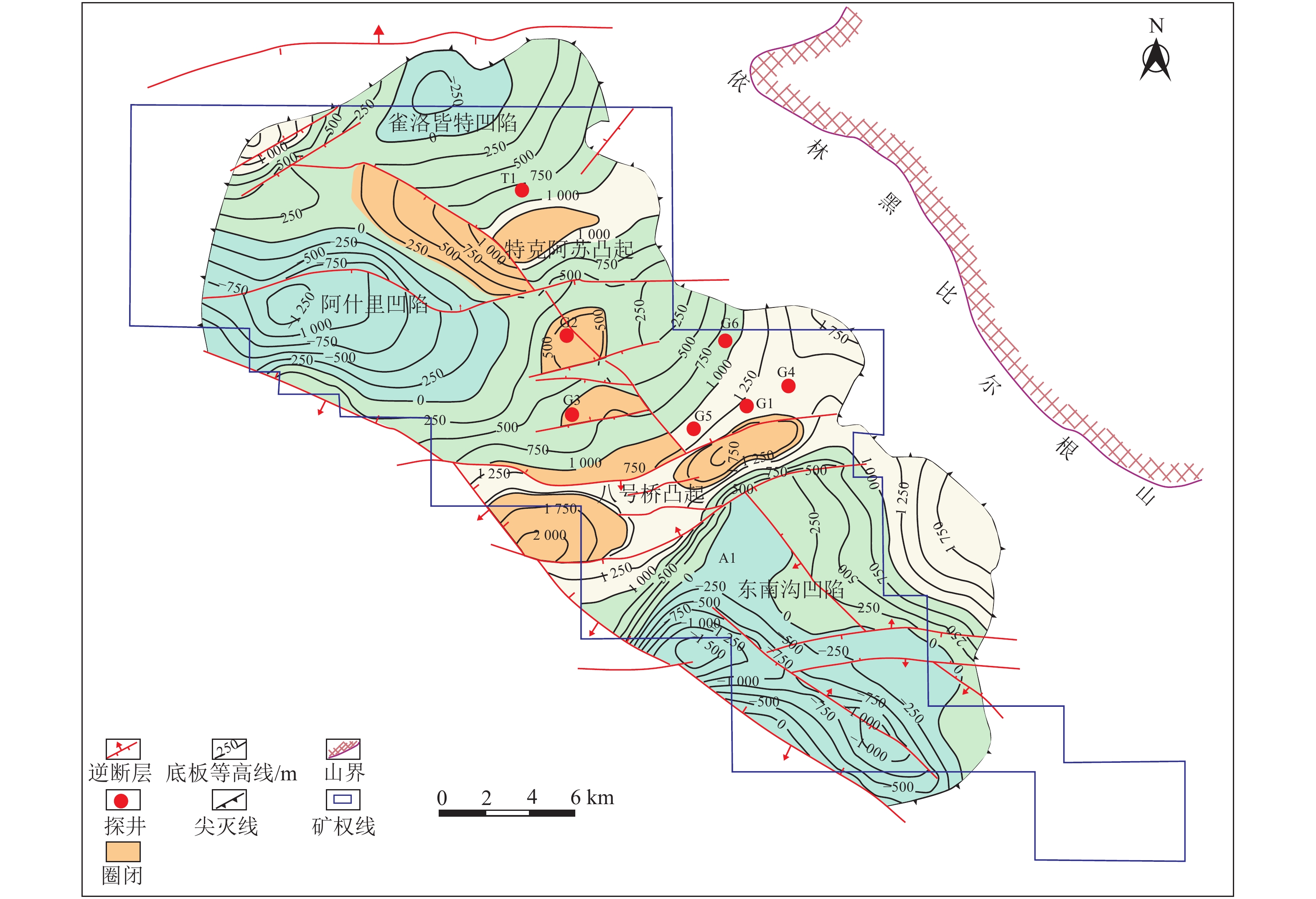
桑树坪煤矿位于陕西渭南,地表为山峁沟谷地貌,主采二叠系山西组3号煤和石炭系太原组11号煤,其中11号煤距底板奥陶系灰岩含水层近,受奥灰水害威胁极为严重(图9)。地面高程+430~+750 m,平均为+590 m;煤层埋深240~560 m,平均为400 m;奥灰顶界面高程+140~+210 m,平均为+175 m;奥灰含水层水位+380 m;底板与奥灰含水层间距16.5~21.5 m,承受最大水压为1.23 MPa,最大突水系数0.072 MPa/m。3105工作面实测底板破坏深度14.8 m,最小有效隔水层厚度仅有1.7 m。工作面回采面临极为严重的底板奥灰含水层突水威胁。
3.1 治理模式选取
由于煤层底板无薄层太原组灰岩,因此改造层位选择奥陶系灰岩顶部峰峰组风化充填带。由于3105工作面及周边对应地表为山峁沟谷地貌,沟壑纵横钻机进场施工难度高,且民事协调难度大,赔青费用高。因此,3105工作面区域治理不具备地面施工条件;另外,煤层底板所承受奥灰含水层最大水压为1.23 MPa,小于井下钻孔安全施工6 MPa的要求,确定区域治理钻孔施工采用井下定向钻进方式。综合分析,3105工作面采用C2S1D1井下厚层灰岩定向钻孔改造模式进行煤层底板含水层超前区域治理。
3.2 治理关键参数
基于工程成本和浆液性能考虑,注浆过程中主要采用水灰比相对较大的水泥浆液进行注浆,因此,在参数计算过程中采用牛顿型水泥浆液参数。在注浆过程中孔口注浆压力与受注地层裂隙注浆点处的有效压力存在中间流动过程的动力损失,计算公式见下式,因此,通过计算转换可得到有效注浆压力。
$$ {p_1} = p + {p_{\rm{s}}} - {p_\text{ξ}} $$ (1) 式中:p1为作用到灌浆段中点上的实际压力;p为孔口处压力表显示的压力;ps为浆液自重产生的压力;pξ为浆液在流经自压力表至灌浆段中点一段路程上的流动损失。
根据超前区域注浆改造范围将水平分支钻孔间距设置为40 m,基于水平孔倾斜单裂隙牛顿型流体扩散控制方程,计算得到桑树坪煤矿底板奥灰超前区域治理中注浆时间下限,其注浆改造试算参数见表4。
表 4 桑树坪煤矿超前区域注浆改造试算参数Table 4. Trial calculation parameters of grouting transformation in advanced regional control of Sangshuping Coal Mine浆液参数 孔口注浆压力/MPa 有效注浆压力/MPa 钻孔半径/m 静水压力/MPa 水灰比 黏度/(Pa·s) 相对密度/(kg·m−3) 1 0.1198 1424 3 4.30 0.048 2.05 2 0.0967 1248 4.14 3 0.0742 1160 4.06 经过计算得到6 000 s内不同水灰比下浆液扩散距离变化曲线(图10)。根据水平分支孔间距40 m,为保证注浆效果,水灰比为1∶1的浆液注浆时间不能低于3 800 s,水灰比为2∶1的浆液注浆时间不能低于3 200 s,水灰比为3∶1的浆液注浆时间不能低于2 600 s。
3.3 工程布设与应用效果
改造层位为进入奥灰层位后23~31 m,平均27 m;孔深660 m;三开裸孔段孔径96 mm。工作面回采前在井下巷道施工钻场,沿工作面走向布设定向钻孔14个,钻孔平面投影间距约40 m,垂直深度位于奥陶系灰岩顶面以下15~20 m,对于揭露的奥灰含水层出水位置采用下行式注浆方式,具体钻孔布设如图11所示。
工作面回采揭露表明,采用井下超前区域治理模式有效探查并改造了煤层底板含水层的富水位置,保障了工作面安全。
4 展 望
随着煤矿开采深度增加,煤炭开采面临底板高压岩溶含水层水害威胁愈发严重,为华北型煤田煤层底板超前区域治理工作提出了新的要求:
(1) 深部煤层底板岩溶含水层突水机理。煤层底板突水机理是指导底板超前区域治理层位和模式选择的依据。以往广泛应用的底板突水系数对于深部煤层底板突水评价适用性较差,目前其他突水机理研究成果尚未有效揭示深部煤层采动过程中底板应力、裂隙和水压等影响因素的耦合致灾机制,而采动过程中应力状态转换、水压损伤、裂隙通道起裂等变化存在相互影响和制约,如何揭示其内在关系是底板突水机理研究发展的重要方向。
(2) 煤矿底板导水通道超前精准探查。由于煤层底板灰岩岩溶裂隙分布的非均质性特征,利用水平定向钻实现导水通道精准探查是实现超前区域治理中“有的放矢、精准可控注浆”的基础。而导水通道精准探查需采用物探、钻探和化探等手段,综合判识。因此如何利用物探、钻探、化探相结合的技术手段,实现采前、采中分阶段全面精准探查,准确判识潜在导水通道的分布范围、充填结构、导水性能等,实现导水通道的智能化精准判识,将是底板导水通道超前精准探查研究的重要方向。
(3) 煤层底板超前区域治理。现阶段煤层底板超前区域治理技术相对成熟,但注浆材料、浆液配比、注浆压力、注浆时间、注浆量等关键注浆参数选取的智能化水平仍存在不足,如何实现注浆参数随受注地层空隙性、导水性、渗透性等特征而智能化调控是超前区域治理技术发展的方向。
5 结 论
a. 基于注浆改造过程中钻孔施工位置、注浆层位选择和钻进方式,建立了5种超前区域注浆改造主模式,确定了各类模式的确定方法和准则。结合注浆材料、钻孔布设形态,形成超前区域注浆改造亚类划分。
b. 形成了煤层底板超前注浆加固定向钻孔螺旋钻杆回转钻进、稳定组合钻具定向钻进和螺杆钻具随钻测量定向钻进等多种钻进方式耦合的钻进工艺。
c. 确定了冲洗液消耗量中钻液漏失量大于30 m3/h,压水试验渗透率大于10 Lu,单位注浆量大于10 t/m的地层通道导水性判识标准,得出了不同构造类型的导水性能类型,实现了通道导水性分区。
d. 分析了注浆材料及浆液选配和调控、注浆终结标准、钻孔布置间距和方向、注浆控制因素等,提出了基于受注地层特征、注浆材料、浆液性能、浆液扩散规律、底板注浆改造要求和工艺等因素的超前注浆浆液扩散控制工艺。
e. 提出了基于冲洗液消耗量、钻孔涌水量、渗透率和改造层厚度4个指标的超前区域注浆效果定量评价分析方法及基于灰色关联度分析的注浆效果检验定性评价方法,开发了井下水平定向钻孔的孔间电磁波透视仪,形成了底板灰岩超前注浆效果检验综合评价装备技术体系。
-
表 1 后峡盆地主要煤层显微组分特征
Table 1 Maceral characteristics of main coal seams in Houxia Basin
煤
层显微组分体积分数/% 镜质组 惰质组 壳质组 B7 50.20~71.09/60.65 17.43~33.00/25.22 0.40~1.78/1.09 B8 58.03~76.36/64.92 17.02~36.25/29.30 1.74~4.02/2.94 B9 48.55~63.84/56.20 29.11~43.64/36.38 1.26~3.09/2.20 注:50.20~71.09/60.65表示最小~最大值/平均值,其他同。 表 2 研究区气样分析、含气量及生产数据
Table 2 Gas sample analysis, gas content and production data in the study area
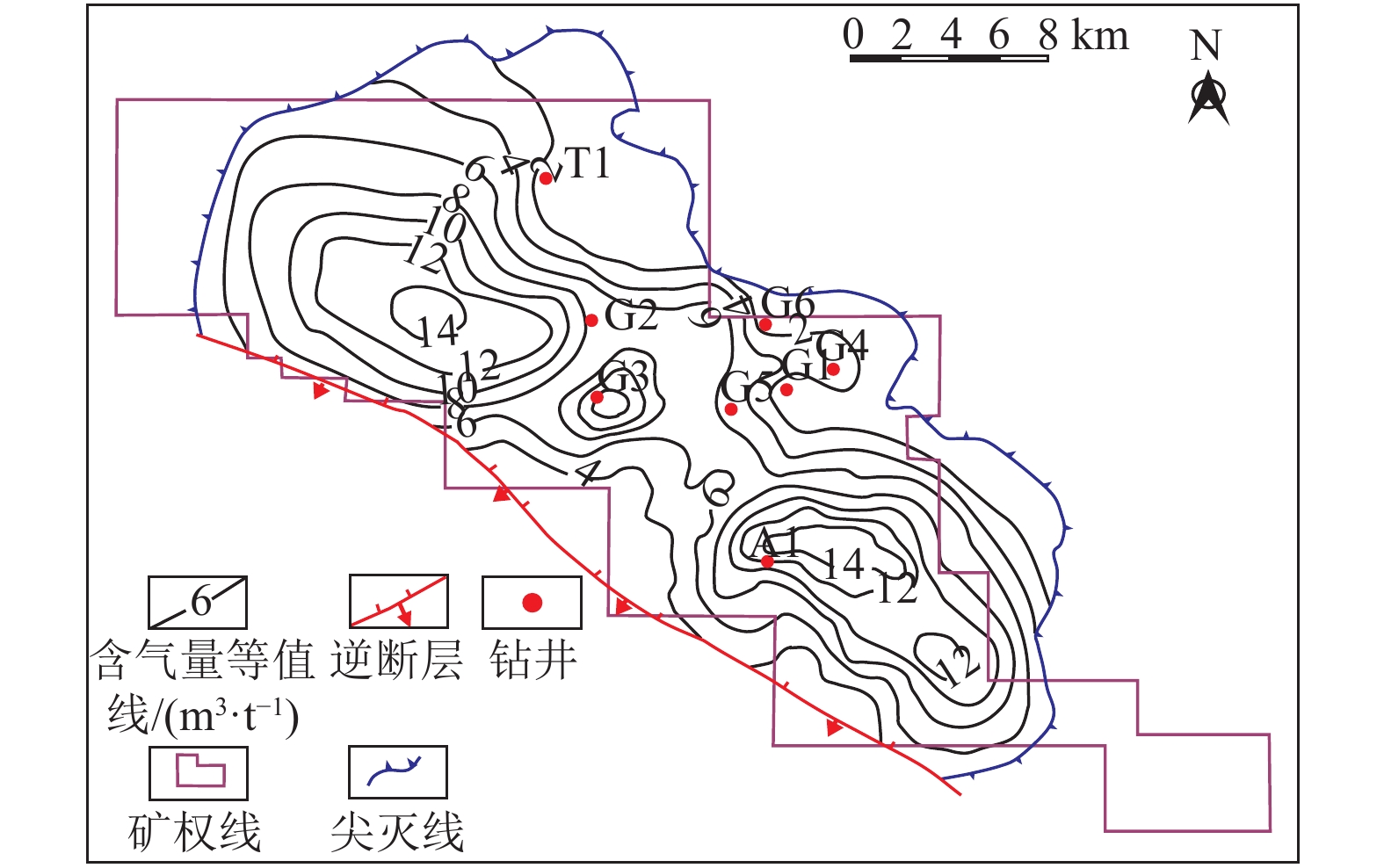
井号 δ13C1/‰ δDCH4/‰ φ(CH4)/% φ(C2H6)/% φ(C3H8)/% φ(CH4)/φ(C2H6+C3H8) 含气量/(m3·t−1) 临储比 目前最高产量/(m3·d−1) G2 −45.3 −218.7 86.114 0.468 0.101 151.34 7.33 0.67 1 100 G3 −49.7 −229.1 94.129 0.346 0.168 183.13 11.70 0.99 900 G5 −57.8 −257.3 93.887 0.111 0.058 555.54 5.20 0.41 500 A1 −48.6 −215.6 82.522 1.291 0.030 62.47 12.30 0.77 1 330 T1 −52.4 −248.2 94.783 0.416 0.164 163.42 1.35 0.25 100 -
[1] 邹才能,张国生,杨智,等. 非常规油气概念、特征、潜力及技术:兼论非常规油气地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(4):385−399. ZOU Caineng,ZHANG Guosheng,YANG Zhi,et al. Geological concepts,characteristics,resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon:On unconventional petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(4):385−399. DOI: 10.11698/PED.2013.04.01 [2] 李五忠,田文广,孙斌,等. 低煤阶煤层气成藏特点与勘探开发技术[J]. 天然气工业,2008,28(3):23−24. LI Wuzhong,TIAN Wenguang,SUN Bin,et al. Characteristics of pooling and exploration and development of CBM in low–rank coals[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2008,28(3):23−24. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.03.006 [3] 孙粉锦,田文广,陈振宏,等. 中国低煤阶煤层气多元成藏特征及勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(6):10−18. SUN Fenjin,TIAN Wenguang,CHEN Zhenhong,et al. Low−rank coalbed methane gas pooling in China:Characteristics and exploration orientation[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(6):10−18. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.06.002 [4] 王涛,邓泽,胡海燕,等. 国内外低阶煤煤层气储层特征对比研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(9):41−50. WANG Tao,DENG Ze,HU Haiyan,et al. Study on characteristics comparison of low rank coal coalbed methane reservoirs at home and abroad[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(9):41−50. [5] 俞益新,唐玄,吴晓丹,等. 澳大利亚苏拉特盆地煤层气地质特征及富集模式[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(3):160−167. YU Yixin,TANG Xuan,WU Xiaodan,et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation mode of coalbed methane in Surat basin of Australia[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(3):160−167. [6] 张玉垚,程晓茜,弓小平,等. 新疆典型矿区低煤阶煤层气成藏差异对比研究[J]. 中国矿业,2019,28(6):172−179. ZHANG Yuyao,CHENG Xiaoqian,GONG Xiaoping,et al. Comparative research on the difference of low rank CBM accumulation in typical Xinjiang mining area[J]. China Mining Magazine,2019,28(6):172−179. [7] 时小松,文桂华,张继坤,等. 天山后峡盆地后峡区块煤层气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(增刊1):1−4. SHI Xiaosong,WEN Guihua,ZHANG Jikun,et al. Exploration potential of coalbed methane in Houxia block of Tianshan Houxia basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(Sup.1):1−4. [8] KOTARBA M J. Composition and origin of coalbed gases in the Upper Silesian and Lublin Basins,Poland[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2001,32(1):163−180. DOI: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00134-0
[9] SCOTT A R. Hydrogeologic factors affecting gas content distribution in coal beds[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2002,50(1/2/3/4):363−387. DOI: 10.1016/S0166-5162(02)00135-0
[10] 田文广,邵龙义,张继东,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部侏罗系煤层气成因探究[J]. 中国矿业,2015,24(5):81−85. TIAN Wenguang,SHAO Longyi,ZHANG Jidong,et al. Analysis of genetic types of the coal bed methane of Jurassic Formation,southern Ordos Basin[J]. China Mining Magazine,2015,24(5):81−85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.05.017 [11] 陶明信. 煤层气地球化学研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 自然科学进展,2005,15(6):648−652. TAO Mingxin. Research status and development trend of coalbed methane geochemistry[J]. Progress in Natural Science,2005,15(6):648−652. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2005.06.002 [12] WHITICAR M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane[J]. Chemical Geology,1999,161(1/2/3):291−314. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3
[13] 巢海燕,王延斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘临汾区块煤层气成因及其影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(7):1769−1777. CHAO Haiyan,WANG Yanbin. Origin of coalbed methane and its influence in Linfen,southeastern Ordos basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(7):1769−1777. [14] 王相业,孙保平. 鄂尔多斯盆地兴县地区煤层气地球化学特征及成因[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(4):156−164. WANG Xiangye,SUN Baoping. Geochemical characteristics and their origin of CBM in Xingxian area,Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(4):156−164. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.022 [15] 方世虎,郭召杰,贾承造,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中–新生界沉积物重矿物分析与盆山格局演化[J]. 地质科学,2006,41(4):648−662. FANG Shihu,GUO Zhaojie,JIA Chengzao,et al. Meso–cenozoic heavy minerals’ assem blages in the southern Junggar Basin and its implications for basin–orogen pattern[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2006,41(4):648−662. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.008 [16] 郭召杰,吴朝东,张志诚,等. 乌鲁木齐后峡地区侏罗系沉积特征、剥露过程及中新生代盆山关系讨论[J]. 高校地质学报,2005,11(4):558−567. GUO Zhaojie,WU Chaodong,ZHANG Zhicheng,et al. Mesozoic–cenozoic relationships between Tianshan Mountain and Peripheral basins:Evidences from sedimentology and exhumation of Jurassic in Houxia area,Urumqi[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2005,11(4):558−567. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.012 [17] 李荣西,张锡云,金奎励. 用镜质体反射率重建沉积盆地构造演化特征[J]. 矿物学报,2001,21(4):705−709. LI Rongxi,ZHANG Xiyun,JIN Kuili. Application of vitrinite reflectance to reconstruction of the tectonic features of the Bohai gulf basin[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2001,21(4):705−709. [18] 邱楠生,杨海波,王绪龙. 准噶尔盆地构造—热演化特征[J]. 地质科学,2002,37(4):423−429. QIU Nansheng,YANG Haibo,WANG Xulong. Tectono–thermal evolution in the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2002,37(4):423−429. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.005 [19] 叶建平,武强,王子和. 水文地质条件对煤层气赋存的控制作用[J]. 煤炭学报,2001,26(5):459−462. YE Jianping,WU Qiang,WANG Zihe. Controlled characteristics of hydrogeological conditions on the coalbed methane migration and accumulation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2001,26(5):459−462. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.05.003 [20] 刘洪林,李景明,王红岩,等. 水文地质条件对低煤阶煤层气成藏的控制作用[J]. 天然气工业,2008,28(7):20−22. LIU Honglin,LI Jingming,WANG Hongyan,et al. Control of hydrogeological conditions on accumulation of coalbed methane in low–rank coal[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2008,28(7):20−22. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.07.006 [21] 朱文静. 乌鲁木齐后峡地区水环境状况及不利水文条件分析[J]. 地下水,2020,42(4):168−170. ZHU Wenjing. Analysis of water environment and adverse hydrological conditions in Houxia area of Urumqi[J]. Ground Water,2020,42(4):168−170. [22] 刘大锰,李俊乾. 我国煤层气分布赋存主控地质因素与富集模式[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(6):19−24. LIU Dameng,LI Junqian. Main geological controls on distribution and occurence and enrichment patterns of coalbed methane in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2014,42(6):19−24. [23] 李传亮. 毛管压力是油气运移的动力吗?:与李明诚教授商榷[J]. 岩性油气藏,2008,20(3):17−20. LI Chuanliang. Is capillary pressure the driving force in oil and gas migration?:Discussion with Prof. Li Mingcheng[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2008,20(3):17−20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.03.004 [24] 唐俊红,高忆平,施明才,等. 含油气盆地微渗漏甲烷运移机制研究进展[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(2):64−69. TANG Junhong,GAO Yiping,SHI Mingcai,et al. A preliminary review of gas migration mechanisms of methane microseepage in hydrocarbon–prone areas[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Dianzi University(Natural Sciences),2019,39(2):64−69. [25] 王勃,巢海燕,郑贵强,等. 高、低煤阶煤层气藏地质特征及控气作用差异性研究[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(10):1396−1401. WANG Bo,CHAO Haiyan,ZHENG Guiqiang,et al. Differences of coalbed methane geological characteristics and gas–controlling function between low rank coal and high rank coal[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2008,82(10):1396−1401. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.10.014 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 桑树勋,李瑞明,刘世奇,周效志,韦波,韩思杰,郑司建,皇凡生,刘统,王月江,杨曙光,秦大鹏,周梓欣. 新疆煤层气大规模高效勘探开发关键技术领域研究进展与突破方向. 煤炭学报. 2024(01): 563-585 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 涂志民,闻星宇,李鹏,吴鹏,蒲仁海,闫肃杰,李慧琼. 后峡盆地复杂构造煤层气成藏主控因素. 西安科技大学学报. 2024(03): 501-511 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李彬,邱峰,张晓洲,王子豪,蔡益栋. 二连盆地巴彦宝力格煤田伊敏组低煤阶煤层气成藏条件及有利区预测. 大庆石油地质与开发. 2023(04): 20-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 康玉国,张明. 沁水盆地东缘龙泉地区煤层气成藏条件及主控因素. 东北石油大学学报. 2022(03): 1-12+129 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载: